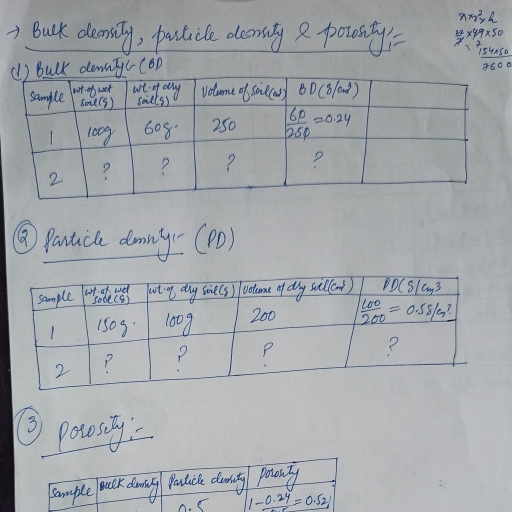
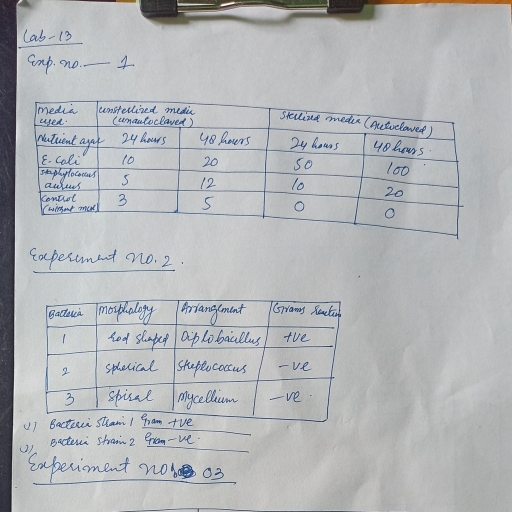
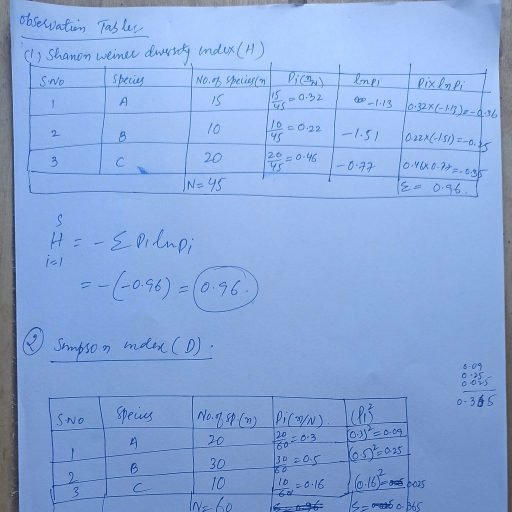
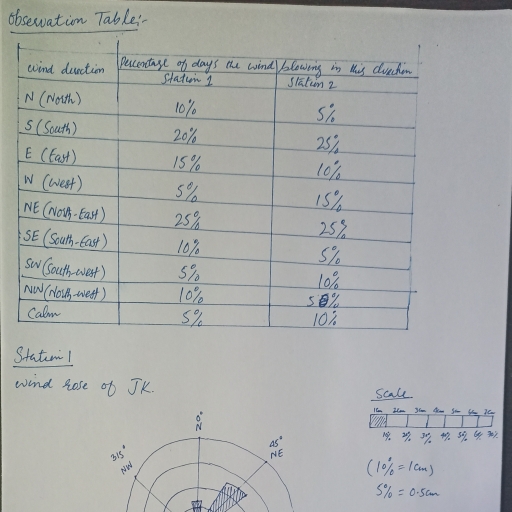
Page 1 :
Components of Ecosystem
Page 2 :
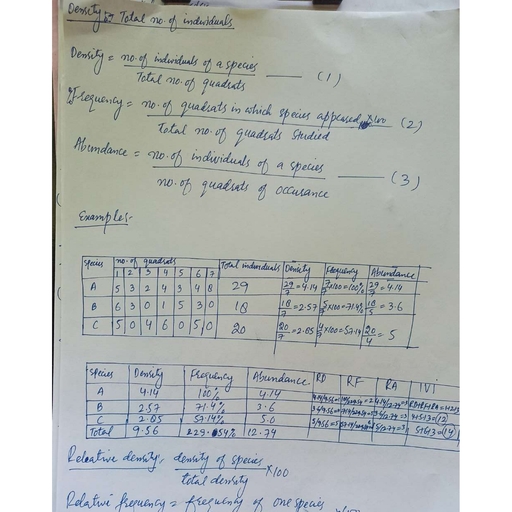
COMPONENTS OF ENVIRO:, ATMOSPHERE-STRUCTURE AND CO}, , Atmosphere (Gr. atmos=steam, vapour; sphaira=sphere) is gase, earth from all sides and is attached to the earth’s surface by gravita, all the necessary gases for the sustenance of life. About 5.8 bili, surrounds earth and half of its weight lies within less than 4.8 km of, earth and saves living organisms from hostile environment of outer s, 1600 km from earth surface. The composition of atmosphere is shown in table | LL., , Besides gases and water vapour atmosphere also has Solid/ Dust particles. Innumerable dust, particles are found suspended in the atmosphere. These particles consist of sand particles, pollen, grains, small organism, ocean salt, smoke, soot ash, particles of meteors etc. These solid Particles, perform the function of absorbing, reflecting and scattering the radiation. The blue colour of the, , is due to selective scattering of dust particles. Dust particles are an important contributory fac, mn, the form of clouds, fog and hailstorm because of hygroscopic in character.
Page 3 :
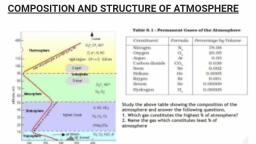
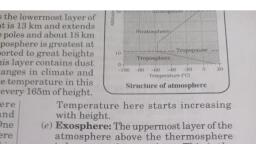
STRUCTURE OF ATMOSPHERE, , On the bases of characteristics of temperature and air pressure the atmosphere can be divided, inlofive layers. (i) Troposphere (ii) Stratosphere (iii) Mesosphere (iv) Thermosphere (v) Exosphere., , (i) Troposphere (Gr. Tropos=turn,trope;sphaira=sphere), , Characteristics, , The lowest layer of the atmosphere is known as Troposphere. It shows following characteristics:, * — Itcontains 90% of gases., , * The eltitude of troposphere is 8 km at pole and 16 km at equator., , ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE, , * The temperature decrease with increases height at the rate of 6.5°C/Km. This rate of decrease, of temperature is called normal lapse rate., , * The troposphere is marked by temperature inversion; turbulence and eddies. It is, meteorologically the most significant zone in the entire atmosphere., , * All weather phenomena like cyclone, anticyclone, storm, lightening and Precipitation occ, here; as all water vapour and solid particle lies with in this layer., * Vertical mixing occurs here. It is the most active zone of atmosphere. The, , temperature, end of Troposphere is around -70°C to -75°C,, , * The boundary line separating troposphere from stratosphere known as tropopause ra, where mixing stop. Tropopause is an inversion layer, where the air temperature icine, decrease with height and remains constant through its thickness,
Page 4 :
(ii) Stratosphere (Gr. Strato=layer;sphaira=sphere), Stratosphere lies above tropopause. The upper limit of the stra, Characteristics, , * _ Itis free from violent weather changes. It is stable zone wit!, components. ;, Temperature in the layer remains constant for some distance but then rise to reach a level, O°C at 50 km altitude. This rise is due to the Presence of ozone layer. The lower portion of, the stratosphere has maximum concentration of ozone (15-35km) to absorb ultraviolet rays., , * The lower stratosphere just above tropopause provides ideal condition for flying large, airplanes, as clouds are usually absent,, , * Little dust or water vapours are present. Cirrus clouds are occasionally formed in lower, atmosphere. The boundary between stratosphere and mesosphere is called as stratopause., , Troposphere and Stratopshere form 99.9% mass of atmosphere.
Page 5 :
(iti) Mesosphere((Gr. Mesos=middle;sphaira=sphere), , * — Itexists above the stratosphere and directly below the mesopause. It extends up to height of, 80 km above the earth,, , ; ae, * Temperature falls with elevation due to decreasing solar heating and increases cooling by |, CO, radiative emission. The temperature decreases from 0°C to - 100°C at meso, , * — In the upper part of the mesosphere (60-80 km) oxygen exist in its atomic for, burn in this layer while entering into atmosphere.