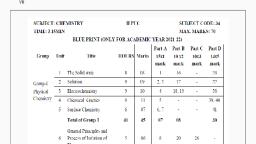
Page 1 :
13.11YEAR PUC PRACTICAL EXAMINATION, VIVA QUESTIONS, FOR FUNCTIONAL GROUPS IN ORGANIC COMPOUNDS, ALCOHOLS, , 1., Ans., , Which is the årnctional group ofalcohol ?, -OH (Alcoholic group), , 2., Ans., , Name a test for alcohols, Ceric ammonium nitrate test., , 3., , Explain Ceric ammonium nitrate test., , Ans., , When an alcohol is shaken with Ceric ammonium nitrate solution, pink or red colour appears., , 4., Ans., , Which type of alcohol reacts slowly with Lucas reagent?, Primary alcohols., , 5., , Which type of alcohol reacts instantaneously with Lucas reagent?, , Ans., , Tertiary alcohols., , 6., , Ans., , Name the chemical reagent used to distinguish primary alcohol, secondary alcohol and tertiary, alcohol ?, Lucas reagent., , 7., Ans., , What is Lucas reagent?, A mixture of anhydrous ZnC12and Conc. HCI is called Lucas reagent., , 8., Ans., , What is the meaning of2 0alcohol?, The alcohol in which -OH group is attached to secondary carbon atom., , 9., Ans., , What is the general formula ofprimary alcohol?, R-CHÜOH, , 10., Ans., , What is the general formula ofsecondary alcohol?, R-CH-RI, OH, , PHENOLS, , 1., , Ans., 2., Ans., , What is phenolic - OH group?, , -OH group which is directly bonded to Benzene ring., hydrogen carbonate) Why?, Phenol does not displace C02 from NaHC03 solution (Sodium, Since phenol is less acidic than carbonic acid., , Write any two tests for phenols., 3., Ans. i) Neutral Ferric Chloride test, ii) Phthalein dye test, phenol., Explain Neutral ferric chloride test for, chloride, a violet colour is obtained., Ans. When phenol is treated with Neutral ferric, Explain phthalein dye test for phenol., is heated, cooled and, mixture, The, ., H2S04, Conc., and, Ans. Phenol is mixed with phthalic anhydride, coloured solution is formed., pink, A, hydroxide., sodium, dilute, a, into, poured, test ?, Why pink colour is formed in phthalein dye, 6., Ans. It is due to formation ofphenolphthalein.
Page 2 :
7., , Name the organic compound formed in phthalein dye test for phenol., , Ans., , phenolphthalein., , 8., , What is neutral ferric chloride solution?, , Ans., , Aqueous solution of Neutral ferric chloride is acidic due to hydrolysis. It is made neutral by, adding, , 9., Ans., , Write the formula ofphenol., C6H50H, , 10., Ans., , Why phenol should not touch with bear hands ?, It is highly corrosive., , ALDEHYDES AND KETONES, 1., Ans., , What is the common functional group found in aldehydes and ketones?, Carbonyl group (>C=O), , 2., Ans., 3., Ans., 4., Ans., 5., Ans., , What is the functional group of aldehydes?, -CHO (aldehydic group), , 6., Ans., , What is the functional group ofketones?, >CO (ketonic group), Name the common test for aldehydes and ketones, 2, 4 - DNP hydrazine test, Expand 2,4 - DNP hydrazine, 2,4 - Dinitro phenyl hydrazine, , Which coloured precipitate. is obtained when an aldehyde or ketone is treated with 2,4 - DNP, hydrazine ?, Orange coloured precipitate., , Name the orange coloured product formed when benzaldehydeis treated with 2,4-DNP, Ans., , hydrazine., Benzaldehyde 2,4 - DNP hydrazone., What is Tollen 's reagent?, Ammonical silver nitrate solution is called Tollen 's reagent., , 8., Ans., 9., Ans., , Explain Tollen 's reagent test., When an aldehyde is heated with Tollen's reagent, a black ppt. (silver) is formed., , 10., Ans., , Name a test for ketones., m-dinitrobenzene test or Sodium nitroprusside test., , CARBOXYLIC ACIDS, 1., Ans., , What is the functional group ofCaboxylic acids?, -COOH (Carboxyl group), , 2., Ans., 3., Ans., , Explain litmus test for carboxylic acids., When a blue litmus paper or blue litmus solution is treated with a carboxylic acid, it turns to red., Explain Sodium bicarbonate test for caboxylic acids., When a carboxylic acid is treated with sodium bicarbonate solution, effervescence occurs due, to the liberation of C02 gas.
Page 3 :
4., , How can you confirm the liberation of C02 gas during sodium bicarbonate test for carboxylic, acids?, , Ans., , By passing C02 gas into lime water which turns milky., , 5., , What is lime water?, , Ans. A solution ofcalcium hydroxide., 6., Ans., , 7., , Explain Esterification test for carboxylic acids., A carboxylic acid is mixed with an alcohol and a few drops of Conc. H2 S04 . The mixture is, heated and pour into sodium carbonate solution, fruity odour is obtained., Name the ester formed when acetic acid is heated with ethyl alcohol in presence of Conc., , Ans., , Ethyl acetate., , 8., Ans., , Other than carboxylic acid which acid is used in esterification test?, Conc. H2 S04, , 9., , What is the role of Conc. H2S04 in esterification?, , Ans., , Dehydrating agent., , 10., Ans., , Name the tests for carboxylic acids., 1. Litmus paper test, 2. Sodium bicarbonate test, , 3. Esterificationtest, , AMINES, 1., , Whatis the general formula of 10, 20 and 30amines ?, , Ans., , | amines : R-NH2, , 2., Ans., 3., Ans., , Name the confirmatory test for primary amines., Carbylamine test which is answered by both aliphatic and aromatic primary amines., How do you distinguish between aliphatic and aromatic primary amines ?, By azo-dye test which is answered only by aromatic primary amines., , 4., Ans., , Which is the functional group ofprimary amines?, -NH2(amino group), , 5., Ans., , Which type of amines answers carbylamine test?, All primary amines., What type ofodour is observed in carbylamine test?, Offensive or bad odour is observed., , 6., Ans., , Ans., , 20amines : R-NH-R I, , 30amines : R-N-R, , I, , Explain azo dye test for primary amine., An aromatic primary amine is dissolved in dil.HCl and mixed with ice cold sodium nitril, solution, to this ß-naphthol solution in NaOH is added, a red dye is formed., , 9., Ans., , Explain carbylamine test for primary amines., (KOH), a bad smell, When a primary amine is heated with chloroform and alcoholic potash, carbylamine is obtained., Why bad smell is obtained in carbylamine test?, Due to liberation ofcarbylamine., , 10., Ans., , What is alcoholic potash?, A solution of KOH dissolved in alcohol., , Ans., , 3,