Page 1 :
Applied Science - Physics (22202), Practical No. 4: Force on the roller on an inclined plane, Practical Significance, I., The force laws, together with the laws of motion, are the foundations of classical, mechanics. They are based on experimental observations and were formulated more, than three centuries ago by Isaac Newton (1642-1727)., An inclined plane, also known as a ramp, is a flat supporting surface tilted at an angle,, with one end higher than the other, used as an aid for raising or lowering a load. The, inclined plane is one of the six classical simple machines defined by Renaissance, scientists. Inclined planes are widely used to move heavy loads over vertical obstacles;, examples vary from a ramp used to load goods into a truck, to a person walking up a, pedestrian ramp, to an automobile or railroad train climbing a grade., Moving an object up an inclined plane requires less force than lifting it straight up, at a, cost of an increase in the distance moved. The mechanical advantage of an inclined, plane, the factor by which the force is reduced, is equal to the ratio of the length of the, sloped surface to the height it spans. Due to conservation of energy, the same amount of, mechanical energy (work) is required to lift a given object by a given vertical distance,, disregarding losses from friction, but the inclined plane allows the same work to be, done with a smaller force exerted over a greater distance., Relevant Program Outcomes (POs), PO1 - Basic knowledge, PO3 - Experiments and practice, PO8 – Individual and teamwork, PO10 - Life-long learning, II., III., Relevant Course Outcomes, Apply laws of motion in various applications., Practical Outcome, To Find: The downward force, along an inclined plane, acting on a roller due to gravity, and its relationship with the angle of inclination., IV., Competency and Practical Skills, a. Measurement skills, b. Error estimation skills, V., VI., Relevant Affective Domain Related Outcomes, a. Follow safe practices, b. Demonstrate working as a leader/ a team member, c. Follow ethical practices, Maharashta Stete Beard of Technieal Eduaation, 27
Page 2 :
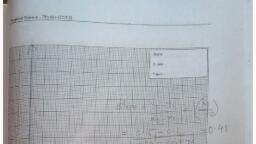
4 oil ;t fo6 making, Applied Science- Physics (22202), 4 oil iz fos, 45, Aylley., Psa.lley.atgiv.enangles, 0.16, 081, 10.86, 4., 50, Actual Procedure Followed:, Tested, tte., ree..., XII., 55, as......, 6., d appora ts., the., 60, gr.en.ingles, Inclined, 180 +, 170, XIII. Resources Used (with proper specifications), 160, incined plaDe, lles, Ap, A tselley, Aaeight., An......, 150 -, 140-, 130, 120, XIV. Precautions followed, 11, 1 Palley should. be, Priction less, 10, 2) Bas., should be, stable, I boizonte!, XV., Observations and Calculations:, a. Least count of spring balance =.......g wt., b. Zero error of spring balance (e) =........g wt., c. Zero correction of spring balance (c) = (+e)=., d. Observed weight of the roller (wo) =., e. Corrected weight of the roller (w-mg) (wo+ c) ......g wt., f. Observed weight of the pan (po) =...2..g wt., g. Corrected weight of the pan (p)= (po+c), XVI. Result, 1. Downwa, g=980emls?, g wt., 2. The grap, =.5.0 g wt., XVII. Inter, Da, .g wt., mass of the rollers (n) = 5ag, Tables for angle of inclination and weights in pan, Angle, Weight in pan when, Total weight when, Force acting, on roller, downward, Error, Sr., roller moves, roller moves, of, No inclination, w sine, W - mg, sine, Upward Downward Upward Downward, sine, %3D, XVIII. Co, (0), (degree), mg sin0, Wi, W2, W =, Wi+p, (gwt), W2=, W2+p, (gwt), 26, 25, 26, (gwt), (g wt), WW, W=., 1, 30, 0.5, 22, 35, 3, Q-57, 40, 0-67, 23, 24, 26, 27, 28, 23, 24, 25, 26, Maharashtra State Board of Technical Education, Maharas, 30, (m 6) M
Page 3 :
Applied Science - Physics (22202), Maharashtra State Board of Technical Education, 45, 071, 27, 28, 29, 30, 25, 26, 27, 28, 0.76, 4., 29, s0, 31, 32, 50, 27, 26, 1081, 27, 28, 29, 55, 10.86, 60, 30, Graph between sin 0 and W, 180, Scale :, X-axis : 1 cm 0.05 of sin 0, Y-axis : 1 cm = 10 g wt of W, 170, 160-, 150 -, w/, 140, 130, 120, 110, 100, 0.5, 0.6, 0.7, 0.8, 0.9, sin e, Fig. Graph between sin 0 and W. It is a straight line., XVI. Results, 1. Downwards force on the body of weight W mg on an inclined plane is mg sin, 2. The graph between W and sin 0 is a straight line, i.e. W a sin, XVII. Interpretation of Results, Daanwards., W-mg., mg.., fosce, ..an he bode.. weign, inclined plans 's., an, on, Sin, XVIII. Conclusions and Recommendations:, of Spring balances 5kg, of Spoing, Least, Count, ..Zego ogpof, balance = g.unt., 31
Page 4 :
Hosmal.a face that. is.corbing, Applied Science - Physics (22202), XIX. Practical Related Questions, 1. What is inclined plane?, 2. What is the relation between downward force and angle of inclination of the plas, 3. What is the normal reaction on the inclined plane?, 4. Why is the glass plate fixed on an inclined plane?, Space to write answers, 12. An incliped planealso.known, as, Sea.pp.omting..Sans tace titles, flat, ang.le., at, cn....., 2] If, at. on., its, body, angle with the. hoizon.t,, caeight. mg, of mass is inclined, acts, 3] The, Hormal, sear bion o a, reaction ,'s the, Scmpface that is.worhing, resul.bant, against, gaavity.., Maharashtra State Board of Technical Education, Maharashtra State, 32