Page 1 :
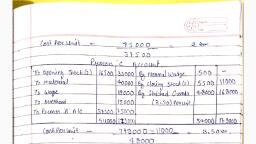
O Standard quartity for actual production (SQ) = 80 x 30 = 2,400 units, (ii) Actual price per unit for materials used (AP) = 9,000/3,000 = Rs. 3 per unit., (i) Actual quantity used (AQ) = Opening Stock + Purchases - Closing Stock, (i) Material Usage Variance, 9.39, SP = Standard or Budgeted Price, AP = Actual Price, RSQ = Revised Standard Quantity, Or, Budgeted Sales Units of a Product, Total Budgeted Units, x Total Actual Units Sold, 1 Sales Variances (Profit Method), Sales Margin Value Variance, Or, Budgeted Profit – Actual Profit, = (BQ × SRP1) – (AQ × ARPI), = (SRPI – ARPI) × AQ, = (BQ – AQ) x SRP., (RSQ – AQ) x SRP, (BQ – RSQ) x SRP, (1), %3D, (2) Sales Margin Price Variance, (3) Sales Margin Volume Variance, (4) Sales Margin Mix Variance, (5) Sales Margin Qty. (sub-volume) V. =, %3D, %3D, Standard Rate of Profit per unit, (Std. sale price p.u. - Std. cost p.u.), = Actual Rate of Profit per unit, (Actual sale price p.u., Where; SRPT, %3D, ARPT, Standard cost p.u.), क्रमिक उदाहरण (Graded Ilustrations), दाहरण (IIustration) 22 | (सामग्री विचरण) : निम्नलिखित सूचना से ( अ ) सामग्री लागत विचरण;, (ब) सामग्री मूल्य विचरण; तथा (स ) सामग्री उपयोग विचरण का परिकलन कीजिये-, From the following particulars, compute (a) the Material Cost Variance; (b) the, Material Price Variance, and (c) the Material Usage Variance., Quantity of materials purchased, Value of materials purchased, Standard quantity of materials required per ton of output, Standard rate of materials, Opening stock of materials, Closing stock of materials, Output during the period, हल (Solution), 3,000 Units, Rs. 9,000, 30 units, Rs. 2.50 per unit, Nil, 500 units, 80 tonnes, (SQ x SP) – (AQ × AP), (2,400 x Rs. 2.50) – (2,500 × Rs. 3), = (Rs. 6,000 – Rs. 7,500) = Rs. 1,500 (A), (SP – AP) x AQ, (Rs. 2.50 – Rs. 3) × 2,500 = Rs. 1,250 (A), (SQ - AQ) x SP, (2,400 – 2,500) × Rs. 2.50, 0. Material Cost Variance, %3D, %3D, %3D, (1) Material Price Variance, %3D, = Rs. 250 (A), %3D, जाँच (Check) :, Material Cost Variance =, दिम्पणियाँ :, Material Price Variance + Material Usage Variance, Rs. 1,250 (A) + Rs. 250 (A), Rs. 1,500 (A), %3D, %3D, = Nil + 3,000 – 500 = 2,500 units, %3D, %3D, Scanned with CamScanner
Page 3 :
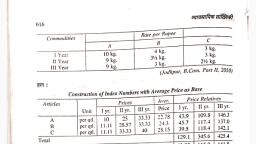
) सामग्री मिश्रण विचरण; तथा (v) सामग्री उत्पादन या सामग्री उप उपयोग विचरण।, गणना कीजिये- (i) सामग्री लागत विचरण; (ii) सामग्री मूल्य विचरण ( iii ) सामग्री उपयोग विचरण;, Material Sub-usage Variance (MSUV), e variance; (iv) Material mix variance; and (v) Material yield or material sub-usage, Compute- (i) Material cost variance; (ii) Material price variance (iii) Material, 9.41, (1), USage, sariance., A (Solution), Standard Mix, Actual Mix, Qty., Kg., Rate, Атоunt, Qty., Kg., Chemicals, Rate, Атоunt, Rs., Rs., Rs., Rs., 150, 4, 600, 140, 230, 4.20, 588, 200, 400, 1,000, 2,400, 1,104, 2,860, 4.80, C, 6., 440, 6.50, 750, 4,000, 810, 4,552, Revised Standard Quantity (RSQ), SQ, x TAQ, TSQ, Chemical A, 150, x 810 = 162 kg., %3D, 750, 200, 750, Chemical B, x 810 = 216 kg., %3D, 400, Chemical C, x 810 = 432 kg., 750, Computation of Material Variances, Material Cost Variance (MCV) = SC – AC, Rs., Rs., = Rs. 4,000 - Rs. 4,552, 552 (A), This is account for :, () Material Price Variance (MPV), (SP - AP) x, AQ, A = (4.00 – 4.20) × 140, B = (5.00 – 4.80) × 230, C = (6.00 – 6.50) × 440, (i) Material Usage Variance (MUV), (SQ – AQ) x SP, A = (150 – 140) × Rs. 4, B = (200 – 230) × Rs. 5, C = (400 – 440) × Rs. 6, (a) Material Mix Variance (MMV), (RSQ - AQ) :, 28 (A), 46 (F), 220 (A), %3D, 202 (A), %3D, 40 (F), 50 (A), 240 (A), 350 (A), x SP, A = (162 – 140) × Rs. 4, B = (216 - 230) × Rs. 5, C = (432 – 440) × Rs. 6, (6) Material Yield Variance (MYV), (AY – SY) x, 88 (F), 70 (A), 48 (A), %3D, 30 (A), 320 (A), 350 (A), x SR =, (500 – 540) x Rs. 8, Or, (SQ - RSQ) x SP, Scanned with CamScanner