Page 1 :
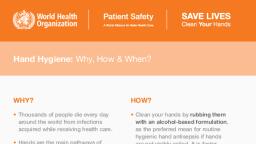
Theory: Thousands of people die, Aim: To learn hand washing technique., Aim: To learn hand washing technique., Theory: Thousands of people diejevery, acquired while receiving health care. Hands are the main pathways of germ, transmission during health care. Hand hygiene is therefore the most important, measure to avoid the transmission_of harmful germs_and prevent health care-, tione, đay around the world from infections, associated infections., Hand hygiene helps to stop the spread of germs, including ones that can cause, antibiotic-resistant infections. Antibiotic resistance happens when germs like bacteria, and fungi develop the ability to defeat the drugs designed to kill them That means, the germs are not killed and continue to grow. Infections caused by antibiotic-, resistant germs are difficult, and sometimes impossible, to treat. Keeping your hands, clean by washing your hands with soap and water or using alcohol-based hand, sanitizer is one of the, best ways to prevent germs from spreading and avoid, infections. Any health-care worker, caregiver or person involved in direct or indirect, patient care needs to be concerned about hand hygiene and should be able to, perform it correctly and at the right time. Clean your hands by rubbing them with an, alcohol-based formulation, as the preferred mean for routine hygienic hand, antisepsis if hands are not visibly soiled. It is faster, more effective, and better, tolerated by your hands than washing with soap and water. Wash your hands with, soap and water when hands are visibly dirty or visibly soiled with blood or other, body fluids or after using the toilet. If exposure to potential spore-forming, pathogens is strongly suspected or proven, including outbreaks of Clostridium, difficile, hand washing with soap and water is the preferred means,, don't have soap and water, use a hand sanitizer with at least 60% alcohol. If, you don't have hand sanitizer or soap, but do have water, rub your hands together, under the water and dry them with a clean towel or air dry. Rubbing your hands, under water will rinse some germs from your hands, even though it's not as effective, as washing with soap., If, you, Hand care: Take care of your hands by regularly using a protective hand cream or, lotion, at least daily. Do not routinely wash hands with soap and water immediately, before or after using an alcohol-based hand rub. Do not use hot water to rinse your, hands. After hand rubbing or hand is washing, let your hands dry completely before, putting on gloves. Washing hands with soap and water is the best way to remove all, - 37 -, Scanned by TapScanner
Page 2 :
types of germs and chemicals. If soap and water are not available, use an alcohol-, Practical Manua, Social Pharmacy (F.Y. D. Pharm), based hand sanitizer with at least 60% alcohol., Points to remember, Do not wear artificial fingernails or extenders when in direct contact with patients, Keep natural nails short., Result: Understood hand washing techniques., Scanned by TapScanner
Page 3 :
Practical Manu, Social Pharmacy (F.Y. D. Pharm), 2, 1, Rub hands palm to palm, Apply enough soap to cover, all hand surfaces, Wet hands with water, 3, 4, Right palm over left dorsum, with interlaced fingres, and vice versa, Palm to palm with fingers, interlaced, Back of fingers to opposing, palms with fingers interlocked, 7, 8, 6., Rotational rubbing of left thumb Rotational rubbing, backwards, and forwards with clasped, fingers of right hand in left, palm and vice versa, Rinse hands with water, clasped in right palm, and vice versa, 9., 11, Dry thoroughly with single, Use towel to turn off faucet, ...and your hands are safe, use towel, Figure: Hand Washing Technique, Scanned by TapScanner, 5, 10
Page 4 :
Aim: To learn cough and sneeze etiquette., Theory: Coughing and sneezing are a body's natural reaction to an allergy or, infection. But since they can potentially transmit the disease to another person, we, must not forget to follow cough and sneeze manners A cough produces, approximately 3000 droplets, whereas a sneeze releases an estianted 40,000, dropiets, Covering coughs and sneezes and keeping hands clean can help prevent the spread, of serious respiratory illnesses like influenza, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV)., whooping cough, and COVID-19., Germs can be easily spread by:, Coughing, sneezing, or talking. Touching your face with unwashed hands after, touching contaminated surfaces or objects. Touching surfaces or objects that may be, frequently touched by other people, Simple cough and sneeze etiquette:, 1. Step far away from people and cover your mouth and nose when coughing or, sneezing., 2. Do not roughly clear your nose or throat while in the presence of others. Not only, is it unhygienic, but it also revolts another person., 3. If you have an urge to cough or sneeze, do it by folding of your elbow or into a, tissue., 4. If and when you use tissues, dispose them in a responsible manner. Bin it as, 'medical waste' and do not toss it around like it was harmless stuff., 5. Bin the used tissues in no-touch receptacles for disposal as touching the, receptacle, again and again, is not advisable., 6. Wash your hands or use a hand sanitiser every time you touch your mouth or, nose., 7. Wear an N95 or N99 mask when you are in the company of others., 8. If you know you have any kind of flu - however serious or not - sit as far away, from others as possible., 9. Avoid touching your face with your hands (or even if you have just wiped your, sick child's nose). When one touches the face with unwashed, uncleaned hands,, the cold and flu viruses get a chance to enter the mucous membranes of the nose, and eyes and cause infection., -41-, Scanned by TapScanner
Page 5 :
Social Pharmacy (F.Y. D. Pharm), Practical Manua, 10. When you know you have an infection, avoid travel. You can always travel later, when you are healthier and thus contribute to breaking the chain of infection., Result: Understood Cough and sneeze etiquettes., Scanned by TapScanner