Page 1 :
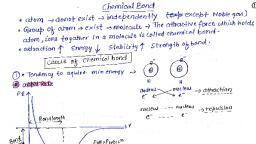
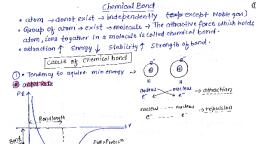
Chemical bonding, The attractive force which holds various constituents like atom, ions, etc. together in, different chemical species is called a chemical bond., Why do atoms combine? (ii) Why are only certain combinations possible? Eg: hydrogen exists, as H2 and not as H3, (iii) Why do some atoms combines while certain others do not? Eg: Two H atoms combine to, form H2 but two helium atoms do not combine to form He2, (iv) Why do molecules possess definite shapes? Eg: CO2 is linear, but H2O is V- shaped., Similarly, BF3 is planar but NH3 is pyramidal., To look into the reasons for the above questions, different theories and concepts have been put, forward from time to time., , Kossel-Lewis approach, In 1916, Kossel and Lewis successfully gave explanation for chemical bonding. According to, them “only outer electrons participate in bond formation and inner electrons remain protected.”, The study on the inert gas suggested that neither they combine chemically with other elements, nor among themselves. From the study of electronic configuration of inert gas, it is clear that, inert gases are chemically inert because they have 8 electrons in their except in the case of, helium which has 2 electrons.
Page 2 :
Octet rule, The atoms of different elements combine with each other in order to complete the eight, electrons (octet) in the outermost shell or two electrons (duplet) in the case of H, Li, or Be, to attain stable inert gas configuration. This is known as electronic theory or octet rule., , Lewis symbols, Lewis symbols (also known as Lewis dot diagrams or electron dot diagrams) are diagrams that, represent the valence electrons of an atom. In these diagram outer electrons are represented by, dots or crosses., , Electronegativity, The measure of ability of an atom in a chemical bond to attract shared electrons to itself is, called electronegativity., , Types of chemical Bonds, Depending upon the strength of chemical bond, there are two types of chemical bonds, (1) Strong bond, (2) Weak bond
Page 3 :
Strong chemical bonds are classified as follows