Page 1 :
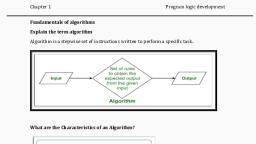
PROBLEM SOLVING METHODOLOGY, , PROBLEM SOLVING METHODOLOGY, , > Introduction, , The term problem solving is used in many disciplines, sometimes with different perspectives and, often with different terminologies. The problem-solving process starts with the problem, specification and end with a correct program., , The steps to follow in the problem-solving process are:, , Problem definition, , Problem Analysis, , Algorithm development, , Coding, , Testing & Debugging, , Documentation & Maintenance, , The stages of analysis, design, programming, implementation and maintenance form the life cycle, of the system., , Y Problem definition: This step defines the problem thoroughly., Here requirements are specified. This step includes understanding the problem very well. The, problem solver must understand problem very well to solve problem efficiently., , ¥ Problem Analysis: Analyzing the problem or analysis involves identifying the following:, e Inputs, i.e. the data you have to work with., e Outputs i.e. the desired results., e Any additional requirements on the solutions., , ¥ ALGORITHM: An Algorithm is a step-by-step procedure to solve a given problem., e The word algorithm originates from the word ‘algorism’ which means process of doing, arithmetic with Arabic numerals., e In 9th-century Arab Mathematician, Mohammed Al-Khowarizmi, who developed, methods for solving problems which is, used specific step-by-step instructions., , Characteristics of algorithm: A well-defined algorithm has the five basic characteristics as, follows:, , 1. Input: Algorithm starts with procedural steps to accept input data. The algorithm must, accept one or more data to be processed., , 2. Definite: Each operational step or operation must be definite i.e. each and every instruction, must clearly specify that what should be done., , 3. Effective: Each operational step can at least in principle is carried out by a person using a, paper and pencil ina minimum number of times., , 4. Terminate: After some minimum number operation algorithm must come to an end., , Output: An algorithm is written to solve the problem, therefore it must produce one or, , more computed result or answer called output., , we, , Example: An algorithm to find the area of a rectangle can be expressed as follows:, , Given the length | and the breadth b, this algorithm finds the area of rectangle rec., Step 1: START, , Prof. K Adisesha vac
Page 2 :
PROBLEM SOLVING METHODOLOGY, , Step 2: {Read the vales of 1, b], INPUT I, b, , Step 3: {Calculate are of rectangle], rec=1*b, , Step 4: [Print the area of rectangle], OUTPUT rec, , Step 5: [End of Algorithm], STOP, , In the above example, we used = that represents assignment., , 1. Design an algorithm to find the average of four numbers, , Step |: START, , Step 2: INPUT A, B, C, D, , Step 3: [Calculate] AVG = (A+B+C+D)/4, Step 4: OUTPUT AVG, , Step 5: STOP, , 2. Design an algorithm to calculate the Simple Interest, given the Principal (P), and Rate (R), and Time (T), , Step 1: START, Step 2: INPUT P, T,R, Step 3: [Calculate] SI = (P*T*R)/100, Step 4: OUTPUT SI, Step 5: STOP, 3. Design an algorithm to find the greatest of three number (A, B, C), Step |: START, Step 2: INPUT A, B,C, Step 3: [Assign A to large], Large =A, Step 4: {Compare large and B], If ( B > large ), Large = B, Endif, Step 5: {Compare large and C], If (C > large), Large = C, Endif, Step 6: [Print the largest number], OUTPUT large, Step 7: STOP, 4. Design an algorithm to find factorial of a number ( N ), Step 1: START, Step 2: INPUT N, Step 3: [Initialize factorial to 1], Fact = |, Step 4: [compute the factorial by successive multiplication], , Prof. K Adisesha |
Page 3 :
PROBLEM SOLVING METHODOLOGY, , Repeat for I= 1 to N, , Fact = Fact * I, [End of Step 4 for loop], Step 5: [Print factorial of given number], OUTPUT Fact, Step 6: STOP, 5. Design an algorithm to find Fibonacci series ( N ), Step |: START, Step 2: INPUT N, Step 3: [Initialize the variables], First = 0, Second = |, Term = 2, Step 4: [Print the values of first and second], PRINT First, Second, Step 5: Third = First + Second, Step 6: Repeat while ( term <= N ), PRINT Third, First = Second, Second = Third, , Third = First + Second, Term = Term + |, {End of While loop], Step 7: STOP, , > Advantage of Algorithm, 1. It is a step-by-step representation of a solution to a given problem, which is very easy to, understand., 2. Ithas got a definite procedure, which can be executed within a set period of time., 3. Itis independent of programming language., 4. Itis easy to debug as every step has got its own logical sequence., , > Disadvantage of Algorithm, e = Itis time-consuming, e An algorithm is developed first which is converted into a flowchart and then into a, computer program., , > Analysis of Algorithm: There may be more than one approach to solve a problem. The, choice of a particular algorithm depends on the following performance analysis and, measurements., e Space complexity: The amount of memory needed by the algorithm to complete its run., e¢ Time Complexity: The amount of time, the algorithm needed to complete its run., When we analyze an algorithm depends on input data, there are three cases, e Best Case, e Average Case, e Worst Case, , Prof. K Adisesha Hi
Page 4 :
PROBLEM SOLVING METHODOLOGY, , FLOWCHART: A Flowchart is a pictorial or graphical representation of an algorithm., Flowchart plays an important role in the programming of a problem and helpful in understanding, the logic of program. Once the flow chart is drawn, it becomes easy to write program in any high, , level language., , Flowcharts are classified into two categories:, , 1;, 2., , Program Flowcharts, , System Flowcharts, , Program flowcharts present a diagrammatic representation of a sequence of instructions, for solving a program., , System flowcharts indicate the flow of data throughout a data processing system, as well, as the flow into and out of the system. Such flowcharts are widely used by designers, to, explain a data processing system., , > Importance of Flowchart, , 1., , Communication: Flowcharts are better way of communication of the logic of a program., , 2. Effective Analysis: With the help of flowchart, problem can be analyzed in way that is, , more effective., , Proper documentation: Program flowcharts serve as a good program documentation,, which is needed for various programs., , Efficient coding: The flowchart acts as guide or blueprint during the system analysis and, program development phase., , Proper Debugging: The flow chart helps in debugging process., , Efficient program maintenance: The maintenance of a program become easy with the, help of flowcharts., , Symbols Used In Flowcharts, , , , , , , , Name Function, Indicates any type of internal, Process operation inside the Processor, or Memory, , , , , , , , , , Used for any Input / Output, (W/O) operation. Indicates that, the computer is to obtain data, , or output results, Used to ask a question that can, Decision be answered in a binary, format (Yes/No, True/False), Allows the flowchart to be, drawn without intersecting, lines or without a reverse, flow., , input/output, , , , , , Connector, , , , , , Used to invoke a subroutine or, an Interrupt program., , Indicates the starting or ending, , Predefined Process, , , , , , , , , , , , , , OHIO e NF, , , , Terminal of the program. process, or, interrupt program, tl + Flow Lines Shows direction of flow., ne, , , , , , , , , , , , Prof. K Adisesha g
Page 5 :
PROBLEM SOLVING METHODOLOGY, , , , Example: Design a flow chart and an algorithm to find the area, of a square., 4) gmuer gt anes, Step 2: INPUT Side LT, Step 3: {Calculate Area] is Ee, , , , , , , , Area = Side * Side, , Step 4: OUTPUT Area, Step 5: STOP, , Design a flow chart and an algorithm to find the larger of two, , numbers., , Step 1: Start, , Step 2: Input A and B, , Step 3: If(A>B) then, Output A, Else, Output B, [End if], , Step 4: Stop, , , , > tetas of Flowcharts, Flowcharts provide an excellent means of communication, which is very easy to, understand., 2. It has got a definite procedure, which shows all the major parts of a program, It is easy to, convert it into a program., 3. Itis independent of programming language., 4. Itis easy to debug as every step has got its own logical sequence., , > Disadvantages of Flowcharts, 1. It is time-consuming and it requires the uses of a number of symbols which are to be, properly represented., 2. The represented of complex logic is difficult in a flowchart., 3. Alterations and modifications can be only made by redrawing the flowcharts., , > Pseudo code:, , e This is an abstract representation of program in English statement., e Inpseudo code, English words & phrases are used to represent operations., e Advantages: Easy to read, understand & modify., , > Coding or Programming: The process of writing program instructions for an analyzed, problem in a programming language., e It is the process of translating the algorithm or flowchart into the syntax of given purpose, language., e You must convert each step of the algorithm into one or more statements in a programming, language such as C, C++, and Java etc., , Prof. K Adisesha a