Page 1 :
TRANSPORT IN PLANTS, Passive symport and antiports, In a flowering, plant water, mineral, nutrients, organic nutrients and hormones are, transported. In a small distance they are moved by, diffusion and cytoplasmic steaming., Some proteins allow diffusion only if two, types of molecules move together. In a symport,, both molecules cross the membrane in same, direction. In an antiport they move in opposite, direction. If only one molecule is transported, through membrane is called uniport., Transport of substances over along distance is, through xylem and phloem. it is called, translocation. transport of substances in xylem is, unidirectional that means from root to stem., Carrter protein, Uniport A-, Means of transprot, diffusion:- diffusion is a passive process, i.e here, no energy is used. Diffusion is the movement of, substances from region of higher concentration to, the region of lower concentration., Antiport A, Symport -, Membrane, A pressure formed in the substances due to the, diffusion is called diffusion pressure.( D.P), Figure 11.2 Facilitated diffusion, Active transpert, Eg. spreading of a drop of ink in water, This type of transport uses energy. It is, carried out by membrane proteins. It take place, against the concentration gradient., diffusion rates are affected by, a) the gradient of concentration, b) the permeability of the membrane., c) temperature, d) pressure, Comparison of diffrent transport, Simple, diffusion, Facilitated, diffusion, property, Active, transport, facilitated diffusion, Requires special, membrane proteins, No, Yes, Yes, The diffusion rate depends on the size of, substances . The smaller substances move faster., The diffusion of substance across the membrane, Highly selective, No, Yes, Yes, Transport satureates No, Yes, Yes, also depend on solubility of it in lipids. Lipid, soluble substances move faster. Substances with, Uphill teransport, No, No, Yes, hydrphilic moiety, find difficult to pass through the, membrane. Their movement has to be facilitated., Require ATP, No, No, Yes, That means such substances are moved by the help, of proteins present tin the membrane. Such, diffusions take place with the help of proteins is, Water potential, it is, chemical potential of water. It is denoted, called facilitated diffusion., by the symbol Yw., In, facilitated, diffusion, there, is, no, The water potential of pure water is the, maximum, it is 0. if solute is added it is, decreased to negative value., Solute potential ( 4s ). and pressure potential, (4p. jare thetwo components of ww., expenditure of energy., Facilitated diffusion is very specific. That means, selective., Porins:- they are the proteins that form huge pores, in, the, outer, membranes, of the plastids,, mitochondria and some bacteria. Aquaporins are, the water channels made up of eight different types, of aqua porins., So, Uw. = Us+ p, U, will be negative, - 1 -, KR
Page 2 :
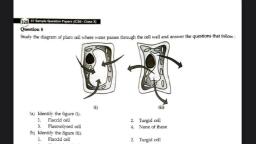
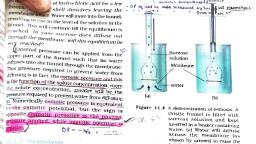
By endosmosis the cytoplasm exerts a pressure, against the cell wall , is called turgor pressure., OSMOSIS, Osmosis is the simple diffusion across a, semi permeable membrane. Here water move from, a region of high water potential to a region of, lower water potential. As a result of osmosis a, pressure is exerted, is called osmotic pressure. If, we give a pressure against the osmotic pressure, the process of osmosis will stop. If we increase, such pressure again; the osmosis take place in, reverse direction. This is called reverse osmosis., Imbibition, Here water is absorbed by the solids, colloids and result in the increase in volume., Eg. Absorb water by dry seeds, dry wood., The prerequisite for the imbibition are:, 1. water potential, absorbent and the liquid imbibed, 2. affinity between the adsorbent and liquid, gradient between the, The reverse osmosis is used for the purification of, water., water absorption, Pressure, water from soil is absorbed by the root hair. Then, from there it is moved deeper through two, pathway., a) apoplast pathway, b) sympläst pathway, Sucrose, solution, Membrane, Plasmodesmata, Plasma membrane, water, (a), (b), F.pidermis I, Cortex, Endodermis, Pericycle, Osmosis are of two type.; endosmosis and, Xylem, exosmosis., D= symplast, Casparian strip, V = apoplast, Endosmosis: if a cell is placed in the hypoto:nic, solution the water will move in to the cell. It is, Figure 11.6 Pathway of water movement in the root, called endosmosis. Due to the endosmosis the celi, apoplast: here water moves through inter cellular, spaces and cell wall., become turgid, Exosmosis: if a cell is placed in the hypertonic, solution the water will move out of the cel!. It is, Symplast: here water move by crossing the cell, membrane, and through the plasmodesmata., called exosmosis. Due to, exosmɔsis the cell, become flaccid., Hypotonic solution, comparatively less concentration, c JED ITT OF sd Endodermis, be brianoltebuz lo odi uea, means, the solution with, Xylem, Symplastic, path, lo agrl o Isibo, Hypertonic solution means the solution with, comparatively high concentration, vlno Jesd 1s, o voT oqe, Plasmolysis, sbr d ito dot usiv, T2oApoplastie o o igerCasparian, I si path innly teoCortex u strip, Phloem, When water move out of the cell the cell, Hie na, Pericycle, (by exosmosis) membrane shrinks and detaches, from the cell wall. This process is called, plasmolysis., Water movement up a plant, Can be explained by various theories., Water lost from cytoplasm first and then from, vacuole during plasmolysis., -2-, KR
Page 3 :
1. Root pressure theory, Transpiration – demerits, 1. leads to wilting and death of plant, Root pressure is the pressure developed, inside the root due to the accumulation of water., This pressure helps for the upward movement., uptake of mineral ions, Guttation is the process take place by the, phenomenon of root pressure., Minerals are absorbed and transported by both, active and passive mode., Guttation is the water loss from plants in the form, of liquid. It take place at the openings of veins of, leaf blade and leaf tip., It occurs in herbs. and take place in night., Phloem transport, The prepared food from leaves are transported to, different regions of the plant through the phloem., Sometimes it is stored at some parts. That part is, 2. Transpiration pull theory, called sink., Transpiration is a water loss process in, plants. Transpiration takes place through stomata, and cuticle. Transpired water is in the form of, Form sink tihe food again move to different parts, when it is needed. So here we can see a source to, sink trazıspori and sink to source transport. So the, phloern transpcrt is a bidirectional one., vapour., When transpiration take place in leaves a, But the xyiem transport is unidirectional., pull is occurred. that pull affects at the root xylem., So that pull result in the absorption of water and, upward movement of water., Pressure flow hypothesis is used to explain the, phloem transport from source to sink., It is because of the presence of continuous, column of water in the xylem from leaf to root., The glucose formed in the leaves then converted, Vinto sucrose and reach at companion cell, and then, into sieve tubes by active transport. This produce a, hypertonic condition inside the phloem. So water, in the adjacent xylem move into the phloem by, osmosis. Then the phloem sap will move to lower, The continuous column of water is maintained by, the two special properties of water; cohesion and, adhesion, pressure area., 1. cohesion: is the affinity between the similar, molecules. Here water noiecules show, affinity., 2. adhesion: is the affinity between the, dissimilar molecules. Here the affinity, between the water molecule and inner wall, of xylem., Transpiration - merits, 1. creates transpiration pull, 2. helps in the absorption and upward, movement of water, 3. helps in the absorption and upward, movement of minerals, 4. cools leaf surfaces, 5. maintains the structure and shape of plants, by keeping cells turgid., ..RAJESH.K..HSST Botany, GHSS Naduvannur, Kozhikod.., 3-, KR