Page 1 :
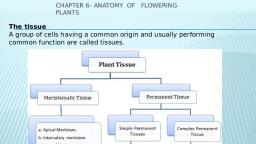
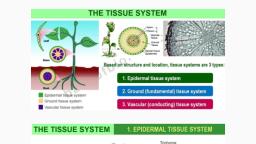
« The first formed primary phloem consists of narrow sieve tubes and referred as, protophloem., « The later formed phloem has bigger sieve tubes and is referred to as metaphloem., , THE TISSUE SYSTEM :, , « On the basis of their structure and location there are three types of tissue systems., o Epidermal tissue system., o Ground or fundamental tissue system., o Vascular or conducting tissue system., , Epidermal tissue system :, , « Forms the outermost covering of the whole plant body and comprises:, o Epidermal cells., o Stomata, o Epidermal appendages like trichomes and hair s;, « Epidermis consists of single layer parenchymatous, « Cells are elongated, compactly arranged, which form *ontinuous layer., « Epidermis is usually single layered., « Outside the epidermis covered with waxy *hicw layer called cuticle., « Cuticle absent in epidermis of root., « Stomata are the structure present in ihe epidermis of leaf., « Stomata regulate the process of transpiration and gaseous exchange., , , , , , Stomata :, , « Each stoma composed of twy bear shaped cell called guard cells., , « Ingrasses the guard cells.ar2 duro-bell shaped., , « Outer wall of guard cell is tatn.and inner wall is thick., , « Guard cell possesses chloreplast and regulates the opening and closing of stomata., , « Epidermal cells in the vicinity of guard cell called subsidiary cells., , « Stomatal aperture, guard cells and subsidiary cells together called stomatal, apparatus., , « The root hairs are unicellular elongations of the epidermal cells and help absorb water, and mineral from the soil., , Trichomes :, , « Onstem the epidermal hairs are called trichomes., , « Trichomes are usually multicellular., , « May be branched or unbranched and soft or stiff., , « Sometimes secretory., , « Trichomes help in preventing water loss due to transpiration.