Page 1 :
Chapter 5, PRINCIPLES O F INHERITANCE A ND VARIATION, Genetics, It deals with the inheritance, as well as the Variation of characters from parents to offspring . It is, the study of genes and chromosomes, Inheritance, Inheritance is the process by which characters are passed on from parent to progeny., Variation, It is the tendency of offspring to differ from their parents. The main reason for variations are, Crossing over and Mutation, Allele, They are alternative form of a gene / Genes which code for a pair of contrasting traits are known as, alleles., Phenotype, The physical appearance of an organism is called Phenotype. Eg: Tall plant, blue eye, round seed., True breeding line, A true breeding line is one that, having undergone continuous self-pollination, shows the stable trait, inheritance and expression for several generation., Genotype, The complete genetic constitution of an organism is called Genotype. Eg: Tt,TT,RR,Rr,YY,Yy, Homozygous (True breeding/Pure line), An organism with 2 identical allele of a gene. Eg:TT,RR,YY,YY,rr,tt, Heterozygous, An organism with 2 different allele of a gene. Eg:Tt,Rr,Yy, Character and Trait, A character is a heritable feature that varies among individuals. Eg: Flower color,Plant Height,seed, shape, Eye colour. A trait is a variant for character, Eg: white or purple colors for flowers, Dwarf, plant, Round seed, Blue eye., Reason for selecting garden pea plant (Pisum sativum), 1. It has short life cycle so it gives quic results., 2. Plants shows clear contrasting character, 3. Being a herb, it is Easy to cultivate, 4. It has bisexual flower, 5. It is generally self pollinated and so self fertilised. However , it can e Cross pollination is easy if, self pollination is prevented., Monohybrid cross- Inheritance of one gene
Page 2 :
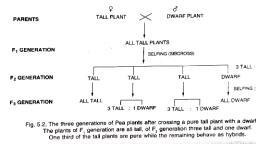
Monohybrid cross is the cross involving two forms of a single character. Mendel crossed tall plants, and dwarf pea lant to study the inheritance of one gene. Mendel observed that all the F1 progenies, were tall (Like one of its parent and none were dwarf ) He then self pollinated the F1 progeny (Tall, plants ) to generate F2. He observed that 75% of the F2 progenies were tall and 25% were dwarf, (Ie: 3:1) Ie: characters that was not seen in the F1 generation expressed in the F2 (dwarf), He also found that ,The tall and dwarf traits were identical to their parental type and did not show, any blending, that is all the offspring were either tall or dwarf, none were of in between height no, blending of characters in offsprings., Based on this observation Mendel proposed that something being was being stably passed down, unchanged from parents to offspring through gametes over successive generation. Mendel called it, as factors. Now we called them as genes., PUNNET SQUARE, It was developed by British geneticist Reginald C Punnet. It is the graphical representation to, calculate the probability of all possible genotype of an offspring in a genetic cross . The possible, gametes are written on 2 sides, usually on the top row and left column. All possible combinations, are written in boxes below in square., , Monohybrid genotypic ratio= 1:2:1, Monohybrid phenotypic ratio =3:1, Back cross, It is the cross of F1 progeny with one of its parent
Page 3 :
Test cross, It is the crossing of F1 progeny with its recessive parent ., It is used to find unknown genotype of an individual., , Law Of Dominance, The main points are ..., • The characters are controlled by discrete units called factors., • Factors occur in pair., • In a dissimilar pairs of factors (Heterozygous) ,one member of pairs dominates over the, other. (The dominated one is called Dominant , and other character is called Recessive), Law of segregation, This law is based on the fact that the alleles do not show any blending and that both the characters, are recovered as such in the F2 generation though one of these is not seen at the F1 stage ., During gamete formation 2 factors for a character present in an individual will separate from each, other and enter into each gamete.