Page 1 :
Kerala Higher Secondary, Plus Two Zoology, , PART - 1, TLB’S Biology Classes
Page 2 :
ZOOLOGY TOPICS, , TLB’S Biology Classes
Page 3 :
ZOOLOGY TOPICS, , TLB’S Biology Classes
Page 4 :
HUMAN REPRODUCTION, Sexually, Reproducing, organisms may, be Oviparous, and Viviparous, , TLB’S Biology Classes
Page 5 :
HUMAN REPRODUCTION, , Human beings are Sexually, Reproducing organisms., , TLB’S Biology Classes
Page 6 :
HUMAN REPRODUCTION, Whom do you love more ?, Father ?, Mother?, Brother?, Sister?, Teacher?, TLB’S Biology Classes
Page 7 :
HUMAN REPRODUCTION, Yes, of course the answer is, , Mother, , TLB’S Biology Classes
Page 8 :
HUMAN REPRODUCTION, , Pregnancy lasts for, about 280 days or, 40 weeks, , TLB’S Biology Classes
Page 9 :
HUMAN REPRODUCTION, , TLB’S Biology Classes
Page 10 :
HUMAN REPRODUCTION, , Which parts of our body help, us to become the father or, mother of a baby ?, , TLB’S Biology Classes
Page 11 :
HUMAN REPRODUCTION, , What are the events in, Human Reproduction?, , TLB’S Biology Classes
Page 12 :
HUMAN REPRODUCTION, What are the events in, Human Reproduction?, 1. Gametogenesis, Production of sperms in males, and ovum in females, , TLB’S Biology Classes
Page 13 :
HUMAN REPRODUCTION, What are the events in, Human Reproduction?, 2. Insemination, Transfer of sperms into, the female genital tract, , TLB’S Biology Classes
Page 14 :
HUMAN REPRODUCTION, What are the events in, Human Reproduction?, , 3. Fertilisation, Fusion of male and, female gametes, , TLB’S Biology Classes
Page 15 :
HUMAN REPRODUCTION, What are the events in Human Reproduction?, , 4. Development of blastocyst, , TLB’S Biology Classes
Page 16 :
HUMAN REPRODUCTION, What are the events in Human Reproduction?, 4. Implantation, Attachment of blastocyst, to the uterine wall, , TLB’S Biology Classes
Page 17 :
HUMAN REPRODUCTION, What are the events in Human Reproduction?, 5. Gestation, Development of embryo, , TLB’S Biology Classes
Page 18 :
HUMAN REPRODUCTION, What are the events in Human Reproduction?, 5. Parturition, Delivery of the baby, , TLB’S Biology Classes
Page 19 :
EVENTS IN HUMAN RERODUCTION, gametogenesis, , Production of sperms in males and ovum in females, , insemination, , transfer of sperms into the female genital tract, , fertilisation, , fusion of male and female gametes, , development of, blastocyst, implantation, gestation, parturition, , attachment of blastocyst to the uterine wall, Development of embryo, delivery of the baby, TLB’S Biology Classes
Page 21 :
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM, , TLB’S Biology Classes
Page 22 :
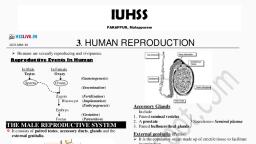
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM, , , The male reproductive, system is located in the, pelvis region, , . It includes, , a pair of testes, , accessory ducts, , Accessory glands, , external genitalia., TLB’S Biology Classes
Page 23 :
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM, , Scrotum, , , The testes are situated outside the, abdominal cavity within a pouch, called scrotum., , , , The scrotum helps in maintaining, the low temperature of the testes, (2–2.5oC lower than the, normal, , internal, , temperature), spermatogenesis., , necessary, , body, for, TLB’S Biology Classes
Page 24 :
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM, , Testicular lobules, , , , , , , In adults, each testis is oval in, shape, with a length of about 4, to 5 cm and a width of about 2, to 3 cm., The testis is covered by a, dense covering., Each testis has about 250, compartments, called, , testicular lobules, , TLB’S Biology Classes
Page 25 :
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM, , seminiferous tubules, , , , Each lobule contains, one to three highly, coiled, seminiferous, tubules, in, which, sperms are produced., , TLB’S Biology Classes
Page 26 :
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM, , Spermatogonial cells and Sertoli Cells, , , Each seminiferous tubule is lined on, its inside by two types of cells called, , male germ cells (spermatogonia), and Sertoli cells, , , The, , male, , germ, , cells, , undergo, , meiotic divisions finally leading to, sperm formation,, , , While Sertoli cells provide nutrition, to the germ cells., , TLB’S Biology Classes
Page 27 :
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM, , Interstitial cells or Leydig cells, , , The regions outside the seminiferous, tubules, , called, , contain, , small, , interstitial, blood, , spaces,, , vessels, , and, , interstitial cells or Leydig cells., , , Leydig cells synthesise and secrete, testicular, , hormones, , called, , androgens., , TLB’S Biology Classes
Page 30 :
Male sex accessory ducts, , , , The epididymis leads to, vas deferens that ascends, to the abdomen and loops, over the urinary bladder., , , , It receives a duct from, seminal vesicle and opens, into, , urethra, , as, , the, , ejaculatory duct., TLB’S Biology Classes
Page 31 :
Male sex accessory ducts, , , , These, , ducts, , store, , and, , transport the sperms from the, testis to the outside through, urethra., , , The urethra originates from, the, , urinary, , bladder, , and, , extends through the penis to, its external opening called, urethral meatus, TLB’S Biology Classes
Page 32 :
Male sex accessory ducts, Conduction of sperms through Accessory ducts, , TLB’S Biology Classes
Page 33 :
Penis, , , MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM, , The penis is the male external, genitalia ., , , , It is made up of special tissue that, helps in erection of the penis to, facilitate insemination., , , , The enlarged end of penis called, the glans penis is covered by a, loose, , fold, , foreskin., , of, , skin, , called
Page 34 :
Male sex accessory glands, , , •, •, •, , , , , The male accessory glands, include, paired seminal vesicles,, a prostate and, paired bulbourethral glands., Secretions of these glands, constitute the seminal plasma, which is rich in fructose,, calcium and certain enzymes., The, secretions, of, bulbourethral, glands, also, helps in the lubrication of the, penis.
Page 35 :
Male sex acessory glands, • They include, , A pair of seminal, vesicles., A prostate gland., A pair of bulbourethral glands., • .