Page 1 :
PLUS TWO, , Chapter 3, , HUMAN REPRODUCTION
Page 2 :
●, , REPRODUCTION, ●, , ●, , A biological process in which an organism, gives rise to young ones (offspring) similar to, itself., It enables the continuity of the species,, generation after generation
Page 3 :
●, , Asexual reproduction, ●, , ●, , When offspring is produced by a single parent with, or without the involvement of gamete formation., , Sexual reproduction, ●, , When two parents (opposite sex) participate in the, reproductive process and also involve fusion of, male and female gametes.
Page 4 :
●, , Oviparous, ●, , ●, , This means oviparous animals lay eggs. These, eggs develop and hatch into young individuals., , Viviparous, ●, , Giving birth to living offspring that develop, within the mother's body as for most mammals.
Page 6 :
●, , Gametogenesis, ●, ●, , ●, , Male gametes are sperms and female gametes are, egg/ovum., , ●, , Formation of sperm is called spermatogenesis, , ●, , Formation of egg is called oogenesis, , Insemination, ●, , ●, , it is the formation of gametes., , it is the transfer of sperms into the female genital tract., , Fertilisation, ●, , it is the fusion of male and female gamete. It results in, the formation of Zygote.
Page 7 :
●, , Implantation, ●, , ●, , Gestation, ●, , ●, , ●, , The formation and development of blastocyst, and its attachment to the uterine wall, , Embryonic development within the uterus of, mother is called gestation., Human gestation period is 9 month., , Parturition, ●, , Delivery of the baby is the parturition
Page 8 :
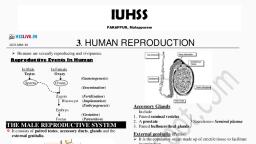
THE MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM, The male reproductive system is located in the, pelvis region. Male reproductive system, includes, , I. A pair of testes., II. Accessory ducts., III. Accessory glands., IV. External genitalia
Page 9 :
●, , Testes, ●, , ●, , ●, , ●, , The testes are situated outside the abdominal, cavity within a pouch called scrotum., Each testis has about 250 compartments called, testicular lobules., Each Testicular lobule contains one to three, highly coiled seminiferous tubules in which, sperms are produced., Each seminiferous tubule is lined on its inside, by two types of cells called Male germ cells, (spermatogonia) and Sertoli cells.
Page 10 :
●, , ●, , ●, , ●, , The male germ cells undergo meiotic divisions finally, leading to sperm formation, Sertoli cells (Nursing cells ) provide nutrition to the, germ cells., The regions outside the seminiferous tubules called, interstitial spaces, contain small blood vessels and, interstitial cells or Leydig cell., Leydig cells synthesise and secrete testicular, hormones called androgens. Other immunologically, competent cells are also present.
Page 15 :
●, , ●, , ●, , ●, , The epididymis leads to vas deferens that, ascends to the abdomen and loops over the, urinary bladder., Vas deferens receives a duct from seminal, vesicle and opens into the urethra as the, ejaculatory duct., These ducts store and transport the sperms, from the testis to the outside through urethra., Urethra originates from the urinary bladder, and extends through the penis to its external, opening called urethral meatus.
Page 16 :
●, , External Genitalia, ●, ●, , ●, , The penis is the male external genitalia ., It is made up of special tissue ( Spongy erectile, tissue ) that helps in erection of the penis to, facilitate insemination., The enlarged end of penis called the glans, penis is covered by a loose fold of skin called, foreskin.
Page 17 :
●, , Accessory Glands, ●, , i)Paired seminal vesicles,, , ●, , ii)A prostate, , ●, , iii)Paired bulbourethral glands, , ●, , ●, , ●, , ●, , Secretions of all these glands constitute the, seminal plasma which is rich in fructose, calcium, and certain enzymes., The secretions of bulbourethral glands also helps, in the lubrication of the penis., Seminal plasma along with sperm is called Semen
Page 18 :
THE FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM, ●, , The female reproductive system is located in pelvic region, , ●, , a) A pair of ovaries, , ●, , b) Accessory ducts, , ●, , ●, , The oviducts, , ●, , Uterus, , ●, , Vagina, , c) External genitalia, ●, , Mons pubis,, , ●, , Labia majora,, , ●, , Labia minora,, , ●, , Hymen and, , ●, , Clitoris
Page 19 :
Ovaries, ●, ●, , ●, , ●, , ●, , ●, , Ovaries are the primary female sex organs, The ovaries are located one on each side of the lower, abdomen, Ovaries produce the female gamete (ovum) and several, steroid hormones (ovarian hormones-Estrogen and, progesteron), Each ovary is about 2 to 4 cm in length and is connected, to the pelvic wall and uterus by ligaments., Each ovary is covered by a thin epithelium which, encloses the ovarian stroma., The stroma is divided into two zones – a peripheral, cortex and an inner medulla
Page 20 :
Accessory ducts, ●, ●, , ●, , ●, , ●, , Oviducts (fallopian tubes), Each fallopian tube is about 10-12 cm long), the, part closer to the ovary is the funnel-shaped, infundibulum., The edges of the infundibulum possess finger-like, projections called fimbriae, which help in, collection of the ovum after ovulation., The infundibulum leads to a wider part of the, oviduct called ampulla., Isthmus has a narrow lumen and it joins the, uterus
Page 22 :
●, , ●, , ●, , ●, , Uterus (Womb), The shape of the uterus is like an inverted, pear., The uterus opens into vagina through a, narrow cervix., The cavity of the cervix is called cervical, canal which along with vagina forms the, birth canal.
Page 23 :
●, , i) Perimetrium:●, , ●, , ii) Myometrium:●, , ●, , It is the The external thin membranous layer of, uterus, It is the middle thick layer of uterus. It contains, smooth muscle. The myometrium exhibits, strong contraction during delivery of the baby., , iii)Endometrium, ●, , It is the inner most layer of uterus and is a, glandular layer. The Endometrium undergoes, cyclical changes during menstrual cycle
Page 24 :
External genitalia, ●, , i)Mons pubis, ●, , ●, , ii)The labia majora, ●, , ●, , They are fleshy folds of tissue, which extend down from the, mons pubis and surround the vaginal opening., , iii)The labia minora, ●, , ●, , It is a cushion of fatty tissue covered by skin and pubic hair., , They are paired folds of tissue under the labia majora., , iv)Hymen, ●, , The opening of the vagina is often covered partially by a, membrane called hymen., , • v)Clitoris, ●, , The clitoris is a tiny finger-like structure which lies at the upper, junction of the two labia minora above the urethral opening.
Page 26 :
Mammary gland, ●, , ●, , ●, , ●, , ●, , Glandular tissue and Variable amount of fat., The glandular tissue of each breast is divided into, 15-20 mammary lobes containing clusters of cells, called alveoli ., The cells of alveoli secrete milk, which is stored in, the cavities (lumens) of alveoli. The alveoli open, into mammary tubules., The mammary tubules of each lobe join to form a, mammary duct., Several mammary ducts join to form a wider, mammary ampulla which is connected to lactiferous, duct through which milk is sucked out.