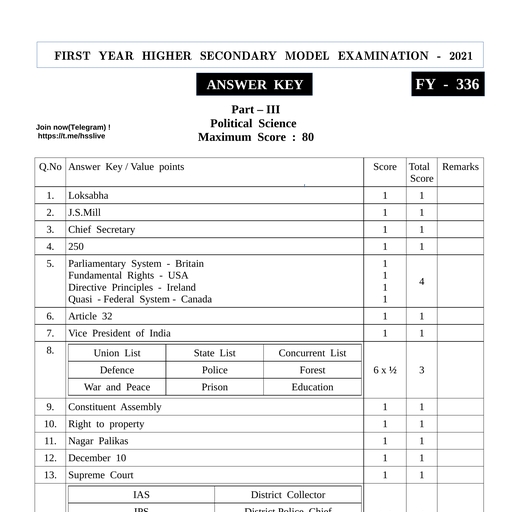
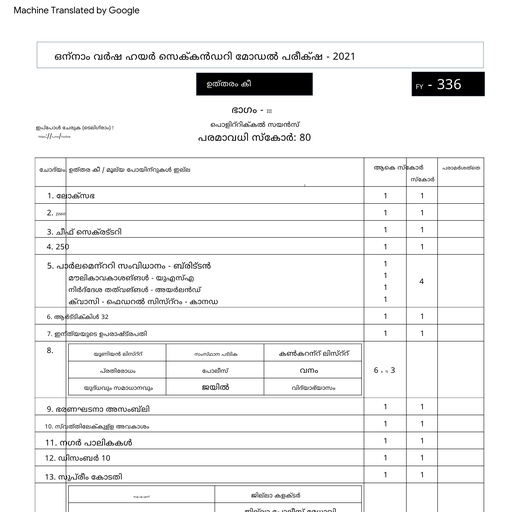
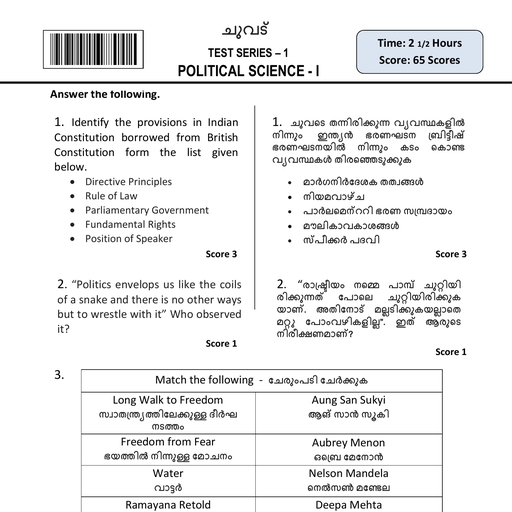
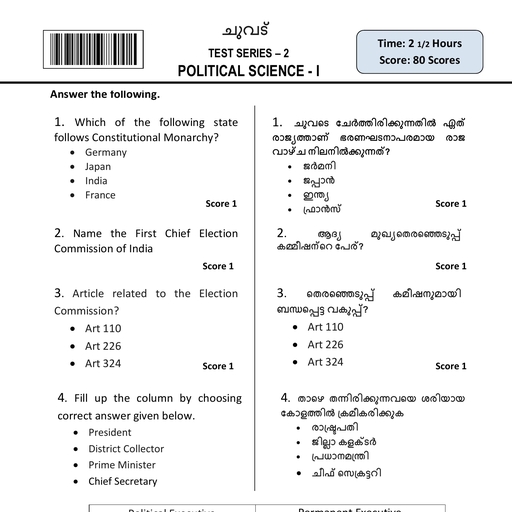
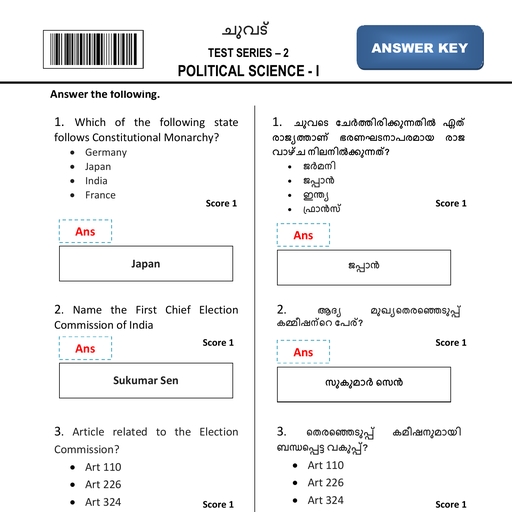
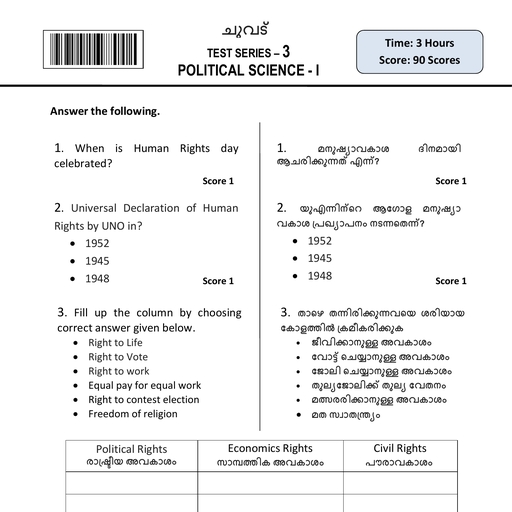
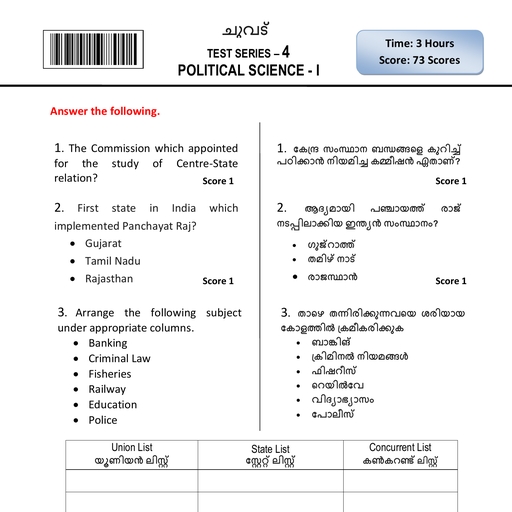
Page 5 :
E PLUS KERALA, , 4. India’s External Relations, India gained independence at a time when the world was, facing great challenges. The devastating World War II caused huge economic, problems. Following the end of colonial rule, new independent states were, formed in Africa and Asia. The main challenges faced by the new countries, were the establishment of democracy and the elimination of poverty. Partitionrelated issues along with international issues and economic backwardness have, challenged India. Domestic and external circumstances have influenced India's, foreign policy making., , Objectives of Indian Foreign Policy, -, , Promote world peace., Maintain better relations between countries., Respect international law., Settle disputes between countries., Resist the colonialism., Oppose the racist issues., Propagate Non Alignment policy., Strengthen the United Nations., , Non Alignment policy, After World War II, the capitalist bloc under the United States, and the socialist bloc under the Soviet Union were formed. Most of the states, had joined any blocs to receive financial and military aid. In return, member, states were forced to surrender the sovereignty and independence powers of the, country to the super powers. But Jawaharlal Nehru, India's first foreign, minister, refused to lose the independence and sovereignty won by foreign, powers. India decided to adopt a non-salignment policy of equal distance from, the two power blocs. India has encouraged the newly independent countries of, Asia, Africa and to adopt a non-aligned policy., The first meeting of the countries that decided to adopt a non-aligned policy, was convened in April 1955 in Bandung. The first meeting of the Non, Alignment Movement was held in Belgrade in 1961. The name Non Alignment, Movement was proposed by VK Krishna Menon., , Objectives of Jawaharlal Nehru's foreign policy, Jawaharlal Nehru, India's first foreign minister, put forward a foreign, policy with three main objectives., Protect the hard earned sovereignty of india., Protect the territorial integrity of India., Promote the rapid economic development of India.
Page 6 :
E PLUS KERALA, , India and China, India was one of the first countries to recognize the communist, government that came to power after the Chinese Revolution of 1949. The two, countries initially enjoyed good relations. The Panchasheel Agreement was, signed on April 29, 1954 by Indian Prime Minister Jawaharlal Nehru and, Chinese Prime Minister Chou En-lai. Jawaharlal Nehru, who had good relations, with Chinese leaders, was not interested in deploying troops on the Indo-China, border. Nehru entrusted border protection to the paramilitary unit. But leaders, like Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel pointed out the possibility of an attack from the, Chinese side. Nehru completely ruled out such a possibility. But relations with, China soon deteriorated. Two issues had seriously affected India-China, relations., 1. The Tibetan Issue - China invaded Tibet in the 1950s and tried to suppress, Tibetan culture. Initially, India was involved in the Tibetan issue. But after the, signing of the Pentateuch, India was forced to remain silent on the Tibetan, issue. India accepted China’s claims over Tibet after signing Panchasheeel, agreement. One of its clause was about respecting each other’s territorial, integrity and sovereignty. As the situation in Tibet deteriorated, Dalai Lama,, the spiritual leader of Tibet, and his followers sought political asylum in India., China has accused India of providing support to anti-China activities.., 2. Boundary Dispute - China refused to accept the Mac Mahon Line, the, Indo-Chinese border settled during British rule. China has claimed the Aksai, Chin area in the Ladakh region of Jammu and Kashmir and Arunachal Pradesh., , The Sino-Indian War of 1962, The Indo-China conflict turned into a war in 1962. China invades, Ladakh and the NEFA region. China has made clear progress in both areas. The, war ended on November 21, 1962, when China unilaterally declared a ceasefire., , Consequences of war, 1., The image of India inside and outside the country has faded., 2., Failure caused national humiliation., 3., National consciousness was strengthened., 4., Defense Minister VK Krishna Menon and top military officials had, resigned., 5., The image of Nehru faded., 6., The first no-confidence motion against the Central Government was, introduced in the Lok Sabha., 7., The Congress lost some post-war by-elections., 8., Split in the Communist Party of India. The CPI (M) was formed., 9., Nagaland got state status., 10. Manipur and Tripura got the right to elect legislatures
Page 7 :
E PLUS KERALA, , India-Pakistan relations, The relationship between India and Pakistan has been complicated, from the beginning for various historical reasons. In October 1947, tribal, infiltrators from Pakistan invaded Kashmir. Despite the ongoing India-Pakistan, dispute over Kashmir, countries have been able to co-operate in at least some, areas., 1., The two countries co-operated in returning women abducted during, the, Partition period to their original families., 2., India and Pakistan signed the Indus Water Treaty in1960 ., , The War of 1965, In 1965, Pakistan invades the Rann of Kutch region of Gujarat and, Jammu and Kashmir. The Indian army counter attacked and reached near, Lahore. The United Nations intervened and the war ended. The Tashkent, Agreement was signed by the Prime Minister of India Lal Bahadur Shastri and, the ruler of Pakistan Ayub Khan on January 10, 1960., , The 1971 war, Pakistan was made up of East Pakistan and West Pakistan. The, centres of power in Pakistan were taken over by leaders from West Pakistan., The people of East Pakistan were considered as second class citizens. In 1970,, Pakistan held its first general election. The people of East Pakistan have given a, verdict against the neglect of West Pakistan. The Awami League, the political, party of East Pakistan, defeated the Pakistan People's Party, the political party, of West Pakistan. But the Pakistani military government refused to hand over, power to Awami League leader Sheikh Mujib Ur Rahman. The Pakistani, military regime arrested Mujib Ur Rahman and unleashed a reign of terror in, East Pakistan. The people of East Pakistan, came together under the Mukti, Bahini and stood firm for a separate nation named Bangladesh. The US and, China supported Pakistan. India signed a 20-year Treaty of Peace and friendship, with the Soviet Union. In December 1971, the Pakistani army invaded India., The Pakistani army had to surrender in the face of a strong Indian counter, attack with the support of the people of East Pakistan. The independent nation, of Bangladesh was formed. The Shimla Agreement was signed between the, Prime Minister of India, Indira Gandhi, and the President of Pakistan, Zulfikar, Ali Bhutto on July 3, 1972., , Consequences of war, 1., 2., 3., 4., 5., , Formation of Bangladesh., Nationwide Jubiliation., National pride increased, Indira Gandhi's popularity increased., The Congress won the Assembly elections held after the war
Page 8 :
E PLUS KERALA, , India's Nuclear policy, Jawaharlal Nehru played an important role to develop the, nuclear policy of India. Homi J bhabha, a scientist, gave precise advice to, Jawaharlal Nehru. Nehru sought to shape modern India with the help of science, and technology. India's position was that nuclear energy should be used for, peaceful purposes. But India has argued that the Nuclear Non-Proliferation, Treaty, led by the United States, the Soviet Union, Britain, France and China,, which own nuclear weapons, is discriminatory. Therefore, India refused to sign, such agreements. Following China's nuclear test, India also decided to test, nuclear weapons. On May 18, 1974, India conducted its first nuclear test in the, Pokhran Desert in Rajasthan under the secret name of Smiling Budha. In May, 1998, India conducted its second nuclear test, Operation Shakti. Important, principles of Indian nuclear policy are given below., 1., Ensure nuclear disarmament., 2., Nuclear weapons will not be used first by India., 3., India will not use nuclear weapons against countries that do not have, nuclear, weapons., 4., India's goal is a nuclear-free world., , PREPARED BY, MATHEW JOSEPH, വീഡിയോ കാണുവാനായി ചിത്രങ്ങളിൽ CLICK ചെയ്യുക.