Page 1 :
1o., Wave Optics, Wave front -, A wavefront is defined as the conti-, nuous locus of those partices of a medium, which, are vibrating in the same phase., Depending, wave front car be of three types :, li) spherical wave front -, on the shape of the source of light,, when the source of light is a, point, source, the wavefront, is a sphere with centre at the source, (ii) Cylindrical wave front -, when the source of light is linear la slit)., then all the points equidistant from the source, lie on a cylinder. Therefore the wavefront is, cylin, derical., A, a, Gi) Plane Wavefront -, when the point Source, light is at very large distance, a small partion of, spherical, OY. linear Source of, orcylinderical wave front appears to be plan, such a wavefront is calld a plane wavefront., * If we draw a set of straight lines which are, perpendicular to the wavefront then these lines are, cailed the ray of light., Scanned with CamScanner
Page 2 :
The given tigures (a) ,(b) and (6) represents the, wavefront annd, wave front (PWF), diverging spherical 'wave foont (pswF), and Converging, rays of lignt corres ponding to plane, spherical wavefront (CSWF) espectively, Diverging, SWF, Converging, SWF, PWF, RAYS, RAYS, RAYS, Huygen's Principle-, in which, The Huyger's principle tells the, the wavefro is propogated further in a medium., way, According to Huygeris -, (i) Every point on the given wavefront ( Called, primary wavefront) acts, disturbance , called secondary wavelets, which travel, in all directions with the velocity of light in the, medium., as, a fresh source of new, (ii) A surface touching these secoundary wavelets, tangent, tially in the forward direction at any instant gives, the new wavefront at that instant. This is called, secondary wave front., gives, A2 A A1, PROPAGATION, OF, LIGHT WAVE, B1, B2 B, B1, Scanned with CamScanner
Page 3 :
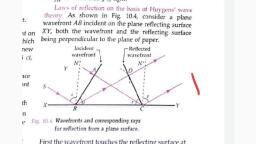
Reflection on the basis of Wave Theory -, Huygen's principle can be wsed to explain the, phenomena of reflection and refraction of light, In the given figure AB is a plane wave front, incident on a plare mior M,M2 at LBAA' =°Li., 1, 2, 3, are perpendicular to AB., are the Coresponding incident, rays, which, 3, 2, 2', D', N, M1, A, M2, According to Huygens principle, every point on, AB is a source of secondary wovelets. Let the secondary, wavelets from B strike M,m2 at A' in t seconds., BA' :, ext, The secondary wavelets from A will travel the, Same distance cxt in the same time. Therefore,, A as centre and cxt as radius , draw an arc, so, that -, with, AB' = Cxt, 2., From A' draw a tangent plane AB' touching, the spherical arc tangentially at B'. Therefore A'e', is the secondary wave front after t seconds. This, would advance in the direction of rays 1,2' and 3',, which are the corresponding reflected says perpendi-, cular to A'e'., Scanned with CamScanner
Page 4 :
angle of incidence, angle of reflection, A AA'B and A AAB',, Нence, =LBAA', and, Y = LB'A'A, %3D, In, AA. is Common, and, BA' = AB =, : 90', Cxt, LB =, A AA'B an A AA'B are congruent., LBAA', = Lo'A'A, which is the first law of reflection., i.e., Li = Lr, Further the incident wavefront AB, the reflecting, Swrface MIM2 and the reflected wavefoont A'B' ari, all perpendicular to the plane of the paper., Theretore imcident ray, normal to the mirror, MIM 2 and reflected Tay au lie in the plane of the, paper. This is second daw of reflection., Refraction on the basis of Wave Theory-, In the given figure XY is a plane surface, that separates a denser medium ok refractive, index i from a rarer medium., If y, is velocíty of, light in rarer medium, and V2 is veloity of, Light in denser medium, then, Rarer-C,, A', Y, as M, =, and M;=, C, A, Denser-C2, 2', 0-, or, V2, Scanned with CamScanner
Page 5 :
Here AB is a plane wavefront incident on, XY at L, L BAA' =, Li ., 1, 2, and 3 are Hthe corres-, ponding incident, rays, normal to AB., According to Huygen's principle, every point, AB is a, source of secondlary wavelets., on, SOur, Let the secondary wavelets from 3 strike xy at, A' in t seconds., : V,xt, The secondary wavetets from A travel in the, denser medlium with a velocity V2 and would, distance (Y2xt) in t seconds, Therefore, with A as centre and radius egual to (V2xt), 2, Cover, a, draw, an, arc B'., From A', draw, spherical arc tangentially 'at B'i Therefore A'š is, the secondary wăvefront after t sec. This would, advance in the direction of rays 1,2' and 3',which, are the Corresponding refracted rays, perpedicular, to A'B'., Let p be the angle of refraction. As angle of, refraction is equal to the angle which the refracted, plane wavefront A'B' makes with the refracting, surface AA, therefore, tangent plane touching the, a, L AA'B = LY, In a aa'B,, Sini, BA, Vxt, %3D, %3D, AA, AA!, In A AA'B',, AB, siny =, AA!, AA, Sini, sinr, (by eq 0), Sini, sint, H, Sini = Msine, %3D, Or, which Proves Snell's Law of refraction., Scanned with CamScanner