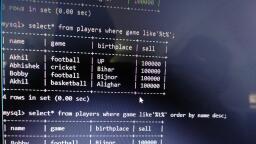
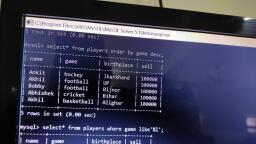
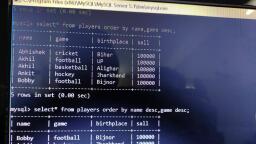
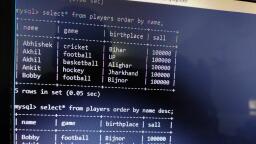
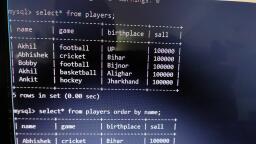
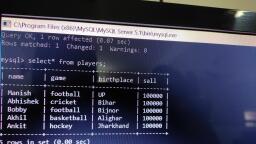
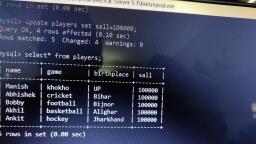
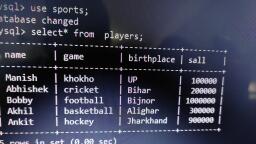
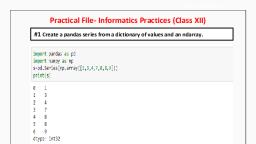
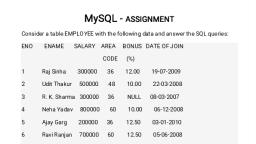
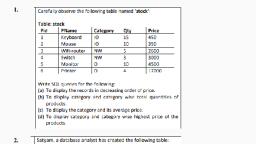
Page 1 :
KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SILVASSA, CLASS – XII, SUBJECT – INFORMATICS PRACTICES, SUPPORT MATERIAL, SQL – STRUCTURED QUERY LANGUAGE, Question Bank, [1 mark questions] Q.NO. 1-21, 1), , Ans:2), Ans:3), Ans :4), , The avg( ) function in MySQL is an example of …………………., (i), Math Function, (ii), Text Function, (iii), Date Function, (iv), Aggregate Function, (v), Aggregate Function, The …………. Command can be used to make changes in the rows of table in, SQL., UPDATE, The SQL Command that will display the current time and date., Select now();, , Themid()functioninMySql is an exampleof, a. Mathfunction, , ., , b. Textfunction, c. DateFunction, d. AggregateFunction, Ans:5), , b. Text Function, , Ans:6), Ans:7), , Instr( ), , Ans:8), , 10, , Ans:9), Ans:10), , The, another., , function is used in SQL to find one string into, , MID () and SUBSTR () function in SQL serves the same purpose. (Yes/No), Yes, , Write the output for the following SQL command:, Select round(15.193 , -1);, Write a SQL query to display date after 10 days of current date on your, system., Select curdate()+10;, 1 mark for correct SQL command, Write the output for the following sql command:, Select SUBSTR(‘ABCDEFG’, -5 ,3), UBS, , Which keyword is used to arrange the result of order by clause in, descending order?, a. DSEC, b. DES
Page 2 :
Ans:11), , Ans :12), , Ans :13), , Ans:14), , Ans:15), Ans:16), Ans :17), , c. DESCE, d. DESNO, a. DESC, The clause that is used to arrange the result of SQL command into, groups, a. Orderby, b. Groupin, c. Groupsby, d. Groupby, d.Group By, Find the Output of SQL command :, select concat (concat (‘Inform’, ‘atics’),‘Practices’);, a. InformaticsPractices, b. InformaticPractices, c. Informpractices, d. Inform aticspractices, a. InformaticsPractices, Write the output of the following SQL, command. select round (19.88,1);, a.19.88, b. 19.8, c. 19.9, d. 20.0, c. 19.9, The now() function in MySql is an example of ., a. Math function, b. Text function, c. Date Function, d. Aggregate Function, c. Date Function, The………….command can be used to makes changes in the structure of, a table in SQL., ALTER, Write the SQL command that will display the time and date at which, the command got executed., Select sysdate();, Write the output of the followingSQLcommand., select round(15.872,1);, a. 15.87, , b.15.9, c.15.8, d.16, , Ans:18), , b. 15.9, Manish wants to select all the records from a table named “Students”, where the value of the column “FirstName” ends with an “a”. Which of, the following SQL statement willdothis?, a. SELECT * FROM Students WHERE FirstName =‘a’;, b. SELECT * FROM Students WHERE FirstName LIKE‘a%’;, c. SELECT * FROM Students WHERE FirstName LIKE‘%a’;
Page 3 :
d., Ans:-, , SELECT * FROM Students WHERE FirstName = ‘%a%’;, , d. SELECT * FROM Students WHERE FirstName = ‘%a%’;, , 19), Ans:20), Ans:21), , The command can be used to add a new column tothetable., ALTER, Which SQL command is used to describe the structure of the table?, DESC, , Ans:22), , ii) Referential Integrity, , Ans:23), , ii) 5,7, , Ans:24), , i), , Ans:25), , Foreign, i), ii), iii), iv), , A table ‘Student’ contains 5 rows and 4 columns initially. 2 more rows are, added and 1 more column is added . What will be the degree and, cardinality of the table student after adding these rows and columns?, i), 7, 5, ii), 5,7, iii), 5,5, iv), None of theabove, Insert into student values(1,’ABC’,’10 Hari Nagar’) is a type of which, command :, i), DML, ii), DDL, iii), TCL, iv), DCL, , DML, , What will be the output of - select mid('Pyhton Programming’,3,9);, i), tonProgr, ii), tonProgr, iii), htonProg, iv), htonProg, , iii) hton Prog, Write the output of the following SQL statement:, SELECT TRUNCATE(15.79,-1) , TRUNCATE(15.79,0),, TRUNCATE(15.79,1);, a., b., c., d., , Ans:26), , Ans:27), , Key in a table is used to enforce, Data dependency, ReferentialIntegrity, Views, IndexLocations, , 15, 10, 10, 10, , 15, 15.7, 15, 10, , 15.7, 15.9, 15.7, 15.9, , c. 10, 15, 15.7, The COUNT( ) in MySQL is an example of :, a. Math function, b. Text function, c. Date Function, d. Aggregate Function, d. Aggregate Funcion, …….. which of the following sublanguages of SQL is used to query
Page 4 :
Ans:28), , Ans:29), , information from the database and to insert tuples into, delete tuples, from and modify tuples in the database?, a. DML, b. DDL, c. Query, d. Relational Schema, a. DML, The ……… clause of SELECT query allows us to select only those rows in, the result that satisfied a specified condition., a. WHERE, b. FROM, c. HAVING, d. LIKE, a. WHERE, Write the output of the following SQL command., select substr(“COMPUTER”,3,4);, a. MPUT, b. PUTE, c. PU, d. MP, , Ans: 30), , a. MPUT, The now() function in MySql is an example of ___________________., a. Math function, b. Text function, c. Date Function, , Ans :31), Ans:32), Ans :33), , d. Aggregate Function, c. Date Function, The _________ command is used to make the changes in a table, permanent., COMMIT, Give SQL command that will display the current month from the date, and time., MONTH( ), Which of the following keywords will you use in the following query to, displayallthe records of students whose name start with S?, SELECT * from studentwherename, , Ans :34), , LIKE, Which of the following is anaggregatefunction:, a. Upper(), b. Trim(), c. Date(), d. Sum(), , Ans:-, , d. SUM(), , “S%”
Page 5 :
35), , Write the output of the following SQL, command:, SELECT left(“Jammu Region”, 5);, a. Region, b. Jammu, c. JammuRegion, , Ans:36), , Ans:, 37), , d. None of theabove., b. Jammu, What will be the output of thefollowing code?, SELECT MOD(14,3);, 2, What will be the result of the following query based on the tablegiven, here., SELECT COUNT(Salary) FROM Instructor;, , Ans:-, , 38), Ans:39), Ans:40), Ans:41), Ans:42), , COUNT(Salary), -------------------5, Write the command to delete all the data of the table ‘activity’, retainingonly structure., DELETE FROM ACTIVITY;, Write the output for the following SQL commands, Select round(15.193 , -1);, 10, Write a SQL query to display date after 20 days of current date on your, system., SELECT CURDATE( ) + 10;, Write the output for the following sql command, Select SUBSTR(‘ABCDEFG’, -5 ,3), CDE, Which keyword is used to arrange the result of order by clause in, descending order?, a. DSEC
Page 6 :
Ans:, 43), , Ans:44), Ans:45), Ans:46), , Ans:47), , Ans:48), , Ans:49), , Ans:50), Ans:51), Ans:52), , Ans:-, , b. DES, c. DESC, d. DESNO, C. DESC, Write the output of the following SQL command., Select round(14.872,1), a)14.87, b)14.9, c)14.8, d) 15, b) 14.9, The, commandcanbeusedtochangethesizeofcolumntothe, table., ALTER, The, commandcanbeusedtomakeschangesinthe, rows of a table in SQL., Update, Write the output of the following SQL command., select round (49.88);, a. 49.88, b. 49.8, c. 49.0, d. 50, d. 50, Write the output of the following SQL command., select round (19.88,1);, a. 19.88, b. 19.8, c. 19.9, d. 20.0, c. 19.9, Select count(*) fromEmployee;, The above query will not consider the following:, a) Numericvalue, b)Textvalue, c)Nullvalue d) Date, value, c) NULL Value, Which of the following is/are not correct aggregate functions inSQL:, a. AVG() b)COUNT(), c)TOTAL(), d)MAX(), c) Total( ), The, command can be used to make changes in the definition of a, table in SQL., ALTER, Write the SQL clause used to sort the records of atable., ORDER BY, Write the output of the following SQL command., select round(15.857,-1);, a. 15.8, b. 15.9, c. 15.0, d. 20, 20
Page 7 :
53), , Ans:54), Ans:55), , Ans:, 56), , The now()function in MySql is anexampleof, , a. Mathfunction, b. Textfunction, c. Date Function, d. Aggregate Function, c. Date Function, The command can be used to makes changes in the, structure of a table inSQL., ALTER, Write the SQL command that will display the time and date at which, the, command got executed., SELECT NOW();, In SQL NULL value means :, (i) 0 value (ii) 1 value (iii) None value (iv) None of the, above, , Ans:57), , iii) None value, , Ans:58), , 2, , Ans:59), , d. Aggregate Function, , Ans:60), Ans:61), , Find the output of SQL Query:SELECT MOD(11, 3);, The MAX() function in MySql is an example of, ___________________., a. Math function, b. Text function, c. Date Function, d. Aggregate Function, Write the output of the following SQL command., select round(314.82,-1);, a. 314.0, b. 310.0, c. 314.8, d. 300.0, , d. 300, What will be the output of the following SQL command:, SELECT LTRIM(“, RAJKUMAR, “);, “RAJKUMAR, “, (Removes spaces from left side), Write the output of the following SQL command., select pow(2.37,3.45);, a. 17.62, b. 19.62, c. 18.35, d. 15.82, , Ans:62), , ., , b. 19.62, Having clause is used with ____________________________function., a. Math function, b. Text function
Page 8 :
c. Date Function, d. Aggregate Function, Ans:63), , Aggregate Function, Write the output of the query:, select instr('Toolbarbar','bar');, , Ans:64), , Ans, 65), Ans:66), Ans:-, , 5, alter() function in MySql is part of ___________________, a. DDL command, b. DML Command, c. TCL command, a. DDL Command, 1 mark for the correct answer, The ____________command can be used to arrange data in some order in a table in SQL., , ORDER BY, Write the name of the clause used with SELECT command to search for a specific pattern in the, strings., , LIKE, , [2 marks questions] Q.NO. 24 - 33, 1), , Ans:-, , State any two differences between single row functions and multiple row functions., OR, What is the difference between the order by and group by clause when used along with the select, statement. Explain with an example., Differences between single row functions and multiple row functions. (i) Single row functions work on, one row only whereas multiple row functions group rows (ii) Single row functions return one output, per row whereas multiple row functions return only one output for a specified group of rows., , OR The order by clause is used to show the contents of a table/relation in a sorted manner with, respect to the column mentioned after the order by clause. The contents of the column can be, arranged in ascending or descending order., The group by clause is used to group rows in a given column and then apply an aggregate function, egmax(), min() etc on the entire group. (any other relevant answer), Single row v/s Multiple row functions 1 mark for each valid point, , 2), , Ans:-, , Group by v/s Order by 1 mark for correct explanation 1 mark for appropriate example, Consider the decimal number x with value 8459.2654. Write commands in SQL to: i. round it off to a, whole number ii. round it to 2 places before the decimal., i., ii., , select round(8459.2654);, select round(8459.2654,-2);
Page 9 :
3), , Ans:-, , 4), , 1 mark each for correct answer of part (i) , (ii), Anjali writes the following commands with respect to a table employee having fields, empno,, name, department, commission., Command1 : Select count(*) from employee;, Command2: Select count(commission) from employee;, She gets the output as 4 for the first command but gets an output 3 for the second command., Explain the output with justification., This is because the column commission contains a NULL value and the aggregate functions do not, take into account NULL values. Thus Command1 returns the total number of records in the table, whereas Command2 returns the total number of non NULL values in the column commission., Consider the following SQL string: “Preoccupied”, Write commands to display:, a. “occupied” b. “cup”, OR, Considering the same string “Preoccupied” Write SQL commands to display:, a. the position of the substring ‘cup’ in the string “Preoccupied” b. the first 4 letters of the string, , Ans:-, , a. select substr("Preoccupied", 4);, or, select substring("Preoccupied", 4);, or, select mid("Preoccupied",4);, or, select right(("Preoccupied"”, 8);, b. select substr("Preoccupied" ,6,3);, or, select substring("Preoccupied", 6,3);, or, select mid(("Preoccupied" ,6,3);, OR, a. select instr 'Preoccupied' , ‘ 'cup'));, b. select left 'Preoccupied',4);, 1 mark for each correct answer of part (a) , (b), , 5), , What is the difference between the where and Having clause when used along with, the select statement. Explain with an example., OR, Explain the difference between Update and Alter command with help of an, example., , Ans, , Where clause is used to apply condition on individual rows and not supports aggregate function, While Having clause is used to apply condition on groups and it supports aggregate functions.
Page 10 :
Eg: SELECT * FROM EMP WHERE SALARY > 50000;, Eg: SELECT * FROM EMP GROUP BY DEPTNO HAVING COUNT(*) > 2;, OR, UPDATE command is a part of DML command and used to update the data of rows of a table., While ALTER command is a part of DDL command and used to change the structure of a table like, adding column, removing it or modifying the datatype of columns., Eg: UPDATE EMP SET SALARY = 20000;, ALTER EMP ADD EMP_DOJ DATE;, 6), , Write the output of following queries:i., , SELECT LEFT(‘Toolbar’, 4);, , ii., I., II., , Ans:7), , SELECT SUBSTR('Aakila', -3);, ‘ila’, ‘Tool’, , Raghav writes the following commands with respect to a table Flight having, Fields FLCODE, START, DESTINATION, NO_STOPS., Command1 : Select count(*) from FLIGHT;, Command2: Select count(DESTINATION) from FLIGHT;, He gets the output as 5 for the first command but gets an output 3 for the, second command. Explain the output with justification., , Ans:-, , This is because the column DESTINATION contains a NULL value and the aggregate functions do not, take into account NULL values. Thus Command1 returns the total number of records in the table, whereas Command2 returns the total number of non NULL values in the column DESTINATION., , 8), , Write the output for following queries:, i., , select MOD(11,4) "Modulus", power(3,2) "Raised";, , ii., , select CURDATE( )+10;, OR, , Ans:-, , i., , select length('CORONA COVID-19');, , ii., , select lcase('COMputer Science');, , i. Modulus, -------------3, , Raised, ---------9, , ii. currentdate + 10 days aftward date will come, or, i. 15, ii. ‘computer science’, 9), , Consider the decimal number x with value 7459.3654. Write commands in SQL, to:
Page 11 :
i) round it off to a whole number, ii), round it to 2 places before the decimal., (i), (ii), , Ans:-, , 10), , select round(7459.3654, 0), select round(7459.3654, -2), , Shailly writes the following commands with respect to a table Employee, having fields, empno, name, department, commission., Command1 :SELECT COUNT(*) FROM EMPLOYEE;, Command2 :SELECT COUNT(COMMISSION) FROM EMPLOYEE;, She gets the output as 7 for the first command but gets an output 5 for the, second command. Explain the output with justification., , Ans:-, , This is because the column commission contains a NULL value and the aggregate, functions do not take into account NULL values. Thus Command1 returns the total, number of records in the table whereas Command2 returns the total number of non, NULL values in the column commission., , 11), , Consider the following SQL string: “SELFMOTIVATION”. Write commands to, display:, a. “MOTIVATION”, b. “MOT”, OR, Considering the same string “SELFMOTIVATION”. Write SQL commands to, display:, a. the position of the substring ‘MOTIV’ in the string “SELFMOTIVATION”, b. the last 6 letters of the string, , Ans:-, , a. select substr(“SELFMOTIVATION”, 5), b. select substr(“SELFMOTIVATION”, 5, 3), OR, a. select instr(“SELFMOTIVATION”, “MOTIV”), b. select right(“SELFMOTIVATION”, 6), , 12), , Ans:-, , 13), , Ans:-, , (student may use other functions like – substring/ mid/ right ..etc, State any two differences between Update and alter commands., OR, What is datatype? What are the main objectives of datatypes?, Data types are mean to identify the type of data and its associated functions., The main objectives of datatypes is to clarify the type of data a variable can store and which, operations can be performed on it., Consider the decimal number n with value 278.6975. Write commands in SQL :, i., That gives output 279, ii., That gives output 280, i) select round(278.6975);
Page 12 :
14), , (ii) select round(278.6975,-1);, or some other queries that produces same results., 1 mark each for correct answer of part (i) , (ii), (i) Consider a table “Employee” that have fields - empno, name, department, salary., Based on the above table “Employee”, Manvendra has entered the following SQL command:, SELECT * FROM Employee where Salary = NULL;, But the Query is not executing successfully. What do you suggest to him in order to execute this, query i.e. write the correct query., (ii) Write a SQL query to display the details of those employees whose Salary column has some, values., , Ans:-, , 15), , Ans:-, , (i) select * from Employee where Salary is NULL;, (ii) select * from Employee where Salary is not NULL;, 1 mark each for correct answer of part (i) , (ii), Consider the following SQL string: “Master Planner”., Write commands to display:, a. “Master”, b. “Plan”, OR, Considering the same string “Master Planner”., Write SQL commands to display:, a. the position of the substring ‘Plan’ in the string “Master Planner”, b. the Last 4 letters of the string, a. select substr("Master Planner",1,6);, b. select substr("Master Planner",8,4); or some other queries that produces same results., 1 mark each for correct answer of part (i) , (ii), OR, a. select instr("Master Planner","Plan");, b. select right("Master Planner",4); or some other queries that produces same results., , 16), , Ans:17), , Ans:18), , Ans:-, , 1 mark each for correct answer of part (i) , (ii), What are multiple row functions? Give examples, OR, What is Group by clause? How can we specify condition with Group by clause? Explain with an, example., Consider the decimal number N with value 87654.9876. Write commands in SQL to:, i. round it off to a whole number, ii. round it to 2 places before the decimal., State any two differences between single row functions and multiple row functions., OR, What is the difference between the order by and group by clause when used along with the select, statement. Explain with an example., 19. Differences between single row functions and multiple row functions., (i) Single row functions work on one row only whereas multiple row functions group rows (ii), Single row functions return one output per row whereas multiple row functions return only
Page 13 :
one output for a specified group of rows., OR, The order by clause is used to show the contents of a table/relation in a sorted manner with, respect to the column mentioned after the order by clause. The contents of the column can, be arranged in ascending or descending order., The group by clause is used to group rows in a given column and then apply an aggregate, function egmax(), min() etc on the entire group. (any other relevant answer), Single row v/s Multiple row functions 1 mark for each valid point, Group by v/s Order by 1 mark for correct explanation 1 mark for appropriate example, 19), , Ans:-, , 20), , Ans:-, , 21), Ans:22), , Ans:-, , 23), , Give the output of :, i), Selectround(123.93);, ii), Selectround(123.93,1);, i) 124, ii) 123.9, Consider the following SQL string: “Mental Toughness Helps You Succeed”, Write commands to display following using functions:, a. “Toughness”, b. “Succeed”, OR, Considering the same string: “Mental Toughness Helps You Succeed”, Write SQL commands to display:, a. the position of the substring ‘’Helps’ in the string “Mental Toughness Helps YouSucceed”, the first 6 letters of thestring, i), Select mid(‘Mental Toughness Helps You Succeed’, 8, 9), ii), Select right(‘Mental Toughness Helps You Succeed’, 7);, OR, i) select instr("Mental Toughness Helps You Succeed",’Helps’);, ii) select left("Mental Toughness Helps You Succeed",6);, 1 Mark each for correct function usage, Find out the error in the following SQL command and correct the same., Select * from employee group by dept where sum(salary) > 2000000, Select * from employee group by dept where sum(salary) > 2000000 in this query in place of WHERE, clause HAVING clause to be used., , Helps Abhay to Compare Having clause and Order by clause?, Or, Shewani has recently started working in MySQL. Help her in understanding the, difference between where and having clause., Having clause is used in conjunction with group by clause in MySQL. It is used to provide, condition based on grouped data. On the other hand, order by clause is an independent, clause used to arrange records of a table in either ascending or descending order on the, basis of one or more columns, OR, COUNT(*) returns the number of items in a group, including NULL values and, duplicates. COUNT(expression) evaluates expression for each row in a group and, returns the number of non null values, 2 marks of correct explanation & for any other relevant answer., Write commands in SQL to:, i. round off value 56789.8790 to nearest thousand’splace.
Page 14 :
ii., , Ans:24), , Ans:-, , 25), , Ans:-, , 26), , Display day from date13-Apr-2020., i., SelectROUND(56789.8790,-3);, ii., SelectDAY(‘2020-04-13’) 1 mark each for correctanswer., Given Table Course:, , Find out the output for given SQL command:, SELECT TID, COUNT(*),, MIN(FEES), FROM COURSE, HAVING COUNT(*)>1;, Ans:, TIDCOUNT(*)mIN(FEES), 101, 2, 12000, , GROUP, , BY, , TID, , 2 marks for correct output, Consider the following SQL strings: S1= “INDIA” S2=”MY” & S3=”DI”, Write commands to display:, a. “MYINDIA”, b. “india”, OR, Considering the same string as, above Write SQL commands to, display:, a. The position of the string S3 in the stringS1., The first 4 letters of the concatenation of string S1 andS2., a. SelectCONCAT(s2,S1);, b. SelectLCASE(S1), OR, a. SelectINSTR(S1,S3);, b. Select LEFT(CONCAT(S1,S2));, 1 mark each for correct SQLcommand., What is importance of primary key in a table? How many primary keys can be therefor a, table?, OR, Explain working of TRIM( ) function with proper examples., , Ans:-, , Primary Key : A column of collection of columns to identify a tuple in a relation. It is used, to search / locate row in a relation. There can be only one primary key in atable. 1 mark for, correct definition with propersignificance., 1 mark for stating only one primary key in a table.
Page 15 :
OR, TRIM () function is used to remove leading and trailing spaces from a string a table. It can be, used as, TRIM(String), For example;, SELECT TRIM(' bar');, -> 'bar', 1 mark for stating purpose of the functions 1 mark for correct example., , 27), , Consider the following‘Student’table., , (i) What will be the most suitable datatype for the grade column andwhy?, (ii) Write a command to insert Suman’s record with the data as shown in thetable., Ans:-, , (i) Gender column datatype char(1) as all the possible values can be accommodatedand it, will be spaceefficient., (ii) INSERT INTO Student (Rollno, Sname, Subject, Marks) VALUES (“003”, ”SUMAN”,, “IP”, 75);, , 28), Ans:-, , 1 mark for each correct answer, Explain the working of ORDER BY clause of SELECT query withproperexample., The ORDER BY keyword is used to sort the result-set in ascending or descending order., The ORDER BY keyword sorts the records in ascending order by default. To sort the records in, descending order, use the DESC keyword., 1 mark for correct explanation. 1 mark for appropriateexample, , 29), , Consider a string “AS YOUknow MORE”, Write the queries for the following tasks., (i) Write a command to display“know”., (ii) Write a command to display number of characters in thestring., OR, Consider a string “You Grow more” stored in a column, str. What will be the output of the following queries?, (i) SELECTUPPER(str);, (ii) SELECTsubstr(str,-9,4);, Ans:-, , (i) select mid(“AS YOU knowMORE”,8,4);, (ii) select length(“AS YOU knowMORE”);
Page 16 :
OR, (i) YOU GROWMORE, (ii) Grow, 1 mark for each correct answer, , [3 marks question] Q.NO. 37, 1), , A relation Vehicles is given below :, , Write SQL commands to:, a. Display the average price of each type of vehicle having quantity more than 20., b. Count the type of vehicles manufactured by each company., c. Display the total price of all the types of vehicles., Ans:- a. select Type, avg(Price) from Vehicle group by Type having Qty>20;, b. select Company, count(distinct Type) from Vehicle group by Company;, c. Select Type, sum(Price* Qty) from Vehicle group by Type;, a. ½ mark for the Select with avg(), ½ mark for the having clause, b. ½ mark for the Select with count() , ½ mark for group by clause, c. ½ mark for the Select with sum() , ½ mark for the group by clause, 2), , Consider the table Garment and write the query:, , i. Display the Minimum price of the Garment., ii. Count and display the number of GARMENT from each SIZE where number of, GARMENTS are more than 1, iii. Display the sum of price of each color garment, Ans:- i. SELECT MIN(PRICE) FROM GARMENT;, ii. SELECT SIZE,COUNT(*) FROM GARMENT, GROUP BY SIZE
Page 17 :
HAVING COUNT(*)>1;, iii. SELECT COLOUR,SUM(PRICE) FROM GARMENT GROUP BY COLOUR;, 3), , A relation SALESMAN is given below:, SNO SNAME, A01 Kushagra Jain, A02 Prakhar Sharma, B03 Trapti Singh, B04 Shailly, C05 LakshayLawania, C06 Naresh, D07 Krishna Singh, , SALARY, 30000, 50000, 30000, 80000, 20000, 70000, 50000, , BONUS, 45.25, 25.50, 35.00, 45.00, 10.25, 12.75, 27.50, , DATEOFJOIN, 29-10-2019, 13-03-2018, 18-03-2017, 31-12-2018, 23-01-1989, 15-06-1987, 18-03-1999, , AREA, Delhi, Ajmer, Jhansi, Delhi, Jaipur, Ajmer, Jhansi, , Write SQL commands to perform the following operations:, i) Count the number of salesman area-wise., ii) Display the month name for the date of join of salesman of area ‘Ajmer’, iii) Display the total salary paid to all salesman., Ans:- (i) select area, count(sname) as “Number of salesman” from Salesman group by area;, , (ii) select monthname(dateofjoin) from Salesman where area=’Ajmer’;, (iii) select sum(salary) from Salesman;, , 4), , 37, , Consider the given table Faculty :Faculty_Id, , First_name, , Last_name, , Hire_date, , Salary, , 1102, , Sulekha, , Mishra, , 12-10-1997, , 25000, , 1203, , Naveen, , Vyas, , 23-12-1994, , 18000, , 1404, , Rakshit, , Soni, , 25-08-2003, , 32000, , 1605, , Rashmi, , Malhotra, , 18-09-2004, , 21000, , 1906, , Amit, , Srivastava, , 05-06-2007, , 28000, , Write SQL commands to :, a. To display details of those faculty members whose First_name ends with ‘t’., b. Display all records in descending order of Hire_date., c. Find the maximum and minimum salary., Ans:- a. Select * from Faculty where First_name like ‘%t’;, b. Select * from Faculty order by Hire_date desc;, , 5), , c. Select max(Salary), min(Salary) from Faculty;, 1 mark for each correct answer, Given the table CARDEN having following data:, CCode, 501, 503, 502, 509, , CarName, A-Star, Indigo, Innova, Qualis, , Company, Suzuki, Tata, Toyota, Toyota, , Color, Red, Silver, White, Silver, , Capacity, 3, 3, 7, 4, , Charges, 14, 12, 15, 14
Page 18 :
Ans, , 510, Wagon R, Suzuki, Red, 4, Write SQL Commands for the following :, a. Display the average charges of each type of car company having capacity more than3., b. Count the totalcars manufactured by eachcompany., c. Display the total charges of all the types ofvehicles., a. select company, avg(charges) from carden group by company having capacity>3;, b. select Company, count(*) from carden group by Company;, c. Select company, sum(charges) from carden group by company;, 1 mark each for correct answer, , 35, , 6), , TABLE NAME : PHARMADB, , Write SQLcommands to a & b and ouput for c:, a. To display sum of price for each PharmacyName having more than 1drug., b. Display pharmacy name in descending order of drugid, c. SELECT PharmacyName, COUNT(*) FROM PharmaDB GROUP BY PHARMACY NAME, Ans:-, , a. Select sum(price) from pharmadb group by pharmacyname havingcount(*)>1;, b. Select PharmacyName from Pharmadb order byDrugID;, a., RxPharmacy, 2, RajMedicos, , 1, , MyChemist, , 2, , a. ½ mark for the Select with sum(), ½ mark for the havingclause, b. ½ mark for the Select ,½ mark for the order byclause, 1 marks for correctoutput., 7), , Consider a MySQLtable ‘product’, P_ID, P01, P02, P03, P04, , 3, PROD_NAME, Notebook, Pencil Box, Water Bottle, School Bag, , PROD_PRICE, 85, 76, 129, 739, , PROD_QTY, 500, 200, 50, 70, , (i) Display maximumPROD_QTY., (ii) Display the value of each product where the value of each product is calculated as, PROD_PRICE * PROD_QTY, (iii) Display average PROD_PRICE., Ans:-, , (i) SELECT MAX(PROD_QTY) FROMproduct;
Page 19 :
(ii) SELECT PROD_PRICE*PROD_QTY AS ‘Value’ FROMproduct;, (iii) SELECT AVG(PROD_PRICE) FROMproduct;, 1 mark for each correct query, 8), , [5 marks question] – Q.39, 1), , Write the SQL functions which will perform the following operations:, i), To display the name of the month of the current date ., ii), To remove spaces from the beginning and end of a string, “ Panorama “., iii), To display the name of the day eg, Friday or Sunday from your date of birth, dob., iv), To display the starting position of your first name(fname) from your whole name (name)., v), To compute the remainder of division between two numbers, n1 and n2, OR, Consider a table SALESMAN with the following data:, , Ans:-, , Write SQL queries using SQL functions to perform the following operations:, a) Display salesman name and bonus after rounding off to zero decimal places., b) Display the position of occurrence of the string “ta” in salesman names., c) Display the four characters from salesman name starting from second character., d) Display the month name for the date of join of salesman, e) Display the name of the weekday for the date of join of salesman, i), monthname(date(now())), ii), trim(“ Panaroma “), iii), dayname(date(dob)), iv), instr(name, fname), v), mod(n1,n2), 1 mark for each correct answer, OR, i), ii), iii), iv), , Select sname, round(bonus,0) from Salesman;, Select instr(Sname, “ta”) from Salesman;, Select mid(Sname,2,4) from Salesman; alternative answer, Select Substring(Sname,2,4) from Salesman; iv) Select monthname(DateofJoin) from, Salesman;, v), Select dayname(DateofJoin) from Salesman;, 1/2 mark each for correct usage of Select and round(), 1/2 mark each for correct usage of Select and instr()
Page 20 :
1/2 mark each for correct usage of Select and substr(), 1/2 mark each for correct usage of Select and monthname(), 1/2 mark each for correct usage of Select and dayname(), Note : Instead of substr() , substring() may be accepted as correct, 2), , Consider a table Teacher with the following data:, , Write SQL queries using SQL functions to perform the following operations:, a) Convert all the names into lower case., b) Display the position of occurrence of the string “sh” in Name., c) Display the four characters from Department starting from second character., d) Display the month name for the date of admission., e) Display the name of the weekday for the date of admission., OR, Write the SQL functions which will perform the following operations:, i) To display the day of month of current date., ii) To remove spaces from the beginning and end of a string, “ Informatics, Practices, , “., , iii) To display the name of the day eg. Friday or Sunday from your date of birth, dob., iv) To convert your name into Upper case., v) To compute the mode of two numbers num1 and num2., Ans:-, , i. SELECT LOWER(NAME) FROM TEACHER;, ii. SELECT INSTR(NAME, ‘sh’) FROM TEACHER;, iii. SELECT MID(Department, 2,4) FROM TEACHER;, iv. SELECT MONTHNAME(DateofAdm) FROM TEACHER;, v. SELECT DAYNAME(DateofAdm) FROM TEACHER;, OR, i. SELECT DAYOFMONT(CURDATE());, ii. SELECT TRIM(“ Informatics Practices “;, iii. SELECT DAYNAME(“2015-07-27”);, iv. SELECT UPPER(Name);, v. SELECT MOD(num1,num2);
Page 21 :
3), , Write the SQL functions which will perform the following operations:, i) To display the name of the month of the current date., ii) To remove spaces from the beginning and end of a string, “ KV Sangathan “., iii) To display the name of the day eg, Friday or Sunday from your date of birth, dob., iv) To print the value of square root of 2 upto 2 decimal points., v) To compute the remainder of division between two numbers, n1 and n2, OR, Write SQL for question from (i) to (iv) and output for SQL queries (v) and (vi),, which are based on the table: KV given below:, , (i), (ii), (iii), (iv), (v), (vi), , Ans:-, , Print the details of KVs whose StationCode between 300 and 500, Print the details of KVs whose name ends with AFS, Print the details of KVs of Jaipur region, Print the number of KVs Zone-wise, Select Region, count(KVName) from KV where Zone=’West’ group by Region, Select * from KV where substr(KVName, 2, 3)=’and’ or StationCode=390;, , (i) select month(current_date());, (ii) select trim(“ KV Sangathan “);, (iii) select dayname(dob) from student;, (iv) select round(sqrt(2) , 2);, (v) select n1 % n2;, OR, (i), (ii), (iii), (iv), (v), (vi), , select * from KV where StationCode between 300 and 500;, select * from KV where KVName like ‘%AFS’;, select * from KV where Region=’Jaipur’;, select Zone, count(KVName) from KV group by Zone;, Region, count(KVName), Ahmedabad, 2, Jaipur, 3, KVCode, 1019, 1020, 1702, , KVName, Gandhidham IFFCO, Gandhidham, Railway, Uri, , StationCode, 11, , Region, Ahmedabad, , Zone, West, , 11, 390, , Ahmedabad, Jammu, , West, North
Page 22 :
4), , Write the SQL statement for the following:, i), To display names “Mr. James” and “Ms. Smith” in lower case., ii), To display current date and time., iii), To extract date from a given datetime value ‘2020-12-21 09:30:37’., iv), To remove trailing spaces from string “ Technology Works ”, v), To compute the remainder of division between 125 and 17., OR, Consider the following table Garments. Write SQL commands for the following statements., Table : Garments, GCode, , GName, , Price, , MCode, , Launch_Date, , 10001, , Formal Shirt, , 1250, , M001, , 2008-12-12, , 10020, , Frock, , 750, , M004, , 2007-09-07, , 10007, , Formal Pant, , 1450, , M001, , 2008-03-09, , 10024, , Denim Pant, , 1400, , M003, , 2007-04-07, , 10090, , T-Shirt, , 800, , M002, , 2009-05-12, , a) To update the Price of Frock to 825., b) To print the average price of all the Garments., c) To display the Garments Name with their price increased by 15%., d) To delete the rows having MCode as M002., e) To display the details of all the Garments which have GCode less than 10030., Ans:-, , (i) select lower(“Mr. James”), lower(“Ms. Smith”);, (ii) select now();, (iii) select date(“2020-12-21 09:30:37”);, (iv) select rtrim(“ Technology Works ”);, (v) select mod(125,17);, 1 mark for each correct answer, OR, a. Update Garments set price=825 where GName=’Frock’;, b. select avg(price) from Garments;, c. selectDName, price*1.15 as ‘Increased_Price’ from Garments;, d. delete from Garments where MCode=’M002’;, e. select * from Garments where GCode<10030;, , 5), , 1 mark for each correct answer, Write the SQL functions which will perform the following operations:, i) To display the name of the month of your birthdate., ii) To remove spaces from the beginning of astring,“ Python“., iii) To display the day of the week eg, Sunday from currentdate., iv) To display the starting 3 characters from your name., v) To compute the power of 2 to the power3
Page 23 :
Id, S001, S002, S003, S004, , SName, ABC, Computronics, AllInfotech, TechShoppe, GeekTencoSoft, , S005, , HitechSolution, , OR, Consider the table : Shop, Area, Bonus, CP, 1000.89, GKII, CP, Nehru, Place, GKII, , DateofOpen, 2010-11-20, , 2345.987, 761.46, 456.923, , 2015-09-12, 2013-07-25, 2019-10-10, , 1000.025, , 2008-12-20, , a) Display shop name and bonus after rounding off to zero decimalplaces., b) Display the position of occurrence of the string “tech” in shopnames., c) Display three characters from shop name starting from secondcharacter., d) Display the month name for the date of opening ofshop, e) Display the name of the shop in allcapitals., Ans:-, , i)select monthname(‘1998-11-20’);, ii)select ltrim(‘ Python’);, iii)select dayname(now());, iv)select left(‘Nitin’,3);, v)Select power(2,3);, 1 mark each for correct function, OR, , a), b), c), d), e), , Select Sname,round(Bonus,0) from Shop;, Select instr(SName,’tech’) from Shop;, Select mid(SName,2,3) from Shop;, Select monthname(DateOfOpen) from shop;, Select Upper(SName) from shop;, , 1 mark each for the correct query, 6), , Ans:-, , Consider the following data frame of automobile, , Write SQL queries using SQL functions to perform the following operations:, a) Display company name and body wheel base after rounding off to nearest, ten’sdecimalplaces., b) Display the position of occurrence of the string “dan” in bodystyle., c) Display the 3 characters from company name starting from secondcharacter., d) Display the year of manufacturing forsedan;, e) Display the name of the weekday for the manufacturingdate., a) Select company, round(wheel-base,-1) from automobile;, b) Select instr(body-style,’dan’) fromautomobile;, c) Select substr(company,2,3) from automobile;/mid(company,2,3), d) Select year(dateofmanufacture) from automobile wherebody-style=’sedan’;
Page 24 :
e) Select dayname(dateofmanufacture) from automobile;, a) 1/2 mark each for correct usage of Select andround(), b) 1/2 mark each for correct usage of Select and instr(), c) 1/2 mark each for correct usage of Select and substr(), d) 1/2 mark each for correct usage of Select year and whereclause, 1/2 markeach, 7), , Consider the below mentioned tableof‘CLOTH’, DCODE, DESCRIPTION, PRICE, 10001, FORMAL SHIRT, 1250, 10020, FROCK, 750, 10012, INFORMAL SHIRT, 1450, 10019, EVENING GOWN, 850, 10090, TULIP SKIRT, 850, 10023, PENCIL SKIRT, 1250, 10089, SLACKS, 850, Write the commands for the following:, , 5, MCODE, M001, M004, M002, M003, M002, M003, M003, , LAUNCHDATE, 12–JAN–08, 09–SEP–07, 06–JUN–08, 06–JUN–08, 31–MAR–07, 19–DEC–08, 20–OCT–08, , (i) Display first three letters of description e.g. ‘FRO’ for‘FROCK’, (ii) Display the description after removing leading spaces ifany., (iii) Display number of characters taken by eachdescription., (iv) Display the number of MCODE in thetable., (v) Display the day of the LAUNCHDATE. Eg. ‘Monday’, ’Tuesday’etc, OR, (i) Display total price of products launched in year2008., (ii) Display minimum price of product for each materialcode(MCODE)., (iii) Display the most recentLAUNCHDATE., (iv) Display the description in lower casealphabets., (v) Display remainder of price divided by10.