Page 2 :
@Cbsebookshub - Join Us on Telegram, , CBSE Term II, , 2022, , Informatics, Practices, Class XII, , CLICK HERE FOR MORE
Page 4 :
@Cbsebookshub - Join Us on Telegram, , CBSE Term II, , 2022, , Informatics, Practices, Class XII, Complete Theory Covering NCERT, Case Based Questions, Short/Long Answer Questions, 3 Practice Papers with Explanations, , Author, , Debapriya Chakraborty, , ARIHANT PRAKASHAN (School Division Series)
Page 5 : @Cbsebookshub - Join Us on Telegram, , ARIHANT PRAKASHAN (School Division Series), , © Publisher, No part of this publication may be re-produced, stored in a retrieval system or by any means,, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, scanning, web or otherwise without the written, permission of the publisher. Arihant has obtained all the information in this book from the sources, believed to be reliable and true. However, Arihant or its editors or authors or illustrators don’t take any, responsibility for the absolute accuracy of any information published and the damage or loss suffered, thereupon., , All disputes subject to Meerut (UP) jurisdiction only., , Administrative & Production Offices, Regd. Office, ‘Ramchhaya’ 4577/15, Agarwal Road, Darya Ganj, New Delhi -110002, Tele: 011- 47630600, 43518550, , Head Office, Kalindi, TP Nagar, Meerut (UP) - 250002, Tel: 0121-7156203, 7156204, , Sales & Support Offices, Agra, Ahmedabad, Bengaluru, Bareilly, Chennai, Delhi, Guwahati,, Hyderabad, Jaipur, Jhansi, Kolkata, Lucknow, Nagpur & Pune., , ISBN : 978-93-25797-06-2, PO No : TXT-XX-XXXXXXX-X-XX, Published by Arihant Publications (India) Ltd., For further information about the books published by Arihant, log on to, www.arihantbooks.com or e-mail at
[email protected], Follow us on, , CBSE Term II, , 2022
Page 7 :
@Cbsebookshub - Join Us on Telegram, , Contents, CHAPTER, , MySQL Functions and Querying using SQL, , -, , CHAPTER, , Aggregate Functions and Querying, , -, , CHAPTER, , Computer Networks, , -, , CHAPTER, , Introduction to Internet and Web, , -, , Practice Papers, , -, , -, , Watch Free Learning Videos, Subscribe arihant, , Channel, , þ Video Solutions of CBSE Sample Papers, þ Chapterwise Important MCQs, þ CBSE Updates
Page 8 :
@Cbsebookshub - Join Us on Telegram, , Syllabus, CBSE Term II Class XII, Distribution of Theory Marks, No., , Units, , ., , Database Query using SQL, , ., , Introduction to Computer Networks, , Marks, , Total, , Unit, , Database Query using SQL, Ÿ Math functions: POWER , ROUND , MOD ., Ÿ Text functions: UCASE UPPER , LCASE LOWER , MID SUBSTRING, LENGTH , LEFT , RIGHT , INSTR , LTRIM , RTRIM , TRIM ., , SUBSTR ,, , Ÿ Date Functions: NOW , DATE , MONTH , MONTHNAME , YEAR , DAY ,, DAYNAME . Aggregate Functions: MAX , MIN , AVG , SUM , COUNT ;, using COUNT ., Ÿ Querying and manipulating data using Group by, Having, Order by., , Unit, , Introduction to Computer Networks, Ÿ Introduction to networks, Types of network: LAN, MAN, WAN., Ÿ Network Devices: modem, hub, switch, repeater, router, gateway., Ÿ Network Topologies: Star, Bus, Tree, Mesh., Ÿ Introduction to Internet, URL, WWW and its applications- Web, email, Chat, VoIP., Ÿ Website: Introduction, difference between a website and webpage, static vs, dynamic web page, web server and hosting of a website., Ÿ Web Browsers: Introduction, commonly used browsers, browser settings, add-ons, and plug-ins, cookies., , CBSE Term II, , 2022
Page 13 :
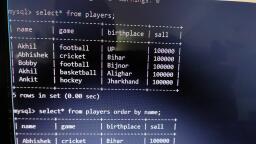
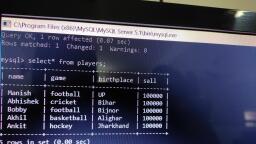
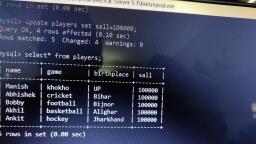
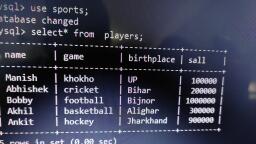
@Cbsebookshub - Join Us on Telegram, , 1, , CBSE Term II Informatics Practices XII, , CHAPTER 01, , MySQL Functions and, Querying using SQL, In this Chapter..., l, , Types of SQL Functions, , l, , String/Text Functions, , l, , Mathematical Functions, , l, , Date/Time Functions, , MySQL function performs a pre-defined task and returns a, single value such as a numerical, string or date/time value., Functions operate on zero, one, two or more values provided, to them, these values are called parameters or arguments., MySQL support number of built-in functions., To use any function, we need to specify the column to which, the function should be applied., e.g. SELECT function(column_name), FROM table_name;, , To specify multiple columns, you can write as follows:, e.g. SELECT *, function(column_name), or, , FROM table_name;, SELECT column_name1,function(column_name2),, column_name3, FROM table_name;, , Mathematical Functions, MySQL provides a number of functions used for performing, mathematical calculations on database. Mathematical, functions are very important in SQL to implement different, mathematical concepts in queries. Some mathematical, functions are explained with examples as follows:, , POWER()/POW(), This function returns the value of a number raised to the, power of another number., Syntax POWER(M,N) or POW(M,N), where, M is the base and N is an exponent., e.g. mysql> SELECT POWER(2,2);, The above query produces the following output:, POWER(2,2), , Types of SQL Functions, SQL provides two types of functions, which are as follows :, (i) Single-row Functions This type of function work with, a single-row at a time., It returns a result for each row of the table, on, which the query is performed. Examples of, single-row functions include CHAR(),CONCAT(),, INSTR(), etc., (ii) Multiple-row Functions This type of function work, with data of multiple-rows at a time and return a single, output value., Examples of multiple-row functions include SUM(),, AVG(), COUNT(), etc., , 4, , mysql> SELECT POWER(2,−3);, , The above query produces the following output:, POWER(2,–3), 0.125, , mysql> SELECT POWER(30,0.2);, , The above query produces the following output :, POWER(30,0.2), 1.97435048583482
Page 14 :
@Cbsebookshub - Join Us on Telegram, , 2, , CBSE Term II Informatics Practices XII, , ROUND(), , mysql> SELECT MOD(− 25,7);, , This function rounds up the number to the upwards or, downwards to the nearest whole number., Syntax ROUND(M,N) or ROUND(M), where, M is the number to be rounded off and N is the, number of places to which the number should be rounded, off. If N is not specified, then it is assumed zero (0)., e.g. mysql> SELECT ROUND(4.65,1);, The above query produces the following output:, , The above query produces the following output:, MOD(–25,7), –4, , mysql> SELECT MOD(25.4,7);, , The above query produces the following output:, MOD(25.4,7), 4.4, , ROUND(4.65,1), 4.7, , String/Text Functions, , mysql> SELECT ROUND (−5.43);, , The above query produces the following output:, ROUND(—5.43), —5, , The string/text functions of SQL are used to extract, change,, format or alter character strings. They accept a character, string as an input and provides character string or numeric, values as an output. Some string/text functions are explained, with example as follows :, , UPPER()/UCASE(), mysql> SELECT ROUND (5.43);, , The above query produces the following output:, ROUND(5.43), 5, , This function converts the characters of a string into the, uppercase characters., Syntax UPPER(str/column_name), or, UCASE(str/column_name), e.g. mysql> SELECT UPPER('mystring');, The above query produces the following output:, , mysql> SELECT ROUND (1.645,0);, , UPPER('mystring'), , The above query produces the following output:, , MYSTRING, ROUND(1.645,0), , Table : Item, , 2, , Icode, , Descp, , Price, , QOH, , Sold, , 101, , Stationary, , 54.89, , 700, , 350, , 102, , Food, , 650.78, , 1200, , 340, , 103, , Sports, , 700.90, , 3000, , 500, , ROUND(3.45, —1), , 104, , Food, , 1400.00, , 900, , 120, , 0, , 105, , Sports, , 6700.00, , 790, , 540, , mysql> SELECT ROUND (3.45,−1);, , The above query produces the following output:, , e.g. Write a query to display the item description in, uppercase letter from table Item., , MOD(), This function returns the remainder of a number dividing by, another number., Syntax MOD(Dividend, Divisor), e.g. mysql> SELECT MOD(11,4);, The above query produces the following output:, MOD(11,4), , mysql> SELECT UPPER(Descp) FROM Item;, , The above query produces the following output:, UPPER(Descp), STATIONARY, FOOD, SPORTS, FOOD, SPORTS, , 3, , or mysql> SELECT UCASE(Descp) FROM Item;
Page 15 :
@Cbsebookshub - Join Us on Telegram, , 3, , CBSE Term II Informatics Practices XII, , The above query produces the following output:, , e.g. mysql> SELECT SUBSTR, ('EASYCALCULATION',5,11);, , UCASE(Descp), STATIONARY, FOOD, SPORTS, FOOD, SPORTS, , LOWER()/LCASE(), This function converts the characters of an argument string, to the lowercase characters. The return value has the same, data type as the argument., Syntax LOWER(str/column_name), or LCASE(str/column_name), e.g. mysql> SELECT LOWER('MYSQL');, The above query produces the following output:, LOWER('MYSQL'), , The above query produces the following output:, SUBSTR('EASYCALCULATION',5,11), CALCULATION, , mysql> SELECT SUBSTR, ('EASYCALCULATION',7);, , The above query produces the following output:, SUBSTR('EASYCALCULATION',7), LCULATION, , Write the output of the following command., mysql> SELECT SUBSTR(Descp,3,4) FROM Item WHERE, QOH=700;, , The above query produces the following output:, , mysql, , SUBSTR(Descp,3,4), atio, , e.g. Write a query to display the item description in, lowercase letter from table Item., mysql> SELECT LOWER(Descp) FROM Item;, , The above query produces the following output:, , Write the output of the following command., mysql> SELECT MID('Informatics Practices',2,8);, , The above query will produce the following output:, LOWER(Descp), stationary, food, sports, food, sports, , or mysql> SELECT LCASE(Descp) FROM Item;, The above query produces the following output:, , MID('Informatics Practices',2,8), nformati, , Write the output of the following command., mysql> SELECT UPPER(MID(Descp,2,8)) FROM Item, WHERE Icode=101;, , The above query will produce the following output:, , LCASE(Descp), , UPPER(MID(Descp,2,8)), , stationary, food, sports, food, sports, , TATIONAR, , SUBSTRING()/SUBSTR()/MID(), This function returns the substring specified number of, characters) from a particular position of a given string., Syntax SUBSTR(str/column_name,pos,len), or SUBSTRING(str/column_name,pos,len), or MID(str/column_name,pos,len), where, str is a string from which a substring is returned, pos, is an integer indicating the string position and len is an, integer indicating the length of the substring., , LENGTH(), This function returns the length of the string in bytes. It, includes the count of blank spaces in the string., Syntax LENGTH(string/column_name), e.g. mysql> SELECT LENGTH('easycalculation');, Above query produces the following output :, LENGTH('easycalculation'), 15, , Write a query to display the item code and length of each, item’s description.
Page 16 :
@Cbsebookshub - Join Us on Telegram, , 4, , CBSE Term II Informatics Practices XII, , mysql> SELECT Icode, LENGTH(Descp) FROM Item;, RIGHT('India',3), , Above query produces the following output:, , dia, , Icode, , LENGTH(Descp), , 101, 102, 103, 104, 105, , e.g. Write a query to view last three characters of employee’s, address from the table Empdetail., , 10, 4, 6, 4, 6, , mysql> SELECT RIGHT(EmpAdd,3) FROM Empdetail;, , Above query produces the following output:, RIGHT(EmpAdd,3), , LEFT(), This function returns a specified number of characters from, the left of the string. This function returns NULL, if any, argument is NULL., Syntax LEFT(string,length), e.g. mysql> SELECT LEFT('India',3);, Above query produces the following output:, LEFT('India',3), Ind, , Table: Empdetail, EmpNo, , EmpName, , EmpAdd, , EmpSal, , E01, , Ajay, , Jaipur, , 45000.00, , E02, , Vimal, , Chennai, , 60000.00, , E03, , Vinay, , Jabalpur, , 56000.00, , E04, , Rina, , Delhi, , 90000.00, , e.g. Write a query to view first three characters of employee’s, name from the table Empdetail., mysql> SELECT LEFT(EmpName,3) FROM Empdetail;, , Above query produces the following output:, LEFT(EmpName,3), , pur, nai, pur, lhi, , INSTR(), This function takes a string and a substring of it as arguments, and returns an integer which indicates the position of the, first occurrence of the substring within the string., Syntax INSTR(ori_str/column_name, sub_str), where, ori_str is the string to be searched and sub_str is the, string to be searched from ori_str., e.g. mysql> SELECT INSTR('firstexam','e');, Above query produces the following output:, INSTR('firstexam','e'), 6, , e.g. Consider all the names of employees from Empdetail, table. Write a query to find the position of letter ‘i’ in, Empdetail table, where employee salary is between 50000, and 60000., mysql> SELECT EmpName, INSTR(EmpName,'i') FROM, Empdetail, WHERE EmpSal BETWEEN 50000 AND 60000;, , Above query produces the following output:, , Aja, Vim, Vin, Rin, , RIGHT(), Working of this function is just reverse of LEFT function. It, returns a specified number of characters from the right of the, string. This function returns NULL, if any argument is, NULL., Syntax RIGHT(string,length), e.g. mysql> SELECT RIGHT('India',3);, Above query produces the following output:, , EmpName, Vimal, Vinay, , INSTR(EmpName,'i'), 2, 2, , TRIM(), This function is used to return a string after removing all, prefix or suffix spaces from the given string., Syntax TRIM([{BOTH|LEADING|TRAILING} [remstr] FROM], str/column_name), , Here, BOTH indicates the prefixes and suffixes from both, left and right are to be removed., LEADING indicates only the leading prefixes are to be, removed., TRAILING indicates only the trailing suffixes are to be, removed.
Page 17 :
@Cbsebookshub - Join Us on Telegram, , 5, , CBSE Term II Informatics Practices XII, , remstr is the string to be removed. It is optional, if not, specified and spaces are removed., FROM it is a keyword., str is a string from where remstr is to be removed., e.g. Case 1 If no specifier is given, BOTH is assumed and, the string is trimmed from both end., mysql> SELECT TRIM(' India ');, , Above query produces the following output:, TRIM(' India '), India, , Case 2 If leading specifier is given, then the prefix part is, trimmed., mysql> SELECT TRIM(LEADING '!', FROM '!!!!India!!!!');, , Above query produces the following output:, TRIM(LEADING '!' FROM '!!!!India!!!!'), India!!!!, , Case 3 If trailing specifier is given, then the suffix part is, trimmed., , RTRIM ('It is a string argument, , '), , It is a string argument, , Date/Time Functions, MySQL stores date in date/time format, representing the, century, month, year, day and hours. The date and time, functions are used to perform operations on the date/time, data stored in the database. The default date format is, YYYY-MM-DD in MySQL., Some date/time functions are explained with examples as, follows:, , DATE(), This function returns only DATE part from the given, date/time argument., Syntax Date(dt), Here, dt is the DateTime expression., e.g. mysql> SELECT DATE('2021-09-30 20:29:13');, Above query produces the following output:, DATE('2021-09-30 20:29:13'), , mysql> SELECT TRIM (TRAILING '!' FROM, '!!!!India!!!!');, , 2021-09-30, , Above query produces the following output:, TRIM(TRAILING'!'FROM'!!!!India!!!!'), !!!!India, , LTRIM(), This function removes the leading spaces from the characters, of a string passed as an argument. Spaces in the middle or, trailing spaces are not removed., Syntax LTRIM(str/column_name), e.g. mysql> SELECT LTRIM('It is a string, argument');, Above query produces the following output:, LTRIM (', , It is a string argument’), , It is a string argument, , RTRIM(), This function removes the trailing space from the characters, of a string passed as an argument. Spaces in the middle or, leading spaces are not removed., Syntax RTRIM(str/column_name), e.g. mysql> SELECT RTRIM('It is a string, argument');, Above query produces the following output:, , MONTH(), This function returns the MONTH part from the date, argument within a range of 1 to 12 (January to December), and it returns 0 if MONTH part of the date contains NULL., Syntax MONTH(date/column_name), e.g. mysql> SELECT MONTH('2021-09-30');, Above query produces the following output:, MONTH('2021-09-30'), 9, , Table: Club, Coach_id Coachname Age Sports, , Dateofapp, , Pay, , Sex, , 1, , KUKRAJA, , 35 KARATE, , 1996-03-27, , 1000.00, , M, , 2, , RAVINA, , 34 KARATE, , 1998-01-20, , 1200.00, , F, , 3, , KARAN, , 34 SQUASH, , 1998-02-19, , 2000.00, , M, , Write a query to display the month of all applicants whose, age is 35., mysql> SELECT MONTH(Dateofapp) FROM Club WHERE, Age=35;, , Above query produces the following output:, MONTH(Dateofapp), 3
Page 18 :
@Cbsebookshub - Join Us on Telegram, , 6, , CBSE Term II Informatics Practices XII, , MONTHNAME(), , Above query produces the following output:, , This function returns the name of the month from a date, specified as an argument., Syntax MONTHNAME(date/column_name), e.g. mysql> SELECT MONTHNAME('2021-09-30');, Above query produces the following output:, MONTHNAME('2021-09-30'), September, , YEAR('2021-09-30'), 2021, , Write a query to display the year of application for all female, coaches., mysql> SELECT YEAR(Dateofapp) FROM Club WHERE, Sex='F';, , Above query produces the following output:, , Write a query to display the month of application for all, coaches whose getting more than 1200 as pay., , YEAR(Dateofapp), 1998, , mysql> SELECT MONTHNAME(Dateofapp) FROM Club WHERE, Pay>=1200;, , Above query produces the following output:, MONTHNAME(Dateofapp), January, February, , DAY(), This function returns the day of the month (from 1 to 31), from a date specified as an argument., Syntax DAY(date/column_name), e.g. mysql> SELECT DAY('2021-09-30');, Above query produces the following output:, DAY('2021-09-30'), 30, , DAYNAME(), It returns the name of the week day from a date specified as, an argument., Syntax DAYNAME(date/column_name), e.g. mysql> SELECT DAYNAME ('2021-09-30');, Above query produces the following output:, DAYNAME('2021-09-30'), Thursday, , Write a query to display the day name of application for all, female coaches., mysql> SELECT DAYNAME(Dateofapp) FROM Club WHERE, Sex='F';, , Above query produces the following output:, , Write a query to display the day of application for all coaches, whose getting more than 1200 as pay., , DAYNAME(Dateofapp), Tuesday, , mysql> SELECT DAY(Dateofapp) FROM Club WHERE, Pay>=1200;, , Above query produces the following output:, DAY(Dateofapp), 20, 19, , YEAR(), This function returns the YEAR part from the given date, argument. The return value is in the range of 1000 to 9999 or, 0 for null date., Syntax YEAR(date/column_name), e.g. mysql> SELECT YEAR('2021-09-30');, , NOW(), This function returns the current date and time in the format, ‘YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS’ or YYYYMMDDHHMMSS, format., Syntax NOW(), e.g. mysql> SELECT NOW();, Above query produces the following output:, NOW(), 2021-09-30 21:22:07
Page 19 :
@Cbsebookshub - Join Us on Telegram, , 7, , CBSE Term II Informatics Practices XII, , Chapter, Practice, PART 1, Objective Questions, l, , Multiple Choice Questions, 1. Which type of SQL function work with a, single-row at a time?, , (a) Multiple-row functions, (b) Single-row functions, (c) Both (a) and (b), (d) None of the above, Ans. (b) Single-row functions work with a single-row at a time. It, returns a result for each row of the table, on which the, query is performed., , 2. Which function accepts a character string as an, input and provides character string or numeric, values as an output?, (a) Text, (b) Date, (c) Time, (d) Math, Ans. (a) Text function accepts a character string as an input and, provides character string or numeric values as an output., , 3. Which of the following is the correct syntax of, LCASE( ) function?, (a) LCASE(row_name), (b) LCE(column_name), (c) LCASE(str/column_name), (d) None of the above, Ans. (c) This function converts the characters of an argument, string to the lowercase characters. The syntax is, LCASE(str/column_name) or LOWER(str/column_name)., , 4. Which of the following function converts the, characters of an argument string to the uppercase, characters?, (a) UCASE( ), (b) UPPER( ), (c) Both (a) and (b), (d) None of the above, Ans. (c) This function converts the characters of a string into the, uppercase characters. The syntax is, UPPER(str/column_name) or UCASE(str/column_name)., , 5. The correct output of, mysql>SELECT TRIM(LEADING '&' FROM '&&& India &&&, ');, (a) India &&, (b) India &&&, (c) && India, (d) &&& India, Ans. (b) This function is used to return a string after removing all, prefix or suffix spaces from the given string. In other words,, this function removes leading and trailing spaces from a, given string. LEADING indicates only the leading prefixes, are to be removed., , 6. The default date format is, (a) MM-DD-YYYY, (b) YYYY-MM-DD, (c) DD-MM-YYYY, (d) None of these, Ans. (b) The default format for dates in MySQL is fixed as, YYYY-MM-DD and we have to follow that., , 7. Which of the following function returns an integer, that indicates the position of the first occurrence of, the sub-string within the string?, (a) INSTR( ), (b) RTRIM( ), (c) LENGTH( ), (d) TRIM( ), Ans. (a) The syntax of the INSTR function is, INSTR(ori_str/column_name,sub_str), where, ori_str is the string to be searched and, sub_str is the string to be searched from ori_str., , 8. Write the output of the following SQL command., SELECT ROUND (47.89);, (a) 47.88, (b) 47.8, (c) 48.0, (d) 50, Ans. (c) The ROUND() function rounds up the number to the, upwards or downwards to the nearest whole number., , 9. Which of the following function returns the name, of the month from selected date?, (a) MONTH(date), (b) MONTH_NAME(date), (c) MONTHNAME(date), (d) NAME_MONTH(), Ans. (c) mysql> SELECT MONTHNAME ('2021-09-30');, Above query produces the following output:, MONTHNAME('2021-09-30'), September
Page 20 :
@Cbsebookshub - Join Us on Telegram, , 8, , CBSE Term II Informatics Practices XII, , 10. Which of the following function returns only the, day number from month of selected date?, (a) DAY(date), (b) DAYNO(date), (c) DAY_NUMBER(date), (d) DATE(date), Ans. (a) mysql> SELECT DAY('2021-09-30');, Above query produces the following output:, , WHERE CNO =‘C5’ OR CNO =‘C9’, , DAY('2021-09-30'), , (b) mysql>SELECT UPPER(CITIES)FROM Customers WHERE, , 30, , CNO =‘C5’ OR ‘C9’, , 11. What will be returned by the given query?, SELECT ROUND(153.669,2);, (a) 153.6, (b) 153.66, (c) 153.67, (d) 153.7, Ans. (c)ROUND() function will round off the decimal places up, to 2 places., , 12. What will be returned by the given query ?, SELECT INSTR('INDIA', 'DI');, (a) 2, (b) 3, (c) −2, (d) −3, Ans. (b) INSTR function returns the starting index of the, substring that is passed as second argument in the function., l, , (a) mysql>SELECT LENGTH(CNAME) FROM Customers;, (b) mysql>SELECT LEN(CNAME) FROM Customers;, (c) mysql>SELECT COUNT(NAME) FROM Customers;, (d) mysql>SELECT COUNT(CNAME) FROM Customers;, (ii) Choose the correct query to display the city names, in lower case letter whose CNO is either C5 or C9., (a) mysql>SELECT UPPERCASE(CITIES)FROM Customers, , (c) mysql>SELECT UPPER(CITIES)FROM Customers WHERE, CNO =‘C5’ OR CNO =‘C9’, , (d) mysql>SELECT UPPER(CITIES)FROM Customers WHERE, CNO IS EITHER ‘C5’ OR ‘C9’, , (iii) Choose the correct query to display the length of, customer’s name for those customers whose name, end with R or L., (a) mysql>SELECT LEN(CNAME)FROM Customers WHERE CNAME, LIKE ‘%R’ OR CNAME LIKE ‘%L’;, , (b) mysql>SELECT LENGTH(CNAME)FROM Customers WHERE, CNAME LIKE ‘%R’ OR CNAME LIKE ‘%L’;, , (c) mysql>SELECT LENGTH(CNAME)FROM Customers WHERE, CNAME = ‘%R’ OR CNAME = ‘%L’;, , Case Based MCQs, , (d) mysql>SELECT LENGTH(CNAME)FROM Customers WHERE, , 13. Shanya Kumar is working with the following table, Customers:, Table : Customers, CNO, , CNAME, , CITIES, , C1, , SANYAM, , DELHI, , C2, , SHRUTI, , DELHI, , C3, , MEHER, , MUMBAI, , C4, , SAKSHI, , CHENNAI, , C5, , RITESH, , INDORE, , C6, , RAHUL, , DELHI, , C7, , AMEER, , CHENNAI, , C8, , MINAKSHI, , BANGLORE, , C9, , ANSHUL, , MUMBAI, , She has been given some queries to develop . Help, her to achieve the task., Shanya Kumar is working with the following table, Customers : (Put the table), She has been given some queries to develop. Help, her to achieve the task., (i) Choose the correct query to display the length of, customer’s name., , CNAME LIKE ‘%R’ OR LIKE ‘%L’;, , (iv) Choose the correct query to display the Customer’s, name and their respective cities merged together, for all the customers whose CNO is ending with 8., (a) mysql>SELECT MERGE(CNAME,CITIES) Customers WHERE, CNO LIKE ‘%8’;, , (b) mysql>SELECT CNAME,CITIES FROM Customers WHERE, CNO LIKE ‘%8’;, , (c) mysql>SELECT CONCAT(CNAME,CITIES) Customers, WHERE CNO = ‘%8’;, , (d) mysql>SELECT CONCAT(CNAME,CITIES) FROM Customers, WHERE CNO LIKE ‘%8’;, , (v) Choose the correct query to display the left most 4, letters from the customers who lives in Mumbai or, Banglore., (a) mysql>SELECT LEFT(CNAME)FROM Customers, WHERE CITIES =‘MUMBAI’ OR CITIES =, ‘BANGLORE’;, , (b) mysql>SELECT LEFT(CNAME,3)FROM Customers, WHERE CITIES =‘MUMBAI’ OR CITIES =, ‘BANGLORE’;
Page 21 : @Cbsebookshub - Join Us on Telegram, , 9, , CBSE Term II Informatics Practices XII, , (c) mysql>SELECT LEFT(CNAME,4)FROM, , Ans. (i), ROUND (6.5675,2), , C u s t o m e r s W H E R E C I T I E S =‘ M U M B A I ’ O R, ‘BANGLORE’;, , 6.57, , (d) mysql>SELECT LEFT(CNAME,4)FROM Customers, WHERE CITIES =‘MUMBAI’ OR CITIES =, ‘BANGLORE’;, Ans. (i) (a) mysql>SELECT LENGTH(CNAME) FROM Customers;, (ii) (c) mysql>SELECT UPPER(CITIES)FROM Customers, WHERE CNO =‘C5’ OR CNO =‘C9’, (iii) (b)mysql>SELECT LENGTH(CNAME)FROM Customers, WHERE CNAME LIKE ‘%R’ OR CNAME LIKE ‘%L’;, (iv) (c) mysql>SELECT CONCAT(CNAME,CITIES) FROM, Customers WHERE CNO LIKE ‘%8’;, (v) (d) mysql>SELECT LEFT(CNAME,4)FROM Customers, WHERE CITIES =‘MUMBAI’ OR CITIES =, ‘BANGLORE’;, , PART 2, Subjective Questions, l, , Short Answer Type Questions, , (ii), TRUNCATE(5.3456.2), 5.34, , (iii) If curdate is 05/12/2017, then output is 5., (iv), MID('PRE_BOARDCLASS 12',4,6), _BOARD, , 4. Mr. Manav, a database administrator in “Global, Educational and Training Institute” has created, following table named “Training” for the upcoming, training schedule:, Table : Training, Training_Id Name Email_Id, , Topic, , City, , Fee, , ND01, , Mr., Rajan, , Cyber, Security, , New, Delhi, , 10000, , GU01, , Ms.,
[email protected] ICT in, Gurugram 15000, Urvashi, Education, , FD01, , Ms., Neena, , neenarediff.com Cyber, Security, , ND02, , Mr., Vinay, , NULL, , GU02, , Mr.,
[email protected] Cyber, Naveen, Security, , 1. Which type of MySQL function accepts only, numeric values? Give the name of some functions, of that type., Ans. Mathematical functions accept only numeric values and, return the value of same type. These functions are used to, perform mathematical operations on the database data., Some mathematical functions are, POW()/POWER(), ROUND(), etc., , 2. Which SQL function is used to remove leading and, trailing spaces from a character expression X,, where X = ‘LEARNING ###MYSQL####’ (#, denotes a blank space) and also give the output of, X., , e.g. mysql> SELECT TRIM(' LEARNING, ###MYSQL####');, Output LEARNING###MYSQL, Spaces between ‘LEARNING’ and ‘MYSQL’ cannot be, removed., , 3. Write the output of following MySQL queries:, (i) SELECT, (ii) SELECT, (iii) SELECT, (iv) SELECT, , ROUND(6.5675,2);, TRUNCATE(5.3456,2);, DAYOFMONTH(curdate());, MID('PRE_BOARDCLASS 12',4,6);, , Faridabad 12000, , ICT in, New, Education Delhi, , 13000, , Gurugram NULL, , Predict the output of the following queries:, (i) SELECT SUBSTR(City,2,4) FROM Training WHERE, Topic <> 'Cyber Security';, , (ii) SELECT NAME FROM Training WHERE INSTR (Email_Id,, '@')=0;, Ans. (i), SUBSTR(City,2,4), urug, , Ans. TRIM function is used to remove all leading and trailing, spaces from the given character expression., Syntax TRIM([{BOTH|LEADING|TRAILING} [remstr] FROM], str/column_name), , raj@gmail. com, , ew D, , (ii), Name, Ms. Neena, , 5. Which function is used to display the position of, occurrence of a string ‘OUR’ in string ‘COURSE’?, Explain., Ans. The INSTR function searches for given second string into, the first string and returns the position., Syntax INSTR(str1,str2), e.g. mysql>SELECT INSTR('COURSE','OUR');, The output will be 2 because the position of string ‘OUR’ is, at 2 in the given string ‘COURSE’.
Page 22 :
@Cbsebookshub - Join Us on Telegram, , 10, , CBSE Term II Informatics Practices XII, , 6. Predict the output of the following queries:, (i) mysql>SELECT POWER(3,2);, (ii) mysql>SELECT DATE('2009-01-21 02:01:04');, Ans. (i), , POWER (3,2), 9, , (ii), DATE('2009-01-21 02:01:04'), 2009-01-21, , 7. Write the output of the following queries:, (i) mysql>SELECT POWER(-6,3);, (ii) mysql>SELECT YEAR('2014-02-04');, Ans. (i), , POWER (–6,3), –216, , (ii), YEAR ('2014-02-04'), 2014, , 8. Write the output of the following queries:, (i) mysql>SELECT LENGTH('Name');, (ii) mysql>SELECT MID('information',3,2);, Ans. (i), , LENGTH ('Name'), 4, , Ans. (i) mysql>SELECT SUBSTR(Name,3,5) FROM, STUDENT;, (ii) mysql> SELECT UCASE(Name), RollNo FROM STUDENT, WHERE Percentage>70;, , 11. What is the differences between the string function, and numeric function ?, Ans. Differences between string and numeric functions are given, below:, String Function, Numeric Function, Accepts text input., Accepts only numeric values., Returns both numeric and, Returns only numeric values., string values., String functions include, Numeric functions include, ASCII(), CHAR(), LEFT(),, POW( ), ROUND ( ),, etc., TRUNCATE( ), etc., , 12. Mention the type of the functions given below with, their purpose., (i) TRUNCATE( ), (ii) DAYOFMONTH( ), (iii) LEFT( ), Ans. (i) TRUNCATE( ) It is a mathematical function and returns, a number truncated upto specified number of digits., (ii) DAYOFMONTH( ) It is a Date/Time function and, returns the day of month for the specified date., (iii) LEFT( ) It is a string function and returns the leftmost, number of characters as specified., , 13. Give the output of following commands :, (i) mysql>SELECT LEFT ('Swati',4);, (ii) mysql>SELECT RTRIM ('!!!!!Study is, important!!!!!');, , (ii), , MID ('information'3,2), fo, , (iii) mysql>SELECT ROUND(3234.343,1);, where, !!!!! denotes blank spaces., Ans. (i), , 9. Write the output of the following query:, , Swat, , (ii), , Ans., SUBSTR('STUDENT',3,3), , STUDENT (RollNo, Name, Class, Stream,, Percentage), Give the answer of the following questions on the, basis of the above table structure., (i) Write a query to display the 3rd to 7th character, of name attribute., (ii) Write a query to display the name of each, student in uppercase letters with their RollNo,, whose percentage is greater than 70., , RTRIM('!!!!! Study is important !!!!!'), !!!!! Study is important, , UDE, , 10. Consider the following table structure :, , LEFT ('Swati', 4), , (iii), , ROUND (3234.343,1), 3234.3, , 14. Write the output of the following SQL queries:, (i) SELECT SUBSTR(TRIM(' INDIA Is Great ', ,3,6) ;, , (ii) SELECT ROUND(654.67152) +, ROUND(152.4146,2) ;, , (iii) SELECT INSTR('MOBILE PHONE','E') ;, (iv) SELECT DAYOFMONTH('2019-11-22');
Page 23 :
@Cbsebookshub - Join Us on Telegram, , 11, , CBSE Term II Informatics Practices XII, , Ans. (i), , SUBSTR (TRIM (' INDIA Is Great ',3,6), , (iv) SELECT YEAR("1979/11/26"),, MONTH ("1979/11/26"), DAY("1979/11/26"),, MONTHNAME("1979/11/26");, , DIA Is, , (ii), , (v) SELECT LEFT("INDIA",3), RIGHT("Computer, Science",4);, , ROUND(654.67152)+ ROUND(152.4146,2), , (vi) SELECT MID("Informatics",3,4),, , 807.41, , (iii), , SUBSTR("Practices",3);, Ans. (i), , INSTR ('MOBILE PHONE', 'E'), , POW(2,3), , 6, , (iv), , 8, , (ii), , DAYOFMONTH ('2019-11-22'), , ROUND(123.2345,2),ROUND(342.9234,–1), , 22, , 123.23 343.0, , 15. Wrtie any four differences between single-row, functions and multiple-row functions., , (iii), LENGTH("Informatics Practices"), , [NCERT], , Multiple-row functions /, Aggregate functions, It operates on a single row at, It operates on multiple, a time., rows., It returns one result per row., It returns one result for, multiple rows., It can be used in SELECT,, It can be used in the, WHERE and ORDER BY clause. SELECT clause only., Mathematical, String and Date, MAX(), MIN(), AVG(),, functions are examples of, SUM(), COUNT() and, single-row functions., COUNT(*) are examples, of multiple-row functions., , 21, , Ans. Single-row functions, , (iv), YEAR("1979/11/26"),MONTH("1979/11/26"),, DAY("1979/11/26"),MONTHNAME("1979/11/26"), 1979, , 11, , 26, , November, , (v), LEFT("INDIA",3),RIGHT("Computer Science",4), IND ence, , (vi), MID("Informatics",3,4),SUBSTR("Practices",3), , 16. Write the name of the functions to perform the, following operations:, [NCERT], (i) To display the day like “Monday”, “Tuesday”,, from the date when India got independence., (ii) To display the specified number of characters, from a particular position of the given string., (iii) To display the name of the month in which you, were born., (iv) To display your name in capital letters., Ans. (i), (ii), (iii), (iv), l, , DAYNAME( ), MID( ) or SUBSTR( ) or SUBSTRING( ), MONTHNAME( ), UPPER( ) or UCASE( ), , Long Answer Type Questions, 17. Write the output produced by the following SQL, commands:, [NCERT], (i) SELECT POW(2,3);, (ii) SELECT ROUND(123.2345, 2), ROUND(342.9234,−1);, (iii) SELECT LENGTH("Informatics Practices");, , Form actices, , 18. Consider the following table Club :, Table : Club, COACH_ID COACH AGE, NAME, , SPORTS Date_of_Joining PAY, , 1, , Rajesh, , 30 Karate, , 2, , Anuj, , 35, , 1999-08-25, , 1000, , Swimming 2000-01-05, , 750, , 3, , Shuchi, , 25 Basketball, , 4, , Reetika, , 28 Badminton 2002-08-25, , 1400, , 5, , Virendra, , 32 Cricket, , 1500, , 2005-01-04, 1996-05-17, , 1200, , Give the answer of the following questions on the, basis of the above table., (i) Write a query to display the substring of 4, characters of the name of each coach, starting, from second character, with their age., (ii) What will be the output of the following query?, mysql>SELECT LENGTH(COACHNAME) FROM Club WHERE, AGE>30;
Page 24 :
@Cbsebookshub - Join Us on Telegram, , 12, , CBSE Term II Informatics Practices XII, , (iii) Write a query to display the day for the, Date_of_Joining column., (iv) What will be the output of the following query?, , (b) SELECT Name, Stipend FROM Graduate WHERE, Subject="Chemistry" OR Subject="Physics";, , (c) SELECT * FROM Graduate WHERE Subject LIKE 'C%', AND Average=68;, , mysql>SELECT PAY*0.25+1000, , (d) SELECT Name FROM Graduate WHERE DIV=2;, , FROM Club, WHERE COACHNAME LIKE ‘R%’;, , (v) Write a query to display 3 characters from left of, coach name., Ans. (i) mysql>SELECT SUBSTR (COACHNAME,2,4) , AGE FROM, Club;, (ii), , Ans. (i) SELECT Name FROM Graduate WHERE Div=1;, (ii) SELECT Name, Stipend, Subject, Stipend *12 FROM, Graduate;, (iii) INSERT INTO Graduate VALUES (11, 'Kajol', 300,, 'Computers', 75,1);, (iv) (a), LEFT(NAME,3), , LENGTH (COACHNAME), , Rub, Vik, Moh, , 4, 8, , (b), , (iii) mysql>SELECT DAY(Date_of_Joining);, (iv), PAY*0.25+1000, 1250, 1350, , 400, 300, 350, 400, 250, , 2, , output for (iv) on the basis of table Graduate., Table : Graduate, Average, , Karan, Divya, Arun, John, Robert, SNO Name, , 19. Write SQL commands for (i) to (iii) and write the, , Stipend Subject, , Stipend, , (c), , (v) SELECT LEFT (COACHNAME,3) FROM Club;, , SNo Name, , Name, , (d), , Div, , Divakar, , 400, , Physics, , 68, , 1, , John, , 2, , Divakar, , 450, , Computers, , 68, , 1, , Mohan, , 3, , Divya, , 300, , Chemistry, , 62, , 2, , 4, , Arun, , 350, , Physics, , 63, , 1, , 5, , Sabina, , 500, , Mathematics, , 70, , 1, , 6, , John, , 400, , Chemistry, , 55, , 2, , 7, , Robert, , 250, , Physics, , 64, , 1, , No Itemname, 1 White lotus, , 8, , Rubina, , 450, , Mathematics, , 68, , 1, , 9, , Vikas, , 500, , Computers, , 62, , 1, , 300, , Mathematics, , 57, , 2, , (i) List the names of those students who obtained Div 1., (ii) Display a report, listing Name , Stipend , Subject, and amount of stipend received in a year assuming, that the Stipend is paid every month., (iii) To insert a new row in the Graduate table :, 11,‘‘KAJOL”,300, ‘‘COMPUTERS”,75,1, (iv) Give the output of the following SQL statement, based on table Graduate:, (a) SELECT LEFT(NAME,3) FROM Graduate WHERE SNO>7;, , Average Div, , Computers, , 68, , 1, , Name, , Karan, , Mohan, , 450, , Subject, , Divya, , 1, , 10, , Stipend, , 20. Write SQL commands for (i) to (v) and write the, output for (vi) on the basis of table Furniture., Table : Furniture, Type, Double Bed, , Dateofstock Price, 23/02/02, 30000, , 2 Pink feather, , Baby Cot, , 20/01/02, , 3 Dolphin, , Baby Cot, , 19/02/02, , 4 Decent, , Office Table 01/01/02, , 7000, , Discount, 25, 20, , 9500, , 20, , 25000, , 30, 25, , 5 Comfort Zone Double Bed, , 12/01/02, , 25000, , 6 Donald, , Baby Cot, , 24/02/02, , 6500, , 15, , 7 Royal finish, , Office Table 20/02/02, , 18000, , 30, , 8 Royal tiger, , Sofa, , 22/02/02, , 31000, , 30, , 9 Econo sitting, , Sofa, , 13/12/01, , 9500, , 25, , 10 Eating, paradise, , Dining Table 19/02/02, , 11500, , 25, , 11 WoodComfort Double Bed, , 23/03/03, , 25000, , 25, , 12 Old Fox, , Sofa, , 20/02/03, , 17000, , 20, , 13 Micky, , Baby Cot, , 21/02/03, , 7500, , 15
Page 25 :
@Cbsebookshub - Join Us on Telegram, , 13, , CBSE Term II Informatics Practices XII, , (i) To show all information about the baby cots from, the Furniture table., (ii) To list the itemname which are priced at more than, 15000 from the Furniture table., (iii) To list itemname and type of those items, in which, date of stock is before 22/01/02 from the Furniture, table in the descending order of itemname., (iv) To display itemname and dataofstock of those, items, whose type is “ Sofa” from Furniture table., (v) To insert a new row in the Furniture table with the, following data:, 14,‘‘Velvet touch” , ‘‘Double Bed”,{25/03/03},, 25000,30, (vi) Give the output of the following SQL statement, based on table Furniture., (a) SELECT LEFT(Itemname,3) FROM Furniture WHERE, , (d), , 625000, 340000, 112500, , 21. Consider the following table named “Product”,, showing details of products being sold in a grocery, shop., Table : Product, PCode, P01, , Type="Double Bed";, , (b) SELECT MONTHNAME(Dateofstock) FROM Furniture, (c) SELECT * FROM Furniture WHERE Itemname LIKE, 'E%';, , (d) SELECT Price*Discount FROM Furniture WHERE, Dateofstock>31/12/02;, Ans. (i) SELECT * FROM Furniture WHERE Type= "Baby Cot";, FROM, , Furniture, , WHERE, , (iii) SELECT Itemname, Type FROM Furniture WHERE, Dateofstock < "22/01/02" ORDER BY Itemname, DESC;, , Manufacture, Surf, , P02, , Tooth Paste, , 54, , Colgate, , P03, , Soap, , 25, , Lux, , P04, , Tooth Paste, , 65, , Pepsodent, , P05, , Soap, , 38, , Dove, , P06, , Shampoo, , 245, , Dove, , Com, Woo, , 22. Given the following table Employee :, , (v) I N S E R T, INTO, Furniture, VALUES, (14,, 'Velvet, touch',, 'Double, Bed',, "25/03/03", 25000, 30);, (vi) (a), LEFT(Itemane,3), whi, , Table : Employee, MONTHNAME(Dateofstock), , No. Name, 1 Pankaj, , February, December, February, , (c), IterName Type, , Dateofstock Price Dsicount, , 9, , Econo, sitting, , 13/12/01, , 10, , Eating, Dining 19/02/02, paradise Table, , NO, , UPrice, 120, , Ans. (i) CREATE TABLE Product(, PCode char(3) PRIMARY KEY,, PName varchar(25) NOT NULL,, UPrice int(4),, Manufacture varchar(30));, (ii) PCode, (iii) SELECT PCode,PName, UPrice FROM Product WHERE, Manufacture="Dove";, (iv) UPDATE Product SET UPrice =UPrice+0.12*UPrice, WHERE Manufacture="Dove";, , (iv) SELECT Itemname , Dateofstock FROM Furniture, WHERE Type= 'Sofa';, , (b), , PName, Washing Powder, , Write SQL queries for the following and output(s), produced by executing the following queries on the, basis of the information given above in the table, Product., (i) Create the table Product with appropriate data, types and constraints., (ii) Identify the primary key in table Product., (iii) List the product code, product name and price in, with their product name for all Dove manufacture., (iv) Increase the price by 12 per cent for all the, products manufactured by Dove., , WHERE Type="Sofa";, , (ii) SELECT, Itemname, Price>15000;, , Price*DIscount, , Sofa, , 9500, , 25, , 11500, , 25, , Age Department, 54 Engg., , Dateofrtd, 10/01/97, , Salary, 1200, , Sex, M, , 41 Estbl., , 24/03/98, , 2000, , F, , 2, , Shalini, , 3, , Sanjay, , 32 Engg., , 12/12/96, , 3500, , M, , 4, , Sudha, , 25 Science, , 01/07/99, , 4700, , F, , 5, , Rakesh, , 32 Engg., , 05/09/97, , 2500, , M, , 6, 7, 8, , Shakeel, Surya, Shikha, , 40 Language, 44 Estbl., 33 Science, , 27/06/98, 25/02/97, 31/07/97, , 3000, 2100, 2600, , M, M, F
Page 26 :
@Cbsebookshub - Join Us on Telegram, , 14, , CBSE Term II Informatics Practices XII, , Write SQL commands for (i) to (v)., (i) To show all information about the employees of, Engg. branch., (ii) To list the names of female employees who are in, Science branch., (iii) To list the names of all employees with their date, of retirement in ascending order., (iv) To display employee’s name , salary , age for, male employees only., (v) To insert a new row in the Employee table with, the following data:, 9,‘‘Rohit”,46,‘‘Language”,{22/06/98},2300,‘‘M”, Ans. (i) SELECT * FROM Employee WHERE Branch= 'Engg.';, (ii) SELECT Name FROM Employee WHERE Sex= 'F' AND, Department= 'Science';, , (ii) Give the output of the following SQL queries:, (a) SELECT Desig,Plevel FROM Worker WHERE Desig LIKE, '%or';, , (b) SELECT RIGHT(Name,3) FROM Worker WHERE, Plevel='P002';, , (c) SELECT YEAR(DOJ) FROM Worker;, Ans. (i) (a) SELECT * FROM Worker ORDER BY DOB DESC;, (b) SELECT Name, Desig FROM Worker WHERE Plevel, IN ("P001", "P002");, (c) SELECT * FROM Worker WHERE DOB, "19-JAN-1984" AND "18-JAN-1987";, (d) INSERT INTO Worker VALUES, (19, 'Daya kishore', 'Operator',, 'P003','19-Jun-2008', '11-Jul-1984');, (ii) (a), Desig, , (iii) SELECT Name, Dateofrtd FROM Employee ORDER BY, Dateofrtd;, (iv) SELECT Name, Salary, Age FROM Employee WHERE, Sex= 'M';, , (i) and (ii) parts of this question., Table : Worker, Ecode Name, , Desig, , 11, , Supervisor P001, , Radhey, Shyam, , Plevel, , Plevel, , Supervisor P001, Operator, P003, Operator, P003, , (b), , (v) INSERT INTO Employee VALUES (9, 'Rohit', 46,, 'Language',"22/06/98",2300, 'M');, , 23. Consider the following table WORKER and answer, , BETWEEN, , RIGHT(Name,3), med, nya, , (c), , YEAR(DOJ), 2004, , DOJ, , DOB, , 2009, , 13-Sep-2004, , 23-Aug-1981, , 2006, 2005, , 12, , Chander Operator, Nath, , P003, , 22-Feb-2010 12-Jul-1987, , 13, , Fizza, , Operator, , P003, , 14-June-2009 14-Oct-1983, , 15, , Ameen, Ahmed, , Mechanic, , P002, , 21-Aug-2006 13-Mar-1984, , 18, , Sanya, , Clerk, , P002, , 19-Dec-2005 09-June-1983, , (i) Write SQL commands for the following statements:, (a) To display the details of all workers in, descending order of DOB., (b) To display Name and Desig of those workers, whose Plevel is either P001 or P002., (c) To display the content of all the workers, whose, DOB is in between ‘19-JAN-1984’ and, ‘18-JAN-1987’., (d) To add a new row with the following:, 19, ‘Daya kishore’, ‘Operator’, ‘P003’,, ‘19-Jun-2008’, ‘11-Jul-1984’, , 24. Write the SQL functions which will perform the, following operations:, (i) To display the name of the month of the current, date., (ii) To remove spaces from the beginning and end of, a string “ Panaroma ’’., (iii) To display the name of the day e.g. Friday or, Sunday from your date of birth, dob., (iv) To display the starting position of your first, name(fname) from your whole name (name)., (v) To compute the remainder of division between, two numbers n1 and n2., [CBSE SAMPLE PAPER 2020], Ans. (i) MONTHNAME(date(now())), (ii) TRIM (“ Panaroma ’’), (iii) DAYNAME(date(dob)), (iv) INSTR(name, fname), (v) MOD(n1,n2)
Page 27 :
@Cbsebookshub - Join Us on Telegram, , 15, , CBSE Term II Informatics Practices XII, , 25. Consider a table Salesman with the following data:, Table : Salesman, SNO SNAME, , SALARY, , BONUS, , DATE_OF_, JOIN, , A01, , Beena Mehta, , 30000, , 45.23, , 29-10-2019, , A02, , K. L. Sahay, , 50000, , 25.34, , 13-03-2018, , B03, , Nisha Thakkar 30000, , 35.00, , 18-03-2017, , B04, , Leela Yadav, , 80000, , NULL, , 31-12-2018, , C05, , Gautam Gola, , 20000, , NULL, , 23-01-1989, , C06, , Trapti Garg, , 70000, , 12.37, , 15-06-1987, , D07, , Neena Sharma 50000, , 27.89, , 18-03-1999, , Write SQL queries using SQL functions to perform, the following operations:, (i) Display salesman name and bonus after rounding, off to zero decimal places., , (ii) Display the position of occurrence of the string, “ta” in salesman names., (iii) Display the four characters from salesman name, starting from second character., (iv) Display the month name for the date of join of, salesman., (v) Display the name of the weekday for the date of, join of salesman., Ans. (i), (ii), (iii), or, (iv), (v), , SELECT, SELECT, SELECT, SELECT, SELECT, SELECT, , SNAME, ROUND(BONUS,0) FROM Salesman;, INSTR(SNAME, "ta") FROM Salesman;, MID(SNAME,2,4) FROM Salesman;, SUBSTRING(SNAME,2,4) FROM Salesman;, MONTHNAME(DATE_OF_JOIN) FROM Salesman;, DAYNAME(DATE_OF_JOIN) FROM Salesman;
Page 28 :
@Cbsebookshub - Join Us on Telegram, , Chapter Test, Multiple Choice Questions, , 1. Which of the following performs a pre-defined task and returns some type of result?, (a) Database, (c) Implementation, , (b) SQL function, (d) None of these, , 2. Which SQL function remove the leading blank spaces from a string ?, (a) CHAR( ), (c) LCASE( ), , (b) CONCAT( ), (d) LTRIM( ), , 3. Which of the following function returns the value of a number raised to the power of another number?, (a) ROUND( ), (c) POW( ), , (b) POWER( ), (d) Both (b) and (c), , 4. Which of the following function returns only date part from the given date/time argument?, (a) DATE( ), (c) DATECUR( ), , (b) CURDATE( ), (d) None of these, , 5. Identify single-row functions of MySQL amongst the following., (a) TRIM(), (c) ROUND(), , (b) MAX(), (d) Both (a) and (c), , Short Answer Type Questions, , 6. Write the output of the following SQL queries:, (i) SELECT INSTR(‘INTERNATIONAL’, ‘NA’);, (ii) SELECT LENGTH(MID(‘NETWORK’,2,3));, (iii) SELECT ROUND(563.345,−2);, (iv) SELECT DAYOFYEAR(‘2014-01-30’);, , 7. State differences between date functions NOW( ) and DAY( ) of MySQL., Long Answer Type Questions, , 8. Write SQL command for questions (i) to (v) on the basis of table Teacher., Table: Teacher, No, , Name, , Department, , Dateofjoining, , Salary, , Sex, , 1, , Raja, , Computer, , 21/05/98, , 8000, , M, , 2, , Sangita, , History, , 21/05/97, , 9000, , F, , 3, , Ritu, , Sociology, , 29/08/98, , 8000, , F, , 4, , Kumar, , Linguistics, , 13/06/96, , 10000, , M, , 5, , Venkat, , History, , 31/10/99, , 8000, , M, , 6, , Sidhu, , Computer, , 21/05/86, , 14000, , M, , 7, , Aishwarya, , Sociology, , 11/01/88, , 12000, , F, , (i) To select all the information of teacher in computer department., (ii) To list the name of female teachers in History department., (iii) To list all names of teachers with date of admission in ascending order., (iv) To display teacher’s Name, Department and Salary of female teacher., (v) To insert a new record in the Teacher table with the following data:, 8,”Mersha”,”Computer”, ‘01/01/2000’,12000,”M”
Page 29 :
@Cbsebookshub - Join Us on Telegram, , 17, , CBSE Term II Informatics Practices XII, , 9. Write SQL command for questions (i) to (v) on the basis of table Interiors., Table : Interiors, No, , Itemname, , Type, , Dateofstock, , Price, , Discount, , 1, , Red_rose, , Double Bed, , 23/02/02, , 32000, , 15, , 2, , Soft touch, , Baby Cot, , 20/01/02, , 9000, , 10, , 3, , Jerry’s home, , Baby Cot, , 19/02/02, , 8500, , 10, , 4, , Rough wood, , Office Table, , 01/01/02, , 20000, , 20, , 5, , Comfort zone, , Double Bed, , 12/01/02, , 15000, , 20, , 6, , Jerry look, , Baby Cot, , 24/02/02, , 7000, , 19, , 7, , Lion king, , Office Table, , 20/02/02, , 16000, , 20, , 8, , Royal tiger, , Sofa, , 22/02/02, , 30000, , 25, , 9, , Park sitting, , Sofa, , 13/12/01, , 9000, , 15, , 10, , Dine Paradise, , Dining Table, , 19/02/02, , 11000, , 15, , 11, , White wood, , Double Bed, , 23/03/03, , 20000, , 20, , 12, , James 007, , Sofa, , 20/02/03, , 15000, , 15, , 13, , Tom look, , Baby Cot, , 21/02/03, , 7000, , 10, , (i) To show all information about the sofas from the Interiors table., (ii) To list the itemname which are priced at more than 10000 from the Interiors table., (iii) To list Itemname and Type of those items, in which Dateofstock is be 22/01/02 from the Interiors table in descending order, of Itemname., (iv) To display Itemname and Dateofstock of items whose discount is more than 15., (v) To insert a new row in the new one table with the following data:, 14,” True Indian” , ”Office Table”,{28/03/03},15000,20, , Answers, Multiple Choice Questions, 1. (b), , 2. (d), , 3. (d), , 4. (a), , 5. (d), , For Detailed Solutions, Scan the code
Page 30 :
@Cbsebookshub - Join Us on Telegram, , 18, , CBSE Term II Informatics Practices XII, , CHAPTER 02, , Aggregate Functions, and Querying, In this Chapter..., l, , ORDER BY Clause, , l, , GROUP BY Clause, , l, , HAVING Clause, , Aggregate functions are also known as group functions, they return a result only in single row based on group of rows, rather, than on single row. It always used with SELECT command and in ORDER BY and HAVING clauses., SQL aggregate functions return a single value, calculated from values in a column., Consider the following table Club:, Table : Club, Coachid, , Age, , Sports, , Dateofapp, , Pay, , Gender, , 1, , Coachname, Kukreja, , 35, , Karate, , 1996-03-27, , 1000, , M, , City, Mumbai, , 2, , Ravina, , 34, , Karate, , 1998-01-29, , 12000, , F, , Chennai, , 3, , Karan, , 34, , Squash, , 1998-02-19, , 2000, , M, , Delhi, , 4, , Tarun, , 33, , Basketball, , 1998-01-01, , 1500, , M, , Delhi, , 5, , Zubin, , 36, , Swimming, , 1998-01-12, , 750, , M, , Delhi, , 6, , Asha, , 32, , Tennis, , 1996-09-23, , 900, , Null, , Delhi, , AVG(), This function returns the average value of a specified column., Syntax SELECT AVG(column_name) FROM table_name;, e.g., Write a query to display the average pay of coaches., mysql> SELECT AVG(Pay) FROM Club;, , Above query produces the following output:, AVG(Pay), 3025.0000, , COUNT(), This function returns the total number of values or rows of the specified field or column. COUNT (*) is a special function, as it, returns the count of all rows in a specified table. It includes all the null and duplicate values., Syntax SELECT COUNT(*) FROM table_name;
Page 31 :
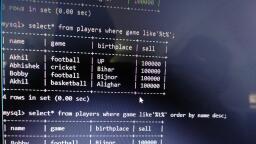
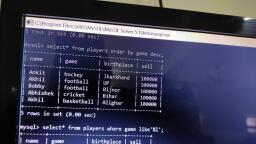
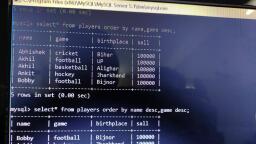
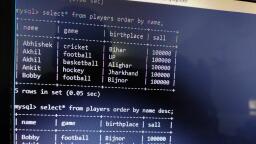
@Cbsebookshub - Join Us on Telegram, , 19, , CBSE Term II Informatics Practices XII, , e.g., , Write a query to display the total pay of all coaches., mysql> SELECT COUNT(*) FROM Club;, , Above query produces the following output:, COUNT(*), 6, , SUM(), This function returns the sum of values in the specified, column. The SUM works on numeric fields only. Null values, are excluded from the result returned., Syntax SELECT SUM(column_name) FROM table_name;, e.g. Write a query to display the total pay of all coaches., mysql> SELECT SUM(Pay) FROM Club;, , DISTINCT Keyword with COUNT(), Function, The DISTINCT keyword helps us in removing the, duplicates from the result. When it is used with aggregate, function COUNT, it returns the number of distinct rows in a, specified table., Syntax SELECT COUNT(DISTINCT column_name) FROM, table_name;, , e.g. Write a query to display the number of coaches from, table Club., mysql>SELECT COUNT(DISTINCT Sports) FROM Club;, , Above query produces the following output:, , Above query produces the following output:, SUM(Pay), 18150, , ORDER BY Clause, The ORDER BY clause is used to sort the result set along a, specified column. The ORDER BY clause sorts the records, in ascending order by default., If you want to sort the records in descending order, you can, use the DESC keyword., Syntax SELECT column_name(s), FROM table_name, ORDER BY column_name(s) ASC/DESC;, , COUNT(DISTINCT Sports), , Table: Persons, , 5, , P_ID LastName, , FirstName, , Address, , MAX(), , 1, , Hansen, , Ola, , Timoteivn 10 Sandnes, , This function returns the largest value from the selected, columns., Syntax SELECT MAX(column_name) FROM table_name;, e.g. Write a query to display the maximam pay availed by the, coaches., , 2, , Svendson, , Tove, , Borgvn 23, , Sandnes, , 3, , Pettersen, , Kari, , Storgt 20, , Stavanger, , mysql> SELECT MAX(Pay) FROM Club;, , Above query produces the following output:, MAX(Pay), 12000, , MIN(), This function returns the smallest value from the selected, column., Syntax SELECT MIN(column_name) FROM table_name;, e.g. Write a query to display the minimum pay availed by the, coaches., mysql> SELECT MIN(Pay) FROM Club;, , Above query produces the following output:, MIN(Pay), 750, , City, , Now, we want to select all the persons from the table, Persons. However, we want to sort the persons by their last, name in ascending order. We will use the following, statement:, mysql>SELECT * FROM Persons ORDER BY, LastName ASC;, , The result set will look like this:, P_ID LastName, 1, 3, 2, , FirstName Address, , Hansen, Ola, Pettersen Kari, Svendson Tove, , Timoteivn 10, Storgt 20, Borgvn 23, , City, Sandness, Stavanger, Sandnes, , GROUP BY Clause, The GROUP BY clause can be used with SELECT, statement, if we want to select multiple records and group of, results by one or more columns. AS keyword is optional and, is used to assign a temporary name to the column or table., Syntax SELECT column1, column2, FROM table_name, WHERE [conditions], GROUP BY column1, column2, ORDER BY column1, column2
Page 32 :
@Cbsebookshub - Join Us on Telegram, , 20, , CBSE Term II Informatics Practices XII, , Consider the following Employee table, Table : Employee, , GROUP BY Category_id, ORDER BY Category_id;, , EmpID EmpName EmpEmail PhoneNumber Salary City, 1, , Nidhi, , nidhi@sam 9955669999, ple.com, , 50000 Mumbai, , 2, , Anay, , anay@samp 9875679861, le.com, , 55000 Pune, , 3, , Rahul, , rahul@sam 9876543212, ple.com, , 35000 Delhi, , 4, , Sonia, , sonia@sam 9876543234, ple.com, , 35000 Delhi, , 5, , Akash, , akash@sam 9866865686, ple.com, , 25000 Mumbai, , Write a query to retrieve the number of employees in each, city., SELECT COUNT(EmpID), City, FROM Employee, GROUP BY City;, , There will be 3 records selected. These are the results that, you should see:, , 2, 2, 1, , 1, 4, 1, , The HAVING clause can be used only with the SELECT, statement. HAVING is applied to summarised rows, (summarised with GROUP BY). In which the completed data, is firstly fetched and then separated according to condition., The HAVING clause was added to MySQL because the, WHERE keyword could not be used with aggregate, functions., Syntax SELECT column1, column2, , City, Delhi, Mumbai, Pune, , Product_name, , 25, 50, 75, , FROM table1, table2, WHERE [ conditions ], GROUP BY column1, column2, HAVING [ conditions ], ORDER BY column1, column2, , Let's look at how to use the GROUP BY clause with the, COUNT function in SQL., In this example, we have a table called Products with the, following data:, Table : Products, Product_id, , Total_products, , HAVING Clause, , This would produce the following result:, COUNT(EmpID), , Category_id, , Consider the following table Order:, Table : Order, O_ID, , OrderDate, , OrderPrice, , 1, , 2015/01/23, , 1000, , Customer, Rubeen, , 2, , 2014/11/15, , 1600, , Sheena, , 3, , 2014/11/12, , 700, , Jensen, , Category_id, , 4, , 2013/10/22, , 500, , Rubeen, , 1, , Pear, , 50, , 5, , 2013/10/16, , 2000, , Jensen, , 2, , Banana, , 50, , 6, , 2012/09/30, , 300, , Sheena, , 3, , Orange, , 50, , 4, , Apple, , 50, , 5, , Bread, , 75, , 6, , Sliced Ham, , 25, , 7, , Kleenex, , NULL, , Enter the following SQL statement:, SELECT Category_id, COUNT(*) AS Total_products, FROM Products, WHERE Category_id IS NOT NULL, , mysql>SELECT Customer, SUM(OrderPrice), FROM Order, GROUP BY Customer, HAVING SUM(OrderPrice) <2000;, , Above query produces the following output:, Customer, Rubeen, Sheena, , SUM (OrderPrice), 1500, 1900
Page 33 :
@Cbsebookshub - Join Us on Telegram, , 21, , CBSE Term II Informatics Practices XII, , Chapter, Practice, PART 1, Objective Questions, l, , Multiple Choice Questions, 1. Which of the following is not an aggregate function?, , (a) AVG(), (b) ADD(), (c) MAX(), (d) COUNT(), Ans. (b) There is no aggregate function named ADD() but SUM(), is an aggregate function which performs mathematical sum, of multiple rows having numerical values., , 2. Which aggregate function returns the count of all, rows in a specified table?, (a) SUM(), (c) COUNT(), , (b) DISTINCT(), (d) None of these, , Ans. (c) COUNT() function returns the total number of values or, rows of the specified field or column., , 3. In which function, NULL values are excluded from, the result returned?, (a) SUM(), , (b) MAX(), , (c) MIN(), , (d) All of these, , Ans. (d) NULL values are excluded from the result returned by, all the aggregate functions., , 4. The AVG() function in MySQL is an example of, (a) Math function, (c) Date function, , (b) Text function, (d) Aggregate function, , Ans. (d) The AVG() function returns the average value from a, column or multiple-rows., So, the AVG ( ) function in MySQL is an example of, aggregate function., , 5. Which of the following function count all the values, except NULL?, (a) COUNT(*), , (b) COUNT(column_name), , (c) COUNT(NOT NULL), , (d) COUNT(NULL), , Ans. (a) All aggregate functions exclude NULL values while, performing the operation and COUNT(*) is an aggregate, function., , 6. What is the meaning of “GROUP BY” clause in, MySQL?, , (a) Group data by column values, (b) Group data by row values, (c) Group data by column and row values, (d) None of the mentioned, Ans. (a) Through GROUP BY clause we can create groups from a, column of data in a table., , 7. Which clause is similar to “HAVING” clause in, MySQL?, (a) SELECT, (b) WHERE, (c) FROM, (d) None of the mentioned, Ans. (b) HAVING clause will act exactly same as WHERE clause., i.e. filtering the rows based on certain conditions., , 8. Which clause is used with an “aggregate, functions”?, (a) GROUP BY, (b) SELECT, (c) WHERE, (d) Both (a) and (c), Ans. (a) “GROUP BY” is used with an aggregate functions., , 9. What is the significance of the statement “GROUP, BY d.name” in the following MySQL statement?, SELECT name, COUNT (emp_id), emp_no, FROM department, GROUP BY name;, (a) Counting of the field “name” on the table “department”, (b) Aggregation of the field “name” of table “department”, (c) Sorting of the field “name”, (d) None of the mentioned, Ans. (b) “GROUP BY” clause is used for aggregation of field., Above statement will find the aggregation of the field, “name” of table “department”., , 10. What is the significance of the statement “HAVING, COUNT (emp_id)>2” in the following MySQL, statement?, SELECT name, COUNT (emp_id),emp_no, FROM department, GROUP BY name, HAVING COUNT (emp_id)>2;, (a) Filter out all rows whose total emp_id below 2, (b) Selecting those rows whose total emp_id>2, (c) Both (a) and (b), (d) None of the mentioned, Ans. (c) “HAVING” clause are worked similar as “WHERE”, clause i.e. filtering the rows based on certain conditions., GROUP BY command places conditions in the query using
Page 34 :
@Cbsebookshub - Join Us on Telegram, , 22, , CBSE Term II Informatics Practices XII, , HAVING clause. So, all the groups having employee count, greater than 2 will be displayed., , 11. What is the significance of “ORDER BY” in the, following MySQL statement?, SELECT emp_id, fname, lname, FROM person, ORDER BY emp_id;, (a) Data of emp_id will be sorted, (b) Data of emp_id will be sorted in descending order, (c) Data of emp_id will be sorted in ascending order, (d) All of the mentioned, Ans. (c) Sorting in ascending or descending order depends on, keyword “DESC” and “ASC”. The default order is, ascending., , 12. What will be the order of sorting in the following, MySQL statement?, SELECT emp_id, emp_name, FROM person, ORDER BY emp_id, emp_name;, (a) Sorting {emp_id, emp_name}, (b) Sorting {emp_name, emp_id}, (c) Sorting {emp_id} but not emp_name, (d) None of the mentioned, Ans. (a) In the query, first “emp_id” will be sorted then, emp_name with respect to emp_id., , 13. Which of the following is not a valid SQL, statement?, (a) SELECT MIN(pub_date) FROM books GROUP BY, , category HAVING pub_id = 4;, (b) SELECT MIN(pub_date) FROM books WHERE, , category = 'COOKING';, (c) SELECT COUNT(*) FROM orders WHERE customer# =, 1005;, (d) SELECT MAX(COUNT(customer#)) FROM orders, GROUP BY customer#;, Ans. (a) HAVING clause is wrongly applied on attribute “pub_id”, rather than attribute “category”., , 14. If emp_id contain the following set {9, 7, 6, 4, 3, 1,, 2}, what will be the output on execution of the, following MySQL statement?, SELECT emp_id, FROM person ORDER BY emp_id;, (a) {1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 7, 9}, (b) {2, 1, 4, 3, 7, 9, 6}, (c) {9, 7, 6, 4, 3, 1, 2}, (d) None of the mentioned, Ans. (a) “ORDER BY” clause sort the emp_id in the result set in, ascending order and in absence of keyword ASC or DESC, in the ORDER BY clause the default order is ascending., , 15. Find odd one out?, (a) GROUP BY, (c) ASC, , Ans. (a) “ORDER BY”, “DESC”, “ASC” are related to sorting, whereas “GROUP BY” is not related to sorting., l, , Case Based MCQs, Direction Read the case and answer the following, questions., , 16. A School in Delhi uses database management, system to store student details. The school, maintains a database 'school_record' under which, there are two tables., Student Table Maintains general details about, every student enrolled in school., StuLibrary Table To store details of issued books., BookID is the unique identification number issued, to each book. Minimum issue duration of a book is, one day., [CBSE Question Bank 2021], Student, Type, Field, numeric, StuID, StuName, varchar(20), varchar(50), StuAddress, StuFatherName varchar(20), numeric, StuContact, StuAadhar, numeric, varchar(5), StuSection, varchar(1), , StuLibrary, Type, numbric, numbric, Date, Date, , Field, BookID, StuID, Issued_date, Return_date, , (i) Identify the SQL query which displays the data of, StuLibrary table in ascending order of student ID., I. SELECT * FROM StuLibrary ORDER BY BookID;, II. SELECT * FROM StuLibrary ORDER BY StuID;, III. SELECT * FROM StuLibrary ORDER BY StuID ASC;, IV. SELECT * FROM StuLibrary ORDER BY StuID DESC;, Choose the correct option, which displays the, desired data., (a) Both I and IV, (b) Both I and II, (c) Both III and IV, (d) Both II and III, Ans. (d) Since the default order of sorting is ASC or ascending,, therefore if it is not mentioned in the query the query will, take the default order., , (ii) The primary key for StuLibrary table is/are ……., (a) BookID, (b) BookID,StuID, (c) BookID,Issued_date, (d) Issued_date, Ans. (a) Because BookID will have unique and NOT NULL, values., , (iii) Which of the following SQL query will display, dates on which number of issued books is greater, than 5?, (a) SELECT Issued_date FROM StuLibrary GROUP BY, , Issued_date WHERE COUNT(*)>5;, (b) DESC, (d) ORDER BY, , (b) SELECT Issued_date FROM StuLibrary GROUP BY, , Return_date HAVING COUNT(*)>5;
Page 35 :
@Cbsebookshub - Join Us on Telegram, , 23, , CBSE Term II Informatics Practices XII, , (c) SELECT Issued_date FROM StuLibrary, , GROUP BY Issued_date HAVING, COUNT(*)>5;, (d) SELECT Issued_date FROM StuLibrary GROUP BY, Return_date WHERE COUNT(*)>5;, Ans. (c) SELECT Issued_date FROM StuLibrary GROUP BY, Issued_date HAVING COUNT(*)>5;, , 17. Table: Book_Information, , Table: Sales, , Column Name, , Column Name, , Book_ID, , Store_ID, , Book_Title, , Sales_Date, , Price, , Sales_Amount, , (iv) Which SQL statement lets you find the total, number of stores in the SALES table?, (a) SELECT COUNT(Store_ID) FROM Sales;, (b) SELECT COUNT(DISTINCT Store_ID) FROM, Sales;, (c) SELECT DISTINCT Store_ID FROM Sales;, (d) SELECT COUNT(Store_ID) FROM Sales GROUP BY, Store_ID;, Ans. (d) SELECT COUNT(Store_ID) FROM Sales GROUP BY, Store_ID;, , (v) Which SQL statement allows you to find the total, sales amount for Store_ID 25 and the total sales, amount for Store_ID 45?, (a) SELECT Store_ID, SUM(Sales_Amount) FROM, Sales WHERE Store_ID IN ( 25, 45) GROUP BY, Store_ID;, , (i) Which SQL statement allows you to find the, highest price from the table Book_Information?, (a) SELECT Book_ID,Book_Title,MAX(Price) FROM, Book_Information;, (b) SELECT MAX(Price) FROM Book_Information;, (c) SELECT MAXIMUM(Price) FROM, Book_Information;, (d) SELECT Price FROM Book_Information ORDER BY, Price DESC ;, Ans. (b) SELECT MAX(Price) FROM Book_Information;, , (ii) Which SQL statement allows you to find sales, amount for each store?, (a) SELECT Store_ID, SUM(Sales_Amount) FROM Sales;, (b) SELECT Store_ID, SUM(Sales_Amount) FROM Sales, ORDER BY Store_ID;, (c) SELECT Store_ID, SUM(Sales_Amount) FROM Sales, GROUP BY Store_ID;, (d) SELECT Store_ID, SUM(Sales_Amount) FROM Sales, HAVING UNIQUE Store_ID;, Ans. (c) SELECT Store_ID, SUM(Sales_Amount) FROM Sales, GROUP BY Store_ID;, , (iii) Which SQL statement lets you to list all store name, whose total sales amount is over 5000 ?, (a) SELECT Store_ID, SUM(Sales_Amount) FROM Sales, GROUP BY Store_ID HAVING SUM(Sales_Amount) >, 5000;, (b) SELECT Store_ID, SUM(Sales_Amount) FROM Sales, GROUP BY Store_ID HAVING Sales_Amount > 5000;, (c) SELECT Store_ID, SUM(Sales_Amount) FROM Sales, WHERE SUM(Sales_Amount) > 5000 GROUP BY, Store_ID;, (d) SELECT Store_ID, SUM(Sales_Amount) FROM Sales, WHERE Sales_Amount > 5000 GROUP BY Store_ID;, Ans. (a) SELECT Store_ID, SUM(Sales_Amount) FROM Sales, GROUP BY Store_ID HAVING SUM(Sales_Amount) >, 5000;, , (b) SELECT Store_ID, SUM(Sales_Amount) FROM, Sales GROUP BY Store_ID HAVING Store_ID, IN ( 25, 45);, (c) SELECT Store_ID, SUM(Sales_Amount) FROM Sales, WHERE Store_ID IN (25,45);, (d) SELECT Store_ID, SUM(Sales_Amount) FROM Sales, WHERE Store_ID = 25 AND Store_ID =45 GROUP BY, Store_ID;, Ans. (b) SELECT Store_ID, SUM(Sales_Amount) FROM Sales, GROUP BY Store_ID HAVING Store_ID IN ( 25, 45);, , PART 2, Subjective Questions, l, , Short Answer Type Questions, 1. What are the aggregate functions in SQL?, , Ans. Aggregate function is a function where the values of, multiple-rows are grouped together as input on certain, criteria to form a single value of more significant meaning., Some aggregate functions used in SQL are, SUM ( ), AVG( ), MIN(), etc., , 2. What is the purpose of GROUP BY clause in, MySQL? How is it different from ORDER BY, clause?, [CBSE 2012], Ans. The GROUP BY clause can be used to combine all those, records that have identical value in a particular field or a, group of fields., Whereas, ORDER BY clause is used to display the records, either in ascending or descending order based on a, particular field. For ascending order ASC is used and for, descending order, DESC is used. The default order is, ascending order.
Page 36 :
@Cbsebookshub - Join Us on Telegram, , 24, , CBSE Term II Informatics Practices XII, , 3. Shanya Khanna is using a table EMPLOYEE. It, has the following columns:, Admno, Name, Agg, Stream [column Agg contains, Aggregate marks], She wants to display highest Agg obtained in each, Stream., She wrote the following statement:, SELECT Stream, MAX(Agg) FROM EMPLOYEE;, , But she did not get the desired result. Rewrite the, above query with necessary changes to help her get, the desired output., [CBSE Outside Delhi 2014], Ans. SELECT Stream, MAX(Agg), , FROM EMPLOYEE, GROUP BY Stream;, , 4. What is the differences between HAVING clause, and WHERE clause?, Ans., WHERE clause, WHERE clause is used to, filter the records from the, table based on the specified, condition., , HAVING clause, HAVING clause is used to, filter record from the groups, based on the specified, condition., , WHERE clause implements HAVING clause implements in, in row operation., column operation., WHERE clause cannot, contain aggregate function., , HAVING clause can contain, aggregate function., , WHERE clause can be used HAVING clause can only be, with SELECT, UPDATE, used with SELECT statement., DELETE statement., WHERE clause is used, HAVING clause is used with, with single row function like multiple row function like, UPPER, LOWER etc., SUM, COUNT etc., , Ans. SELECT ord_date, COUNT (DISTINCT doctor_code), , FROM Patients, GROUP BY ord_date;, , 7. Consider the following table Employee :, Table: Employee, 100 Steven, , King, , Sking, , 1987-06-17 AD_PRES 24000.00, , 101 Neena, , Kochhar Nkochhar 1987-06-18 AD_VP, , 17000.00, , 90, , 102 Lex, , De Haan Ldehaan 1987-06-19 AD_VP, , 9000.00, , 60, , 6000.00, , 60, , 103 Alexander Hunold Ahunold 1987-06-20 IT_PROG, , 90, , 104 Bruce, , Ernst, , Bernst, , 1987-06-21 IT_PROG, , 4800.00, , 60, , 105 David, , Austin, , Daustin, , 1987-06-22 IT_PROG, , 4800.00, , 60, , 106 Valli, , Pataballa Vpataballa, , 1987-06-23 IT_PROG, , 4800.00 100, , Write a query to get the total salary, maximum,, minimum, average salary of employees (Job_ID, wise), for Dept_ID 90 only., Ans. SELECT Job_ID, SUM(Salary), AVG(Salary),, , MAX(Salary), MIN(Salary), FROM Employee, WHERE Dept_ID = ‘90’, GROUP BY Job_ID;, , 8. Why is it not allowed to give String and Date type, arguments for SUM () and AVG() functions?, Ans. SUM() and AVG() functions take an argument of type, numeric only. So, sum and Avg are not defined the String, and date data., , 9. Write the query for (i) and predict the output for, (ii) and (iii):, Table : Product, P_ID, , ProductName, , Manufacture Price, , following columns :, , TP01, , TALCOM POWDER, , LAK, , 40, , Code, Name, Salary, Dept_code, , FW05, , FACE WASH, , ABC, , 45, , He wants to display maximum salary department, wise. He wrote the following command :, , BS01, , BATH SOAP, , ABC, , 55, , SH06, , SHAMPOO, , XYZ, , 120, , SELECT Deptcode, Max(Salary) FROM Employee;, , FW12, , FACE WASH, , XYZ, , 95, , 5. Gopi Krishna is using a table Employee. It has the, , But he did not get the desired result., Rewrite the above query with necessary changes to, help him get the desired output. [CBSE Delhi 2014], Ans. SELECT Deptcode, Max(Salary), , FROM Employee, GROUP BY Deptcode;, , 6. Write a query that counts the number of doctors, registering patients for each day. (If a doctor has, more than one patient on a given day, he or she, should be counted only once .), , (i) To count the product manufacture wise from the, table Product., (ii) SELECT Manufacture,MAX(Price),, MIN(Price), COUNT(*)FROM Product GROUP BY, Manufacture;, , (iii) SELECT Manufacture, MAX(Price) FROM, Product;, Ans. (i) SELECT COUNT(ProductName),Manufacture, , FROM Product, GROUP BY Manufacture;
Page 37 :
@Cbsebookshub - Join Us on Telegram, , 25, , CBSE Term II Informatics Practices XII, , (ii), LAK, , 40, , 40, , 1, , ABC, , 55, , 45, , 2, , XYZ, , 120, , 95, , 2, , (iii), , l, , XYZ, , 11. Consider the table FANS:, Table: FANS, , 120, , Long Answer Type Questions, 10. Write commands in SQL for (i) to (iii) and output, for (iv) and (v):, , [CBSE Sample Paper 2020], , Table: Store, StoreId Name, , Location City, , S101, , Planet, Fashion, , Bandra, , Mumbai, , 7, , 2015-10-16 40000, , S102, , Vogue, , Karol, Bagh, , Delhi, , 8, , 2015-07-14 120000, , S103, , Trends, , Powai, , Mumbai, , 10, , 2015-06-24 30000, , S104, , Super, Fashion, , Thane, , Mumbai, , 11, , 2015-02-06 45000, , S105, , Annabelle South, Extn., , Delhi, , 8, , 2015-04-09 60000, , Rage, , Delhi, , S106, , Defence, Colony, , NoOfEmp DateOpen SalesAmt, , 5, , 2015-03-01 20000, , (i) To display names of stores along with Sales, Amount of those stores that are located in, Mumbai., (ii) To display the details of store in alphabetical, order of name., (iii) To display the City and the number of stores, located in that City, only if number of stores is, more than 2., (iv) SELECT MIN(DateOpen) FROM Store;, (v) SELECT COUNT(StoreId), NoOfEmp FROM Store, GROUP BY NoOfEmp HAVING MAX(SalesAmt)<60000;, Ans. (i) SELECT, , Name,SalesAmt FROM Store WHERE, City=‘Mumbai’;, (ii) SELECT * FROM Store ORDER BY Name;, (iii) SELECT City, COUNT(*) FROM Store GROUP BY, Store HAVING COUNT(*)>2;, (iv), , MIN(DateOpen), 2015-02-06, , (v), , COUNT(StoreId) NoOfEmp, 1, 1, 1, 1, , 10, 11, 5, 7, , FAN_ID FAN_NAME FAN_CITY, , FAN_DOB, , F001, , SUSHANT, , MUMBAI, , 1998-10-02, , FAN_MODE, MAIL, , F001, , RIYA, , MUMBAI, , 1997-12-12, , LETTER, , F003, , ANIKA, , DELHI, , 2001-06-30, , BLOG, , F004, , RUDRA, , AJMER, , 2005-08-22, , MAIL, , F006, , MIARA, , KOLKATTA, , 1998-11-01, , BLOG, , Write MySQL queries for the following questions., (i) To display the details of fans in descending order, of their DOB., (ii) To display the details of FANS who does not, belong to AJMER., (iii) To count the total number of fans of each fan mode., (iv) To display the DOB of the youngest fan., [CBSE Sample Paper 2020], Ans. (i) SELECT * FROM FANS ORDER BY FAN_DOB DESC;, (ii) SELECT * FROM FANS WHERE, , FAN_CITY<>‘AJMER’;, (iii) SELECT FAN_MODE, COUNT(*) FROM FANS, , GROUP BY, , FAN_MODE;, (iv) SELECT MAX(FAN_DOB) FROM FANS;, , 12. Consider the table DOCTOR given below. Write, commands in SQL for (i) to (ii) and output for (iii), to (v)., Table : DOCTOR, ID DOCName Department, , DOJ, , Gender, , Salary, , 1 Amit Kumar Orthopaedics, , 1993-02-12, , M, , 35000, , 2 Anita Hans, , 30000, , 1998-10-16, , F, , 3 Sunita Maini Gynaecology, , Paediatrics, , 1991-08-23, , F, , 40000, , 4 Joe Thomas, , Surgery, , 1994-10-20, , M, , 55000, , 5 Gurpreet, Kaur, , Paediatrics, , 1999-11-24, , F, , 52000, , 6 Anandini, Burman, , Oncology, , 1994-03-16, , F, , 31000, , 7 Siddharth, Dang, , Surgery, , 1995-09-08, , M, , 47000, , 8 Rama, Mukherjee, , Oncology, , 2000-06-27, , F, , 54500, , (i) Display the names and salaries of doctors in, descending order of salaries., (ii) Display names of each department along with total, salary being given to doctors of that department., (iii) SELECT SUM(Salary) FROM DOCTOR WHERE, Department==‘Surgery’;, , (iv) SELECT Department, COUNT(*) FROM DOCTOR GROUP BY, Department;
Page 39 :
@Cbsebookshub - Join Us on Telegram, , Chapter Test, Multiple Choice Questions, , 1. We can use the aggregate functions in select list or the ........ clause of a select statement. But they cannot be used in a, ........ clause., (a) WHERE, HAVING, , (b) GROUP BY, HAVING, , (c) HAVING, WHERE (d) GROUP BY, WHERE, , 2. If emp_id contain the set {-1, -2, 2, 3, -3, 1}, what will be the output on execution of the following MySQL statement?, SELECT emp_id, FROM person, ORDER BY emp_id;, (a) {-3, -2, -1, 1, 2, 3}, (c) {1, 2, 3, -1, -2, -3}, , (b) {-1, 1, -2, 2, -3, 3}, (d) None of the mentioned, , 3. Select correct SQL query from below to find the temperature in increasing order of all cites., (a) SELECT city FROM weather ORDER BY temperature;, (b) SELECT city, temperature FROM weather;, (c) SELECT city, temperature FROM weather ORDER BY temperature;, (d) SELECT city, temperature FROM weather ORDER BY city;, , 4. The HAVING clause acts like a WHERE clause, but it identifies columns that meet a criterion, rather than rows., (a) True, (c) Depend on query, , (b) False, (d) Depend on column, , 5. The HAVING clause, (a) acts exactly like WHERE clause., (b) acts like a WHERE clause but is used for columns rather than groups., (c) acts like a WHERE clause but is used for groups rather than rows., (d) acts like a WHERE clause but is used for rows rather than columns., , Short Answer Type Questions, , 6. Write a query to display the Sum, Average, Highest and Lowest marks of the students grouped by subject and, sub-grouped by class., , 7. Amisha wants to group the result set based on some column's value. Also, she wants that the grouped result should, appear in a sorted order . In which order will she write the two clauses (for sorting and for grouping). Give example to, support your answer., , 8. The following query is producing an error. Identify the error and also write the correct query., SELECT * FROM EMP ORDER BY NAME WHERE SALARY>=5000;, , Long Answer Type Questions, , 9. Consider the following table GARMENT, write SQL commands for the statements (i) to (v)., Table : GARMENT, GCODE, , DESCRIPTION, , PRICE, , FCODE, , READYDATE, , 10023, , PENCIL SKIRT, , 1150, , F03, , 19-DEC-08, , 10001, , FORMAL SHIRT, , 1250, , F01, , 12-JAN-08, , 10012, , INFORMAL SHIRT, , 1550, , F02, , 06-JUN-08, , 10024, , BABY TOP, , 750, , F03, , 07-APR-07, , 10090, , TULIP SKIRT, , 850, , F02, , 31-MAR-07, , 10019, , EVENING GOWN, , 850, , F03, , 06-JUN-08, , 10009, , INFORMAL PANT, , 1500, , F02, , 20-OCT-08, , 10007, , FORMAL PANT, , 1350, , F01, , 09-MAR-08, , 10020, , FROCK, , 850, , F04, , 09-SEP-07, , 10089, , SLACKS, , 750, , F03, , 20-OCT-08, , [CBSE Question Bank 2021]
Page 40 :
@Cbsebookshub - Join Us on Telegram, , 28, , CBSE Term II Informatics Practices XII, , (i) To display GCODE and DESCRIPTION of each GARMENT in descending order of GCODE., (ii) To display the details of all the GARMENT, which have READYDATE in between 08-DEC-07 and 16-JUN-08 (inclusive if both, the dates)., (iii) To display the average PRICE of all the GARMENT, which are made up of fabric with FCODE as F03., (iv) To display fabric wise highest and lowest price of GARMENT from GARMENT table. (Display FCODE of each GARMENT, along with highest and lowest price)., (v) To display GCODE whose PRICE is more than 1000., , 10. Consider the following table SALE, write SQL commands for the statements (i) to (iv)., , [NCERT], , Table: SALE, InvoiceNo, , CarId, , CustId, , SaleDate, , PaymentMode, , EmpID, , SalePrice, , Commission, , I00001, , D001, , C0001, , 2019-01-24, , Credit Card, , E004, , 613247.00, , 73589.64, , I00002, , S001, , C0002, , 2018-12-12, , Online, , E001, , 590321.00, , 70838.52, , I00003, , S002, , C0004, , 2019-01-25, , Cheque, , E010, , 604000.00, , 72480.00, , I00004, , D002, , C0001, , 2018-10-15, , Bank Finance, , E007, , 659982.00, , 79197.84, , I00005, , E001, , C0003, , 2018-12-20, , Credit Card, , E002, , 369310.00, , 44317.20, , I00006, , S002, , C0002, , 2019-01-30, , Bank Finance, , E007, , 620214.00, , 74425.68, , (i) Display the number of cars purchased by each customer from the SALE table., (ii) Display the customer Id and number of cars purchased if the customer purchased more than 1 car from SALE table., (iii) Display the number of people in each category of payment mode from the table SALE., (iv) Display the PaymentMode and number of payments made using that mode more than once., , Answers, Multiple Choice Questions, 1. (b), , 2. (a), , 3. (c), , 4. (b), , 5. (c), , For Detailed Solutions, Scan the code
Page 41 :
@Cbsebookshub - Join Us on Telegram, , 29, , CBSE Term II Informatics Practices XII, , CHAPTER 03, , Computer, Networks, In this Chapter..., l, , Benefits of Network, , l, , Network Devices, , l, , Types of Network, , l, , Network Topology, , A computer network is a collection of computers and other, hardware interconnected by communication channels that, allows sharing of resources and information. A computer, networking is the practice for enchancing information, between two or more computer devices together for the, purpose of data sharing., These purpose of having computer network is to send and, receive data stored in other devices over the network. These, devices are often referred as nodes., , Benefits of Network, Computer network is very useful in modern environment., Some of the benefits of network are discussed below, (i) File Sharing Networking of computer helps the user to, share data files., (ii) Software and Hardware Sharing We can install the, applications on the main server, therefore the user can, access the applications centrally., So, we do not need to install the software on every, machine. Similarly, hardware can also be shared., (iii) Application Sharing Applications can be shared over, the network and this allows implementation of, client/server applications., (iv) User Communication This allows users to, communicate using E-mail, newsgroups, video, conferencing within the network., (v) Access to Remote Database This allows users to access, remote database, e.g. airline reservation database may, be accessed for ticket booking., , Types of Network, Based on the size and the coverage area, networks are, categorised into the following types, , Local Area Network (LAN), In a LAN, a group of computers and other devices are, connected over a relatively short distance. Generally, it is a, privately owned networks within a single building or campus,, upto a few kilometres in size., Users can share expensive devices, such as laser printers, as, well as data on LAN and can also use the LAN to, communicate with each other, by sending mails or engaging, in chat sessions., Mostly, cables are used to connect the computers in LANs., However, there is also a limit on the number of computers, that can be attached to a single LAN. Now-a-days, we also, have WLAN(Wireless LAN) which is based on wireless, network., , Metropolitan Area Network (MAN), This is basically a bigger version of LAN and normally uses, similar technology. It might cover few buildings in a city and, might either be private or public., This is a network which spans a physical area (in the range of, 5 km to 50 km) that is larger than a LAN but smaller than a, WAN. MANs are usually characterised by very high-speed, connections using optical fibers or other digital media and, provides uplink services to Wide Area Networks (WANs) and, the Internet. e.g. in a city, a MAN, which can support both
Page 42 :
@Cbsebookshub - Join Us on Telegram, , 30, data and voice might even be related to local cable television, network. It is also frequently used to provide a shared, connection to other networks using a link to a WAN., , Wide Area Network (WAN), WAN spans a large geographical area, often a country or a, continent and uses various commercial and private, communication lines to connect computers. Typically, a, WAN combines multiple LANs that are geographically, separated., Like the LAN, most WANs are not owned by any one, organisation, but rather exist under collective or distributed, ownership and management. The world’s most popular WAN, is the Internet., , CBSE Term II Informatics Practices XII, , connection to several computers with the central node or, server. It is a multi-port device, which provides access to, computers., All incoming data packets received by the hub are sent to all, hub ports and from them the data is sent to all the computers, connected in a hub network., There are two types of hub, which are as follows, (i) Active Hub It acts as repeaters. It amplifies the signal, as it moves from one device to another., (ii) Passive Hub It simply passes the signal from one, connected device to another., , Switch, , PAN refers to a small network of communication. It is a, computer network organised around an individual person., These networks typically involve a mobile computer, a cell, phone and/or a handheld computing devices such as a PDA., Person can use these networks to transfer files including, E-mail and calendar appointments, digital photos and music., These are used in a limited range, which is in the reachability, of individual person. It generally covers a range of less than, 10 metres and can be constructed with cables or wirelessly., Few examples of PAN are Bluetooth, Wireless USB, Z-Wave, and Zigbee., , A switch is a hardware device, which is used to connect, devices or segments of the network into smaller subsets of, LAN segments., The main purpose of segmenting is to prevent the traffic, overloading in a network. Switch forwards a data packet to a, specific route by establishing a temporary connection, between the source and the destination. After the, transmission or once the conversation is done, the connection, is terminated., There is a vast difference between switch and hub. A hub, forward each incoming packet (data) to all the hub ports,, while a switch forwards each incoming packet to the, specified recipient., , Virtual Private Network (VPN), , Gateway, , VPN is an encrypted connection over the Internet from a, device to a network. It can be used to access region restricted websites, shield your browsing activity from prying, eyes on public Wi-Fi and more., It prevents unauthorised people from eavesdropping on the, traffic and allows the user to conduct work remotely. VPN, technology is widely used in corporate environments., , A gateway is a device, which is used to connect dissimilar, networks. The gateway establishes an intelligent connection, between a local network and external networks, which are, completely different in structure., The gateway is a node in a network, which serves as a proxy, server and a firewall system and prevents the unauthorised, access. It holds the information from a website temporarily,, so that the repeated access to same website or web page, could be directed to the proxy server instead of actual web, server. Thus, it helps in reducing the traffic load., , Personal Area Network (PAN), , Network Devices, Hardware device that are used to connect computers,, printers, fax machines and other electronic devices to a, network are called network device. There are many types of, network devices used in networking and some of them are, described below:, , Repeater, It is a hardware device, which is used to amplify the signals, when they are transported over a long distance. The basic, function of a repeater is to amplify the incoming signal and, retransmit it, to the other device. Repeaters are mainly used, for extending the range. If you want to connect two, computers, which are more than 100 metres apart you need, repeater., , Hub, A hub is a device, used with computer systems to connect, several computers together. It acts as a centralised, , Bridge, It serves a similar function as switches. A bridge filters data, traffic at a network boundary. Bridges reduce the amount of, traffic on a LAN by dividing it into two segments. Traditional, bridges support one network boundary, whereas switches, usually offer four or more hardware ports. Switches are, sometimes called multi-port bridges., , Router, A router is used to connect different networks together. i.e., for two or more LANs to be interconnected, you need a, router., It is a hardware device, which is designed to take incoming, packets, analyse the packets, moving and converting the, packets to another network interface, dropping the packets,, directing packets to the appropriate locations, etc.
Page 43 :
@Cbsebookshub - Join Us on Telegram, , 31, , CBSE Term II Informatics Practices XII, , MODEM (MOdulator-DEModulator), , Star Topology, , It is a device that converts digital signal to analog signal, (modulator) at the sender’s site and converts back analog, signal to digital signal (demodulator) at the receiver’s end,, in order to make communication possible via telephone, lines. It enables a computer to transmit data over telephone, or cable lines., There are two types of MODEM, which are as follows, (i) Internal Modem Fixed within a computer., (ii) External Modem Connected externally to a, computer., When a network contains largest number of, system/computer it needed modem., , In star topology, each communicating device is connected to a, central node which is a networking device like a hub or a, switch., The central node can be either a broadcasting device means, data will be transmitted to all the nodes in the network or a, unicast device means the node can identify the destination and, forward data to that node only., Node 2, , Network Topology, , Hub, , The arrangement of computers and other peripherals in a, network is called its topology., In a computer network, there are some types of physical, topology, they are, , Node 5, , Bus Topology (Linear Topology), , Server, , Node 4, , Star topology, , A bus topology is an arrangement in which the computers, and the peripheral devices are connected to a common, single data line., Laser, Printer, , Node 3, , Node 1, , Scanner, , There are various advantages of star topology are as follows:, Installation of star topology is very easy as all the nodes are, directly connected to the central node or server., Easy to detect faults and remove it., Failure of single system will not bring down the entire, network., Allows several types of cables in same network., There are various disadvantages of star topology are as follows:, Requires more cable length than bus topology., If hub or server fails, the entire network will be disabled., Difficult to expand, as the new node has to connect all the, way to central node., l, , l, , l, , Router, , l, , l, , Bus topology, , l, , l, , All the computers or devices are directly connected to the, data line. The data is transmitted in small blocks known as, packets. Each packet has a header containing the, destination address., When data is transmitted on the cable, the destination, node identifies the address on the packet and thereby, processes the data., There are various advantages of bus topology are as follows:, All the nodes are connected directly, so very short cable, length is required., The architecture is very simple, reliable and linear., Bus topology can be extended easily on either sides., There are various disadvantages of bus topology are as, follows:, In case of any fault occurred in data transmission, fault, isolation is very difficult. We have to check the entire, network to find the fault., Becomes slow with increase in number of nodes., Only a single message can travel at a particular time., l, , l, , Tree Topology, A tree topology is an extension and variation of bus topology., Its basic structure is like an inverted tree, where the root acts, as a server. In tree topology, the nodes are interlinked in the, form of tree., If one node fails, then the node following that node gets, detached from the main tree topology., Server, , l, , l, , l, , l, , Tree topology
Page 44 :
@Cbsebookshub - Join Us on Telegram, , 32, There are various advantages of tree topology are as, follows :, The tree topology simulates hierarchical flow of, data. So, it is suitable for applications, where, hierarchical flow of data and control is required., We can easily extend the network., Faulty nodes can easily be isolated from the rest, of the network., There are various disadvantages of tree topology are, as follows :, Long cables are required., There are dependencies on the root node., Installation and reconfiguration are very, difficult., , CBSE Term II Informatics Practices XII, , Server, , l, , Node 1, , Node 4, , l, , l, , l, , Node 3, , l, , Mesh Topology, It is also known as completely interconnected, topology. In mesh topology, every node has a, dedicated point-to-point link to every other node., This topology is also more secure as compared to, other topologies because each cable between two, nodes carries different data., , Node 2, , Mesh topology, , l, , There are various advantages of mesh topology are as follows:, Excellent for long distance networking., Communication possible through the alternate e-Route, if one path, is busy., A network can handle large amount of traffic since multiple nodes, can transmit data simultaneously., There are various disadvantage of mesh topology are as follows:, Long wire/cable length is required., Wiring is complex and cabling cost is high in creating such, networks., l, , l, , l, , l, , l
Page 45 :
@Cbsebookshub - Join Us on Telegram, , 33, , CBSE Term II Informatics Practices XII, , Chapter, Practice, PART 1, Objective Questions, l, , Multiple Choice Questions, 1. Which of the following is a collection of, independent computers and other hardware, interconnected by communication channels?, , (a) Computer, (b) Networking, (c) Sharing, (d) None of the above, Ans. (b) A computer networking is the practice for exchanging, information between two or more computer devices, together for the purpose of data sharing., , 2. Which of the following is an advantage of, networking?, (a) Application sharing, (b) File sharing, (c) User communication, (d) All of these, Ans. (d) Computers connected in a network are able to share, applications, files, resources etc. They also can communicate, with each other., , 3. Network formed between computers which are, spread across the continents is called, (a) LAN, (b) WAN, (c) MAN, (d) WLAN, Ans. (b) Network formed between computers which are spread, across the continents is called WAN. A WAN combines, multiple LANS that are geographically separated., , Ans. (c) It is a device that converts digital signal to analog, signal (modulator) at the sender’s site and converts back, analog signal to digital signal (demodulator) at the receiver’s, end., , 6. A modem is connected in between a telephone line, and a, (a) computer, (b) serial port, (c) network, (d) communication adapter, Ans. (a) Modems has to be connected internally or externally, with a computer., , 7. Geometric arrangement of devices on the network, is called, (a) topology, (b) protocols, (c) media, (d) LAN, Ans. (a) Geometric arrangement of devices on the network is, called topology. It is the arrangement of how computers will, be connected with each other., , 8. In which of the topology, network components are, connected to the same cable?, (a) Star, (b) Ring, (c) Bus, (d) Mesh, Ans. (c) In bus topology, network components are connected to, the same cable. The figure explains the arrangement:, Laser, Printer, , Server, , Scanner, , Router, , 4. Which of the following refers to a small, single site, network?, (a) DSL, (b) RAM, (c) WAN, (d) PAN, Ans. (d) PAN refers to a small network of communication. It is a, computer network organised around an individual person., These networks typically involve a mobile computer, a cell, phone and/or a handheld computing devices such as a PDA., , 5. Modulation and demodulation is performed by, (a) microwave, (c) modem, , (b) satellite, (d) gateway, , Bus topology, , 9. Which is the name of the network topology in, which there are bi-directional links between each, possible node?, (a) Ring, (b) Mesh, (c) Tree, (d) None of these, Ans. (b) In mesh topology, every node has a dedicated, point-to-point link to every other node, that is why, bi-directional links are possible.
Page 46 :
@Cbsebookshub - Join Us on Telegram, , 34, , CBSE Term II Informatics Practices XII, , 10. Suggest the most suitable type of network topology, he should use in order to maximise speed and make, each computer independent of network, breakdowns., [CBSE Question Bank 2021], (a) Bus topology, (b) Star topology, (c) Ring topology, (d) Mesh topology, Ans. (b) Start Topology allows several types of cables in same, network, which increases speed. Failure of single system, will not bring down the entire network and all system are, connected to the central hub., , 11. In order to allow data transfer from server to only, the intended computers which network device is, required in the lab to connect the computers?, [CBSE Question Bank 2021], (a) Switch, (b) Hub, (c) Router, (d) Gateway, Ans. (a) Switch forwards a data packet to a specific route by, establishing a temporary connection between the source and, the destination., , 12. ……………… network device is known as an, intelligent hub., , [CBSE Question Bank 2021], (a) Switch, (b) Hub, (c) Router, (d) Gateway, Ans. (a) A hub forward each incoming packet (data) to all the hub, ports, while a switch forwards each incoming packet to the, specified recipient., , 13. Which of the following topology contains a, backbone cable running through the whole length, of the network?, (a) Star, (b) Bus, (c) Mesh, (d) Tree, Ans. (b) A bus topology is an arrangement in which the, computers and the peripheral devices are connected to a, common single data line., , 14. Computer connected to a star topology fails, the, entire network will, (a) also fail, (b) work unaffectedly, (c) only server will work, (d) None of the above, Ans. (b) In star topology, each communicating device is, connected to a central node which is a networking device, like a hub or a switch. So, when the hub fails the whole, network goes down., But when any computer in the star topology fails, the other, computers in the network continue to work unaffectedly., , 15. Network device that sends the data over optimising, paths through connected loop is, (a) gateway, (b) hub, (c) router, (d) bridge, Ans. (c) Network device that sends the data over optimising paths, through connected loop is router., , 16. In specific, if systems use separate protocols, which, one of the following devices is used to link two, systems?, (a) Repeater, (b) Gateway, (c) Bridge, (d) Hub, Ans. (b) If the system used separate protocols, gateway device is, used to link two systems., , 17. If all devices are connected to a central hub, then, topology is called, (a) bus topology, (b) ring topology, (c) star topology, (d) tree topology, Ans. (c) If all devices are connected to a central hub, then, topology is called star topology., l, , Case Based MCQs, 18. Beauty lines fashion incorporation is a fashion, company with design unit and market unit at, Bangalore 135m away from each other. The, company recently connected their LANs using, Ethernet cable to share the stock related, information. But after joining their LAN’s they are, not able to show the information due to loss of, signal in between., (i) Which device out of the following should you, suggest to be installed for a smooth, communication?, (a) Modem, (c) UPS, , (b) Repeater, (d) None of these, , (ii) Which network is suitable to connect computers, across different cities?, (a) WAN, (c) PAN, , (b) MAN, (d) LAN, , (iii) The company wants to increase their bandwidth, and speed for communication at any cost. Which of, the following cable(s) is/are suitable for that?, (a) Coaxial Cable, (c) Both (a) and (b), , (b) Optical Fibre, (d) None of these, , (iv) What will be the best possible connectivity out of, the following? You will suggest to connect the new, set up of offices in Bangalore with its London based, office., (a) Satellite Link, (c) Ethernet, , (b) Infrared, (d) None of these, , (v) Which of the following device will be suggested by, you to connect each computer in each of the, buildings?, (a) Switch, (b) Modem, (c) Gateway, (d) None of these, Ans. (i) (b) They should use repeater. As repeater is a device used, to amplify the signals., (ii) (b) MAN It is a computer network that connects, computers within a metropolitan area, which could be a, single large city, multiple cities and towns.
Page 47 :
@Cbsebookshub - Join Us on Telegram, , 35, , CBSE Term II Informatics Practices XII, , (iii) (b) Optical Fibre They are designed for long-distance,, high-performance data networking and, telecommunications. Compared to wired cables, fiber, optic cables provide higher bandwidth and transmit, data over longer distances., (iv) (a) Satellite Link Through satellites communication, across countries is easily possible., (v) (a) Switch is a networking hardware that connects, devices on a computer network to receive and forward, data to the destination device. Therefore, switch will, help in communication between each of the buildings., , PART 2, Subjective Questions, l, , 1. Write down any two points of differences between, LAN, MAN and WAN., [NCERT], Ans. Two major points of differences among LAN, MAN and, WAN are as follows:, LAN, , MAN, , WAN, , Geographical Generally within Within a city Across the, Area, a building, continents, Distance, , Upto 5 km, , Upto 160 km Unlimited, , 2. Which device is used to connect dissimilar, networks?, Ans. A gateway is a device, which is used to connect dissimilar, networks. The gateway establishes an intelligent connection, between a local network and external network, which are, completely different in structure. Gateway also serve as, proxy server and a firewall system that prevents the, unauthorised access., , 3. Identify the following devices:, (i) An intelligent device that connects several nodes, to form a network and redirects the received, information only to intended node(s)., (ii) A device that regenerates (amplifies) the, received signal and re-transmits it to its, destinations., (iii) A device that is used to connect different types of, networks. It performs the necessary translation, so that the connected networks can communicate, properly., (iv) A device that converts data from digital bit, stream into an analog signal and vice-versa., [Delhi 2014], Ans. (i) Switch, (iii) Router, , (ii) Repeater, (iv) Modem, , Also, illustrate how four computers can be, connected with each other using star topology of, network?, Ans. Advantage of Bus Topology In bus topology, computers can, be connected with each other using server (host) along a, single length of cable., Four computers can be connected with each other using star, topology in the following way:, , 5. In networking, what isWAN? How is it different, from LAN?, , Short Answer Type Questions, , Basics, , 4. Write one advantage of bus topology of network., , Ans. The network which connects the different countries is, known as WAN., Differences between LAN and WAN are as follows:, LAN, , WAN, , LAN stands for Local Area WAN stands for Wide Area, Network., Network., The speed of LAN is high. The speed of WAN is slower, than LAN., There is less congestion in There is more congestion in, LAN., WAN., There is more fault, tolerance in LAN., , There is less fault tolerance in, WAN., , LAN’s design and, maintenance is easy., , WAN’s design and maintenance, is difficult than LAN., , LAN covers small area,, i.e. within the building., , WAN covers large geographical, area., , Transmission medium, WAN uses satellite link as a, used in LAN is co-axial or transmission or communication, UTP cable., medium., , 6. Define hub and write its functions and types., Ans. A hub connects several computers together and acts as a, central node or server., Functions of a Hub, ¢, ¢, , Interconnects number of computers or users., All the incoming data packets received by the hub are, send to all hub ports and from their, the data is sent to, all the computers, connected in a hub network., , Hub are of two types, (i) Active Hub It acts as repeater. It amplifies the signal as, these move from one device to another., (ii) Passive Hub It simply passes the signal from one, connected device to another., , 7. Mr. Kavye Shastri, General Manager of Unit, Nations corporate recently discovered that the, communication between his company’s accounts
Page 48 :
@Cbsebookshub - Join Us on Telegram, , 36, , CBSE Term II Informatics Practices XII, , office and HR office is extremely slow and signals, drop quite frequently. These offices are 120 m away, from each other and connected by an ethernet, cable., (i) Suggest him a device which can be installed in, between the offices for smooth communication., (ii) What type of network is formed by having this, kind of connectivity out of LAN, MAN and, WAN?, [Delhi 2012], Ans. (i) The device that can be installed between the office for, smooth communication is repeater., (ii) The type of network is Local Area Network (LAN)., , 8. Define repeaters with its two types., Ans. Repeaters are used to amplify the signals, when they are, transported over a long distance., Repeaters are of two types, (i) Amplifier It amplifies or boosts the incoming signals. So,, it amplifies both the signal and any concurrent noise., (ii) Signal Repeater It only amplifies the signal and filters, out the noise signals. So, we get only the clear signal at, the receiver end., , (iii) We would prefer switch over other network devices, when we want to segment networks into different, sub-networks to prevent traffic overloading., , 12. Define the following terms:, (i) Baud, (ii) Hubs, (iii) Repeaters, Ans. (i) Baud Baud is a unit of measurement for the, information-carrying capacity of a communication, channel., (ii) Hubs In computer networking, a hub is a small, simple,, low-cost device that joins multiple computers together., (iii) Repeaters It is a device that amplifies and restores the, signal before it gets degraded and transmits the, original signal back to the destination. A repeater is a, re-generator and not an amplifier., , 13. Write a short note on mesh topology., Ans. In a mesh topology, every device is connected to another, device via a particular channel., Every device is connected with another via dedicated, channels. These channels are known as links., Server, , 9. When the computer network uses telephone lines, as communication channel then MODEM is used, as a data communication device. Now, explain the, working of MODEM., , Node 1, , Node 4, , Ans. Modem performs the task of modulation at sender’s site and, Demodulation at the receiver’s site. Basically, our computer, generates data in the form of digital signals, which need to, be forwarded to the receiver through telephone lines. Since,, telephone lines can carry only analog signals. So, digital, signals need to be converted to analog signals at sender’s, site, this is called modulation., Node 3, , 10. Write one advantage of star topology over bus, topology and one advantage of bus topology over, star topology., , Advantages of mesh Topology, ¢, , Ans. Advantage of star topology over bus topology The star, topology is the most reliable as there is a direct connection, of every nodes in the network with the central node, so any, problem in any node will affect the particular node only., While in bus topology, if problem exists in common, medium, it will affect the entire node., Advantage of bus topology over star topology Extension of, network is very easy in bus topology. We can connect new, node along its length. While in star topology, it is difficult to, expand, as the new node has to connect all the way to, central node and there is not available port in central node., , 11. When would you prefer, (i) hubs over repeaters,, (ii) bridges over hubs and, (iii) switch over other network devices?, Ans. (i) We would prefer hubs over repeaters when the distance, are short., (ii) We would prefer bridges over hubs when we need to, connect multiple networks., , Node 2, , ¢, , ¢, , It is robust., The fault is diagnosed easily. Data is reliable because, data is transferred among the devices through dedicated, channels or links., Provides security and privacy., , Disadvantages of mesh Topology, ¢, ¢, , ¢, , l, , Installation and configuration are difficult., The cost of cables is high as bulk wiring is required,, hence suitable for less number of devices., The cost of maintenance is high., , Long Answer Type Questions, 14. Eduminds University of India is starting its first, campus in a small town Parampur of central India, with its centre admission office in Delhi. The, university has three major buildings comprising of, Admin Building, Academic Building and Research, Building in the 5 km area campus. As a network
Page 49 :
@Cbsebookshub - Join Us on Telegram, , 37, , CBSE Term II Informatics Practices XII, , expert, you need to suggest the network plan as per, (i) to (iii) to the authorities keeping in mind the, distances and other given parameters., Eduminds University, Parampur Campous, , Delhi, Admission, Office, , Academic, Building, , (ii) The most suitable place (i.e. block) to house the server of, this university is Academic Block, because there are, maximum number of computers in this block and, according to 80-20 rule 80% of traffic in a network should, be local., (iii) (c)The efficient device to be installed in each of the, blocks to connect all the computers is switch., , 15. Bias Methodologies is planning to expand their, Research, Building, , Admin, Building, , Expected wire distances between various locations:, Research Building to Admin Building, , 90 m, , Research Building to Academic Building, , 80 m, , Academic Building to Admin Building, , 15 m, , Delhi Admission office to Parampur Campus, , network in India starting with three cities in India, to build infrastructure for research and, development of their chemical products. The, company has planned to setup their main office in, Pondicherry at three different locations and have, named their offices as Back Office, Research Lab, and Development Unit., The company has one more research office namely, Corporate Unit in Mumbai. A rough layout of the, same is as follows:, Corporate, Unit, (Mumbai), , 1450 km, , Pondicherry, Research, Lab, , Expected number of computers to be installed at, various locations in the university are as follows:, Research Building, , 20, , Academic Building, , 150, , Admin Building, , 35, , Delhi Admission Office, , 5, , (i) Suggest the authorities, the cable layout amongst, various buildings inside the university campus, for connecting the building., (ii) Suggest the most suitable place (i.e. building) to, house the server of this organisation, with a, suitable reason., (iii) Suggest an efficient device from the following to, be installed in each of the buildings to connect, all computers., (a) Gateway, (b) Modem, (c) Switch, Ans. (i) The suggested cable layout is as follows :, Academic, Building, , 80, , 15, Admin, Building, , Research, Building, , Back, Office, , Development, Unit, , Approximate distance between these offices is as, follows:, From, , To, , Distance, , Research Lab, , Back Office, , 110 m, , Research Lab, , Development Unit, , 16 m, , Research Lab, , Corporate Unit, , 1800 m, , Back Office, , Development Unit, , 13 m, , In continuation of the above, the company experts, have planned to install the following number of, computers in each of these offices., To, , Distance, , Research Lab, , 158, , Development Unit, , 90, , Back Office, , 79, , Corporate Unit, , 51, , (i) Suggest the kind of network required (out of, LAN, MAN, WAN) for connection each of the, following office unit., (a) Research Lab and Back Office, (b) Research Lab and Development Unit
Page 50 :
@Cbsebookshub - Join Us on Telegram, , 38, , CBSE Term II Informatics Practices XII, , (ii) Which of the following devices will you suggest, for connecting all the computers with each of, their office units?, (a) Switch/Hub, (b) Modem, (c) Telephone, (iii) Suggest a cable/wiring layout for connecting the, company’s local office units located in, Pondicherry. Also, suggest an effective, method/technology for connecting the company’s, office located in Mumbai., [Delhi 2008], Ans. (i) (a) The type of network between the Research Lab and, the Back Office is LAN (Local Area Network)., (b) The type of network between Research Lab and, Development Unit is MAN (Metropolitan Area, Network)., (ii) (a) The suitable device for connecting all the, computers within each of their office units is, switch/hub., (iii) The cable/wiring layout for connection is as follows:, Pondicherry, Research, Lab, Corporate, Unit, [Mumbai], Development, Unit, , Back, Office, , 16. China Middleton Fashion is planning to expand, their network in India, starting with two cities to, provide infrastructure for distribution of their, products., The company has planned to setup their main, office in Chennai at three different locations and, have named their offices as Production Unit,, Finance Unit and Media Unit. The company has its, Corporate Unit in Delhi., A rough layout of the same is as follows:, , Approximate distance between these units is as, follows:, From, , To, , Distance, , Production Unit, , Finance Unit, , 70 m, , Production Unit, , Media Unit, , 15 m, , Production Unit, , Corporate Unit, , 2112 m, , Finance Unit, , Media Unit, , 15 m, , In continuation of the above, the company experts, have planned to install the following number of, computers in each of these units., To, , Distance, , Production Unit, , 150, , Finance Unit, , 35, , Media Unit, , 10, , Corporate Unit, , 30, , (i) Suggest the kind of network required (out of, LAN, MAN, WAN) for each of the following, units., (a) Production Unit and Media Unit, (b) Production Unit and Finance Unit, (ii) Which of the following devices will you suggest, for connecting all computers with each of their, office units?, (a) Switch/Hub, (b) Modem, (c) Telephone, (iii) Suggest a cable/wiring layout for connecting the, company’s local office units located in Chennai., Also, suggest an effective method/technology for, connecting the company’s office unit located in, Delhi., [All India 2008], Ans. (i) (a) The type of network between the Production Unit, and Media Unit is MAN (Metropolitan Area, Network)., (b) The type of network between Production Unit and, Finance Unit is LAN (Local Area Network)., (ii) (a) The suitable device for connecting all the computers, within each of their office units is switch/hub., (iii) The cable/wiring layout for connection is as follows:
Page 51 :
@Cbsebookshub - Join Us on Telegram, , 39, , CBSE Term II Informatics Practices XII, , 17. Bhartiya Connectivity Association is planning to, spread their offices in four major cities of India to, provide regional IT infrastructure support in the, field of education and culture., The company has planned to setup their head office, in New Delhi in three locations and have named, their New Delhi offices as Front Office, Back, Office and Work Office. The company has three, more regional offices as three major cities of India., A rough layout of the same is as follows:, , Delhi. Also, suggest an effective method for, connecting the company’s regional offices East, Office, West Office and South Office with offices, located in New Delhi., Ans. (i) (a) The type of network between the Back Office and the, Work Office is LAN (Local Area Network)., (b) The type of network between the Back Office and the, South Office is WAN (Wide Area Network)., (ii) (a) The suitable device for connecting all the computers, in each of their offices is switch/hub., (iii) The suggested layout for connection is as follows:, , Approximate distances between these offices as per, network survey team is as follows:, Place from, , Place to, , Distance, , Back Office, , Front Office, , 10 m, , Back Office, , Work Office, , 70 m, , Back Office, , East Office, , 1291 m, , Back Office, , West Office, , 790 m, , Back Office, , South Office, , 1952 m, , In continuation of the above, the company experts, have planned to install the following number of, computers in each of their offices., Back Office, , 100, , Front Office, , 20, , Work Office, , 50, , East Office, , 50, , West Office, , 50, , South Office, , 50, , (i) Suggest the network type (out of LAN, MAN,, WAN) for connecting each of the following set of, the their offices., (a) Back Office and Work Office, (b) Back Office and South Office, (ii) Which device will you suggest to be procured by, the company for connecting all the computers, with each of their offices out of the following, devices?, (a) Switch/Hub, (b) Modem, (c) Telephone South Office, East Office and, West Office located with offices located in, New Delhi, (iii) Suggest the cable/wiring layout for connecting, the company’s local offices located in New, , 18. Hindustan Connecting World Association is, planning to start their offices in four major cities in, India to provide regional IT infrastructure support, in the field of education and culture. The company, has planned to setup their head office in New, Delhi in three different locations and have named, their New Delhi offices as Sales Office, Head, Office and Tech Office. The company’s regional, offices are located at Coimbatore, Kolkata and, Ahmedabad., A rough layout of the same is as follows:, , Approximate distances between these offices as per, network survey team is as follows:, Place from, , Place to, , Distance, , Head Office, , Sales Office, , 10 m, , Head Office, , Tech Office, , 70 m, , Head Office, , Kolkata Office, , 1291 m, , Head Office, , Ahmedabad Office, , 790 m, , Head Office, , Coimbatore Office, , 1952 m
Page 52 :
@Cbsebookshub - Join Us on Telegram, , 40, , CBSE Term II Informatics Practices XII, , In continuation of the above, the company experts, have planned to install the following number of, computers in each of their offices., Head Office, , 100, , Sales Office, , 20, , Tech Office, , 50, , Kolkata Office, , 50, , Ahmedabad, Office, , 50, , Coimbatore Office 50, , (i) Suggest the network type (out of LAN, MAN,, WAN) for connecting each of the following set of, their offices., (a) Head Office and Tech Office, (b) Head Office and Coimbatore Office, (ii) Which device will you suggest to be procured by, the company for connecting all computers within, each of their offices out of the following devices?, (a) Modem, (b) Telephone, (c) Switch/Hub, (iii) Suggest the cable/wiring layout for connecting the, company’s local offices located in New Delhi., , Also, suggest an effective method/technology for, connecting the company’s regional offices at, Kolkata, Coimbatore and Ahmedabad., Ans. (i) (a) The type of network between the Head Office and, Tech Office is LAN (Local Area Network)., (b) The type of network between the Head Office and, Coimbatore Office is WAN (Wide Area Network)., (ii) (c) The suitable device for connecting all the computers, in each of their offices is switch/hub., (iii) The suggested layout for connection is as follows:
Page 53 :
@Cbsebookshub - Join Us on Telegram, , Chapter Test, Multiple Choice Questions, , 1. Which of the following is not a feature of networking?, , [CBSE 2011], , (a) Resource sharing, (b) Uninterrupted Power Supply (UPS), (c) Reduced cost, (d) Reliability, , 2. What is the use of bridge in the network?, (a) To connect LANs, (c) To control network speed, , (b) To amplify signals, (d) All of these, , 3. Data is converted in a form so as to travel over telephone lines using this device., (a) Modem, (c) Switch, , (b) Hub, (d) Router, , 4. If a Lawyer sharing the case files via bluetooth from his phone to the client’s phone, considered as which of the network, type?, (a) LAN, (c) MAN, , (b) PAN, (d) CAN, , Short Answer Type Questions, , 5. What is the purpose of switch in a network?, 6. Give two examples of PAN and LAN type of networks., 7. Illustrate the layout for connecting five computers in a bus and a star topology of networks., , [Delhi 2016], [CBSE 2015], , Long Answer Type Questions, , 8. Trine Tech Corporation (TTC) is a professional consultancy company. The company is planning to set up their new offices, in India with its hub at Hyderabad. As a network adviser, you have to understand their requirement and suggest them, the best available solutions. Their queries are mentioned as (i) to (v) below., Block to block distance (in metre), Block (From), , Block (To), , Human Resource, , Conference, , Distance, 110, , Human Resource, , Finance, , 40, , Conference, , Finance, , 80, , Expected number of computers to be in each block, Block, Human Resource, , Computers, 25, , Finance, , 120, , Conference, , 90, , (i) Which will be the most appropriate block, where TTC should plan to install their server?, (ii) Draw a block to block cable layout to connect all the buildings in the most appropriate manner for efficient, communication., (iii) Which of the following device will be suggested by you to connect each computer in each of the buildings?, (a) Switch, (b) Modem, (c) Gateway, (iv) The company is planning to connect its admission office in Hyderabad which is more than 1000 km from company. Which, type of network will be formed?
Page 54 :
@Cbsebookshub - Join Us on Telegram, , 42, , CBSE Term II Informatics Practices XII, , 9. Granuda consultants are setting up a secured network for their office campus at Faridabad for their day-to-day office and web, based activities. They are planning to have connectivity between three buildings and the head office situated in Kolkata., Answer the questions (i) to (iv) after going through the building positions in the campus and other details, which are given, below, Distance between various buildings, Building RAVI to Building JAMUNA, , 120 m, , Building RAVI to Building GANGA, , 50 m, , Building GANGA to Building JAMUNA, Faridabad Campus to Head Office, , 65 m, 1460 km, , Number of Computers, Building RAVI, , 25, , Building JAMUNA, , 150, , Building GANGA, , 51, , Head Office, , 10, , (i) Suggest the most suitable place (i.e. block) to house the server of this organisation. Also, give a reason to justify your, suggested location., (ii) Suggest a cable layout of connections between the building inside the campus., (iii) Suggest the placement of the following devices with justification:, (a) Switch, (b) Repeater, (iv) Consultancy is planning to connect its office in Faridabad which is more than 10 km from head office. Which type of, network will be formed?, , Answers, Multiple Choice Questions, 1. (b), , 2. (a), , 3. (a), , 4. (b), , For Detailed Solutions, Scan the code
Page 55 :
@Cbsebookshub - Join Us on Telegram, , 43, , CBSE Term II Informatics Practices XII, , CHAPTER 04, , Introduction to, Internet and Web, In this Chapter..., l History of Internet, , l Web Browser, , l Working of Internet, , l Electronic Mail, , l World Wide Web (WWW), , l Chat, , l Web Server, , l Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP), , l Website and Web Page, , The term Internet is derived from the words ‘interconnection’, and ‘networks’. A network is a collection of two or more, computers, which are connected together to share information, and resources., The Internet is a worldwide system of computer networks, i.e., network of networks, it is composed of a large number of, smaller interconnected networks. Through Internet,, computers become able to exchange information with each, other and people from all over the world can communicate, with each other easily., , History of Internet, In 1969, the University of California at Los Angeles and the, University of Utah were connected with the beginning of the, ARPANET (Advanced Research Projects Agency NETwork), using 56 kbit/s circuits, which is sponsored by US (United, States) Department of Defense (DoD). The goal of this project, was to connect computers at different Universities and US, defense., In mid 80’s another federal agency, the National Science, Foundation (NSF) created a new high capacity network called, NSFnet (National Science Foundation network), which was, more capable than ARPANET., The only drawback of NSFnet was that it allowed only, academic research on its network and not any kind of private, business on it., Then, several private organisations and people started working, to build their own networks, named private networks, which, , were later (in 1990’s) connected with ARPANET and, NSFnet to form the Internet. The Internet really became, popular in 1990’s after the development of World Wide, Web (WWW)., , Working of Internet, The computers on the Internet are connected to each other, through small networks. These networks are connected, through the gateways to the Internet backbone., All computers on the Internet, communicate with one, another using TCP/IP, which is a basic protocol of the, Internet., TCP/IP manages the transmission of data/file/document on, the Internet by breaking the data/file/document into small, pieces or parts called packets or datagrams. Each packet, contains actual data and address part, i.e. addresses of, destination and source upto 1500 characters. Functioning of, TCP and IP are as follows, (i) TCP It breaks message into smaller packets that are, transmitted over the Internet and also reassembles, these smaller packets into the original message that, are received from the Internet., (ii) IP It handles the address part of each packet, so that, the data is sent to the correct address. Each gateway, on the network checks this address to see where the, message is to be forwarded.
Page 56 :
@Cbsebookshub - Join Us on Telegram, , 44, Advantages of Internet, l, , l, , l, , l, , l, , Greater access to information reduces research time., Allows you to easily communicate with other people., Global reach enables one to connect everyone on the, Internet., Publishing documents on the Internet saves paper., A valuable resource for companies to advertise and, conduct business., , Disadvantages of Internet, l, , l, , l, , l, , l, , Cyber frauds may take place involving credit/debit card, numbers and details., Unsuitable and undesirable material is available that, sometimes can be used by notorious people such as, terrorists., It is a major source of computer viruses., Messages sent across the Internet can be easily, intercepted and are open to abuse by others., It is difficult to check the accuracy of information, available on the Internet., , Uses of Internet, Internet has been the most useful technology of the, modern time, which helps us not only in our daily lives,, but also in our personal and professional lives, developments. Thus, some uses of Internet are as follows, E-Commerce (Auction, buying and selling products etc.), Research (Online journals, magazines, information etc.), Education (E-learning, distance learning etc.), E-Governance (Online filling of application, Income, Tax, Sales Tax etc.), E-Reservation (Online reservation, online ticket, booking etc.), Online Payments (Credit/debit card payments etc.), Video Conferencing, Exchange of Views (Files, music, folders etc.), Social Networking Sites (Facebook, twitter etc.), Entertainment (Play music, videos, games etc.), l, , l, , l, , CBSE Term II Informatics Practices XII, , (iii) Graphical User Interface (GUI) It is a type of interface, that allows users to interact with the web through, graphical icons, buttons, labels, etc. At the time of using, GUI, the user does not need to type any text command., World Wide Web is based on client/server software design. A, client/server software design requires two types of software to, work in communication environment, (i) Client Software It is a type of software, which is used by a, client (or user) to request some information from web, server. e.g. Web browsers., (ii) Server Software It is a type of software, which is used by, the server to answer the requests and provide the, required information. e.g. Microsoft, Oracle, etc., It is possible to use your local computer as a server but usually, you want to have a fixed server, which runs 24 × 7 hours. So,, more advanced and large systems are used as a server instead of, local computers., , WWW Attributes, WWW provides various attributes, which are as follows:, (i) User-friendly The WWW resource works smoothly with, most web browsers, such as Internet Explorer, Firefox etc., (ii) Multimedia documents WWW allows users to create and, display web pages that contain various graphics, audio,, video, animation and text., (iii) Interactive WWW provides interactivity using hyperlinks, and input boxes (i.e. textboxes and checkboxes)., (iv) Frames WWW supports frames that allow users to display, more than one independent section on a single web page., , l, , l, , l, , l, , l, , l, , l, , World Wide Web (WWW), WWW was introduced on 13th March, 1989 by Tim, Berners Lee. It is often abbreviated as the web or WWW, or W3. WWW is a wide area network of Internet that, supports different web protocols., World Wide Web is a common example of information, protocol/service that can be used to send and receive, information over the Internet (between clients and, servers). It supports various types of application such as, (i) Multimedia It includes different types of texts,, movies, music, pictures, graphics, sounds,, animations, etc., (ii) HyperText It includes the links of different types of, information resources., , Web Address or URL, URL stands for Uniform Resource Locator. The term ‘web, address’ is a synonym for a URL that uses the HTTP/HTTPs, protocols. Each website has a unique address called URL., e.g. the website of Microsoft has a web address or URL as, http://www.microsoft.com., URL is usually pronounced by sounding out each letter but in, some quarters, pronounced ‘Earl’. URL is the global address of, documents and other resources on the World Wide Web., The first part of the URL is called a protocol identifier and it, indicates what protocol is to be used. The second part is called, resource name and it specifies the IP address or the domain, name, where the resource is located. The protocol identifier and, the resource name are separated by a colon and two forward, slashes., The Internet structure of the world wide web is build on a set of, rules called HyperText Transfer Protocol (HTTP) and a page, description language called HyperText Markup Language, (HTML)., HTTP uses Internet address in a special format called a URL., The most general form of a URL syntax is as follows:, protocol://domain name/<directory path> /<object, name>
Page 57 :
@Cbsebookshub - Join Us on Telegram, , 45, , CBSE Term II Informatics Practices XII, , Elements of URL, The element of this syntax are as follows:, Part, , Description, , Protocol, , It represents the name of the protocol, which is, used to transfer the data or web page., , Domain name, , It represents the name of web server where the, web page reside. It consists of three elements, as host_name.domain_name.domain_type, , Directory path, , It represents the location of the web page on, the web server or represents the file path on, server., , Object name, , It represents the name of the file with its, extension to specify the file type., , e.g. ftp://www.pcwebopedia.com/en/stuff.exe, http://www.pcwebopedia.com/us/index.html, , The first example specifies an executable file that should be, fetched using the FTP protocol and the second example, specifies a web page that should be fetched using the HTTP, protocol., Here, these URL consists of, Protocol: ftp or http, Host name: www, Domain name: pcwebopedia, Domain type: com, File path: en or us, File name with extension: stuff.exe or index.html, l, , l, , l, , l, , l, , l, , Types of URL, There are mainly two types of URL as follows, (i) Absolute URL It is the type of URL, which uses the, complete web path of a file to provide the location of, the resource, i.e. they provide the actual domain name., e.g. “http://www.oracle.sun.com/en/index.html”, (ii) Relative URL It is the type of URL that defines the, path of an URL on a domain, without including the, domain name. Relative URLs are more convenient, because they are short in length, more portable in, website maintenance., e.g. We specified only, “…/images/house.png”, , Web Server, A web server is a program that runs on a computer connected, to the Internet.It is simply a computer with an Internet, connection that runs software designed to send out HTML,, DHTML, XML or Java based pages and other file formats, such as multimedia files. Web server can refer to either the, hardware or software, that helps to deliver web content that, can be accessed through the Internet. The primary function, of a web server is to deliver web pages on the request of, client using the HTTP. This means delivery of HTML, , documents and any additional content that may be included, in a document such as images, stylesheets and scripts., , Services Provided by a Server, There are different services provided by a server as follows, (i) Centralised File Storage The storage capacity is, directly determined by the disk space that is essential, to store databases, files and other media. Servers help, the users to save their files or data on file server and, access these data on any networked computer., (ii) Resource Sharing In network, printers and scanners, can be attached directly and only authorised users are, able to use these shared equipments (like printers and, scanners). Web server helps for resource sharing, request., (iii) Centralised Backup A website needs backup at regular, intervals of its files and the databases. Web server, helps to maintain backup and save your data from many, adverse situations., There are various types of web server, which are available for, different platforms. Some of the common web servers are, described below:, Apache Web Server, This server was specially developed for the UNIX platform, but is presently available also for the windows and other, platforms. It is an open source and free-distributed software,, available from Apache software foundation., Microsoft Internet Information, Server (Microsoft IIS), It is a protocol server. It is implemented as a set of several, systems such as HTTP, FTP, NTTP. The Microsoft IIS is, built into the Microsoft Windows NT Server operating, system. It is capable for only running on windows platform., Netscape Enterprise Web Server, It is a web server developed by Netscape communications, corporation. The product was renamed Sun Java system web, server, reflecting the product acquisition by Sun, Microsystem. It is used to run the web page and give the, response to client., , Web Hosting, A web hosting service is a type of Internet hosting service, that allows individuals and organisations to make their, website accessible via the World Wide Web. A web host is in, the business of providing server space, web services and file, maintenance for websites controlled by individuals or, companies that do not have their own web servers. Many, ISPs, such as America Online will allow subscribers a small, amount of server space to host a personal web page. Other, commercial ISPs will charge the user a fee depending on the, complexity of the site being hosted., Web hosting can be of four types as follows:
Page 58 :
@Cbsebookshub - Join Us on Telegram, , 46, l, , l, , l, , l, , Free Hosting, Virtual or Shared Hosting, Dedicated Hosting, Co-location Hosting, , Website, A group of related web pages that follow the same theme and, are connected together with hyperlinks is called a website. In, other terms, “A website is a collection of digital documents,, primarily HTML files, that are linked together and that exist, on the web under the same domain”., A website displays related information on a specific topic., Each website is accessed by its own address known as URL, (Uniform Resource Locator)., e.g. http://www.carwale.com is a website, while, http://www.carwale.com/new/ is a web page., , Components of Website, There are various components of website as follows, (i) Navigation It helps users in easily navigating the, complete site and it also helps the search engine to get, an idea of the structure of the website., (ii) Web Hosting Every website has a set of files and, folder in the backend which makes the site possible to, be accessible by everyone in the world and those files, have to be stored somewhere for that web hostings are, used., (iii) Content Blogs will require different content than, service or business websites but content will be needed, for every website., (iv) Home Page The first or main page of a website is, called home page., (v) Address This is the URL or address of a website., (vi) Web Portal It is specially designed website that often, serves as the single point of access for information. It, also has hyperlinks to many other websites., , CBSE Term II Informatics Practices XII, , Dynamic Web Page, An interactive web page is a dynamic web page. A dynamic, web page uses scripting languages to display changing, content on the web page. Such a page generally has .php,, .asp or .jsp as extension., e.g. When you login to your Yahoo E-mail account to check, and to send E-mails. Moreover, the list of E-mail messages, changes as it arrives or as the list is deleted or is moved to, another folder., Differences between Static and Dynamic Web Pages, Key, , Static Web Page, Dynamic Web Page, On other hand dynamic, Definition Static web pages are, generally simple HTML, web pages are the pages, written pages which serve written in some more, as response from browser to complex language such as, server in which all the, ASP.NET in which data is, information and data is, rendered after some, static in nature and it does interpretation and capacity, not get changed until, to produce distinctive, someone changed it, content for different calls., manually., Complexity As mentioned in above, point as data in static web, pages is static and do not, require any interpretation, before rendering so static, web pages are simple in, complexity., , Dynamic web pages on, other hand does the, interpretation process, which make data dynamic, in nature and due to which, dynamic web pages, become complex in, complexity as compare to, static web pages., , Language Static web pages are, generally written in simpler, used, languages such as HTML,, JavaScript, CSS, etc., , On other dynamic web, pages are written in more, complex languages such as, CGI, AJAX, ASP,, ASP.NET, etc., , Rendered For static web pages data, do not changes until, Data, someone changes it, manually and hence data is, static in nature., , On other hand for dynamic, web page data is first, interoperate at server side, and due to which it does, not remain same on every, call and this makes data, dynamic in nature., , Web Page, Web page is an electronic document designed using HTML., It displays information in textual or graphical form. Traversal, from one web page to another web page is possible through, hyperlinks. A web page can be of two types:, , Time, , Static web pages due to, While dynamic web pages, static data take less time to due to dynamic data take, get load., comparatively more time, as compare to static web, pages., , Static Web Page, , Database, , In static web pages, generally no involvement of, database for data, redecoration., , A web page which displays same kind of information, whenever a user visits, is known as a static web page. A static, web page generally has .htm or .html as extension., e.g. A page that contains school or company information. The, content of this page will not change every day unless the, HTML file is manually edited by a programmer who, maintains it., , On other hand in case of, dynamic web page, database is used for data, redecoration., , Differences between Website and Web Page, Website, , Web Page, , Web site is a collection of web, pages displayed on the web, with a client-like browser., , It is part of website that includes, information and content and is, displayed on the browser to user, or visitor.
Page 59 : @Cbsebookshub - Join Us on Telegram, , 47, , CBSE Term II Informatics Practices XII, , Website, , Web Page, , It contains more than one web It is a single document display on, pages that contain information. the browser., It is a combination of web pages Information is usually written in, created using HTML and CSS. HTML language., It is a place used to display, content., , It is content displayed on the, website., , It requires more time to, develop the website as, compared to web pages., , It requires less time to develop a, web page as compared to the, website., , It includes content about, several entities., , It includes content or information, about a single entity., , It can be accessed using HTTP, It can be accessed through web, DNS (Domain Name System) browser., protocols., There is no such extension, included in the URL of the, website., , URL of web page include, extension., , It includes web pages, related, content and hyperlinks., , It might include text, graphics,, hyperlinks, etc., , They are used to provide, They are used to establish, credibility as business and also information with related pictures,, videos to user., to increase the positive, impression about the company, or business that in turn increase, user experience., , Web Browser, A web browser (commonly referred to as a browser) is a, software application for retrieving, presenting and traversing, information resources on the World Wide Web. Hyperlinks, present in resources enable users easily to navigate their, browsers to related resources. Although, browsers are, primarily intended to use the World Wide Web, they can, also be used to access information provided by web servers in, private networks or files in file systems. The popular web, browsers are Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, Internet, Explorer, Opera, Safari, Lynx and Netscape Navigator., Browsers are of two types, (i) Text-Based Web Browsers are the web browsers that, support text only, i.e. these browsers do not support, graphics. e.g. Lynx., (ii) Graphical-Based Web Browsers provide a Graphical, User Interface (GUI) where the user can jump from, one web page to another by clicking on the hyperlink, on a web page. e.g. Chrome, Internet Explorer, Mozilla, Firefox, etc., , Web Browser Toolbar, A major part of the user interface for a browser is the toolbar., This appears at the top of the browser window, above the, viewing pane and it can perform a number of critical, functions., , Major functions of browser toolbar are as follows, (i) Back This takes you one step back in your history, to, the page you were on before the current page., (ii) Forward It allows you to move forward through your, history, to where you were before you used the Back, button., (iii) Address Bar This is a text box that displays the URL of, the current page., (iv) Stop This will be found either just inside the address, bar or just next to it. It only appears when the page is, currently in the process of loading. If you, click it, the page will stop loading., (v) Refresh The Refresh or Reload button looks like a, circular arrow. This button repeats the request that led, to the current page, which usually cause the same page, to load into the browser again., (vi) Bookmark This allows you to bookmark the URL,, saving it to you browser., , Electronic Mail, Electronic mail most commonly referred to as E-mail, is a, method of exchanging digital messages from sender to one or, more recipients. Modern E-mail operates across the Internet, or other computer networks. Some early E-mail systems, required that the sender and the recipient both be online at, the same time, in common with instant messaging. Today’s, E-mail systems are based on Store-and-Forward Model., E-mail servers accept, forward, deliver and store messages., Neither the users nor their computers are required to be, online simultaneously. They need to connect only briefly,, typically to an E-mail server, for as long as it takes to send or, receive messages. Interactions between E-mail servers and, clients are governed by E-mail protocols., , E-mail Addressing, An E-mail address is composed of two separate parts., Your personal identity or account name (user name) on that, mail server., The domain name of the mail server computer on which, you have an E-mail account., An E-mail address is generally of the form, username@domainname., Some examples of E-mail address are:, (i)
[email protected], (ii)
[email protected], In E-mail address, symbol @ is used as a separator. It, separates your account name and mail server name., l, , l, , Advantages of E-mail, l, , l, , E-mails are easy to use. You can organise your daily, correspondence, send and receive electronic messages and, save them on computers., E-mails are fast. They are delivered at once around the, world. No other form of written communication is as fast as, an E-mail.
Page 60 :
@Cbsebookshub - Join Us on Telegram, , 48, l, , l, , l, , CBSE Term II Informatics Practices XII, , The language used in E-mails is simple and informal., When you reply to an E-mail you can attach the original, message so that when you answer the recipient knows,, what you are talking about. This is important if you get, hundreds of E-mails a day., It is possible to send automated E-mails with a certain text., In such a way, it is possible to tell the sender that you are, on vacation. These E-mails are called auto responders., , (i) Instant Messaging (IM) It is an Internet service that, allows people to communicate with each other in real, time through an instant messaging software. Unlike, E-mails, instant messaging allows message from one, person to appear right away on the other person’s, computer screen right after the send button is pressed., Many instant messaging services offer video calling, features, Voice over Internet Protocol and web, conferencing services. Web conferencing services can, integrate both video calling and instant messaging, abilities., (ii) Internet Relay Chat (IRC) It is an application layer, protocol that facilitates communication in the form of, text. The chat process works on a client/server, networking model. IRC clients are computer programs, that users can install on their system or web based, applications running either locally in the browser or on, a third party server. These clients communicate with, chat servers to transfer messages to other clients. IRC, is mainly used for group discussion in chat rooms, called “channels” although it supports private messages, between two users, data transfer and various, server-side and client-side commands., (iii) ICQ (I Seek You) ICQ offers chatting via ICQ, software. It is used as a conferencing tool by, individuals on the Net to chat, E-mail, perform file, transfers, play computer games and more.When you, download ICQ program (which is free) you are, assigned an ICQ number. Two or more people using, ICQ can have the same nick name, but no two people, can have the same ICQ number., (iv) Web Based Chat It is also like IRC but it is different, from it in the sense that it’s on a specific website and, no program is really needed to install on computer., Yahoo chat is a great example of a web based chat., , Disadvantages of E-mail, E-mails may carry viruses. These are small programs that, harm your computer system. They can read out your, E-mail address book and send themselves to a number of, people around the world., Many people send unwanted E-mails to others. These are, called spam mails. It takes a lot of time to filter out the, unwanted E-mails from those that are really important., E-mails cannot really be used for official business, documents. They may be lost and you cannot sign them., Your mailbox may get flooded with E-mails after a certain, time so you have to empty it from time-to-time., l, , l, , l, , l, , Difference between Cc and Bcc, Cc (Carbon copy) allows an E-mail to be send to a large, number of people by writing their respective addresses, separated by commas., Bcc (Blind carbon copy) is Cc, except that the recipient does, not see the list of people in the Bcc field., , Chat, Chatting is the online textual or multimedia conversation. It, is widely interactive text-based communication process that, takes place over the Internet. Chat with people using the, Internet is somewhat similar to using the telephone for the, same purpose. Chatting i.e. a virtual means of, communication that involves the sending and receiving of, messages, share audio and video between users located in, any part of the world., In chatting, you type a message in your chat box, which is, immediately received by the recipient, then the recipient, type a message in response to your message which is, instantly received by you., There are numerous chat programs that you can download,, including Yahoo! messenger, windows live messenger and, skype (all three of these can also do voice and video chat). In, addition, there are many browser based services that do not, require downloading., e.g. Facebook has a built-in chat feature and gmail allows you, to chat with your contacts whenever, you are logged into, your G-mail account., , Voice over Internet, Protocol (VoIP), VoIP is a technology that enables voice communications over, the Internet through the compression of voice into data, packets that can be efficiently transmitted over data networks, and then converted back into voice at the other end. It, requires broadband connection, a computer, special phone or, adaptor., , Advantages of VoIP, l, , l, , Types of Chat, , l, , Chat can be of different types. Given below are some, commonly used types of chat, , l, , The biggest single advantage of VoIP has over standard, telephone systems is low cost., Using services such as true VoIP, subscribers can call one, another at no cost to other party., Routing phone calls over existing data networks eliminate, the need for separate voice and data networks., The ability to transmit more than one telephone call over a, single broadband connection.
Page 61 :
@Cbsebookshub - Join Us on Telegram, , 49, , CBSE Term II Informatics Practices XII, , l, , VoIP consists advance telephone features, e.g. call, routing, screen POP and IVR., , Disadvantages of VoIP, l, , l, , l, , l, , Without power, VoIP phones are useless, so in case of, emergencies during power cuts it cannot be used., It uses Internet protocol’s packets so if packets get, dropped along the way then voice quality drops., Even with its high quality, it cannot match the voice, quality of a normal telephone line., It may not work for emergency service numbers like, Police or Fire services., , Add-ons, Add-ons or extension are tools which integrate into your, browser. They are similar to regular apps or programs, but, only run when the browser runs. Add-ons can allow the, viewing of certain types of web content, such as Adobe, Flash Player, necessary for Netflix movies and YouTube, Videos respectively., Toolbars are another type of add-on, placing a new kind of, search bar at the top of your browser window. Add-ons can, work within the framework of the browser, such as, changing the appearance or adding a search provider or, they can provide separate functions, such as performing, custom functions or adding a status bar., , How Add-ons are Installed?, There are two ways in which add-ons become installed, through an external installer and through the browser’s own, add-on service. The add-on service is the most reliable way, of installing an add-on, with the browser service providing, a relative ‘setting’ process for the general safety of the, add-on. Outside programs can also install add-ons in your, browser as part of its separate installation process., For example, Microsoft Office may place an add-on which, speeds up the browser opening of office documents. These, outside installers, however are also favoured by malware, companies. Add-ons can be added as part of a valid, program installation. These add-ons are also typically the, largest consumers of resources., , How to Remove Add-ons?, Add-ons can be removed in one of two ways. Some add-ons,, particularly ones installed outside of the browser, create an, entry in the ‘Programs’ portion of the control panel., Removing these is done in the same way you uninstall any, other program. Many add-ons, however can only be, removed through the browser’s add-on manager. In firefox,, it is found by clicking the firefox button in the upper left, , corner and selecting Add-ons a menu items which may have a, puzzle piece next to it., Internet explorer offers the add-on manager by clicking the, tools button and clicking manage add-ons., , Plug-ins, It is a piece of software that acts as an add-on to a web browser, and gives the browser additional functionality. Plug-ins can, allow a web browser to display additional content, it was not, originally designed to display. An example of a plug-in is the, free macromedia flash Player, a plug-in that allows the web, browser to display animations using the flash format. As the, web has become more commercial, flash has become a popular, format for displaying ads in web pages., As a result, many web users have been prompted to download, the flash plug-in and have it installed on their systems. Other, popular plug-ins include Quicktime Player (available on the, Apple website) and Acrobat Reader (which in addition to bring, a plug-in for the major browsers) is also a stand alone, application used to display files using the PDF format., , How Plug-ins are Installed?, Most plug-ins are available as free downloads. To install the, plug in, you visit the website of the plug-in’s developer and, click on a link that will download the installer for the plug-in,, you have selected., You can save the installer to an easy to find location such as the, desktop or a specific folder you have created to organise all of, you downloads. Once you have downloaded the installer, you, can open it and follow the prompts to install the plug-in on, your system. You may have to restart your web browser to, enable the additional functionality provided by the plug-in., , Cookies, They are used by web developers to help users navigate their, websites efficiently and perform certain functions. Due to their, core role of enhancing/enabling usability or site processes,, disabling cookies may prevent users from using certain, websites. Cookies are created when a user’s browser loads a, particular website., The website sends information to the browser, which then, creates a text file. Every time the user goes back to the same, website, the browser retrieves and sends this file to the, website's server., Computer cookies are created not just by the website the user, is browsing but also by other websites that run ADS, widgets, or other elements on the page being loaded. These cookies, regulate how the ads appear or how the widgets and other, elements function on the page.
Page 62 :
@Cbsebookshub - Join Us on Telegram, , 50, , CBSE Term II Informatics Practices XII, , Chapter, Practice, PART 1, Objective Questions, l, , Multiple Choice Questions, 1. What can you do with the Internet?, , (a) Exchange information with friends and colleagues, (b) Access pictures, sounds, video clips and other media, elements, (c) Find diverse perspective on issues from a global audience, (d) Exchange information, access pictures, find diverse, perspective on issue from a global audience, Ans. (d) Internet facility are able to exchange information, access, pictures, find diverse perspective on issue from a global, audience., , 2. There are numerous websites, which provide, search facility for searching the contents on, (a) Internet, (b) website, (c) web page, (d) LAN, Ans. (a) There are numerous websites, which provide search, facility for searching the contents on Internet. The Internet, is a huge ocean of information of resources and services such, as interlinked hypertext documents of World Wide Web, (WWW), online chatting, online banking, file transfer and, sharing, online gathering, online education and so on and, websites provide us the facility to search information from, these resources., , 3. The first network is, (a) ARPANET, (b) Internet, (c) NSFnet, (d) NET, Ans. (a) In 1969, the University of California at Los Angeles and, the University of Utah were connected with the beginning, of the ARPANET., , 4. The WWW is made up of the set of interconnected, ……… that are linked together over the Internet., (a) electronic documents, (b) web pages, (c) files, (d) All of the above, Ans. (b) Web pages are the HTML documents which are linked, with each other and together known as website or WWW., , 5. In URL, http://www.arihant.com/index.htm, which, component identifies the path of a web page?, (a) http, (b) www.arihant.com, (c) /index.htm, (d) All of the above, Ans. (c) The most general form of a URL syntax is as follows, , protocol://domain name/<directory path>/<object, name>, So, here we can see /<directory path>/<object name> is, the path., , 6. Which of the following statement(s) is/are true, about URL?, (a) URL stands for Uniform Resource Locator., (b) You can enter URL into address bar., (c) Both (a) and (b), (d) It is not necessary for URL to be unique., Ans. (c) URL stands for Uniform Resource Locator. It is the, global address of documents and other resources on the, World Wide Web and the resources can be searched through, writing resource name on the browser address bar., , 7. A website is a collection of, (a) web server, (b) web page, (c) web browser, (d) WWW, Ans. (b) A group of related web pages that follow the same theme, and are connected together with hyperlinks is called a, website., , 8. Home page helps viewers to find out what they can, find on the particular site. Home page is the, (a) first page of a website, (b) index page, (c) about page, (d) None of the above, Ans. (a) Home page is the first page of a website., , 9. Which of the following website is not used for job, search?, (a) monster.com, (b) recruitment.com, (c) naukri.com, (d) Myspace, Ans. (d) Myspace is not used for searching job and rest all, websites mentioned are used to search job.
Page 63 :
@Cbsebookshub - Join Us on Telegram, , 51, , CBSE Term II Informatics Practices XII, , 10. Web page is created using language, (a) XML, (b) Java, (c) C, (d) HTML, Ans. (d) The HyperText Markup Language or HTML is the, standard markup language for documents designed to be, displayed in a web browser., , 11. By default, web pages are saved in the ………, folder., (a) Download, (b) Document, (c) Picture, (d) Music, Ans. (b) Documents is the default location for all downloaded, web pages., , 16. During an international exchange programme the, students need to connect to a classroom in Russia, using Skype. Samarth helps the students to, connect. Which type of network service is being, used ?, [CBSE Question Bank 2021], (a) Instant messaging, (b) Email messaging, (c) VoIP, (d) WWW, Ans. (c) Through VoIP Samarth can set up his classroom. VoIP is, a technology that enables voice communications over the, Internet through the compression of voice into data packets, that can be efficiently transmitted over data networks., , 12. A browser is a program, which is used to, (a) connect to Internet, (b) create websites, (c) view sites on web, (d) All of the above, Ans. (d) A browser is a program, which is used to connect to, Internet, create websites and view sites on web. Browsers, are primarily intended to use the World Wide Web, they can, also be used to access information provided by web servers, in private networks or files in file systems., , 13. Which of the following is developed by Apple, Incorporation?, (a) Lynx, (b) Opera, (c) Safari, (d) Mozilla Firefox, Ans. (c) Safari is a graphical web browser developed by Apple, Incorporation, which based primarily on open-source, software properties notably including WebKit. It was first, introduced on Mac OS X Panther in 2003, and was later, incorporated to the iPhone and iPod Touch with iPhone OS, 1 in 2007., , 14. Which of the following is the online textual or, multimedia conversation?, (a) VoIP, (b) Chatting, (c) HTML, (d) None of the above, Ans. (b) Chatting, i.e. a virtual means of communication that, involves the sending and receiving of messages, share audio, and video between users located in any part of the world., , 15. After setting up the lab and Internet in the lab,, Samarth is now required to enable videos and, animations to be played on the web browser for, students of multimedia class. Which browser tool, /service can be used for the same?, [CBSE Question Bank 2021], (a) Plug-ins, (b) Add-ons, (c) Control Panel, (d) Download Settings, Ans. (b) Add-ons browser tool/service can be used to enable, videos and animations to be played on the web browser for, students of multimedia class., , l, , Case Based MCQs, Direction Read the case and answer the following, questions., , 17. Web server is a special computer system running, on HTTP through web pages. The web page is a, medium to carry data from one computer system to, another. The working of the web server starts from, the client or user. The client sends their request, through the web browser to the web server. Web, server takes this request, processes it and then, sends back processed data to the client. The server, gathers all of our web page information and sends it, to the user, which we see on our computer system, in the form of a web page. When the client sends a, request for processing to the web server, a domain, name and IP address are important to the web, server. The domain name and IP address are used, to identify the user on a large network., (i) Web servers are, (a) IP addresses, (b) computer systems, (c) web pages of a site, (d) a medium to carry data from one computer to another, , (ii) What does the web server need to send back, information to the user?, (a) Home address, (c) IP address, , (b) Domain name, (d) Both (b) and (c), , (iii) What is the full form of HTTP?, (a) HyperText Transfer Protocol, (b) HyperText Transfer Procedure, (c) Hyperlink Transfer Protocol, (d) Hyperlink Transfer Procedure, , (iv) The ……… translates Internet domain and host, names to IP address., (a) domain name system, (b) routing information protocol, (c) Internet relay chart, (d) network time protocol
Page 64 :
@Cbsebookshub - Join Us on Telegram, , 52, , CBSE Term II Informatics Practices XII, , E-commerce platform vendors like Amazon, Ola who, aggregate several products/services available in the, market and sell them through their portal to customers., (iii) Education The Internet offers a wealth of educational, material on any subject with structured navigation and, search facilities., One can seek any reading material and the Internet, will get it for them from any server in any part of the, world., , (v) Computer that requests the resources or data from, another computer is called as ……… ., (a) server, (b) client, (c) Both (a) and (b), (d) None of these, Ans. (i) (b) Web servers are computer systems., That means a web server is computer software and, hardware that accepts requests via HTTP, the network, protocol created to distribute web content or its secure, variant HTTPs., (ii) (d) Domain name and IP address need to send back, information to the user., (iii) (a) HTTP stands for HyperText Transfer Protocol. It, specifies how to transfer hypertext (linked web, documents) between two computers., (iv) (a) Domain name system is the way the Internet domain, names are stored and translated to IP addresses. The, domain names systems matches the name of website to, IP addresses of the website., (v) (b) Computer that requests the resources or data from, other computer is known as client. Client computer, always make use of the software or hardware in which the, service is made by the server., , PART 2, Subjective Questions, l, , understanding the basics of Internet and web, technologies. He is a bit confused in between the, terms “World Wide Web” and “Internet”. Help him, in understanding both the terms with the help of, suitable examples of each., [NCERT], Ans. World Wide Web is a set of programs, standards and, protocols that allows the multimedia and hypertext files to, be created, displayed and linked on the Internet., e.g. www.microsoft.com, www.amazon.com, etc., Internet is a computer-based world wide communications, network, which is composed of large number of smaller, interconnected networks., e.g. Web, E-mails, Social media, etc., While Internet is a collection of computers or networking, devices connected together; WWW is a collection of, documents, linked via special links called hyperlinks. WWW, forms a large part of Internet but is not the Internet., , 5. Ruhani wants to edit some privacy settings of her, , Short Answer Type Questions, , 1. Define the following terms., , 4. Sahil, a Class X student, has just started, , browser. How can she accomplish her task?, [NCERT], , (a) ARPANET, (b) ISP, (c) URL, Ans. (a) ARPANET stands for Advanced Research Projects, Agency NETwork., (b) ISP stands for Internet Service Provider, (c) URL stands for Uniform Resource Locator, , 2. Define home page. Give two advantages of home, page., , [NCERT], Ans. She can accomplish her task by performing following steps, Step 1 Open your web browser., Step 2 Open browser settings., Step 3 Look for Privacy and Security settings. If not directly, found, click on Advanced settings., Step 4 After reaching Privacy and Security settings she can, edit their setting., , 6. Define the structure of URL with example., Ans., , Ans. A home page is the first page of a website. Two advantages, of home page are as follows:, (i) It helps viewers to find out what they can find on that, site., (ii) Publicity of an individual or a community., , 3. Give any three applications on the Internet., [NCERT], Ans. Some uses of Internet are as follows:, (i) Electronic Mail (E-mail) The first major use of the, Internet is E-mail. People used to E-mail for sharing, information, data files, photos, videos, business, communications and any other files instantaneously, with others., This had enabled faster communication between, people and improve business efficiency., (ii) E-commerce The Internet enables the selling of goods, and services in online mode. There are many, , 7. Mr. Lal owns a factory which manufactures, automobile spare parts., Suggest him the advantages of having a web page, for his factory., Ans. The web page provides the information to the clients, about his factory of spare parts. Moreover, he can receive, the order on the Internet from the clients using the web, page., , 8. Which page does not change until the developer, modifies them?
Page 65 :
@Cbsebookshub - Join Us on Telegram, , 53, , CBSE Term II Informatics Practices XII, , Ans. Static pages do not change until the developer modifies, them. To update a static web page, the file name must be, changed manually., , Key, Language, used, , Static Web Page, Static web pages are, generally written in, simpler languages, such as HTML,, JavaScript, CSS,, etc., , Rendered, data, , For static web, pages data do not, changes until, someone changes it, manually and hence, data is static in, nature., , Time, , Static web pages, due to static data, take less time to get, load., , Database, , In static web pages,, generally no, involvement of, database for data, redecoration., , 9. How is an E-mail different from a chat?, Ans. In order to chat, you need have an account on the same service, as the person you are chatting with. On the other hand, in case, of E-mail, it is not necessary, i.e. you can have an account from, any provider and you can establish your own., , 10. Explain any two attributes of WWW., Ans. Two attributes of WWW are as follows:, (i) User-friendly The WWW resource works smoothly with, most web browsers, such as Internet Explorer, Firefox, etc., (ii) Multimedia documents WWW allows users to create, and display web pages that contains various graphics,, audios, videos, animation and text., , 11. How many types of software are used to work in, communication environment?, Ans. A client/server software design requires two types of, software to work in communication environment:, (i) Client Software It is a type of software, which is used by, a client (or user) to request some information from web, server., (ii) Server Software It is a type of software, which is used by, the server to answer the requests and provide the, required information., , (i) website and web page, (ii) static and dynamic web pages, Ans. (i) Difference between static and dynamic web pages are as, follows, Key, Definition, , Static Web Page, Static web pages are, generally simple, HTML written, pages which serve, as response from, browser to server in, which all the, information and, data is static in, nature and it does, not get changed, until someone, changed it, manually., Complexity As mentioned in, above point as data, in static web pages, is static and do not, require any, interpretation, before rendering so, static web pages are, simple in, complexity., , (ii) Difference between website and web page are as follows, Website, , 12. Differentiate between, , Dynamic Web Page, On other dynamic, web pages are written, in more complex,, languages such as, CGL, AJAX, ASP,, ASP. NET, etc., On other hand for, dynamic web page, data is first, interoperate at server, side and due to which, it does not remain, same on every call, and this makes data, dynamic in nature., While dynamic web, pages due to dynamic, data take, comparatively more, time as compare to, static web pages., On other hand in case, of dynamic web page, database is used for, data redecoration., , Web Page, , Website is a collection of web It is part of website that, includes information and, pages displayed on the web, content and is displayed, with a client-like browser., on the browser to user or, visitor., , Dynamic Web Page, On other hand, dynamic web pages, are the pages written, in some more, complex language, such as ASP. NET in, which data is, rendered after some, interpretation and, capacity to produce, distinctive content for, different calls., , It contains more than one web It is a single document, pages that contain information. display on the browser., , Dynamic web pages, on other hand does, the interpretation, process which make, data dynamic in, nature and due to, which dynamic web, pages become, complex in, complexity as, compare to static web, pages., , It is a combination of web, pages created using HTML, and CSS., , Information is usually, written in HTML, language., , It is a place used to display, content., , It is content displayed, on the website., , It includes content about, several entities., , It includes content or, information about a, single entity., , It can be accessed using, HTTP, DNS (Domain Name, System) protocols., , It can be accessed, through web browser., , There is no such extension, included in the URL of the, website., , URL of web page, include extension., , It includes web pages, related It might include text,, content and hyperlinks., graphics, hyperlinks, etc., They are used to establish, They are used to provide, credibility as business and also information with related, to increase the positive, pictures, videos to users., impression about the company, or business that in turn, increase user experience.
Page 66 :
@Cbsebookshub - Join Us on Telegram, , 54, , CBSE Term II Informatics Practices XII, , 13. Discuss the functioning of a web server with its, explanation., Ans. A web server is a program that runs on a computer, connected to the Internet. It is simply a computer with an, Internet connection that runs software designed to send out, HTML, DHTML, XML or Java based pages and other file, formats such as multimedia files., A web server provides four major functions:, (i) Surfing web pages., (ii) Running gateway programs and returning output., (iii) Controlling access to the server., (iv) Monitoring and logging server access statistics., , 14. What do you understand by the term chatting?, Ans. Chatting is the online textual or multimedia conversation. It, is widely interactive text based communication process that, takes place over the Internet. Chat with people using the, Internet is somewhat similar to using the telephone for the, same purpose. Chatting, i.e. a virtual means of, communication that involves the sending and receiving of, messages, share audio and video between users located in, any part of the world., In chatting, you type a message in your chatbox, which is, immediately received by the recipient, then the recipient, type a message in response to your message which is, instantly received by you., , 15. Distinguish between server and web server., Ans. Differences between server and web server are as follows, Server, , Web Server, , These servers arrange the run These servers arrange the run, environment for enterprises, environment for web, applications., applications., These servers utilise more, resources., , These servers utilise less, resources., , In this server, multi-threading In this server, multi-threading, is supported., is not supported., l, , Long Answer Type Questions, 16. Define WWW., , Ans. World Wide Web (WWW) or Web, the leading information, retrieval service of the Internet (the worldwide computer, network). The Web gives users access to a vast array of, documents that are connected to each other by means of, hypertext or hypermedia links (i.e. hyperlinks), electronic, connections that link related pieces of information in order, to allow a user easy access to them., It supports various types of application such as, Multimedia Information It includes different types of, movies, music, pictures, graphics, sounds, text, etc., HyperText Information It includes the links of different, types of information resources., Graphical User Interface (GUI) A user can point/click on, the graphical icon to request any information instead of, typing in text commands., World Wide Web is based on client/server software design. A, client/server software design requires two types of software, to work in a communication environment., , (i) Client Software It is a type of software, which is used by, a client (or a user) to request some information from web, server, e.g. Web browsers., (ii) Server Software It is a type of software, which is used by, the server to answer the request and provide the, required information, e.g. Microsoft, Oracle, etc. It is, possible to use your local computer as a server but, usually, you want to have a fixed server, which runs 24 × 7, hours. So, more advanced and large systems are used as a, server instead of local computers., , 17. Define Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP). Also,, explain its advantages., [NCERT], Ans. VoIP is an IP telephony term for a set of facilities used to, manage the delivery of voice information over Internet. It, enables a user to make cheap telephone calls over a, broadband Internet connection, instead of using a regular, telephone service., A major advantage of VoIP is that avoids the tolls charged by, ordinary telephone service. A user can make a call locally or, in other parts of US or Canada, or anywhere else in the, world, eliminating long distance fees by using a VoIP, service., The concept of VoIP is used in wireless LAN networks and, sometimes referred to as WVoIP, VoFI, VoWi-Fi and Wi-Fi, VoIP., Advantages of VoIP, (i) The biggest single advantage of VoIP has over standard, telephone systems is low cost., (ii) Using services such as true VoIP, subscribers can call one, another at no cost to other party., (iii) Routing phone calls over existing data networks, eliminate the need for separate voice and data networks., (iv) The ability to transmit more than one telephone call over, a single broadband connection., (v) VoIP consists advance telephone features, e.g. call, routing, screen POP and IVR., , 18. What is website? Also, write its components., Ans. A website is a collection of digital documents, primarily, HTML files, that are linked together and that exist on the, web under the same domain., A website displays related information on a specific topic., Each website is accessed by its own address known as URL, (Uniform Resource Locator)., Components of a website, (i) Web host Group of linked web pages qualify to be, called a website only when hosted on a web server., (ii) Address This is the address of the website (also called, URL of the website)., (iii) Home page Every website has a home page. It is the, first web page that appears when viewers go to a, website., (iv) Design It is the overall look and feel the website has a, result of proper use and integration elements like, nevigation menus, layout etc., (v) Content All the web pages contained in the website, together make up the content of the website., (vi) Navigation Structure The navigation structure of a, website is order of the pages, the collection of what
Page 67 :
@Cbsebookshub - Join Us on Telegram, , CBSE Term II Informatics Practices XII, , links to what. Usually it is held together by atleast, one navigation menu., , 19. Differentiate between absolute URL and relative, URL., Ans. (i) Absolute URL It is the type of URL, which uses the, complete web path of a file to provide the location of, the resource, i.e. they provide the actual domain, name., e.g. “http://www.oracle.sun.com/en/index.html”, (ii) Relative URL It is the type of URL that defines the, path of an URL on a domain, without including the, domain name. Relative URLs are more convenient, because they are short in length, more portable in, website maintenance., e.g. We specified only “…/images/house.png”, , 20. What is the utility of a web server? Write about, the services provided by web server., , 55, Ans. A web server is a program that runs on a computer connected, to the Internet., It is simply a computer with an Internet connection that runs, software designed to send out HTML, DHTML, XML or Java, based pages and other file formats such as multimedia files., Web server can refer to either the hardware or software or, combination of both which helps to deliver web content that, can be accessed through the Internet., The primary function of a web server is to deliver web pages, on the request of client using the HTTP. This means delivery, of HTML documents and any additional content that may be, included in a document such as images, style sheets and, scripts., A web server provides four major functions:, (i) Serving web pages., (ii) Running gateway programs and returning output., (iii) Controlling access to the server., (iv) Monitoring and logging server access statistics.
Page 68 :
@Cbsebookshub - Join Us on Telegram, , Chapter Test, Multiple Choice Questions, , 1. Which of the following project was created by the National Science Foundation?, (a) NSFNet, (c) ARPANET, , (b) WWW, (d) CERN Net, , 2. Which of the following is not a part of the URL?, (a) WWW, (c) Top-level domain, , (b) Domain name, (d) Client workstation, , 3. The basic purpose of URL is to locate, (a) web server, (c) web page, , (b) IP address, (d) node, , 4. Which web page uses scripting languages to display changing content on the web page?, (a) Static web page, (c) Dynamic web page, , (b) Hybrid web page, (d) None of these, , 5. The space provided by a service provider to store website data is called ……………… ., (a) webspace, (c) web hosting, , (b) cloud computing, (d) web store, , Short Answer Type Questions, , 6. How to host a website?, 7. How will you change the browser setting in opera?, Long Answer Type Questions, , 8. Write the process to install the add-ons., 9. Distinguish between chat and E-mail., , Answers, Multiple Choice Questions, 1. (a), , 2. (d), , 3. (a), , 4. (c), , 5. (c), , For Detailed Solutions, Scan the code
Page 71 :
@Cbsebookshub - Join Us on Telegram, , Informatics Practices, Class 12th ( Term II ), , Practice Paper 1, , *, , (Solved), T ime : 2 Hours, Max. Marks : 35, , General Instructions, , 1. There are 9 questions in the question paper. All questions are compulsory., 2. Question no. 1 is a Case Based Question, which has five MCQs. Each question carries one mark., 3. Question no. 2-6 are Short Answer Type Questions. Each question carries 3 marks., 4. Question no. 7-9 are Long Answer Type Questions. Each question carries 5 marks., 5. There is no overall choice. However, internal choices have been provided in some questions. Students have to attempt, only one of the alternatives in such questions., , * As exact Blue-print and Pattern for CBSE Term II exams is not released yet. So the pattern of this, paper is designed by the author on the basis of trend of past CBSE Papers. Students are advised, not to consider the pattern of this paper as official, it is just for practice purpose., , 1. Direction Read the following passage and answer the questions that follows, Web server is a special computer system running on HTTP through web pages. The web page is a medium, to carry data from one computer system to another. The working of the web server starts from the client or, user. The client sends their request through the web browser to the web server. Web server takes this, request, processes it and then sends back processed data to the client. The server gathers all of our web, page information and sends it to the user, which we see on our computer system in the form of a web page., When the client sends a request for processing to the web server, a domain name and IP address are, important to the web server. The domain name and IP address are used to identify the user on a large, network., (i) Web servers are, (a) IP addresses, (c) web pages of a site, , (b) computer systems, (d) a medium to carry data from one computer to another, , (ii) What does the web server need to send back information to the user?, (a) Home address, (c) IP address, , (b) Domain name, (d) Both (b) and (c), , (iii) What is the full form of HTTP?, (a) HyperText Transfer Protocol, (c) Hyperlink Transfer Protocol, , (b) HyperText Transfer Procedure, (d) Hyperlink Transfer Procedure, , (iv) The ……… translates Internet domain and host names to IP address., (a) domain name system, (c) Internet relay chat, , (b) routing information protocol, (d) network time protocol, , (v) Computer that requests the resources or data from another computer is called as ……… ., (a) server, (c) Both (a) and (b), , (b) client, (d) None of these
Page 72 :
@Cbsebookshub - Join Us on Telegram, , 60, , CBSE Term II Informatics Practices XII, , 2. Write a output for SQL queries (i) to (iii), which are based on the table Student given below:, Table : Student, RollNo, , Name, , Class, , DOB, , Gender, , City, , Marks, , 1, , Nanda, , X, , 06-06-1995, , M, , Agra, , 551, , 2, , Saurabh, , XII, , 07-05-1993, , M, , Mumbai, , 462, , 3, , Sonal, , XI, , 06-05-1994, , F, , Delhi, , 400, , 4, , Trisla, , XII, , 08-08-1995, , F, , Mumbai, , 450, , 5, , Sohan, , XII, , 08-10-1995, , M, , Delhi, , 369, , 6, , Marisla, , XI, , 12-12-1994, , F, , Dubai, , 250, , 7, , Neha, , X, , 08-12-1995, , F, , Moscow, , 377, , 8, , Nishant, , X, , 12-06-1995, , M, , Moscow, , 489, , (i) SELECT COUNT(*), City FROM Student GROUP BY City HAVING COUNT(*)>1;, (ii) SELECT MAX(DOB),MIN(DOB) FROM Student;, (iii) SELECT NAME,GENDER FROM Student WHERE City= ‘‘Delhi”;, Or Consider the following table Games. Write SQL commands for the following statements., Table: Games, GCode, , GameName, , Type, , Number, , PrizeMoney, , ScheduleDate, , 101, , Carom Board, , Indoor, , 2, , 5000, , 23/01/2004, , 102, , Badminton, , Outdoor, , 2, , 12000, , 12/12/2003, , 103, , Table Tennis, , Indoor, , 4, , 8000, , 14/02/2004, , 105, , Chess, , Indoor, , 2, , 9000, , 01/01/2004, , 108, , Lawn Tennis, , Outdoor, , 4, , 25000, , 19/03/2004, , (i) To display the details of those Games, which are having PrizeMoney more than 7000., (ii) To display sum of PrizeMoney for each Type of Games., (iii) To display the total number of games available in the above table Games., , 3. Differentiate between DDL comand and DML command., Or Differentiate between CHAR data type and VARCHAR data type., , 4. State any two differences between single-row functions and multiple-row functions., Or What is the difference between the ORDER BY clause and GROUP BY clause., 5. Write the short note on, (i) DAYOFWEEK( ), , (ii) DAYOFYEAR ( ), , 6. Consider the following EMP and DEPARTMENT tables. Write the SQL queries for (i) to (iv) and outputs for SQL, queries (v) to (viii)., Table : EMP, EMPNO, , ENAME, , SEX, , DOB, , DOJ, , DEPTCODE, , 101, , Ram, , M, , 1990-05-02, , 2012-01-02, , D01, , 102, , Aman, , M, , 1992-03-01, , 2013-02-04, , D03, , 103, , Diya, , F, , 1989-01-04, , 2011-01-06, , D04, , 106, , Sandeep, , M, , 1993-04-06, , 2015-01-03, , D02, , 105, , Varun, , M, , 1995-07-08, , 2014-02-04, , D05, , 107, , Komal, , F, , 1994-03-02, , 2013-03-06, , D01, , 104, , Priyanka, , F, , 1995-02-01, , 2012-02-07, , D01
Page 73 :
@Cbsebookshub - Join Us on Telegram, , 61, , CBSE Term II Informatics Practices XII, , Table : DEPARTMENT, DEPT CODE, , DEPTNAME, , PLACE, , D01, , CSE, , MUMBAI, , D02, , IT, , KOLKATA, , D04, , MEDIA, , DELHI, , D03, , HR, , MUMBAI, , D05, , SALES, , DELHI, , (i) To display EMPNO, ENAME, SEX from the table EMP in descending order of EMPNO, (ii) To display the records of all female employee from the table EMP., (iii) To display the EMPNO and ENAME of those employees from the table EMP who are joined between, '2011-01-01’ and ‘2013-01-01’., (iv) To count the number of male employees who have borned before ‘1994-01-01’, (v) SELECT COUNT(*), DEPTCODE FROM EMP GROUP BY DEPTCODE HAVING COUNT > 1;, (vi) SELECT COUNT(DISTINCT DEPTNAME) FROM DEPARTMENT;, (vii) SELECT ENAME, DEPTNAME FROM EMP E, DEPARTMENT D, WHERE E.DEPTCODE = D.DEPTCODE AND EMPNO < 104;, , (viii) SELECT MIN(DOJ) MAX(DOB) FROM EMP;, , 7. Given a table Bookhouse, write SQL query for part (i) to (v)., Table : Bookhouse, No Title, , Author, , Subject, , Publisher, , Qty, , Price, , 1, , Data Structure, , Lips Chute, , DS, , McGraw, , 4, , 217.00, , 2, , DOS Guide, , Nortron, , OS, , PHI, , 3, , 175.00, , 3, , Turbo C++, , Robort Lafore, , Prog, , Galgotia, , 5, , 270.00, , 4, , Dbase Dummies, , Palmer, , DBMS, , PustakM, , 7, , 130.00, , 5, , Mastering Windows, , Cowart, , OS, , BPB, , 1, , 225.00, , 6, , Computer Studies, , French, , FND, , Galgotia, , 2, , 75.00, , 7, , COBOL, , Stern, , Prog, , John W, , 4, , 1000.00, , 8, , Guide Network, , Freed, , NET, , Zpress, , 3, , 200.00, , 9, , Basic for Beginners, , Norton, , Prog, , BPB, , 3, , 40.00, , Schildt, , Prog, , McGraw, , 4, , 350.00, , 10 Advanced Pascal, , (i) Display the title of all books with price between 100 and 300., (ii) Display title and author of all the books having type “Prog” and published by BPB., (iii) Display number of books and average price for each type of publisher., (iv) Display title, price in descending order of price., (v) Display all the books where title starts with “D” and qty is more than 3., Or Given a table Order, write SQL query for part (i) to (v)., Table : Order, Orderno Orderdate, , CName, , Cloc, , Orders(in `), , Payments (in `), , 1, , 12/02/2008, , Avlon, , Delhi, , 100000, , 90000, , 2, , 21/11/2008, , Parason, , Jaipur, , 230000, , 230000, , 3, , 15/10/2008, , Trident, , Raipur, , 120000, , 100000, , 4, , 13/01/2008, , Avlon, , Jaipur, , 240000, , 240000, , 5, , 17/07/2008, , Trident, , Delhi, , 340000, , 310000, , 6, , 16/06/2008, , Nalco, , Chennai, , 140000, , 140000
Page 74 :
@Cbsebookshub - Join Us on Telegram, , 62, , CBSE Term II Informatics Practices XII, , (i) Display the name of companies., (ii) Insert a new row of data as (7,19/02/2007,Nike,Delhi,70000,140000), (iii) Display the maximum and minimum orders placed for each city., (iv) Find number of companies and average orders order by Cloc., (v) List all orders given between 01/01/2008 to 12/10/2008., , 8. Answer the following questions., (i) Write MySQL command that will be used to open an already existing database “CONTACT”., (ii) The Doc_name column of a table Hospital is given below:, Doc_name, Avinash, Hariharan, Vinayak, Deepak, Sanjeev, , Based on the above information , find the output of the following queries., (a) SELECT Doc_name FROM Hospital WHERE Doc_name LIKE ‘%v’;, (b) SELECT Doc_name FROM Hospital WHERE Doc_name LIKE ‘%e%’;, (iii) A table “Transport” in a database has degree 3 and cardinality 8. What is the number of rows and columns in, it?, (iv) Define the degree and cardinality of a relation. Observe the following table and find the degree and, cardinality of the given table., Book Id, , ISBN, , Book Name, , Author, , Publication, , Price, , QTY, , 1001, , 123, , Java, , R. Kumar, , Arihant, , 250, , 50, , 1002, , 124, , C++, , S. Singh, , Bharti, , 350, , 25, , 1003, , 125, , OOP, , M. Khan, , Navbharat, , 220, , 10, , 1004, , 126, , Dot Net, , R. Chand, , Kataria, , 230, , 20, , 1005, , 127, , DBMS, , Korth, , McGraw, , 500, , 10, , (v) Observe the following table carefully and write the names of the most appropriate columns, which can be, considered as (a) Candidate keys and (b) Primary key, Code, , Item, , Qty, , Price, , Transaction, Date, , 1001, , Plastic Folder 14”, , 100, , 3400, , 2014-12-14, , 1004, , Pen Stand Standard, , 200, , 4500, , 2015-01-31, , 1005, , Stapler Mini, , 250, , 1200, , 2015-02-28, , 1009, , Punching Machine Small, , 200, , 1400, , 2015-03-12, , 1003, , Stapler Big, , 100, , 1500, , 2015-02-02, , Or Write SQL queries for (i) to (iv) and find the output for (v)., Table : VEHICLE, VCODE VEHICLETYPE, , PERKM, , V01, , VOLVO BUS, , 150, , V02, , AC DELUXE BUS, , 125, , V03, , ORDINARY BUS, , 80, , V05, , SUV, , 30, , V04, , CAR, , 18
Page 75 :
@Cbsebookshub - Join Us on Telegram, , 63, , CBSE Term II Informatics Practices XII, , Note PERKM is Freight Charges per kilometre, , Table : TRAVEL, CNO, , CNAME, , TRAVELDATE, , KM, , VCO, DE, , NOP, , 101, , K. Niwal, , 2015-12-13, , 200, , VO1, , 32, , 103, , Fredrick Sym, , 2016-03-21, , 120, , V03, , 45, , 105, , Hitesh Jain, , 2016-04-23, , 450, , V02, , 42, , 102, , Ravi Anish, , 2016-01-13, , 80, , V02, , 40, , 107, , John Malina, , 2015-02-10, , 65, , V04, , 2, , 104, , Sahanubhuti, , 2016-01-28, , 90, , V05, , 4, , 106, , Ramesh Jaya, , 2016-04-06, , 100, , V01, , 25, , Note KM is Kilometres travelled, NOP is number of passengers travelled in vehicle., , (i) To display CNO, CNAME, TRAVELDATE from the table TRAVEL in descending order of CNO., (ii) To display the CNAME of all the customers from the table TRAVEL who are travelling by vehicle with code, V01 or V02., (iii) To display the CNO and CNAME of those customers from the table TRAVEL who travelled between, ‘2015-12-31’ and ‘2015-05-01’., (iv) To display all the details from table TRAVEL for the customers, who have travel distance more than 120 KM, in ascending order of NOP., (v) SELECT COUNT(*), VCODE FROM TRAVEL, GROUP BY VCODE HAVING COUNT(*)>1;, , 9. WeAtWork consultants are setting up a secured network for their office campus at Gurgaon for their day-to-day, office and web-based activities. They are planning to have connectivity between 3 buildings and the head office, situated in Mumbai. Answer the questions (i) to (v) after going through the building positions in the campus and, other details, which are given below:, Head office, “Mumbai”, on a, seabeach, , Gurgaon Campus, Building, “Green”, , Building, “Blue”, 0, , Distance between various buildings, Building “GREEN to Building “RED”, , 110 m, , Building “GREEN’’ to Building “BLUE”, , 45 m, , Building “BLUE’’ to Building “RED”, , 65 m, , Building “CAMPUS’’ to ‘‘HEAD OFFICE’’, , 1760 km, , Number of computers, Building “GREEN”, , 32, , Building “RED”, , 150, , Building “BLUE”, , 45, , HEAD OFFICE, , 10, , Building, “Red”
Page 76 :
@Cbsebookshub - Join Us on Telegram, , 64, , CBSE Term II Informatics Practices XII, , (i) Suggest the most suitable place (i.e. building) to house the server of this organization. Also, give a reason to, justify your suggested location., (ii) Suggest a network device needed to connect GREEN and RED building by UTP cable., (iii) Suggest the device to connect all computer in each building., (a) Switch, (b) Repeater, (c) Router, (iv) The organization is planning to provide a high speed link with its head office situated in ‘‘MUMBAI’’ using a, wired connection. Which of the following cables will be most suitable for this?, (a) Optical fibre, (b) Co-axial cable, (c) Ethernet cable, (v) Suggest the most appropriate media to connect Head Office to new office which is planning to setup inside, Arabian Sea where it is not possible to lay cables., Or Write the short note on the following:, (i) Web server, (ii) Purpose of cookies, (iii) Mesh topology, , EXPLANATIONS, 1. (i) (b) Web servers are computer systems., That means a web server is computer software and, hardware that accepts requests via HTTP, the, network protocol created to distribute web content or, its secure variant HTTPs., (ii) (d) Domain name and IP address need to send back, information to the user., (iii) (a) HTTP stands for Hyper Text Transfer Protocol. It, specifies how to transfer hypertext (linked web, documents) between two computers., (iv) (a) Domain name system is the way the Internet, domain names are stored and translated to IP, addresses. The domain name system matches the, name of website to IP addresses of the website., (v) (b) Computer that requests the resources or data from, other computer is known as client. Client computer, always make use of the software or hardware in which, the service is made by the server., 2. (i), COUNT(*), 2, 2, 2, , City, Mumbai, Delhi, Moscow, , (ii), MAX(DOB), , MIN(DOB), , 08-12-1995 07-05-1993, , (iii) SELECT COUNT(GameName) FROM Games;, 3. Differences between DDL and DML commands are as follows, , Key, , DDL, , DML, , Stands for, , DDL stands for, Data Definition, Language., , DML stands for Data, Manipulation Language., , Usage, , DDL statements DML statement is used to, are used to create insert, update or delete the, database, schema, records., constraints, tables, etc., , Classification DDL has no, further, classification., Commands, , CREATE, DROP, INSERT, UPDATE and, RENAME and, DELETE., ALTER., , Or Differences between CHAR and VARCHAR data types are as, follows, , CHAR Data Type, , Gender, , Sonal, , F, , Sohan, , M, , Or (i) SELECT*FROM Games WHERE PrizeMoney > 7000;, (ii) SELECT SUM(PrizeMoney), Type FROM Games, , GROUP BY Type;, , VARCHAR Data Type, , Its full name is CHARACTER. Its full name is VARIABLE, CHARACTER., It stores values in fixed lengths, and are padded with space, characters to match the, specified length., , VARCHAR stores values in, variable length along with, 1-byte or 2-byte length, prefix and are not padded, with any characters., , It can hold a maximum, of 255 characters., , It can hold a maximum of, 65,535 characters., , It uses static memory, allocation., , It uses dynamic memory, allocation., , (iii), Name, , DML is further classified, into procedural DML and, non-procedural DML., , 4. Two main differences between single-row functions and, multiple-row functions are as follows
Page 77 :
@Cbsebookshub - Join Us on Telegram, , 65, , CBSE Term II Informatics Practices XII, , Single-row functions, , Multiple-row functions, , Single-row functions are the, Multiple-row functions, one who work on single row, work upon group of rows, and return one output per row. and return one result for, the complete set of rows., e.g. LOWER, UPPER,, SUBSTR, LENGTH, etc., , e.g. COUNT, MIN, MAX,, AVG, SUM, etc., , Or The ORDER BY clause is used to show the contents of a, table/relation in a sorted manner with respect to the, column mentioned after the ORDER BY clause. The, contents of the column can be arranged in ascending or, descending order., The GROUP BY clause is used to group rows in a given, column and then apply an aggregate function e.g. MAX(),, MIN() etc., on the entire group., 5. (i) DAYOFWEEK ( ), This function returns the week day number (1= Sunday, 2=, Monday, ………, 7 = Saturday) for a date specified as an, argument., Syntax DAYOFWEEK (date/column_name), (ii) DAYOFYEAR( ), This function returns day of the year for a given date in, numeric format. The return value is within the range of, 1 to 366., Syntax DAYOFYEAR (date/column_name), 6. (i) SELECT EMPNO, ENAME, SEX FROM EMP ORDER BY, DESC;, (ii) SELECT * FROM EMP WHERE SEX = ‘F’;, (iii) SELECT EMPNO, ENAME FROM EMP WHERE DOJ, BETWEEN ‘2011-01-01’ AND ‘2013-01-01’;, (iv) SELECT COUNT(EMPNO) WHERE SEX= ‘M’ AND DOJ <, ‘1994-01-01’;, (v), , DEPTCODE, , COUNT (*), 3, , (vi), , D01, , COUNT(DISTINCT DEPTNAME), 5, , (vii), , (viii), , ENAME, , DEPTNAME, , Ram, , CSE, , Diya, , MEDIA, , Aman, , HR, , MIN (DOJ), 2011-01-06, , MAX (DOB), 1995-07-08, , 7. (i) SELECT Title FROM Bookhouse WHERE Price BETWEEN, , 100 AND 300;, (ii) SELECT Title, Author FROM Bookhouse WHERE, Subject=‘Prog’ AND Publisher=‘BPB’;, (iii) SELECT COUNT(*), AVG(Price) FROM Bookhouse, GROUP BY Publisher;, , (iv) SELECT Title, Price FROM Bookhouse ORDER BY, , Price DESC;, SELECT * FROM Bookhouse WHERE Title LIKE ‘D%’, AND Qty>3;, SELECT DISTINCT(CName) FROM Order;, INSERT INTO Order VALUES(8,‘19/02/2007’,, ‘Nike’, ‘Delhi’,70000, 140000);, SELECT Cloc, MAX (Orders), MIN (Orders) FROM, Order GROUP BY Cloc;, SELECT Cloc, COUNT(Cloc), AVG(Orders) FROM, Order GROUP BY Cloc;, SELECT * FROM Order WHERE, Orderdate>‘01/01/2008’ AND, Orderdate<‘12/10/2008’;, USE CONTACT;, , (v), Or (i), (ii), (iii), (iv), (v), , 8. (i), (ii) (a), , Doc_name, Sanjeev, , (b), , Doc_name, Deepak, Sanjeev, , (iii) Number of rows: 8, Number of columns: 3, (iv) Degree of relation It represents the total number of, columns in a relation., The degree of the given table is 7., Cardinality It represents the total number of row in a, relation. The cardinality of the given table is 5., (v) (a) Candidate key - Code, Item, (b) Primary key - Code, Or, (i) SELECT CNO, CNAME, TRAVELDATE, FROM TRAVEL A, VEHICLE B, WHERE A.VCODE = B.VCODE AND ORDER BY, CNO DESC;, (ii) SELECT CNAME FROM TRAVEL, WHERE VCODE = "V01" OR VCODE = "V02";, (iii) SELECT CNO, CNAME FROM TRAVEL, WHERE TRAVELDATE BETWEEN '2015-12-31' AND, '2015-05-01';, (iv) SELECT * FROM TRAVEL, WHERE KM>120 ORDER BY NOP;, (v), , COUNT (*), , VCODE, , 2, , V01, , 2, , V02, , 9. (i) In building RED as it has maximum number of, computers., (ii) Repeater
Page 78 :
@Cbsebookshub - Join Us on Telegram, , 66, (iii) (a) Switch, (iv) (a) Optical fibre, (v) Microwave, Or (i) Web Server A web server is software and hardware that, uses the HyperText Transfer Protocol and some other, protocols to respond to client requests made over the World, Wide Web. The main job of a web server is to display, website content through storing, processing and delivering, web pages to users., Web server hardware is connected to the Internet and, allows data to be exchanged with other connected devices,, while web server software controls how a user accesses, hosted files. The web server process is an example of, client/server model., (ii) Purpose of Cookies Cookies are text files with small pieces, of data — like a username and password — that are used to, identify our computer as we use a computer network., Specific cookies known as HTTP cookies are used to, identify specific users and improve our web browsing, experience. Data stored in a cookie is created by the server, , CBSE Term II Informatics Practices XII, , upon our connection. This data is labeled with an ID unique, to us and our computer. When the cookie is exchanged, between our computer and the network server, the server, reads the ID and knows what information need to, specifically serve to us., (iii) Mesh Topology Mesh topology is an arrangement of the, network in which computers are interconnected with each, other through various redundant connections. There are, multiple paths from one computer to another computer. It, does not contain the switch, hub or any central computer, which acts as a central point of communication., The Internet is an example of the mesh topology. Mesh, topology is mainly used for WAN implementations where, communication failures are a critical concern. Mesh, topology is mainly used for wireless networks., Mesh topology can be formed by using the formula:, Number of cables = (n*(n-1))/2;, where, n is the number of nodes that represents the, network.
Page 79 :
@Cbsebookshub - Join Us on Telegram, , Informatics Practices, Class 12th ( Term II ), , Practice Paper 2, , *, , (Solved), T ime : 2 Hours, Max. Marks : 35, , General Instructions, , 1. There are 9 questions in the question paper. All questions are compulsory., 2. Question no. 1 is a Case Based Question, which has five MCQs. Each question carries one mark., 3. Question no. 2-6 are Short Answer Type Questions. Each question carries 3 marks., 4. Question no. 7-9 are Long Answer Type Questions. Each question carries 5 marks., 5. There is no overall choice. However, internal choices have been provided in some questions. Students have to attempt, only one of the alternatives in such questions., , * As exact Blue-print and Pattern for CBSE Term II exams is not released yet. So the pattern of this, paper is designed by the author on the basis of trend of past CBSE Papers. Students are advised, not to consider the pattern of this paper as official, it is just for practice purpose., , 1. Direction Read the following passage and answer the questions that follows, Consider the table TRAVEL as given below:, Table : Travel, No, , Name, , Tdate, , Km, , Code, , NOP, , 101, , Janish Kin, , 2015–11–13, , 200, , 101, , 32, , 103, , Vedika Sahai, , 2016–04–21, , 100, , 103, , 45, , 105, , Tarun Ram, , 2016–03–23, , 350, , 102, , 42, , 102, , John Fen, , 2016–02–13, , 90, , 102, , 40, , 107, , Ahmed Khan, , 2015–01–10, , 75, , 104, , 2, , 104, , Raveena, , 2016–05–28, , 80, , 105, , 4, , Basis the above table information, answer the following questions., (i) Write query to give the output as:, No, , Name, , Tdate, , Km, , 101, 105, , Janish Kin, Tarun Ram, , 2015-11-13, 2016-03-23, , 200, 350, , (a) SELECT, (b) SELECT, (c) SELECT, (d) SELECT, , * FROM Travel WHERE, * FROM Travel WHERE, No, Name, Tdate, Km, No, Name, Tdate, Km, , Km>200;, Km>=200;, FROM Travel WHERE Km>=200;, FROM Travel WHERE Km BETWEEN 200 AND 350;
Page 80 :
@Cbsebookshub - Join Us on Telegram, , 68, , CBSE Term II Informatics Practices XII, , (ii) Write query to display maximum Km from Travel table., (a), (b), (c), (d), , SELECT MAX (Km) FROM Travel;, SELECT MAXIMUM(Km) FROM Travel;, SELCT HIGHEST (Km) FROM Travel;, None of the above, , (iii) Akhil has given the following command to arrange the data in ascending order of date., SELECT * FROM Travel WHERE ORDER BY Tdate;, , But he is not getting the desired result. Help him by choosing the correct command., (a) SELECT * FROM Travel ORDER BY Tdate;, (b) SELECT * FROM Travel IN ASC;, (c) SELECT Tdate FROM Travel ORDER BY Tdate;, (d) None of the above, , (iv) Choose the correct query to count the number of codes in each code type from Travel table?, (I) SELECT COUNT(Code) FROM Travel ;, (II) SELECT Code,COUNT(Code) FROM Travel GROUP BY Code;, (III) SELECT code,COUNT( DISTINCT Code) FROM Travel;, (IV) SELECT Code, COUNT( DISTINCT Code) FROM Travel GROUP BY Code;, Choose the correct option., (a) Both (II) and (III), , (b) Both (II) and (IV), , (c) Both (I) and (III), , (d) Only (II), , (v) Choose the correct command to display the name of the traveller whose travel date is in year 2016., (a) SELECT, (b) SELECT, (c) SELECT, (d) SELECT, , Name,, Name,, Name,, Name,, , Tdate FROM, Tdate FROM, Tdate FROM, MAX(Tdate), , Travel WHERE YEAR(Tdate)=2016 ;, Travel WHERE Tdate=2016;, Travel WHERE YEAR(Tdate)= =2016;, FROM Travel ;, , 2. What is the use of GROUP BY clause? Give an example., Or What do you understand by degree and cardinality of a table? Give an example., , 3. Given below a table Bookhouse, write SQL query for part (i) to (v)., Table : Bookhouse, No, , Title, , Author, , Subject, , Publisher, , Qty, , Price, , 1, , Data Structure, , Lips chute, , DS, , McGraw, , 4, , 217.00, , 2, , DOS Guide, , Nortron, , OS, , PHI, , 3, , 175.00, , 3, , Turbo C++, , Robort Lafore, , Prog, , Galgotia, , 5, , 270.00, , 4, , Dbase Dummies, , Palmer, , DBMS, , PustakM, , 7, , 130.00, , 5, , Mastering Windows, , Cowart, , OS, , BPB, , 1, , 225.00, , 6, , Computer Studies, , French, , FND, , Galgotia, , 2, , 75.00, , 7, , COBOL, , Stern, , Prog, , John W, , 4, , 1000.00, , 8, , Guide Network, , Freed, , NET, , Zpress, , 3, , 200.00, , 9, , Basic for Beginners, , Norton, , Prog, , BPB, , 3, , 40.00, , 10, , Advanced Pascal, , Schildt, , Prog, , McGraw, , 4, , 350.00, , (i) Display publisher wise total stock value (Qty * Price)., (ii) Display title of the book which is costliest., (iii) Display number of books and total price for each type of publisher., (iv) Display all the books where subject starts with “D” and qty is less than 3., (v) Display all information of books whose price starts with 2.
Page 81 :
@Cbsebookshub - Join Us on Telegram, , 69, , CBSE Term II Informatics Practices XII, , Or Describe different kinds of SQL command with proper examples., , 4., , Table : Employee, Eno, , Ename, , Job, , Salary, , Dept, , 101, , Anupam, , Programmer, , 5000, , 10, , 102, , Mahesh kumar, , Editor, , 2500, , 20, , 103, , Dinesh, , Programmer, , 2700, , 10, , Write SQL queries for the following questions., (i) Display Eno, Ename and Job in descending order of Eno., (ii) Find the maximum salary of department 10., (iii) Count the total employees working in each department., , 5. Answer the following:, (i) Write SQL command used to display the structure of a table., (ii) Mr. lames created a table Client with 2 rows and 4 columns. He added 2 more rows to it and deleted one, column. What is the cardinality and degree of the table Client?, (iii) In MySQL, Reena and Zebi are getting the following output of SELECT statement on a table Employee., Reena, , Zebi, , Lucknow, Delhi, Mumbai, Delhi, Kanpur, Delhi, , Lucknow, Delhi, Mumbai, Kanpur, , Which keyword has Zebi used with a SELECT statement to get the above output?, , 6. What will be the output of the following command?, (i) SELECT POWER(10,2), (ii) SELECT ROUND(14.4743, 1), Or Consider the decimal number x with value 8459.2654. Write commands in SQL., (i) To round it off to a whole number., (ii) To round it to 2 places before the decimal., , 7. What do you mean by network topology? Write different types of topology., Or Write one advantage each of star and bus topology used in networking. Draw a network layout of bus topology, to connect six computers., , 8. JNV School at Hyderabad have their offices according to the following diagram. Go through the details and, answer the questions that follows., JNV, Hyderabad, , MESS, 7, , DORMETORY, 10, SCHOOL, 40, , GATE, 5, , NOIDA, , ADMIN, 10
Page 82 :
@Cbsebookshub - Join Us on Telegram, , 70, , CBSE Term II Informatics Practices XII, , Distance between various wings are given below:, Wings, , Distance ( in metre), , MESS to SCHOOL, , 60, , MESS to DORMETORY, , 110, , MESS to GATE, , 65, , MESS to ADMIN, , 130, , SCHOOL to DORMETORY, , 40, , SCHOOL to GATE, , 50, , SCHOOL to ADMIN, , 68, , DORMETORY to GATE, , 115, , DORMETORY to ADMIN, , 100, , GATE to ADMIN, , 65, , (i) Name the most suitable wing where the server should be installed. Justify your answer., (ii) Draw the cable layout to efficiently connect various wings JNV, Hyderabad and also write the topology., (iii) Suggest a device/software and its placement that would provide data security for the entire network of the, School., (iv) (a) Which device will you suggest to be placed/installed in each of these wings to efficiently connect all the, computers within these wings., (b) Suggest the placement of a repeater in the network with justification., (v) Suggest a device and the protocol that shall be needed to provide wireless Internet access to all, smartphone/laptop users in the campus of JNV, Hyderabad., Or Draw the arrangement for connecting five computers in star and mesh topologies., , 9. Consider a table “Salesman” with the following data:, Table : Salesman, Sno, , Sname, , Salary, , Bonus, , DOJ, , A01, , Beena Mehta, , 30000, , 45.23, , 29-10-2019, , A02, , K.L. Sahay, , 50000, , 25.34, , 13-03-2018, , B03, , Nisha Thakkar, , 30000, , 35.00, , 18-03-2017, , B04, , Leela Yadav, , 80000, , NULL, , 31-12-2018, , C05, , Gautam Gola, , 20000, , NULL, , 23-01-1989, , C06, , Trapti Garg, , 70000, , 12.37, , 15-06-1987, , D07, , Neena Sharma, , 50000, , 27.89, , 18-03-1999, , Write SQL queries using SQL functions to perform the following operations., (i) Display salesman name and bonus after rounding off to zero decimal places., (ii) Display the position of occurrence of the string “ta” in salesman names., (iii) Display the four characters from salesman name starting from second character., (iv) Display the month name for the date of join of salesman., (v) Display the name of the weekday for the date of join of salesman., Or A departmental store MyStore is considering to maintain their inventory using SQL to store the data. As a, database administer, Abhay has decided that :, Name of the database - MyStore, Name of the table - Store, l, , l
Page 83 :
@Cbsebookshub - Join Us on Telegram, , 71, , CBSE Term II Informatics Practices XII, , l, , The attributes of Store are as follows:, , ItemNo-numeric, ItemName-character of size 20, Scode-numeric, Quantity-numeric, Table : Store, ItemNo, , ItemName, , Scode, , Quantity, , 2005, , Sharpener Classic, , 23, , 60, , 2003, , Ball Pen 0.25, , 22, , 50, , 2002, , Get Pen Premium, , 21, , 150, , 2006, , Get Pen Classic, , 21, , 250, , 2001, , Eraser Small, , 22, , 220, , 2004, , Eraser Big, , 22, , 110, , 2009, , Ball Pen 0.5, , 21, , 180, , (i) Identify the attribute best suitable to be declared as a primary key., (ii) Write the degree and cardinality of the table Store., (iii) Insert the following data into the attributes ItemNo, ItemName and Scode respectively in the given table, Store., ItemNo = 2010, ItemName = “Note Book” and Scode = 25, (iv) Abhay want to remove the table Store from the database MyStore., Which command will he use from the following?, (a) DELETE FROM Store;, (b) DROP TABLE Store;, (c) DROP DATABASE MyStore;, (d) DELETE Store FROM MyStore;, (v) Now Abhay wants to display the structure of the table Store, i.e. name of the attributes and their respective, data types that he has used in the table. Write the query to display the same.
Page 84 :
@Cbsebookshub - Join Us on Telegram, , 72, , CBSE Term II Informatics Practices XII, , EXPLANATIONS, 1. (i) (c) SELECT No,Name, Tdate,Km FROM Travel WHERE Km>=200;, (ii) (a) SELECT MAX(Km) FROM Travel;, (iii) (a) SELECT * FROM Travel ORDER BY Tdate;, (iv) (d) SELECT Code,COUNT(Code)FROM TRAVEL GROUP BY Code;, (v) (a) SELECT Name, Tdate FROM Travel WHERE YEAR(Tdate)=2016 ;, 2. The GROUP BY clause is used to group records of a table on the basis of a common value of a column and get a summarised result, for the group as per a defined function, e.g. if in a class students belong to different school houses ,then we can count the number of, students in each house using a GROUP BY command such as:, SELECT COUNT(HOUSE)FROM STUDENT GROUP BY HOUSE;, Or Degree Number of columns/attributes/fields in a table are called table’s degree., Cardinality Number of rows/tuples/records in a table are called table’s cardinality., For example,, , Bookno, , Name, , Author, , Price, , B01, , Good learning, , Xion Z., , 220, , B02, , Smile easy, , T.Singh, , 350, , B03, , I to U, , S.Sandeep, , 250, , Degree is 4 because it has 4 columns and cardinality is 3 because it has 3 rows., 3. (i) SELECT Publisher, Qty*Price AS Total_Stock_Value FROM Bookhouse GROUP BY Publisher;, (ii) SELECT Title FROM Bookhouse WHERE Price=MAX(Price);, (iii) SELECT COUNT(*), SUM(Price) FROM Bookhouse GROUP BY Publisher;, (iv) SELECT Title FROM Bookhouse WHERE Subject LIKE ‘D%’ AND Qty<3;, (v) SELECT * FROM Bookhouse WHERE Price LIKE ‘2%’;, Or SQL commands are instructions. It is used to communicate with the database. It is also used to perform specific tasks, functions, and queries of data. SQL can perform various tasks like create a table, add data to tables, drop the table, modify the table, set, permission for users., Types of SQL commands are as follows, (i) Data Definition Language (DDL) DDL changes the structure of the table like creating a table, deleting a table, altering a table,, etc. All the command of DDL are auto-committed that means it permanently save all the changes in the database., Here are some commands that come under DDL:, CREATE, ALTER, DROP, TRUNCATE, (ii) Data Manipulation Language (DML) DML commands are used to modify the database. It is responsible for all form of changes, in the database. The command of DML is not auto-committed that means it cannot permanently save all the changes in the, database. They can be rollback., Here are some commands that come under DML:, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, (iii) Data Control Language (DCL) DCL commands are used to grant and take back authority from any database user., Here are some commands that come under DCL:, GRANT, REVOKE, 4. (i) SELECT Eno, Ename, Job FROM Employee ORDER BY Eno DESC;, (ii) SELECT MAX(Salary) FROM Employee WHERE Dept=10;, (iii) SELECT COUNT(*), Dept FROM Employee GROUP BY Dept;, 5. (i) The command to display the structure of a table is as follows:, , DESCRIBE table_name;, or DESC table_name;
Page 85 :
@Cbsebookshub - Join Us on Telegram, , 73, , CBSE Term II Informatics Practices XII, , (ii) Cardinality = 4, Degree = 3, where, cardinality are the number of rows and degree is number of columns in a table., (iii) Zebi has used DISTINCT clause with the SELECT command., 6. (i) 100, (ii) 14.5, Or (i) SELECT ROUND(8459.2654);, (ii) SELECT ROUND(8459.2654,−2);, 7. A network topology is the arrangement with which computer systems or network devices are connected to each other. Topologies, may define both physical and logical aspect of the network. Both logical and physical topologies could be same or different in a, same network., There are different types of topology, which are as, Bus Topology In case of bus topology, all devices share single communication line or cable. Bus topology may have problem while, multiple hosts sending data at the same time. It is one of the simple forms of networking where a failure of a device does not affect, the other devices. But failure of the shared communication line can make all other devices stop functioning., Star Topology All hosts in star topology are connected to a central device, known as hub device, using a point-to-point connection., i.e. there exists a point-to-point connection between hosts and hub., As in bus topology, hub acts as single point of failure. If hub fails, connectivity of all hosts to all other hosts fails. Every communication, between hosts, takes place through only the hub. Star topology is not expensive as to connect one more host, only one cable is, required and configuration is simple., Tree Topology, This topology divides the network into multiple levels/layers of network. Mainly in LANs, a network is bifurcated into three types of, network devices. The lowermost is access-layer where computers are attached. The middle layer is known as distribution layer, which, works as mediator between upper layer and lower layer., The highest layer is known as core layer and is central point of the network. i.e. root of the tree from which all nodes fork. All, neighboring hosts have point-to-point connection between them.Similar to the bus topology, if the root goes down, then the entire, network suffers even.though it is not the single point of failure. Every connection serves as point of failure, failing of which divides the, network into unreachable segment., Or Advantage of star topology is that it is most reliable as there is a direct connection of every node with the central node or server., Advantage of bus topology is that all nodes are connected through a single length of a cable, so very short cable length is used., A network layout of bus topology to connect six computers is as follows:, , 8., , (i) SCHOOL, it contains maximum number of computers., (ii) Star topology, JNV, Hyderabad, , MESS, 7, , DORMETORY, 10, SCHOOL, 40, , GATE, 5, , ADMIN, 10
Page 86 :
@Cbsebookshub - Join Us on Telegram, , 74, , CBSE Term II Informatics Practices XII, , (iii) Firewall should be installed in the SCHOOL where the server is located., (iv) (a) Hub/Switch, (b) Repeater should be installed where the distance between the wings is 70 metre or more. As per the above layout no repeater is, required., (v) Devices Wi-Fi or WiMAX or Wi-Fi router, Protocols – 802.11, WAP, 802.16, Or Star Topology, , Mesh Topology, , 9. (i), (ii), (iii), (iv), (v), Or (i), (ii), (iii), (iv), (v), , SELECT, SELECT, SELECT, SELECT, SELECT, , Sname, ROUND(Bonus,0)FROM Salesman;, INSTR(Sname, “ta”) FROM Salesman;, MID(Sname,2,4) FROM Salesman;, MONTHNAME(DOJ) FROM Salesman;, DAYNAME(DOJ)FROM Salesman;, , ItemNo, Degree- 4, Cardinality- 7, , INSERT INTO Store VALUES(2010,’Note Book’,NULL,25);, (b) DROP TABLE Store;, , DESCRIBE Store, or DESC Store;
Page 87 :
@Cbsebookshub - Join Us on Telegram, , Informatics Practices, Class 12th ( Term II ), , Practice Paper 3, , *, , (Solved), T ime : 2 Hours, Max. Marks : 35, , General Instructions, , 1. There are 9 questions in the question paper. All questions are compulsory., 2. Question no. 1 is a Case Based Question, which has five MCQs. Each question carries one mark., 3. Question no. 2-6 are Short Answer Type Questions. Each question carries 3 marks., 4. Question no. 7-9 are Long Answer Type Questions. Each question carries 5 marks., 5. There is no overall choice. However, internal choices have been provided in some questions. Students have to attempt, only one of the alternatives in such questions., , * As exact Blue-print and Pattern for CBSE Term II exams is not released yet. So the pattern of this, paper is designed by the author on the basis of trend of past CBSE Papers. Students are advised, not to consider the pattern of this paper as official, it is just for practice purpose., , 1. Direction Read the following passage and answer the questions that follows, Consider the table Student as given below :, Table : Student, RollNo, , Name, , Class, , 1, , Anand, , XI, , 2, , Chetan, , 3, , DOB, , Gender, , City, , Marks, , 06-06-1997, , M, , Agra, , 430, , XII, , 07-05-1994, , M, , Mumbai, , 460, , Geet, , XI, , 06-05-1997, , F, , Agra, , 470, , 4, , Priti, , XII, , 08-08-1995, , F, , Mumbai, , 492, , 5, , Saniya, , XII, , 08-10-1995, , F, , Delhi, , 360, , 6, , Neha, , X, , 08-12-1995, , F, , Burdwan, , 324, , 7, , Nishant, , X, , 12-06-1995, , M, , Burdwan, , 429, , Based on above table information, answer the following questions., (i) State the command that will give the output as :, Name, Anand, Chetan, Geet, Priti
Page 88 :
@Cbsebookshub - Join Us on Telegram, , 76, , CBSE Term II Informatics Practices XII, , (I) SELECT Name FROM Student, (II) SELECT Name FROM Student, (III) SELECT Name FROM Student, (IV) SELECT Name FROM Student, Choose the correct option., , WHERE Class=‘XI’ AND Class=‘XII’;, WHERE NOT Class=’XI’ AND Class=‘XII’;, WHERE City=“Agra” OR City=“Mumbai”;, WHERE City IN(“Agra”, “Mumbai”);, , (a) Both (I) and (II), (b) Both (III) and (IV), (c) Any of the options (I), (II) and (IV), (d) Only (III), , (ii) What will be the output of the following command?, SELECT * FROM Student WHERE Gender =“F” AND Class = "XII" ORDER BY Marks;, (a), , RollNo, , Name, , Class, , DOB, , Priti, , XII, , 08-08-1995, , Name, , Class, , DOB, , Saniya, , XII, , 08-10-1995, , Name, , Class, , DOB, , 1, , Priti, , XII, , 08-08-1995, , F, , Mumbai, , 492, , 5, , Saniya, , XII, , 08-10-1995, , F, , Delhi, , 360, , 1, , (b), , RollNo, 5, , (c), , RollNo, , Gender, F, , Gender, F, , Gender, , City, , Marks, , Mumbai, , City, , 492, , Marks, , Delhi, , City, , 360, , Marks, , (d) None of the above, , (iii) Prachi has given the following command to obtain the highest marks:, SELECT MAX(Marks) FROM Student WHERE GROUP BY Class;, , But she is not getting the desired result. Help her by writing the correct command., (a) SELECT MAX(Marks) FROM Student WHERE GROUP BY Class;, (b) SELECT Class, MAX(Marks) FROM Student GROUP BY Marks;, (c) SELECT Class, MAX(Marks) GROUP BY Class FROM Student;, (d) SELECT Class, MAX(Marks) FROM Student GROUP BY Class;, , (iv) State the command to display the average marks scored by students of each gender who are in class XI., (I) SELECT Gender, AVG(Marks) FROM Student WHERE Class= “XI” GROUP BY Gender;, (II) SELECT Gender, AVG(Marks) FROM Student GROUP BY Gender WHERE Class=‘‘XI”;, (III) SELECT Gender, AVG(Marks) GROUP BY Gender FROM Student HAVING Class=‘‘XI”;, (IV) SELECT Gender, AVG(Marks) FROM Student GROUP BY Gender HAVING Class =“XI”;, Choose the correct option., (a) Both (II) and (III), (c) Both (I) and (III), , (b) Both (II) and (IV), (d) Only (III), , (v) Help Ritesh to write the command to display the name of the youngest student?, (a) SELECT, (b) SELECT, (c) SELECT, (d) SELECT, , Name,MIN(DOB) FROM Student ;, Name,MAX(DOB) FROM Student ;, Name,MIN(DOB) FROM Student GROUP BY Name ;, Name,MAXIMUM(DOB) FROM Student;
Page 89 :
@Cbsebookshub - Join Us on Telegram, , 77, , CBSE Term II Informatics Practices XII, , 2. Observe the following table LIST and find the degree and Cardinality of the LIST., Table: LIST, NO, , NAME, , EVENTCODE, , EVENTNAME, , 1, , Tara Mani, , 1001, , Programming, , 1, , Tara Mani, , 1002, , IT Quiz, , 2, , Jaya Sarkar, , 1001, , Programming, , 2, , Jaya Sarkar, , 1002, , IT Quiz, , 3, , Tarini Trikha, , 1001, , Programming, , 3, , Tarini Trikha, , 1002, , IT Quiz, , 3. Observe the following table carefully and write the names of the most appropriate columns, which can be, considered as (i) candidate keys and (ii) primary key., Id, , Product, , Qty, , Price, , Transaction Date, , 101, , Plastic Folder 12”, , 100, , 3400, , 2014-12-14, , 104, , Pen Stand Standard, , 200, , 4500, , 2015-01-31, , 105, , Stapler Medium, , 250, , 1200, , 2015-02-28, , 109, , Punching Machine Big 200, , 1400, , 2015-03-12, , 103, , Stapler Mini, , 1500, , 2015-02-02, , 100, , Or Consider the following DEPT and WORKER tables. Write SQL queries for (i) to (iv) and find output for SQL, query (v)., Table: DEPT, DCODE, , DEPARTMENT, , CITY, , D01, , MEDIA, , DELHI, , D02, , MARKETING, , DELHI, , D03, , INFRASTRUCTURE, , MUMBAI, , D05, , FINANCE, , KOLKATA, , D04, , HUMAN RESOURCE, , MUMBAI, , Table: WORKER, WNO NAME, , DOJ, , DOB, , GENDER, , DCODE, , 1001, , George K, , 2013-09-02, , 1991-09-01, , MALE, , D01, , 1002, , Ryma Sen, , 2012-12-11, , 1990-12-15, , FEMALE, , D03, , 1003, , Mohitesh, , 2013-02-03, , 1987-09-04, , MALE, , D05, , 1007, , Anil Jha, , 2014-01-17, , 1984-10-19, , MALE, , D04, , 1004, , Manila Sahai 2012-12-09, , 1986-11-14, , FEMALE, , D01, , 1005, , R SAHAY, , 2013-11-18, , 1987-03-31, , MALE, , D02, , 1006, , Jaya Priya, , 2014-06-09, , 1985-06-23, , FEMALE, , D05, , Note DOJ refers to Date of Joining and DOB refers to Date of Birth of workers., , (i) To display WNO, NAME, GENDER from the table WORKER in descending order of WNO., (ii) To display the NAME of all the FEMALE workers from the table WORKER., (iii) To display the WNO and NAME of those workers from the table WORKER, who are born between, ‘1987-01-01’ and ‘1991-12-01’.
Page 90 :
@Cbsebookshub - Join Us on Telegram, , 78, , CBSE Term II Informatics Practices XII, , (iv) To count and display MALE workers who have joined after ‘1986-01-01’., (v), SELECT COUNT(*), DCODE FROM WORKER, GROUP BY DCODE HAVING COUNT(*)>1;, , 4. Write a SQL command for creating a table 'SUPPLIERS';, Table: SUPPLIERS, Field_Name, , Datatype, , Size, , Product_id, , INTEGER, , 4, , Product_Name, , CHAR, , 10, , Quantity, , INTEGER, , 10, , Price, , DECIMAL, , 7,2, , Phone, , CHAR, , 10, , Or Consider the following table Vehicles :, Table : Vehicles, V_No, , Type, , Company, , Price, , Qty, , AW125, , Wagon, , Maruti, , 250000, , 25, , J0083, , Jeep, , Mahindra, , 4000000, , 15, , S9090, , SUV, , Mitsubishi, , 2500000, , 18, , M0892, , Mini Van, , Datsun, , 1500000, , 26, , W9760, , SUV, , Maruti, , 2500000, , 18, , R2409, , Mini Van, , Mahindra, , 350000, , 15, , Basis on above table intormation, write SQL commands for the following questions., (i) Display the average price of each type of vehicle having quantity more than 20., (ii) Count the type of vehicles manufactured by each company., (iii) Display the total price of all the types of vehicles., , 5. (i)Write a query to display current date on your system., (ii) Display the position of occurrence of string ‘‘OR’’ in the string “CORPORATE LAWYER’’., (iii) Mrs. Kumar is using table Students with the following columns:, Rno,AdmNo,Name,Aggregate, She wants to display all information of students in descending order of name and with ascending order of, aggregate. She wrote the following SQL query and she did not get the desired result., SELECT * FROM Students ORDER BY Name, Aggregate DESC;, , Or Predict the output of the following., (i) SELECT POW(INSTR(“Success@dedication”,“@”),2);, (ii) SELECT MONTH(“2020-11-15”)*POW(2,3);, (iii) Mr. Janak is using a table with following columns:, Name, Class, Course_Id, Course_Name, He needs to display name of students, who have not been assigned any stream or have been assigned, Course_Name that ends with “economics”., He wrote the following query, which did not give the desired result., SELECT Name, Class FROM Students WHERE Course_Name=NULL OR Course_Name=“%economics”;, , Help Mr. Janak to run the query by removing the error and write the correct query.
Page 91 :
@Cbsebookshub - Join Us on Telegram, , 79, , CBSE Term II Informatics Practices XII, , 6. Write the SQL functions which will perform the following operations:, (i) To display the name of the day of the current date., (ii) To remove spaces from the beginning of a string “ Python”., (iii) To display the name of the month e.g. January or February from your date of birth(dob)., (iv) To display the starting position of word “Information” from “Information Technology” ., (v) To compute the power of two numbers a and b ., , 7. (i) Write the name of the most suitable wireless communication channels for each of the following situations., (a) Communication between two offices in two different countries., (b) To transfer the data from one mobile phone to another., (ii) Mr. Chandervardhan is not able to identify the domain name in the given URL. Identify and write it for him., http://www.cbsenic.in/aboutus.htm, Or Expand the following abbreviations :, (i) HTTP, (ii) ARPANET, (iii) VPN, (iv) MODEM, (v) TCP/IP, (vi) DNS, , 8. How is the call quality of a VoIP phone?, Or A company in Mega Enterprises has 4 wings of buildings as shown in the diagram :, W1, , W2, , W3, , W4, , Center to center distances between various buildings:, W3 to W1 - 50m, W1 to W2 - 60m, W2 to W4 - 25m, W4 to W3 - 170m, W3 to W2 - 125m, W1 to W4 - 90m, Number of computers in each of the wing:, W1 - 150, W2 - 15, W3 - 15, W4 - 25, Computers in each wing are networked but wings are not networked. The company has now decided to connect, the wings also., (i) Suggest a most suitable cable layout for the above connections., (ii) Suggest the most appropriate topology of the connection between the wings., (iii) The company wants Internet accessibility in all the wings. Suggest a suitable technology., (iv) Suggest the placement of the following devices with justification if the company wants minimized network, traffic.
Page 92 :
@Cbsebookshub - Join Us on Telegram, , 80, , CBSE Term II Informatics Practices XII, , (a) Repeater, (b) Hub/Switch, (v) The company is planning to link its head office situated in New Delhi with the offices in hilly areas. Suggest a, way to connect it economically., , 9. Modern Public School is maintaining fees records of students. The database administrator, Aman decided that, Name of the database-School, Name of the table-Fees, The attributes of Fees are as follows:, Rollno-numeric, Name-character of size 20, Class-character of size 20, Fees-numeric, Qtr-numeric, Answer any four questions from the following :, (i) Identify the attribute best suitable to be declared as a primary key., (ii) Write the degree of the table., (iii) Insert the following data into the attributes Rollno, Name, Class, Fees and Qtr in Fees table., (iv) Aman want to remove the table Fees from the database School., Which command will he use?, l, , l, , l, , (a) DELETE FROM Fees;, (b) DROP TABLE Fees;, (c) DROP DATABASE Fees;, (d) DELETE Fees FROM Fees;, , (v) Now, Aman wants to display the structure of the table Fees, i.e. name of the attributes and their respective, data types that he has used in the table. Write the query to display the same., Or Consider the table Sports given below. Write commands in SQL for (i) to (iv) and output for (v) to (viii)., Table : Sports, StudentNo, , Class, , Name, , Game1, , Grade1, , 10, , 7, , Sammer, , Cricket, , B, , Game2, Swimming, , Grade2, A, , 11, , 8, , Sujit, , Tennis, , A, , Skating, , C, , 12, , 7, , Kamal, , Swimming, , B, , Football, , B, , 13, , 7, , Venna, , Tennis, , C, , Tennis, , A, , 14, , 9, , Archana, , Basketball, , A, , Cricket, , A, , 15, , 10, , Arpit, , Cricket, , A, , Athletics, , C, , (i) Display the names of the students who have grade ‘A’ in either Game1 or Game2 or both., (ii) Display the number of students having game ‘Cricket’., (iii) Display the names of students who have same game for both Game1 and Game2., (iv) Display the games taken by the students whose name starts with ‘A’., (v) SELECT COUNT(*) FROM Sports;, (vi) SELECT DISTINCT Class FROM Sports;, (vii) SELECT MAX(Class) FROM Student;, (viii) SELECT COUNT(*) FROM Sports GROUP BY Game1;
Page 93 :
@Cbsebookshub - Join Us on Telegram, , 81, , CBSE Term II Informatics Practices XII, , EXPLANATIONS, 1. (i) (b) Both (III) and (IV), (ii) (c), RollNo, , Name, , Class, , DOB, , Gender City, , Marks, , 1, , Priti, , XII, , 08-08-1995, , F, , Mumbai 492, , 5, , Saniya, , XII, , 08-10-1997, , F, , Delhi, , 360, , (iii) (d) SELECT Class, MAX(Marks) FROM Student GROUP BY Class;, (iv) (b) Both (II) and (IV), (v) (b) SELECT Name,MAX(DOB) FROM Student ;, 2. Degree = 4, Cardinality = 6, 3. (i) Candidate Keys :- Id, Product, (ii) Primary Key :- Id, Or (i) SELECT WNO, NAME, GENDER FROM WORKER ORDER BY WNO DESC;, (ii) SELECT NAME FROM WORKER WHERE GENDER = "FEMALE";, (iii) SELECT WNO, NAME FROM WORKER WHERE DOB BETWEEN ‘1987-01-01’ AND ‘1991-12-01’;, (iv) SELECT COUNT(*) FROM WORKER WHERE GENDER = "MALE" AND DOJ > ‘1986-01-01’;, (v), , COUNT (*) DCODE, 2, , D01, , 2, , D05, , 4. CREATE TABLE SUPPLIERS, , (, Product_id INT(4),, Product_Name CHAR(10),, Quantity INT(10),, Price DECIMAL(7,2),, Phone CHAR(10), );, Or (i), (ii), (iii), 5. (i), , SELECT Type, AVG(Price) FROM Vehicle GROUP BY Type HAVING Qty > 20;, SELECT Company, COUNT(DISTINCT Type) FROM Vehicle GROUP BY Company;, SELECT Type, SUM(Price* Qty) FROM Vehicle GROUP BY Type;, mysql>SELECT CURDATE();, Output 2021-11-01, (ii) mysql>SELECT INSTR(“CORPORATE LAWYER”, ‘‘OR”);, Output 2, (iii) SELECT * FROM Students ORDER BY AGGREGATE, NAME DESC;, , Or (i), (ii), (iii), 6. (i), (ii), (iii), (iv), (v), , 64, 88, , SELECT Name, Class FROM Students WHERE Course_name IS NULL OR Course_Name LIKE “%economics”;, DAYNAME(DATE(curdate())), LTRIM(“ Python’’), MONTHNAME(date(dob)), INSTR(“Information Technology”,‘‘Information”), POW(a,b)
Page 94 :
@Cbsebookshub - Join Us on Telegram, , 82, , CBSE Term II Informatics Practices XII, , 7. (i) (a) Satellite communication, (b) Bluetooth or infrared whichever is supported by the phone., (ii) Domain in http://www.cbsenic.in/aboutus.htm is “www.cbsenic.in”., Or (i) HyperText Transfer Protocol, (ii) Advanced Research Projects Agency NETwork, (iii) Virtual Private Network, (iv) Modulator Demodulator, (v) Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol, (vi) Domain Name System, 8. The call quality of cloud communciations systems depends on the speed and reliability of your Internet. You will hear a vast, improvement in call quality compared to traditional landlines. Landlines don’t have as much audio bandwidth, which can result in, muffled or fuzzy calls., VoIP calles achieve this through HD voice technology., Find out your Internet speed by taking the VoIP speed test., Or (i) Most suitable layout according to distance is, , W1, , W2, , W3, , W4, , (ii) Star topology, (iii) Broadband, (iv) (a) Repeaters may be skipped as per above layout, (b) In every wing, (v) Radiowaves, 9. (i), (ii), (iii), (iv), (v), Or (i), (ii), (iii), (iv), (v), (vi), , (because distance is less than 100 m)., , Primary Key – Rollno, Degree of table= 5, , INSERT INTO Fees VALUES(101,‘Aman’,‘XII’,5000);, DELETE FROM Fees;, Describe Fees;, SELECT Name FROM Sports WHERE Grade1=’A’ OR Grade2=‘A’;, SELECT COUNT(*) FROM Sports Where Game1=‘Cricket’ OR Game2=’Cricket’;, SELECT Name FROM Sports WHERE Game1=Game2;, SELECT Game1,Game2 FROM Sports WHERE Name LIKE ‘A%’;, , 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, (vii) 10, (viii) 2, 2, 1, 1