Page 1 :
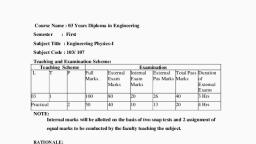
WEST BENGAL STATE COUNCIL OF TECHNICAL & VOCATIONAL, EDUCATION AND SKILL DEVELOPMENT, (A Statutory Body under West Bengal Act XXVI of 2013), (Technical Education Division), Karigari Bhavan, 4th Floor, Plot No. B/7, Action Area-III, Newtown, Rajarhat, Kolkata–700 160, , WBSCTVESD Curriculum for Diploma Courses in Engineering and, Technology, , Semester I, (Common to all Branches), , P, , Total, contact, hrs/, week, , Credi, ts, , Marks, , 1, 1, 1, , 0, 0, 0, , 3, 3, 3, , 3, 3, 3, , 100, 100, 100, , 2, , 0, , 0, , 2, , 2, , 100, , 0, , 0, , 3, , 3, , 1.5, , 100, , Sl., No, , Hours per, week, , Category of, Course Title, Course, 1. Basic Science, Mathematics-I, 2. Basic Science, Applied Physics-I, 3. Basic Science, Applied Chemistry, 4. Humanities &, Communication Skills, Social Science, in English, 5. Engineering, Engineering Graphics, Science, 6. Engineering, Engineering Workshop, Practice, Science, 7. Basic Science, Applied Physics-I Lab, 8. Basic Science, Applied Chemistry Lab, 9. Humanities &, Sports and Yoga, Social Science, 10. Humanities &, Communication Skills, Social Science, in English Lab, Total Credits and Marks, , L, , T, , 2, 2, 2, , *******, , 100, 0, 0, 0, , 0, 0, 0, , 3, 2, 2, , 3, 2, 2, , 1.5, 1, 1, , 0, , 0, , 2, , 2, , 1, , 0, , 0, , 2, , 2, , 1, , 100, , 18, , 1000, , 100, 100, 100
Page 2 :
Syllabus for Engineering Mathematics-I, Course Title:, Course Code:, Number of Credits :, Pre Requisites :, Total Contact Hours :, , Engineering Mathematics-I, BS101/M-I, 3(L: 2+1: T) P: 0, 1) Basic Formulae of Algebra, Trigonometry should be known, 2) Preliminary knowledge of the vector, 45 hrs., , Aim: Engineering Mathematics is the backbone of engineering students. The curriculum of mathematics, has undergone changes from time to time in accordance with the need of engineering branches. The revised, syllabus has been designed keeping in view the emerging needs of all categories of students. Great emphasis, has been laid on the application of various contents like algebra, complex numbers, vectors, trigonometry, and derivative. This course will develop analytical abilities to make exact calculations and provide a, continuing educational base for the students., , Course Objectives: After the completion of the course the students will be able to, apply the basic concepts of logarithm, complex number, quadratic equation and, binomial theorem for solving the engineering and practical problems., find the solutions of vector oriented problems like work done, moment etc by applying, vector algebra., simplify trigonometric expressions and solve trigonometric equations which will be, useful in solving the scientific problems., analyze limit, continuity, derivatives of different functions and physical interpretation, of derivatives which will be applicable in real situation., , Course Content, Unit-1, Algebra, 1.1 Logarithm:, , 3 Hours, , 1.1.1 Definition of natural and common logarithm., 1.1.2 General Properties of logarithm and simple problems, , Page 1 of 6
Page 3 :
Syllabus for Engineering Mathematics-I, 1.2 Complex Numbers:, , 5 Hours, , 1.2.1 Definition of Complex numbers, Real and Imaginary parts of a complex number, Equality of two, complex numbers, Conjugate of a complex number, 1.2.2 Modulus and Argument of a complex number and simple problems, 1.2.3 Polar and Cartesian forms of a complex number and their relation., 1.2.4 Algebraic operations (Addition, Subtraction, multiplication, Division) of complex numbers, 1.2.5 De Moivre's Theorem (without proof) and simple problems., 1.2.6 Cube roots of unity and their properties with problems., , 1.3 Quadratic Equations:, , 4 Hours, , 1.3.1 Definition of Quadratic Equations., 1.3.2 Finding the roots of a quadratic equation, conjugate roots& simple problems, 1.3.3 Nature of the roots using discriminant & problems, 1.3.4 Relation between roots and co-efficients & problems, 1.3.5 Formation of quadratic equations if roots are given., , 1.4 Binomial Theorem:, , 4 Hours, , 1.4.1 Definition of factorial of a number, permutation(, , )& combination (, , ) with formula only, , 1.4.2 Binomial Theorem (without proof) for any index, simple problems on positive index only, 1.4.3 General Term and Middle Term and problems, 1.4.4 Expansion of(1 + ) , (1 − ) , ℎ, , | | < 1, exponential & logarithmic series only (no, , problem), , Unit-2, Vector Algebra, , 7 Hours, , 2.1 Definition of vector and types of vectors, 2.2 Concept of a position vector and Ratio formula& simple problems, 2.3 Rectangular resolution of a vector, 2.4 Equality, addition, subtraction of vectors and multiplication of a vector by a scalar, 2.5 Scalar (dot) and Vector (cross) product of two vectors with properties & simple problems, 2.6 Application of dot product -- work done by a force, projection of a vector upon another, 2.7 Application of cross product -- finding area of a triangle and parallelogram, moment of a force, Page 2 of 6
Page 4 :
Syllabus for Engineering Mathematics-I, Unit-3, Trigonometry, , 10 Hours, , 3.1 Concept of trigonometrical angles, measurement of angles in degree, radian and grade & their relation, only., 3.2 Trigonometrical ratios of angles, associated angles, Trigonometric ratios of some standard angles,, problems, 3.3 Compound angles formula (without proof), multiple, sub-multiple angles & simple problems, 3.4 Solutions of Trigonometrical Equations, simple problems (angle lies between 0 and 2 ), 3.5 Inverse Circular Function & simple problems, 3.6 Properties of triangle, basic formulae only, , Unit-4, Function, Limit & Continuity, Derivative, 4.1 Function, , 2 Hours, , 4.1.1 Definition of variables & constants, 4.1.2 Definition of function with examples, domain and range of a function, 4.1.3 Types of functions (even-odd, increasing-decreasing, inverse, periodic) with simple examples, 4.1.4 Graph of trigonometric functions, sin x, cos x, tan x only, , 4.2 Limit & Continuity, , 2 Hours, , 4.2.1 Definition of limit (with left hand limit & right hand limit), Fundamental Theorem on limit (only, statement), standard limits and simple problems, 4.2.2 Continuity of functions, elementary test for continuity of functions (finite limit), , 4.3 Derivative, , 8 Hours, , 4.3.1 Definition of derivatives, 4.3.2 Derivatives of standard functions, 4.3.3 Rules of differentiation of sum, difference, product and quotient of functions., 4.3.4 Derivatives of composite functions (Chain Rule), 4.3.5 Derivatives of inverse circular functions, implicit functions and logarithmic differentiation, 4.3.6 Derivative of parametric functions, derivative of a function with respect to another function, Page 3 of 6
Page 5 :
Syllabus for Engineering Mathematics-I, 4.3.7 Second order derivatives with simple problems, 4.3.8 Application of derivatives –Physical & Geometrical interpretation of derivative, checking increasingdecreasing functions, finding velocity & acceleration, Maxima-Minima of function of single variable, with simple problems., , Page 4 of 6
Page 6 :
Syllabus for Engineering Mathematics-I, , Examination Scheme:, A. Semester Examination pattern of 60 marks:, 1. Objective questions- 20 marks (1 mark each question), (At least 5 question from each, group), 2. Subjective questions- 40 marks (at least 2 questions of 10 marks from each group), Group- A contains Unit-1 & Unit-2 (At least 40 marks); Group-B contains Unit-3, (At least 20 marks); Group-C contains Unit-4(At least 20 marks), N.B.- Student will answer objective type questions of 20 marks and for subjective question, of 40 marks, taking at least one question from each group of the above three groups., B. For the internal Assessment 40 marks:, 1. Class Test Examination/Internal Examination; 20 marks; choose best two out of three, Class Test Examinations/ Internal Examinations, 2. Class Attendance; 10 marks, 3. Viva/ Quiz/Presentation/Assignment/Project/Report etc.; 10 marks, , Page 5 of 6
Page 8 :
Applied Physics for Sem-I (Theory), Reviewed and prepared by Syllabus-Sub-committee, on the basis of recommendation of AICTE, , Sem –I (Theory), Course Code, Course Title, Number of credits, Prerequisites, Course Category, , :, :, :, :, :, , BS103, Applied Physics-I, 3 (L: 2, T: 1, P: 0), High School Level Physics, BS, , Course Content:, Unit 1: Physical world, Units and Measurements, Physical quantities; fundamental and derived, Units and systems of units ( CGS and SI units),, Dimensions and dimensional formulae of physical quantities, Principle of homogeneity of dimensions, Dimensional equations and their, applications (conversion from one system of units to other, checking of dimensional equations and derivation of simple equations),, Limitations of dimensional analysis., Measurements: Need, measuring instruments, least count, types of Measurement (direct, indirect), Errors in Measurements, (systematic and random), absolute error, relative error, error propagation, error estimation and significant figures., Unit 2: Force and Motion, , Force, Momentum, Conservation of linear momentum, its applications such as recoil of gun, numerical problems rockets, ( concept only), Impulse and impulsive force., Circular motion, definition of angular displacement, angular velocity, angular acceleration, frequency, time period, relation, between linear and angular velocity, linear acceleration and angular acceleration (related numerical), concept of, Centripetal and centrifugal forces with examples (No derivation, only formula) banking of roads and bending of, cyclist,concept and formula and numerical problems., , Unit 3: Work, Power and Energy, Work: Concept and units, examples of zero work, positive and negative work, Friction: concept, types, laws of limiting friction, coefficient of friction, reducing friction and its engineering applications,, Work done in moving an object on rough inclined plane., Energy and its units, kinetic energy and potential energy, Conservation of mechanical energy for freely falling bodies(, simple numerical problems), transformation of energy (examples only)., Power and its units, power and work relationship, calculation of power (numerical problems)., , Unit 4: Rotational Motion, Translational and rotational motion with examples, Definition of torque and angular momentum and their relation,, Conservation of angular momentum (quantitative) and its applications., Moment of inertia and its physical significance, radius of gyration for rigid body, Theorems of parallel and perpendicular, axes (statements only), Moment of inertia of rod, disc, ring and sphere (hollow and solid); (Formulae only). Simple, numerical problems., , Unit 5: properties of Matter, Elasticity: definition of stress and strain, moduli of elasticity, Hooke’s law, significance of stress-strain curve.
Page 9 :
Surface tension: Concept, units, cohesive and adhesive forces, angle of contact, Capillary rise ( formula only), applications, of surface tension, effect of temperature and impurity on surface tension., Viscosity and coefficient of viscosity: terminal velocity, Stoke’s law and effect of temperature on viscosity., Hydrodynamics: Fluid motion, stream line and turbulent flow, Reynold’s number Equation of continuity, Bernoulli’s, Theorem (only formula and numericals) and its applications (mention name only)., , Unit 6: Heat and Thermometry, Concept of heat and temperature, basic concepts of measurements of heat and temperature, modes of heats transfer, (conduction, convection and radiation with examples), Co-efficient of thermal conductivity simple numerical problems., Expansion of solids, liquids and gases, coefficient of linear, surface and cubical expansions of solids and relation amongst, them, specific heats Cp & Cv of a gas and their relationship (Mention only)., , References:, 1., 2., 3., 4., 5., 6., 7., 8., , Text Book of Physics for Class XI& XII (Part-I, Part-II); N.C.E.R.T., Delhi, Applied Physics, Vol. I and Vol. II, TTTI Publications, Tata McGraw Hill, Delhi., Concepts in Physics by HC Verma, Vol. I & II, Bharti Bhawan Ltd. New Delhi, Engineering Physics by PV Naik, Pearson Education Pvt. Ltd, New Delhi, Engineering Physics by DK Bhattacharya & Poonam Tandan; Oxford University Press, New Delhi, Comprehensive Practical Physics, Vol,I & II, JN Jaiswal, Laxmi Publications (P) Ltd., New Delhi, Practical Physics by C.L. Arora, S. Chand Publication., Comprehensive Physics Vol,I & II.
Page 10 :
Applied Physics for Sem-I (Lab), Course Code, Course Tittle, , :, :, , BS107, Applied Physics-I Labs, , Numbers of Credits, Prerequisites, , :, :, , 1 (L:0, T:0, P:2), NIL, , Course Category, , :, , BS, , Course Objectives:, Study of Applied Physics aims to give an understanding of physical world by observations and, predictions. Concrete use of physical principles and analysis in various fields of engineering and, technology is very prominence. The course aims to supplement the factual knowledge gained in the, lecture by first hand manipulation of apparatus. This will develop scientific temper and help to apply the, basic concepts and principles in solving engineering and technology based problems. In addition,, students get necessary confidence in handling equipment and thus learn various skills in measurement., List of Practical’s/Activities(To perform minimum 8 practical’s)., 1. To measure the volume of the material of a given hollow cylinder, using a Vernier calipers., 2. To determine the area of cross section of a thin wire using a screw gauge., 3. To determine radius of curvature of a convex and a concave mirror/ surface using a spherometer., 4. To find the co-efficient of friction between wood and glass using a horizontal board., 5. To determine force constant of a spring using Hook’s law., 6. To find the moment of inertia of a flywheel., 7. To find the viscosity of a given liquid (Glycerin) by Stoke’s law, 8. To find the co-efficient of linear expansion of the material of a rod., 9. To verify Boyle’s law., 10. To determine the relative density of sand by using a sp. gr. Bottle., Reference books:, 1. Text books of Physics for Class-XI & XII (Part-I & II); N.C.E.R.T., Delhi., 2. Comprehensive Practical Physics, Vol-I & II, JN Laxmi Publications (P) Ltd.,, 3. Practical Physics by C.L. Arora, S. Chand Publication.
Page 11 :
Applied Chemistry, Course Code, Course Title, Number of Credits, Prerequisites, Course Category, , :, :, :, :, :, , BS105, Applied Chemistry, 3 (L: 2, T: 1, P: 0), High School Level Chemistry, BS, , Course Objectives:, There are numerous number materials used in fabricating and manufacturing devices for the comfort, of life. The selection, characterization and suitability assessment of natural raw materials essentially, requires principles and concepts of Applied Chemistry for technicians. On successful completion of, this course content will enable technicians to understand, ascertain and analyse and properties of, natural raw materials require for producing economical and eco-friendly finished products., Solve various engineering problems applying the basic knowledge of atomic structure and, chemical bonding., Use relevant water treatment method to solve domestic and industrial problems., Solve the engineering problems using knowledge of engineering materials and properties., Use relevant fuel and lubricants for domestic and industrial applications, Solve the engineering problems using concept of Electrochemistry and corrosion., Instruction on question setting:, Question paper contains three groups A, B and C. Unit 1 and unit 2 are included in group A, unit, 3 and unit 4 in group B, unit 5 in group C., 20 (twenty) number of questions are of objective types consisting of all groups, each carrying 1, (one) mark., 5 (five) questions are to be answered taking at least one from each group (each question carries 8, marks)., Course Content:, Unit 1: Atomic Structure, Chemical Bonding and Solutions, Rutherford model of atom, Bohr's theory (expression of energy and radius to be omitted), and, hydrogen spectrum explanation based on Bohr's model of atom, Heisenberg uncertainty principle,, Quantum numbers - orbital concept. Shapes of s, p and d orbitals Pauli's exclusion principle, Hund's, rule of maximum multiplicity Aufbau rule, electronic configuration., Type of chemical bonding: ionic, covalent, metallic and hydrogen bonds. Example of each type., Hybridization, sp3, sp2, sp, example: BeCl2, BF3, CH4, NH3, H2O; structure of diamond, graphite., Solution - idea of solute, solvent and solution, methods to express the concentration of solutionmolarity (M = mole per liter), ppm, mass percentage, volume percentage and mole fraction., ,, , Unit 2: Water, Graphical presentation of water distribution on Earth (pie or bar diagram). Classification of soft, and hard water based on soap test, salts causing water hardness, unit of hardness and simple, numerical on water hardness., Cause of poor lathering of soap in hard water, problems caused by the use of hard water in boiler, (scale and sludge, foaming and priming, corrosion etc), and quantitative measurement of water, hardness by ETDA method, total dissolved solids (TDS) alkalinity estimation., 1) Water softening techniques - soda lime process, zeolite process and ion exchange process., 2) Municipal water treatment (in brief only) - sedimentation, coagulation, filtration, sterilization., Water for human consumption for drinking and cooking purposes from any water sources and enlist, Indian standard specification of drinking water (collect data and understand standards).
Page 12 :
Applied Chemistry, Unit 3: Engineering Materials, Natural occurrence of metals - minerals, ores of iron, aluminium and copper, gangue (matrix), flux,, slag, metallurgy - brief account of general principles of metallurgy. Extraction of iron from haematite, ore using blast furnace, aluminium from bauxite along with reactions, reactions during copper, extraction. Alloys – definition, purposes of alloying, ferrous alloys and non-ferrous with suitable, examples, properties and applications., General chemical composition, composition based applications (elementary idea only details omitted):, Port land cement and hardening, Glasses Refractory and Composite materials., Polymers - monomer, homo and co polymers, degree of polymerization, simple reactions involved in, preparation and their application of thermoplastics and thermosetting plastics (using PVC, PS, PTFE,, nylon - 6, nylon - 66, Bakelite only), rubber and vulcanization of rubber., Unit 4: Chemistry of Fuels and Lubricants, Definition of fuel and combustion of fuel, classification of fuels, calorific values (HCV and LCV),, calculation of HCV and LCV using Dulong's formula., Proximate analysis and ultimate analysis of coal solid fuel, petrol and diesel - fuel rating (octane and cetane numbers),, Chemical composition, calorific values and applications of LPG, CNG, water gas, coal gas, producer, gas and biogas., Lubrication - function and characteristic properties of good lubricant, classification with examples,, lubrication mechanism - hydrodynamic and boundary lubrication, physical properties (viscosity and, viscosity index, oiliness, flash and fire point, could and pour point only) and chemical properties, (coke number, total acid number saponification value) of lubricants., Unit 5: Electro Chemistry, Electronic concept of oxidation, reduction and redox reactions., Definition of terms: electrolytes, non-electrolytes with suitable examples, Faradays laws of, electrolysis and simple numerical problems., Elementary concept of pH and buffer., Industrial Application of Electrolysis –, • Electrometallurgy, • Electroplating, • Electrolytic refining., Application of redox reactions in electrochemical cells –, • Primary cells - dry cell,, • Secondary cell - commercially used lead storage battery, fuel and Solar cells., Introduction to Corrosion of metals –, • definition, types of corrosion (chemical and electrochemical), H2 liberation and O2 absorption, mechanism of electrochemical corrosion, factors affecting rate of corrosion., Internal corrosion preventive measures –, • Purification, alloying and heat treatment and, External corrosion preventive measures: a) metal (anodic, cathodic) coatings, b) organic inhibitors., , 2
Page 13 :
Applied Chemistry, Suggested Sessional work:, •, , Unit 1: Atomic Structure, Chemical Bonding and Solutions, Assignments: Writing electronic configuration of elements up to atomic number 30, (Z= 30). Numerical on molarity, ppm, mass percentage, volume, percentage and mole fraction of given solution., Seminar:, 1. Quantum numbers,, 2. Discuss the metallic properties such as malleability, ductility,, hardness, high melting point, conductance of heat and electricity,, magnetic properties of metals., Projects:, Model of molecules BeCl2, BF3, CH4, NH3, H2O, , •, , Unit 2: Water, Assignments: Simple problems on hardness calculation., Seminar:, 1. Quality and quantity requirement of water in house and industry., 2. Quality of control measures of effluents (BOD & COD)., Projects:, Collect water samples from different water sources and measure of, hardness of water., , •, , Unit 3: Engineering Materials, Assignments: Preparation of table showing different ores of iron, copper and, aluminium metals along with their chemical compositions and classify, in to oxide sulphide halide ores., Seminar:, Discuss the chemical reactions taking place in Blast Furnace in, extraction of iron; Reactions occurring during extraction of copper and, aluminium metals., Projects:, Make table showing place of availability of different ores in India and, show places on India map., , •, , Unit 4: Chemistry of Fuels and Lubricants, Assignments: Calculation of HCV and LCV of fuel using fuel composition in, Dulong's formula., Seminar:, Chemical structure of fuel components influence on fuel rating., Projects:, Mapping of energy recourses in India. Collection of data of various, lubricants available in the market., , •, , Unit 5: Electro Chemistry, Assignments: Simple problems on Faradays laws of electrolysis., Seminar:, 1. Corrosion rate and units., 2. Corrosion preventions., Projects:, Mapping of area in India prone to corrosion. Collection of data of, various electrochemical cells batteries used in equipment and devices, and available in market. Visit to sites such as Railway station to watch, corrosion area in railways and research establishment in and around, the institution., , 3
Page 14 :
Applied Chemistry, References/Suggested Learning Resources:, (a) Books:, 1) Text Book of Chemistry for Class XI& XII (Part-I, Part-II); N.C.E.R.T., Delhi, 2017-18., 2) Agarwal, & Shikha, Engineering Chemistry, Cambridge University Press; New Delhi, 2015., 3) C.N. R. Rao, Understanding Chemistry, Universities Press (India) Pvt. Ltd., 2011., 4) S. S. Dara & S.S.Umare, Engineering Chemistry, S. Chand. Publication, New Delhi, New, Delhi, 2015., 5) Jain & Jain, Engineering Chemistry, Dhanpat Rai and Sons; New Delhi, 2015., 6) S. Vairam, Engineering Chemistry, Wiley India Pvt.Ltd., New Delhi, 2013., 7) G. H. Hugar & A. N. Pathak, Applied Chemistry Laboratory Practices, Vol. l and Vol. II,, NITTTR, Chandigarh, Publications, 2013-14., 8) Rajesh Agnihotri, Chemistry for Engineers, Wiley India Pvt.Ltd., 2014., (b) Open source software and website address:, 1) www.chemguide.co.uk/atommenu.html (Atomic structure and chemical bonding), 2) www.visionlearning.com (Atomic structure and chemical bonding), 3) wwwcheml.com (Atomic structure and chemical bonding), 4) https://www.wastewaterelearning.com/elearning/ (Water Treatment), 5) www.capital-refractories.com (Metals, Alloys, Cement, and Refractory Materials), 6) www.em-ea.org/guide%20books/book-2/2.1%20fuels%20and%20combustion.pdf (Fuel and, Combustion), 7) www.chemcollective.org (Metals, Alloys), 8) www.wqa.org(Water Treatment), , Applied Chemistry Lab, Course Code, Course Title, Number of Credits, Prerequisites, Course Category, , :, :, :, :, :, , BS109, Applied Chemistry Lab, 1 (L: 0, T: 0, P: 2), NIL, BS, , Course Objectives:, There are numerous number of materials used in fabricating and manufacturing devices for the, comfort of life. The selection, characterization and suitability assessment of natural raw, materials essentially requires principles and concepts of Applied Chemistry for technicians. The, course aims to supplement the factual knowledge gained in the lectures by first hand manipulation, of processes and apparatus. This will develop scientific temper and help to apply the basic, concepts and principles in solving engineering problems., LIST OF PRACTICALS:, Perform any 12 (twelve) Laboratory Practicals:, Volumetric and Gravimetric analysis., 1. Preparation of standard oxalic acid and standard potassium dichromate solution., 2. To determine strength of given sodium hydroxide solution by titrating against standard oxalic, acid solution and phenolphthalein as indicator., 3. Standardization of potassium permanganate solution using standard oxalic acid and, determination of percentage of iron present in given Hematite ore by KMnO4 solution, 4. a) Standardization of sodium thiosulphate using standard potassium dichromate solution by, IODOMETRY., 4
Page 15 :
Applied Chemistry, b) Iodometric estimation of copper in copper pyrite ore., 5. Volumetric estimation of total acid number (TAN) of given oil., 6. Volumetric estimation of, a. Total hardness of given water sample using standard EDTA solution., b. Alkalinity of given water sample using 0.01N sulphuric acid., 7. Proximate analysis of coal, a. Gravimetric estimation moisture in given coal sample., b. Gravimetric estimation ash in given coal sample, Instrumental analysis, 8., 9., 10., 11., 12., 13., 14., 15., , Determine the conductivity of given water sample., Determination of the Iron content in given cement sample using colorimeter., Determination of viscosity of lubricating oil using Redwood viscometer., Determination of flash and fire point of lubricating oil using Able's flash point apparatus., To verify the first law of electrolysis of copper sulfate using copper electrode., Construction and measurement of emf of electrochemical cell (Daniel cell)., To study the effect of dissimilar metal combination on cell emf., To apply thin layer chromatography for separation of mixture of inorganic/organic, compounds., 16. Qualitative detection of ARSENIC in a given sample of water (~5 ppm solution of sodium, arsenite), 17. Determination of dissolved oxygen in a sample of water., 18. Determination of pH value of unknown solution., Reference book, VOGELS INORGANIC QUANTITATIVE ANALYSIS., Members present in Syllabus Committee:, 1. Dr. Ujjval Kumar Bhattacharyya (convener, lecturer, North Calcutta Polytechnic)., 2. Dr. Gandhi Kumar Kar (Professor and head of the Dept. of Chemistry, Presidency, University, Kolkata), 3. Dr. Shyamal Kumar Chattopadhyay (Professor IIEST, Shibpur)., 4. Dr. Mrinal Kanti Bain, lecturer, Calcutta Technical School., 5. Dr. Dipankar Maity, lecturer, Birla Institute of Technology., 6. Dr. Ranjal Paul, Sr. Manager, Sun Pharmaceuticals Baroda., 7. Prolay Roy, lecturer, Memari Government Polytechnic., , 5
Page 16 :
Syllabus of Communication Skills in English, {The syllabus for the subject has been prepared by the Syllabus Sub-committee for the subject, “Communication Skills in English” in accordance with the following instructions / directions, received from Mr. B. Samanta (WBSCTVESD) vide his mail dated Dec. 6, 2019 at 12.04 PM}:“A meeting was held on 31.10.2019 at the Council. In the meeting following decisions were, taken by the Council, 1. It was decided unanimously to adopt the curriculum structure of the AICTE model syllabus, 2019( attached) for all diploma courses of WBSCTVESD., 2. New curriculum structure and syllabus of diploma courses shall be prepared as per, AICTE model Syllabus 2019 and implemented from the next academic session i.e. 2020-21 in, phase manner., 3., Content of the syllabus of diploma courses shall be customized as per the requirement and, as per the advice of the syllabus sub- committee.”, Sl. No., , Code, No., , 1, , HS 101, , 2, , HS105, , Course Title, , Hours per week (Total-4), Lecture Tutorial Practical, , Communication, Skills in, 2, 0, 0, English, Communication, Skills in, 0, 0, 2, English - Lab, Total number of weeks – 17 (seventeen), , Semester, , Credits, , 1, , 2, , 1, , 1, , Preamble:, Engineering is a service, and therefore it exists to meet human needs. Needs are communicated, through language. No engineer, no matter how brilliant, can do a good job if she or he does not, know what the job is for, who they are serving, for what purpose, and what needs to be done to, render this service. Feedback also has to be communicated in language: figures are not enough, without explanation. Communication, spoken or written, is thus essential for any service, provider to do their job., However, in most cases the courses and syllabi offered to STEM undergraduates do not, adequately address the need to make them good communicators. It is often assumed that this, question has been addressed by schooling, or they attempt to adapt liberal arts courses to the, needs of STEM workers, thereby failing to address those needs. In a country such as India where, language learning in general and English learning in particular tend to be neglected or mistaught, this problem is compounded. To be successful, communicative language learning has to, be a two way process, with communication between the teacher and student, and between, students. However, the culture of student passivity in the classroom which prevails in India is, poor soil for these skills to take root., Page 1 of 5
Page 17 :
We have therefore attempted in this course to produce a system that allows, (within the, known constraints) even in a limited form, for project work and conversations, collaboration and, role-play, to mitigate the ‘keep quiet’ culture of the Indian classroom and to encourage young, people to find their voices. Polytechnic, College and university students are just one small step, away from becoming young professionals, and once they take that step their livelihoods (and, also the safety and happiness of their clients) will depend upon how well they can ask and, answer questions in the real world., Without adequate practice, confidence-building and positive reinforcement, the practice of, teaching them the pedantic small points of the rules of English grammar, or obsessing over their, pronunciation, only serves to silence them further. What they need is an environment where they, can communicate with each other and then troubleshoot the results, go over bad communication, and make it better, identify their mistakes and correct them without being terrorised by cultural, stereotypes. Graduate education should be a safe space for them to do this before work in the real, world attaches real penalties to the results of bad communication. With this syllabus and attached, guidelines, we have tried to take a small step in the right direction., Course Title:, , Communication Skills in English, , Course Code No.:, , HS101, , Hours per week:, , 02 (Lecture), Total contact hours / week: 02, , Credits:, , 02, , Course Objectives (AICTE): Communication skills play an important role in career, development. This course aims at introducing basic concepts of communication skills with an, emphasis on developing personality of the students. Thus the main objectives of this course are:, •, •, •, , To develop confidence in speaking English with correct pronunciation, To develop communication skills of the students i.e. listening, speaking, reading and, writing skills, To introduce the need for personality development – Focus will be on developing certain, qualities which will aid students in handling personal and career challenges, leadership, skills etc., , Course Content (Theory), Unit – 1 Communiucation: Theory and Practice, •, •, •, •, , Basics of communication: Introduction, meaning and definition, process of, communication etc., Types of communication: formal and informal, verbal, non-verbal and written. Barriers to, effective communication, 7 Cs for effective communication (considerate, concrete, concise, clear, complete,, correct, courteous)., Art of Effective communication,, Page 2 of 5
Page 18 :
o, o, o, o, o, o, •, , Choosing words, Voice, Modulation, Clarity, Time, Simplification of words, , Technical Communication, , Unit – 2 Soft Skills for Professional Excellence, •, •, •, •, •, , Introduction: Soft Skills and Hard Skills., Importance of Soft Skills., Life skills: Self-awareness and Self-analysis, adaptability, social skills, emotional, intelligence, Interpersonal relationship and empathy etc., Applying soft skills across cultures – Corporate work culture, Work persona,, Professionalism, Time Management, Case Studies, , Unit – 3: Reading Comprehension, Note Taking, Comprehension, vocabulary enhancement and grammar exercises based on reading, of texts., Unit – 4: Professional Writing, The art of writing Report and Memo, CVs, Letters: Job Application and Business, Drafting e-mail, minutes of a meeting, etc, Unit – 5: Vocabulary and Grammar, Remedial Grammar and Exercises, Professional Workplace Communication, Parts of speech, active and passive voice, tenses etc., Course outcomes (AICTE):, At the end of this course, the participants will:, •, •, •, •, , Develop basic speaking and writing skills including proper usage of language and, vocabulary so that they can become highly confident and skilled speakers and, writers., Be informed of the latest trends in basic verbal activities such as presentations,, facing interviews and other forms of oral communication., Also develop skills of group presentation and communication in team., Develop non-verbal communication such as proper use of body language and, gestures, , Page 3 of 5
Page 19 :
Course Title:, , Communication Skills in English - Lab, , Course Code No.:, , HS105, , Hours per week:, , 02 (Practical), Total contact hours / week: 02, , Credits:, , 01, , Course Objectives (AICTE):, Communication skills play an important role in career development. This course aims at, introducing basic concepts of communication skills with an emphasis on developing personality, of the students. Thus the main objectives of this course are:, 1. To develop listening skills for enhancing communication., 2. To develop speaking skills with a focus on correct pronunciation and fluency., 3. To introduce the need for Personality development – Focus will be on developing certain, qualities which will aid students in handling personal and career challenges, leadership, skills, etc. for that purpose group discussion, extempore and other activities should be, conducted during lab classes., Course Content:, Unit – 1:, Basic Common Communication Problems and their Solutions, Unit – 2:, Introduction to Phonetics, Sounds: consonant, vowel. Transcription of words (IPA), weak forms etc., Unit – 3:, Speaking and Listening Skills, Standard and Formal Speech: Oral presentations, Group Discussions, Public Speaking, Business, presentations etc. Conversation practice and role playing, Job interviews, Note taking etc., Unit – 4:, Non-verbal Communication, Proxemics, Haptics and Kinesics, , Page 4 of 5
Page 21 :
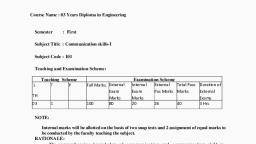
Name of the Course :, , Proposed Syllabus for Engineering Graphics, , Course Code :, , Duration : 17 Weeks, Lecture : Nil, Tutorial : Nil, Practical : 3 hrs./week, Credit : 1.5, , Engineering Graphics, , Semester : First, , Maximum Marks :, Assignment, Class Performance, Viva Voce, , Attendance, External (Viva, Sketch Book & Drawing Sheet), , : 100, : 20, : 20, : 10, : 10, : 40, , Aim :, 1. The Course is aimed to develop the basic graphic skills so that the students can prepare Engineering Drawing in, their practical field., 2. Understand the fundamentals of Engineering Graphics., 3. Read and interpret object drawing., 4. To develop the skills of Computer Aided Drafting and can easily cope up the skill of drafting for modern drawing, offices/industries., , Objectives :, 1. To develop sense of Scale and drawing technique of different curves and their application., 2. To develop drafting and sketching skills, to know the applications of drawing equipment and get familiarize with, Indian Standards related to engineering drawing., 3. To develop concept of Orthographic Projection and to draw Orthographic Views for different objects., 4. To visualize three dimensional objects from Orthographic Views and to draw isometric views/projections., 5. To be familiar with AutoCAD and to develop the skill of drafting in AutoCAD by using different commands., Pre-requisites :, 1. Unambiguous and clear visualization., 2. Sound Pictorial Intelligence., Unit, No., Unit 1, , Unit 2, Unit 3, , Contents, 1.1 Letters and numerals (Single Stroke Vertical), 1.2 Conventions of lines and their applications, 1.3 Concept of Representative Fraction (R.F), Reduced scale, Enlarged scale & Full Scale,, Engineering Scale such as Plain Scale & Diagonal Scale., 1.4 Dimensional Techniques - Unidirectional System and Aligned System., 2.1 Geometrical Construction :, a)Draw Regular Polygons, Ellipse, Parabola, hyperbola, b) Draw Curve passing through given no. of points, cycloid, involute of a circle and polygon, , 3.1 Introduction to Orthographic Projection : Concept of First Angle & Third Angle of projection., Projections of lines( limited to both ends in 1st quadrant) : parallel to the reference planes,, inclined to the reference planes (1st Angle Method), 3.2 Projections of solid body: Regular Polygonal Pyramid, Cylinder, Cone - inclined to only one, reference plane (1st Angle Method)
Page 22 :
Unit 4, Unit 5, Unit 6, , Unit 7, , Sl. No., 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, , 4.1 Conversion of Pictorial Views into orthographic views, (Simple Objects &First Angle Projection Method Only), , 5.1 Introduction to Isometric Projections, Concept of Isometric Scale, and Isometric Views, 5.2 Conversion of Orthographic views into Isometric Views/Projections : Simple Objects e.g. regular, prism, pyramid, cone, cylinder., 6.1 Free hand sketches of engineering elements such as thread profile, nuts, bolts,, studs, set screws, washers, locking arrangements etc. and their conventional, representation (For branches other than Mechanical Engineering, the teachers, should select branch specific elements for free hand sketching), 7.1 Introduction to different commands and toolbars of AutoCAD, a) Draw command : Lines, Circle, Polygon, Arc, Ellipse, Polyline, Fillet, Chamfer,, Hatch, Array (Rectangular & Polar) etc., b) Modify Command : Offset, Trim, Extend, Erase, Fillet, Chamfer, Break, Lengthen,, Copy, Move, Mirror, Stretch, Match Properties, Pedit etc., c) View : Zoom All, Zoom Window, Zoom Extent etc., d) Dimensioning : Dimension Setting, Linear, Aligned, Radial, Diameter, Leader,, Angular etc., c) Text : Text Style, Dtext, Mtext, DDedit etc., d) Format : Limits, Layers, Pan etc., 7.2 Making a few simple 2D drawings in AutoCAD., , Practical Exercise, , Unit No., , Hrs., , Write single stroke vertical alphabets and numerical (7:4 ratio) (Do this exercise in Sketch, Book), , 1, , 02, , Draw regular geometric constructions and redraw/copy the given figure (Do this exercise, in Sketch Book), , 1, , 02, , Draw at least two problems on plain scale and two problems on diagonal scales (Do this, exercise in Sketch Book), , 1, , 03, , Draw problems on ellipse, parabola, involute and cycloid (Do this exercise in Sketch Book), , Draw at least two problems on lines and two problems on solid (First Angle Projection, method) (Do this exercise in A2 size drawing sheet), Plan, Elevation and Side View of at least two pictorial views to be drawn on one A2 size, Drawing Sheet along with dimensions, , 2, 3, , 06, , 4, , 06, , Draw horizontal, vertical, 30˚, 45˚, 60˚, 75˚, different types of lines, dimensioning styles, using Tee and Set Squares / Drafters. (Do this exercise in Sketch Book), , At least Two Isometric Views and two Isometric Projections to be drawn on one A2 size, Drawing Sheet, , 1, , 5, , 02, , 09, , 06
Page 23 :
9, , 10, , Draw free hand sketches / conventional representation of machine elements such as, thread profile, nuts, bolts, studs, set screws, washers, locking arrangements etc., Simple geometrical figures such as triangle, rectangle, polygon, circle, ellipse, and simple, orthographic views of brackets, gaskets etc. to be drawn in AutoCAD and Printout to be, taken on A4 size Sheet. At least two sheets to be prepared., , 6, 7, , Total Period, , Text Books:, , Name of Authors, , Title of the Book, , Edition, , Name of the Publisher, , R.K.Dhawan, , Engineering Drawing, , Revised Edition, 2015, , S.Chand & Co., , N.D.Bhatt, , K. Venugopal &, V. Prabhuraja Raja, Reference Books:, , Engineering Drawing, Engineering Drawing and, Graphics + AutoCAD, , Name of Authors, , Title of the Book, , Basant Agrawal & C M, Agrwal, Dhananjay A Jolhe, , Engineering Drawing, , S.N. Lal, , S.P.Dey, P.S. Gill, , Engineering Drawing, , 53rd Edition, , Edition, , Engineering Drawing with an, Introduction to AutoCAD, AutoCAD 2014, Engineering Drawing, , References :, , 1.Engineering Graphics Syllabus of AICTE Model Curriculum 2019., 2. Syllabus of Technical Drawing (Old) of W.B.S.C.T.E, , Charotkar Publishing House, New Age Publication, , Name of the Publisher, CENGAGE, , Tata McGrew Hill, Tata McGrew Hill, Vikas Publisher, , S.K.Kataria & Sons., , 03, 12, 51
Page 24 :
Engineering Workshop Practice, Course Code, Course Title, Number of Credits, Prerequisites, Course Category, Semester, , :, :, :, :, :, :, , Engineering Workshop Practice, 3(L-0, T-0, P-3), Engineering Science, First, , COMPETENCY, The Engineering Workshop Practice Course should be taught and implemented with the aim to, develop the following Course Outcomes (COs) so that the students will be able to prepare simple, jobs on the shop floor of the engineering workshop., COURSE OUTCOMES, The theory and practical experiences associated with the course, the students will gain the, following industry oriented COs:, , , , , , , , , Read and interpret job drawings, Select tools, equipment and machineries according to the job., Use the hand tools in different shops for performing different operations, Prepare the job according to drawing, Adopt safe working practice., Maintenance of workshop tools, equipment and machineries., Acquaint with the specifications on all raw materials, tools and equipments used., , COURSE CONTENT, Course Content: There are 9 (nine) modules out of which 6 modules should be taught. Selection of, these six modules should be in the following manner., Module 1, 2 and 3 are compulsory and any three from rest as deemed fit for the branch and availability, in the institute., Module No. &, Name, 1. Electrical Wiring, , Details of Workshop Content, 1. Introductory Session, Safety precautions to be followed in Electrical Works, Electric shock, methods of shock treatment, Safety measure: Earthing, Fuse, circuit breakers, etc., Different types of wire-gauge & strands and their, applications, Different tools used in Electrical wiring works, General wiring accessories & their uses., , Hours
Page 25 :
, , , Types of switches and their application., Types of wiring and joints., , 10 hrs, , Practical (any three)- Group works, 1. Study/ demonstration of single phase electrical service, connection from pole to house including consumer, installation., 2. Study of different types of wiring and connection of, Single Phase Motor (Fan)., 3. Circuits for one lamp controlled by one switch by surface, conduit wiring,, 4. Lamp circuits- connection of lamp and socket by separate, switches, Connection of Fluorescent lamp/tube light,, 5. Simple lamp circuits- install bedroom lighting, 6. Simple lamp circuits- install stair case wiring., 7. Wiring of calling-bell, 2. Fitting, , 1. Introductory Session, , , , , , , 3. Welding, , Demonstration of different tools and equipment used in, fitting shop., Study of different precious measuring instrument such, as micrometer, vernier calipers, bevel protectors., Care and maintenance of the above mentioned tools and, equipment., Study of drilling machines and power tools used in, fitting shop., Safety measure to be followed in Fitting shop., , 2. Practical/ Demonstration, Demonstration of different fitting job operations like, chipping, filing, drilling, tapping, sawing, cutting etc., Job Preparation -Individual Works, One simple fitting job involving practice of chipping,, filing, marking, drilling, tapping, cuttingetc., 1. Introductory Session, Purpose of welding, advantages & disadvantages of it, over other joining processes., Types of welding processes (in brief), Specification, usage, care & maintenance of various, welding machines, tools & equipment used in the shop., Selection of welding methods and electrodes., Safety measures & equipment required while working in, welding shop., , 10 hrs, , 10 hrs
Page 26 :
2. Practical/ Demonstration, How to start an Arc & use it for Arc Welding, sustainably., Demonstration of various welding m/c, tools, equipment, available in the shop., Demonstration of shielded metal arc welding (SMAW),, Gas welding and cutting., Repairing of broken metal structures using welding., Defects of welding & their remedies., Job Preparation (Any One)-Individual Works, Job 1 – Butt Joint, Job 2 – Lap Joint, Job 3 – ‘T’ Joint, 4. Carpentry, , 1. Introductory Session, Raw materials used in carpentry shop: wood & alternative, materials., Specification, usage, care & maintenance of various tools,, equipment and machineries used in the Carpentry shop., Types of wood. Difference between hard and soft wood., Timber: characteristics, usage and defects. Difference, between wood and timber., Seasoning of wood., Different types of joints such as cross half-lap joint,, through tenon and mortise joint, dove tail joints, etc., Safety measures to be taken in carpentry shop., 2. Practical/Demonstration, Demonstration of use of different tools, equipment and, machineries., Demonstration of different wood working processes, like, plaining, marking, chiseling, grooving, turning of wood, etc., Job Preparation -Individual Works, One simple job involving any one joint., , 5. Sheet Metal, Working, , 1. Introductory Session, Briefing on different types of sheet metal, like Stainless, Steel Sheet Metal, Copper Sheet Metal, Brass Sheet, Metal, Corrugated Sheet Metal, Galvanized Sheet Metals, etc., and their uses., Demonstration of different types of Tools& machines and, their use in sheet metal work., , 10 hrs
Page 27 :
, , , , , , Demonstration of different types sheet metal joints and, their applications., Demonstration of different types of sheet metal working:, cold working, hot working, warm working, bending,, drawing, end curling, shearing, piercing, sheet metal, presses, etc., Sheet metal joining operation like welding, brazing,, soldering and riveting., Safety measure to be followed in sheet metal work., , 10 hrs, , 2. Practical:, Making of any simple job(example: sheet metal mug), involving different sheet petal operations including, soldering and riveting., 6. Smithy/Forging, , 1. Introductory Session, Purpose of Smithy / Forging Works, Different types of Hearths used for Smithy / Forging, works, Specification, usage, care and maintenance of various, tools and equipment used in the shop., Types of raw materials used in Smithy / Forging shop, & their required temperature for it., Types of fuel used in hearth and the respective, maximum temperature obtained., Uses of Fire Bricks & Clays in Smithy/Forging Work, Shop., Types of heat treatment processes involved in Smithy /, Forging shop and its effect on forged items., Hot forge & cold forge utility., Safety measures & equipment required while working, in Smithy / Forging Shop, 2. Practical/ Demonstration, Practice / Demonstration of firing of hearth / Furnace,, Cleaning of Clinkers and Temperature Control of Fire., Practice / Demonstration on different basic Smithy /, Forging operations such as Upsetting, Drawing down,, Setting down, Necking, Cutting, Bending, Fullering,, Swaging, Punching and Drifting etc., Demonstration on making of, Cube, hexagonal cube, hexagonal bar from round bar., Hexagonal /octagonal flat chisel including tempering of, edges., , 10 hrs
Page 28 :
7. Machine shop, Practice, , Job Preparation (Any one) – group effort by students, Job 1 Making a cold / hot flat chisel, Job 2 Simple Tong, Job 3 Production of any other utility tools/ items -e.g., Chain-links, door ring, hexagonal bolt / square shank, boring tool, fan hook (long S-type) etc., 1., Introductory Session, Purpose of a machine shop/ workshop in industry., Demonstration of all available tools & tackles of, machine shop., Inculcation of basic idea of machine tool;, differentiation between machine & machine tool., Familiarization of all machine tools in the machine, shop., Safety precautions for working in a machine shop., 2., , Practice in Machine Shop, , 10 hrs, , , , Identification of different parts of a lathe and utility of, those parts., Demonstration of all possible machining operation on a, lathe, e.g. turning, facing, parting, taper turning,, drilling, threading etc., Demonstration to operate a drilling machine or shaping, machine and identifying different parts of that m/c tool., Job Practice-(Individual work), Preparation of one job in Lathe, involving simple, machining operations (e.g. turning, facing, grooving,, threading, knurling etc.)., 8. Electronic Shop, , 1. Introductory Session, Discussion on active and passive electronic, components., Discussion on soldering and its use., Introduction on multi-meter and its use., Discussion on use of test equipment in fault finding., Discussion on resistor, capacitor, amplifiers, relay,, diodes, zener diode and LEDs., Safety measure to be followed in electronic shop., 10 hrs, 2. Practical/ Demonstration, Familiarization, identification and testing of active and, passive components., Soldering and de-soldering practice.
Page 29 :
, , , 9. Demonstration, , Use of Multi meter (both Analog and digital)., Demonstration of resistor, capacitor, amplifiers, relay,, diodes, zener diode and LEDs., , Following demonstration may be conducted:, 1. Demonstration of measurement of Current, Voltage,, Power and Energy for an electrical system/ wiring., 2. Demonstration of advanced power tools such as, pneumatic tools, electrical portable grinding tools and, accessories., 3. Demonstration of bourdon tube pressure gauge., 4. Demonstration of ball bearing and roller bearing., 5. Demonstration of portable power tools for Cutting and, drilling, etc., , 10 hrs, , LEARNING OUTCOMES (LOs), At the end of the course, the student will be able to:, , , , Understand the basic safety measure to be followed in different works., Understand basic engineering processes for manufacturing and assembly., , , , Understand and interpret job drawings, produce jobs, and inspect the job for specified dimensions., Understand the various types of wiring systems and acquire skills in electrical wiring., , , , References, [1] S.K. HazraChaudhary, Workshop Technology, Volume I&II, Media Promoters and Publishers,, Mumbai., [2] B.S. Raghuwanshi, Workshop Technology, Volume I&II, DhanpathRai and Sons, New Delhi 2014, [3] K. Venkat Reddy, Workshop Practice Manual, BS Publications, Hyderabad 2014, [4] Kents Mechanical Engineering Hand book, John Wiley and Sons, New York, [5] H.S. Bawa, Workshop Practice, Mcgrawhill HED, , [6] R.P. Singh, Electrical Workshop: Safety, Commissioning, Maintenance & Testing of, Electrical Equipment, Wiley
Page 30 :
Teachers should use the following strategies to achieve the various outcomes of the course., • Different methods of teaching and media to be used to attain classroom attention., , • Massive open online courses (MOOCs) may be used to teach various topics/sub topics., , • 15-20% of the topics which are relatively simpler of descriptive in nature should be given to, the students for self-learning and assess the development of competency through classroom, presentations., • Micro-projects may be given to group of students for hand-on experiences, , • Encouraging students to visit to sites such as Railway station and research establishment, around the institution., , Learning Outcomes:, , At the end of the course student will be able to, , • To express quantitative measurements accurately., , • To practice and adapt good measuring techniques., , • To use various apparatus for precise measurements., , • To understand and differentiate different methods of quantitative analysis., , • To know and understand principles of quantitative analysis using instruments., • To construct different electrochemical cells used in developing batteries., • To understand and appreciate methods of corrosion abetments., , Reference Books:, , 1. Text Book of Chemistry for Class XI & XII (Part-I, Part-II); N.C.E.R.T., Delhi, 2017-18., , 2. Dr. G. H. Hugar and Prof A. N. Pathak, Applied Chemistry Laboratory Practices, Vol. I and Vol. II,, NITTTR, Chandigarh, Publications, 2013-14., 3. Agnihotri, Rajesh, Chemistry for Engineers, Wiley India Pvt.Ltd., 2014., , 4. Jain & Jain, Engineering Chemistry, Dhanpat Rai and Sons; New Delhi, 2015., *******, , Course Code, , :, , HS103, , Prerequisites, , :, , NIL, , Course Title, , Number of Credits, Course Category, , :, :, :, , Sports and Yoga, 1(L:0,T:0,P:2), HS, , Course Objectives:, • To make the students understand the importance of sound health and fitness principles, as they relate to better health., •, •, •, , To expose the students to a variety of physical and yogic activities aimed at stimulating, their continued inquiry about Yoga, physical education, health and fitness., , To create a safe, progressive, methodical and efficient activity based plan to enhance improvement and minimize risk of injury., To develop among students an appreciation of physical activity as a lifetime pursuit and, a means to better health., , First Year Curriculum Structure Common to All Branches, , 30
Page 31 :
Course Content:, • Introduction to Physical Education, o, o, o, •, , o, o, , o, o, o, o, o, , o, , Olympic Symbols, Ideals, Objectives & Values, , Awards and Honours in the field of Sports in India (Dronacharya Award, Arjuna Award,, Dhayanchand Award, Rajiv Gandhi Khel Ratna Award etc.), Meaning & Importance of Physical Fitness & Wellness, Components of Physical fitness, , Components of Health related fitness, Components of wellness, , Preventing Health Threats through Lifestyle Change, Concept of Positive Lifestyle, , Define Anatomy, Physiology & Its Importance, , Effect of exercise on the functioning of Various Body Systems. (Circulatory System, Respiratory System, Neuro-Muscular System etc.), , Kinesiology, Biomechanics & Sports, o, o, o, , •, , Ancient & Modern Olympics (Summer & Winter), , Fundamentals of Anatomy & Physiology in Physical Education, Sports and Yoga, o, , •, , Changing trends in Physical Education, , Physical Fitness, Wellness & Lifestyle, o, , •, , Aims & Objectives of Physical Education, , Olympic Movement, o, , •, , Meaning & definition of Physical Education, , Meaning & Importance of Kinesiology & Biomechanics in Physical Edu. & Sports, Newton’s Law of Motion & its application in sports., Friction and its effects in Sports., , Postures, o, o, o, o, o, o, , Meaning and Concept of Postures., Causes of Bad Posture., , Advantages & disadvantages of weight training., Concept & advantages of Correct Posture., , Common Postural Deformities – Knock Knee; Flat Foot; Round Shoulders; Lordosis, Kyphosis, Bow Legs and Scoliosis., Corrective Measures for Postural Deformities, 31, , First Year Curriculum Structure Common to All Branches
Page 33 :
•, , Doping, o, o, o, , •, , Prohibited Substances & Methods, , Side Effects of Prohibited Substances, , Sports Medicine, o, o, o, , •, , Meaning and Concept of Doping, , First Aid – Definition, Aims & Objectives., , Sports injuries: Classification, Causes & Prevention., , Management of Injuries: Soft Tissue Injuries and Bone & Joint Injuries, , Sports / Games, , Following sub topics related to any one Game/Sport of choice of student out of: Athletics,, Badminton, Basketball, Chess, Cricket, Kabaddi, Lawn Tennis, Swimming, Table Tennis, Volleyball, Yoga etc., o, o, o, o, o, o, , History of the Game/Sport., , Latest General Rules of the Game/Sport., , Specifications of Play Fields and Related Sports Equipment., Important Tournaments and Venues., Sports Personalities., , Proper Sports Gear and its Importance., , References:, 1., 2., 3., , Modern Trends and Physical Education by Prof. Ajmer Singh., Light On Yoga By B.K.S. Iyengar., , Health and Physical Education – NCERT (11th and 12th Classes), , Course Outcomes:, , On successful completion of the course the students will be able to:, (i), Practice Physical activities and Hatha Yoga focusing on yoga for strength, flexibility, and, relaxation., (ii) Learn techniques for increasing concentration and decreasing anxiety which leads to, stronger academic performance., (iii) Learn breathing exercises and healthy fitness activities, (iv) Understand basic skills associated with yoga and physical activities including strength, and flexibility, balance and coordination., (v) Perform yoga movements in various combination and forms., (vi) Assess current personal fitness levels., (vii) Identify opportunities for participation in yoga and sports activities., (viii) Develop understanding of health-related fitness components: cardiorespiratory endurance, flexibility and body composition etc., (ix) Improve personal fitness through participation in sports and yogic activities., (x) Develop understanding of psychological problems associated with the age and lifestyle., 33, , First Year Curriculum Structure Common to All Branches
Page 34 :
(xi), , Demonstrate an understanding of sound nutritional practices as related to health and, physical performance., (xii) Assess yoga activities in terms of fitness value., (xiii) Identify and apply injury prevention principles related to yoga and physical fitness activities., (xiv) Understand and correctly apply biomechanical and physiological principles elated to exercise and training., , *******, , Course Code, , :, , HS105, , Number of Credits, , :, , 1, , Course Title, , Prerequisites, , Course Category, , :, :, :, , Communication Skills in English - Lab, NIL, , (L: 0, T: 0, P: 2), , HS, , Course Objectives:, Communication skills play an important role in career development. This lab course aims at actively, involving students in various activities to improve their communication skills with an emphasis on, developing personality of the students. Thus, the objectives of this course are:, 1. To develop listening skills for enhancing communication., , 2. To develop speaking skills with a focus on correct pronunciation and fluency., , 3. To introduce the need for Personality development- Focus will be on developing certain qualities which will aid students in handling personal and career challenges, leadership skills, etc. for that purpose group discussion, extempore and other activities should be conducted, during lab classes., , Course Content:, Unit 1 Listening Skills, Listening Process and Practice: Introduction to recorded lectures, poems, interviews and speeches,, listening tests., Unit II Introduction to Phonetics, Sounds: consonant, vowel, diphthongs, etc. transcription of words (IPA), weak forms, syllable division, word stress, intonation, voice etc., Unit III Speaking Skills, Standard and formal speech: Group discussion, oral presentations, public speaking, business presentations etc. Conversation practice and role playing, mock interviews etc., Unit IV Building vocabulary, Etymological study of words and construction of words, phrasal verbs, foreign phrases, idioms and, phrases. Jargon/ Register related to organizational set up, word exercises and word games to enhance self-expression and vocabulary of participants., Recommended Readings:, 1. Daniel Jones. The Pronunciation of English. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1956., , 2. James Hartman& et al. Ed. English Pronouncing Dictionary. Cambridge: Cambridge University, , First Year Curriculum Structure Common to All Branches, , 34