Page 2 :
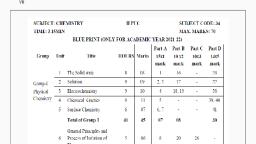
II PUC - CHEMISTRY, Chapter wise Questions, PART – A, I Answer all the questions. 10 x 1 = 10 M, 1) Solutions, 2) Solutions, 3) ElectrocheRÅStry, 4)Chemical Kinetics, 5) Surface Chemistry, 6) p-Block Elements – Question from Group 18 Elements, 7) p-Block Elements – Question from Group 18 Elements, 8) Haloalkanes and Haloarenes, 9) Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic acids, 10) Biomolecules – Question may be from Nucleic acids OR Proteins, PART - B, II Answer any FIVE questions., 5 x 2 = 10 M., 11) The Solid State, 12) Electrochemistry, 0.693, 13) Chemical Kinetics – May be problem on, k, 14) f-Block Elements - Question on Lanthanoids OR Actinoids, 15) Haloalkanes and Haloarenes, 16) Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers – Question may be from Phenol, 17) Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers, 18) Amines – Question from properties, PART - C, III Answer any FIVE questions., 5 x 3 = 15 M, Scanned with CamScanner
Page 3 :
19) p-Block Elements – Group 15 Elements (May be preparation of, ammonia OR nitric acid), 20) p-Block Elements – Group 16 Elements (preparation and, properties of SO2, ozone, Anomalous properties of oxygen,, complete the reaction, Structure of oxoacids of Sulphur, properties, of H2SO4), 21) p-Block Elements – Group 17 Elements (Anomalous properties, of fluorine and reason, complete the reactions, Structure of, oxoacids of Chlorine, aquaregia, Interhalogen compounds are more, reactive than halogens.Why?, 22) d-Block Elements – Properties of 3d Elements (Calculation of, magnetic moment using u =/n(n+ 2) , Formation of coloured, ions, Oxidation states,Stability, Reducing and oxidising nature,, Electrode potentials, Electronic configuration, atomic and ionic, size), 23) d-Block Elements – Properties of 3d Elements (Reason for, catalytic properties, Interstitial Compounds and their, characteristics, Reason for complex formation, Alloy formation), 24) Coordination Compounds-(postulates of Werner's theory OR, crystal field splitting), 25) Coordination Compounds- VBT (Explanation of hybridisation,, geometry and magnetic properties of [Co(NH;)]* OR [COFJ*-, OR [NICLJ OR [Ni(CN).], 26) Coordination Compounds IUPAC naming, co-ordination, number, ambidentate ligand, homoleptic and heteroleptic complex, PART - D, 3 x 5 = 15 M, IV Answer any THREE questions., 7, Scanned with CamScanner
Page 4 :
parameter) OR calculation of number of particles per unit cell for 2, 27) The Solid State - (a) Derivation of packing efficiency in Simple, cube ORFCC (CCP) OR BCC for 3 marks, ZM, d =, 2°NA (calculation of any, (b) Problem on density formula, marks., 28) Solutions-(a)Problem on Molar mass calculation for 3 marks, (b) Difference question OR any question from solutions., 29) Electrochemistry - (a) Problem of 3 marks, (b) 2 marks theory question, 30) Chemical Kinetics - (a) Derivation of k (rate constant) for zero order, OR first order reactions., (b) 2 marks theory question, 31) Surface Chemistry - (a) 3 marks Qn from Colloids, (b) 2 marks question from adsorption, V Answer any FOUR questions., 4 x 5 = 20 M, 32) Haloalkanes and haloarenes- (a) May be SNl OR SN2, mechanism for 2 marks, (b) Name reaction for 2 marks, (c) Any 1 mark question, 33) Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers - (a) May be mechanism for the, conversion of ethanol to ethene for 3 Marks, (b) 2 marks one reaction from phenol OR ether, 34) Aldehydes, Ketones – (a) May be mechanism for the addition of, HCN to carbonyl compounds(aldehyde / ketone) OR Name reaction, (b) 2 marks question, 35) Carboxylic acids – (a) Any one reaction from preparation for 2, marks, 8, Scanned with CamScanner
Page 5 :
(b) Any one reaction from properties for 2 marks, (c) 1 mark Question, 36) Amines - (a) 2 marks Qn from preparation, (b) 2 marks Qn from properties, (c) 1 markQn from basicity, 37) Biomolecules - (a) 2 marks question from carbohydrates, (b) 2 marks question from Proteins (c) 1 mark question from Nucleic, acids, PART – B, Q No 11) Write two differences between crystalline and amorphous, solids., Crystalline Solids, Amorphous Solids, 1.Have definite geometrical, 1. No definite geometrical shape, shape, 2.Have sharp melting point, 2. No sharp melting point, 3. Long range order, 3. Short range order, 4.Anisotropic in nature, 4. Isotropic in nature, OR, Write two differences between Schottky defect and Frenkel defect., Frenkel defect, Schottky defect, 1.Dislocation of ion(cation) from its, 1.Missing of both cation and, normal site to the interstitial site., anion from the crystal lattice., 2.Density remains same., 2.Density decrease., 3.Found in ionic solids having low, 3.Found in ionic solids having, coordination number., high coordination number., 4. Observed when cations and, 4. Observed when cations and, anions differ in their size., anions have similar size., 9., Scanned with CamScanner