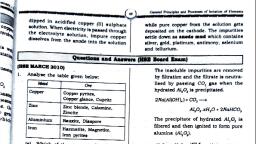
Page 1 :
α-halocarboxylic acid, CH3-CH2-COOH i) Cl2/ Red P ii) H2O, CH3-CHCl-COOH + HCl, `, Propanoic acid, 2-chloropropanoic acid, This reaction is synthetically important since the halogen atom can be replaced by other groups., 4. Electrophilic substitution reactions:, The –COOH group is a deactivating group and meta-directing. So on electrophilic substitution reactions, we, get meta derivatives., e.g., 1. Nitration, , 2. Bromination, , But carboxylic acids do not undergo Friedel-Crafts reactions because the carboxyl group is, deactivating and the catalyst aluminium chloride (Lewis acid) gets bonded to the carboxyl group to form, salts., , 13. AMINES, Amines are the derivatives of ammonia. Like ammonia, the nitrogen atom in amines is also sp 3, hybridised with an unpaired electron in one of the sp3 hybridised orbitals. So the shape of amines is also, pyramidal., Amines are classified into three types – primary (10), secondary (20) and tertiary (30) amines. If one, hydrogen atom of ammonia is replaced by R (alkyl) group, we get 10amine. Their general formula is R-NH2. If, two hydrogen atoms of ammonia are replaced by two R or Ar groups, we get 2 0amine. Their general formula, is R2NH. If three hydrogen atoms of ammonia are replaced by R group, we get 30amine. Their general, formula is R3NH., , Preparation of Amines, 1. Reduction of Nitriles:, Nitriles on reduction with lithium aluminium hydride (LiAlH4) or catalytic hydrogenation produce, primary amines. This reaction is used for ascending in amine series, i.e., for preparation of amines, containing one carbon atom more than the starting amine., R-CN i) LiAlH4 R-CH2-NH2, ii) H2O, E.g. CH3-CN LiAlH4/H2O CH3-CH2-NH2, Ethane nitrile, , Ethanamine, , +2 CHEMISTRY - Focus Area Notes Prepared by Anil Kumar K L, GHSS Ashtamudi, Kollam, , Page 50