Page 2 :
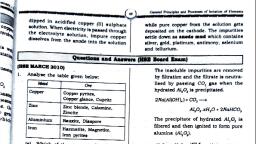
2. From diazonium salts: When an aromatic primary amine (e.g. aniline) is treated with nitrous acid, (prepared by mixing NaNO2 & HCl) at 273-278K, a diazonium salt is formed [Diazotisation, Reaction], which on warming with water we get phenol., , Chemical Reactions of Alcohols, 1. Reaction with hydrogen halides: Alcohols react with hydrogen halides in presence of anhydrous, zinc chloride (ZnCl2) to form alkyl halides., ROH + HX an. ZnCl2 R–X + H2O, The order of reactivity of alcohols with HCl is 30 alcohols > 20 alcohols > 10 alcohols. This difference in, reactivity of three classes of alcohols with HCl helps to distinguish them from one another (Lucas test)., LUCAS TEST: Lucas reagent is a mixture of conc. HCl and anhydrous ZnCl2. Tertiary alcohols react with Lucas, reagent and form turbidity immediately; secondary alcohols form turbidity within 5 minutes while primary, alcohols do not produce turbidity at room temperature. But they give turbidity on heating., 2. Dehydration: On heating with Conc. H2SO4 or H3PO4, alcohols undergo dehydration (removal of, a molecule of water) to form alkenes. Catalysts such as anhydrous zinc chloride or alumina can also be used, for dehydration., , The relative ease of dehydration of alcohols follows the order: Tertiary > Secondary > Primary., For example ethanol undergoes dehydration by heating it with concentrated H 2SO4 at 443 K, we get ethene., , Secondary and tertiary alcohols are dehydrated under milder conditions., , Chemical Reactions of Phenols, 1. Nitration of Phenol: Phenol reacts with Conc. Nitric acid to give an yellow precipitate of 2,4,6trinitrophenol commonly called picric acid., , +2 CHEMISTRY - Focus Area Notes Prepared by Anil Kumar K L, GHSS Ashtamudi, Kollam, , Page 43
Page 3 :
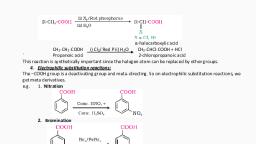
For the preparation of ortho and para nitrophenols, phenol is treated with dil. HNO 3 at low temperature., , The ortho and para isomers can be separated by steam distillation. o-Nitrophenol is steam volatile due to, intramolecular hydrogen bonding while p-nitrophenol is less volatile due to intermolecular hydrogen, bonding which causes the association of molecules., 2. Reimer-Tiemann reaction: Phenol when treated with chloroform in the presence of NaOH, followed by, acidification, we get salycylaldehyde (o-hydroxybenzaldehyde). This reaction is known as Reimer - Tiemann, reaction., , Commercially Important Alcohols – Ethanol, Ethanol is commonly known as spirit or grain alcohol. It is obtained commercially by the fermentation of, sugar. The sugar in molasses, sugarcane or fruits like grapes is converted to glucose and fructose, in the, presence of an enzyme, invertase. Glucose and fructose undergo fermentation in the presence of another, enzyme, zymase to give ethanol and carbondioxide. Both the enzymes invertase and zymase are produced, by yeast., C12H22O11 + H2O Invertase, C6H12O6 + C6H12O6, Sucrose, Glucose Fructose, C6H12O6 Zymase 2C2H5OH + 2 CO2, Ethanol, Fermentation takes place in anaerobic conditions i.e. in absence of air. If air gets into fermentation, mixture, the oxygen of air oxidises ethanol to ethanoic acid (acetic acid), which destroys the taste of alcohol., Ethanol is a colourless liquid. It is used as a solvent in paint industry and in the preparation of a large, number of carbon compounds., The commercial alcohol is made unfit for drinking by mixing it with some copper sulphate (to give it a, colour) and pyridine (a foul smelling liquid). It is known as denaturation of alcohol and the resulting alcohol, is known as denatured spirit., Now Ethanol is manufactured by the hydration of ethene., CH2=CH2 + H2O H+ CH3-CH2-OH, Preparation of Ethers, 1. Williamson synthesis:, Alkyl halide reacts with sodium alkoxide to form ether. This reaction is known as Williamson synthesis., R-X + R’-ONa → R-O-R’ + NaX, CH3-CH2-Br + CH3-ONa, CH3-CH2-O-CH3 + NaBr, Ethyl bromide Sod. methoxide, Ethyl methyl ether (Methoxyethane), , +2 CHEMISTRY - Focus Area Notes Prepared by Anil Kumar K L, GHSS Ashtamudi, Kollam, , Page 44