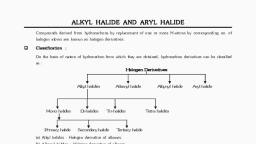
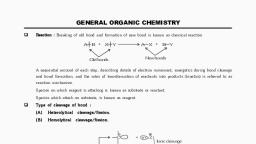
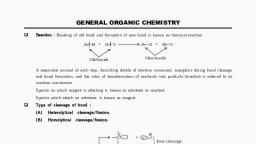
Page 4 :
4, , Haloalkanes and Haloarenes, , 10. The addition of propene with HOCl proceeds via the addition of, (1) H+ in the first step, , (2) Cl+ in the first step, , (3) OH– in the first step, , (4) Either H+ or OH– in first step, , Sol. Answer (2), –, , +, , +, , + HO Cl, , Cl, , Intermediate, HO Cl, HOCl Breaks as : HOCl , And alkene follows electrophilic addition reaction, So at first Cl+ attack., , 11., , CH3, , CH, , CH2 + HOBr, , P ; The major product ‘P’ is, , AL, , S, , Here, in a first step the electrophill (Cl+) will attack over the – e– cloud of alkene leading to electrophillic, addition to alkene., , (1) CH3, , CH, , CH2, , Br, , OH, , TU, TO, RI, , Br, , (2) CH3, , CH, , CH2, , OH Br, , Sol. Answer (2), –, , +, , +, , + HO Br, , (3) CH2, , CH2, , Br, , CH2, , (4) CH3, , OH, , C, , CH3, , OH, , Br, –, , OH, , OH, , XY, , HOBr Breaks as, , Br, , HO Br , HO Br , , Nu E , , , LA, , , , And alkene follows electrolphylic addition reaction. So, Br+ attack at first and then OH attack., CH3, , CH, , Cl I, , CH2, , P , P is, , GA, , 12., , (1) CH3, , CH, , CH2, , I, , Cl, , Cl, , (2) CH3, , CH, Cl, , CH2, I, , (3) CH3, , C, , CH3, , (4) CH3, , CH2, , CH, , I, , Sol. Answer (2), , +, , + –, I – Cl, , +, , I, , Intermediate carbocation, –, , Cl, Cl, , I, An Innovative Institute in Raipur (C.G) for IIT-JEE, NEET & 9 Std.- 12 Std.(PCM & PCB). Cont. @ 919993551234, 918770887703, , I, Cl
Page 7 :
Haloalkanes and Haloarenes, , 7, , Sol. Answer (1), +, , –, N2 Cl + KI, , I, , This is sandmeyer reaction., (Physical and chemical properties), R, , Br, , 20., , CH2, , CH2, , ., , Br, , The reagent R is, (2) H2O, , (3) KCN, , R, , CH2 – CH2 – Br, , TU, TO, RI, , Br, , AL, , Sol. Answer (4), , (4) Na/ether, , S, , (1) NH3, , The Reagent R would be Na/Dry ether this is actually Wurtz reaction and occurs via free radical mechanism., 21. Which of the following halogen exchange reaction will occur in acetone?, (1) R, , I + NaCl, , (3) R, , Cl + NaI, , Sol. Answer (3), , F + KCl, , (4) R, , F + AgBr, , XY, , R – Cl + NaI R – I + NaCl, , (2) R, , This reaction will occur in acetone because of two reasons :, (i) The reactant NaI is more soluble in acetone., , LA, , (ii) Secondly, the formed product NaCl will precipitate out, 22. Which is most reactive nucleophile in polar protic solvent?, (2) Cl–, , (3) Br–, , (4) I–, , GA, , (1) F–, , Sol. Answer (4), , I Br Cl F , (Polar protic medium), Nucleophilicity, , 23. Which is most reactive nucleophile in polar aprotic solvent?, (1) F–, , (2) Cl–, , (3) Br–, , (4) I–, , (3) SCN–, , (4) OH–, , Sol. Answer (1), F Cl Br I, (Polar aprotic medium), Nucleophilicity, , 24. Which cannot act as an ambident nucleophile?, (1) CN–, , (2) NO2−, , An Innovative Institute in Raipur (C.G) for IIT-JEE, NEET & 9 Std.- 12 Std.(PCM & PCB). Cont. @ 919993551234, 918770887703
Page 10 :
10, , Haloalkanes and Haloarenes, , Sol. Answer (2), The order of E2 elimination for alkyl halide follows as 3°R – L > 2° R – L > 1° R – L., Where L = any leaving group., This is because, (i) In 3° R–L, there is more number of – ‘H’. So, the probablity of attack of base on – ‘H’ is more and, hence E2 reactivity increases., (ii) Secondly, the transition state of E2 reaction is more stable in case of E2 reaction is more hyperconjugation, with its incipient double bond character and – ‘H’., S.O. of Ts of E2 reaction., , C, H, , C, , R, , C, , R, (3° R–L), , H, , S, , L –, , C, , H, , R, (2° R–L), , C, H, , C, , H, , H, (1° R–L), , TU, TO, RI, , –, OH, (base), , L –, , AL, , L –, , –, HO, , –, HO, , Where L is leaving gp, , So, E2 reactivity order 3° R – L > 2° R – > 1° R – L, , , , , 31. 2-Bromopentane is heated with EtO Na in ethanol. The major product obtained is, (1) 2-Ethoxypentane, , (2) Pent-1-ene, , Sol. Answer (4), –, , +, , EtO Na, , , , (4) Pent-2-ene, , H, , XY, , Br, , (3) Isobutane, , +, , H, , H, , H (tans-pent-2ene), Major, , Cl, , HNO3/H2SO4, , GA, , 32., , LA, , +, , A, , NaOH, 433 K, , NO2, , OH, , (1), , B ; B is, , (2), , OH, , NO2, , NO2, , Cl, (3), , (4), , NO2, , OH, , Sol. Answer (4), , Cl, , Cl, , OH, , HNO3/H2SO4, , NaOH, , (EAS), , 333, (ArSN), , NO2, , NO2, , An Innovative Institute in Raipur (C.G) for IIT-JEE, NEET & 9 Std.- 12 Std.(PCM & PCB). Cont. @ 919993551234, 918770887703
Page 12 :
12, , Haloalkanes and Haloarenes, , Step Ist :, , Cl, C Cl, , H, , –, , OH, , Cl, , Cl, –, , Cl, , Cl, , C, , Cl, C, , –, , Cl, , Cl, Electrophile, (dichloro carbene), Step IInd : Anilene Vs : CCl2 :, , N, , –, , C, , H, , H, , S, , +, , NH2 + CCl2, , Cl, , AL, , H, , TU, TO, RI, , Intramolecular, Acid-Base reaction, , H, , N, , C, , H, , +, , N, , C, , H, , H, , Cl, , H, , Cl, , +, , XY, , –H, , LA, , N, , +, , GA, , N, , +, , C, , C, , H, , Cl, , H, , –, , OH, , –, , N, , C, , N, , C, , or, , (Stereochemical aspects of nucleophilic substitution reactions and elemination reactions), 35. For SN1 mechanism, which of the following is correct?, (1) Inversion (100%), , (2) Formation of carbocation, , (3) Non-polar solvent, , (4) Elimination, , Sol. Answer (2), In SN1 mechanism, C+ formation in R.D.S. (Slow step), An Innovative Institute in Raipur (C.G) for IIT-JEE, NEET & 9 Std.- 12 Std.(PCM & PCB). Cont. @ 919993551234, 918770887703
Page 18 :
18, , Haloalkanes and Haloarenes, , Sol. Answer (2), , +, Cl, , +, , (Allyl halide), This is good substrate for both SN1 and SN2 reaction., 8., , Which of the following compounds undergoes nucleophilic substitution reaction most easily?, , Cl, Cl, (2), , OCH3, , Cl, (3), , TU, TO, RI, , Cl, , AL, , S, , (1), , (4), , NO2, , CH3, , Sol. Answer (3), , Cl, , Cl, N, , Nu :, , Slow (RDS), , N, , O, O, Carbanion, (intermediate), , Cl, , Nu, , N, , XY, , O, , O, , Nu, , –, , GA, , LA, , Cl, , Nu, , N, O, , O, , Nu, , N, O, 9., , O, , O, , O, , Replacement of Cl of chlorobenzene to give phenol requires drastic conditions. But chlorine of, 2, 4-dinitrochlorobenzene is readily replaced, (1) NO2 donates electron at meta position, , (2) NO2 withdraws electron from ortho/para positions, , (3) NO2 make ring electron rich at ortho & para, , (4) NO2 withdraws electron from meta position, , An Innovative Institute in Raipur (C.G) for IIT-JEE, NEET & 9 Std.- 12 Std.(PCM & PCB). Cont. @ 919993551234, 918770887703
Page 19 :
Haloalkanes and Haloarenes, , 19, , Sol. Answer (2), This is again ArSN reaction. The intermediate of this reaction is carbanion, whose stability can be increase, by electron withdrawing group like –NO2., , CH2OH, + HCl, , 10., , (excess), , A + Mg, , dry ether, , B, , OH, What is B?, , CH2OH, (3), , Cl, , MgCl, , MgCl, , OH, , TU, TO, RI, , Sol. Answer (4), , OH, , (4), , AL, , (2), , (1), , CH2MgCl, , CH3, , S, , CH2MgCl, , Cl, , MgCl, , Mg, dry ether, , + HCl, OH, (A), , OH, , OH, , 11. Ethylidene chloride reacts with aq. KOH to form which of the following compound?, , Sol. Answer (1), , (2) Ethylene glycol, , (3) Ethyl alcohol, , (4) Acetic acid, , XY, , (1) Acetaldehyde, , Clearly, Acetaldehyde will form., , II., , GA, , I., , LA, , 12. The correct order of reactivity of the following compounds towards aqueous NaCN will be, Cl, Cl, , (1) I > II > III > IV, , III. CH3 — CH — CH 3 IV. CH2 = CH—CH2—Br, , CH2 = CH—CH2—Cl, , (2) I > IV > II > III, , (3) IV > II > I > III, , (4) IV > II > III > I, , Sol. Answer (4), , 1. SN reaction order, at allylic carbon atom >> at vinylic 'C' atom., ∵ In case of vinylic 'c', bond strength is more due to resonance which decreases SN1 or SN2 reactivity., , Cl, , Cl, i.e., SN reactivity order, , C, , C, , <<, , Vinylic ‘C’, , C, , C, , C, , allylic 'C', , An Innovative Institute in Raipur (C.G) for IIT-JEE, NEET & 9 Std.- 12 Std.(PCM & PCB). Cont. @ 919993551234, 918770887703
Page 20 :
20, , Haloalkanes and Haloarenes, , 2. SN reaction and leaving tendency of the group., SN reactivity order in terms of leaving group., –I > –Br > –Cl > – F, 3. Case of B – unsaturation increases the SN1 or SN2 reactivity order., Keeping three concept, we can find the case of reaction with NaCN (SN2 order), Br, , Cl, , >, , >, , Cl, , >, , Cl, , Cl, , (1), , >, , >, Cl, , Cl, >, , (3), , (2), , >, , Cl, , Cl, , Cl, , >, , (4), , Cl, , Cl, , Cl, , >, , Cl, , Cl, , Cl, , Cl, , >, , Cl, , Cl, , Cl, , TU, TO, RI, , Cl, , Cl, , Cl, , AL, , Cl, , S, , 13. Which among the following is the correct order of melting point?, , Cl, >, , Cl, , Cl, , LA, , Sol. Answer (3), , XY, , Cl, , Cl, , >, , GA, , The correct order of melting point is, , Cl, , Cl, Cl, , >, Cl, , Cl, , This is because of more symmetrical structure and tight crystal packing., , Cl, , OH, + aq. KOH, , 14., , G, , G, , For which of the following G, above reaction will be the fastest?, (1) –OH, , (2) –CH3, , (3) –NO2, , (4) –CHO, , An Innovative Institute in Raipur (C.G) for IIT-JEE, NEET & 9 Std.- 12 Std.(PCM & PCB). Cont. @ 919993551234, 918770887703
Page 21 :
Haloalkanes and Haloarenes, , 21, , Sol. Answer (3), , As the reaction proceed the SNAr mechanism., So, intermediate is carbanion,, G must be electron withdrawing group (–R) effect, in order to stabilize the intermediate carbanion., , NO2, , (2), , Sol. Answer (4), , NO2, >, , >, , NO2, , NO2, , NO2, , NO2, , (4), , I, , Br, , Cl, , F, , (3), , I, , NO2, , TU, TO, RI, , (1), , NO2, , AL, , Br, , Cl, , F, , S, , 15. Which of the following is least reactive towards nucleophilic substitution?, , >, , ∵ In SNAr the attack of nucleophile is the r.d.s. So, more is the charge on target 'C' atom, more is the SNAr, reactivity., , 16. Among the following, , XY, , Reactivity order towards ArSN, , Cl, , Cl, , Cl, , Cl, , GA, , LA, , NO2, , NO2, , NO2, NO2, , NO2, , I, , II, , III, , IV, , The correct order of reactivity towards ArSN mechanism is, (1) I > III > II > IV, , (2) I > II > IV > III, , (3) III > II > IV > I, , (4) I > IV > II > III, , Sol. Answer (4), , Cl, , Cl, NO2, , >, , NO2, , Cl, NO2, , >, , Cl, , >, NO2, , NO2, , ∵ In SNAr intermediate is carbanion so, electron withdrawing group increases the reactivity., An Innovative Institute in Raipur (C.G) for IIT-JEE, NEET & 9 Std.- 12 Std.(PCM & PCB). Cont. @ 919993551234, 918770887703
Page 28 :
28, , Haloalkanes and Haloarenes, , Sol. Answer (3), The relative stability order of the carbonium ions is as follows., CH2, , CH3, H3C, , C, , H3C, , CH, , CH3, , O2N, , CH2, , CH2, , CH3, , this stablity is on the basis of extent of resonance, hyperconjugation and inductions effect. Which also, Satisfy the experimental facts. So, the correct answer is (3)., 7., , What products are formed when the following compound is treated with Br2 in the presence of FeBr3?, CH 3, , [AIPMT-2014], , CH3, , (3), , CH3, , Br, , CH3, , and, , Sol. Answer (3), , Br, , and, , Br, , CH3, , CH3, , CH3 and, , Br, , Br, , CH3, , Which of the following compounds will undergo racemisation when solution of KOH hydrolyses ?, CH2Cl, , (i), , (2) (ii) and (iv), , Cl + MF, , LA, , In the replacement reaction, , (1) Na, , (3) (iii) and (iv), , (2) K, , CH3, , (iv) H C Cl, C2H5, , [AIPMT-2014], , (4) (i) and (iv), , XY, , Sol. Answer (4), , CH3, (iii) H3C–CH–CH2Cl, , (ii) CH3CH2CH2Cl, , (1) (i) and (ii), , 9., , CH3, , (4), , CH3, , –CH3 group is o, p - directing., 8., , CH 3, , CH 3, , CH 3, , CH3, , Br, , (2), , CH3, , CH3, , S, , and, , Br, , AL, , (1), , CH 3, , Br, , TU, TO, RI, , CH 3, , CF + M . The reaction will be most favourable if M happens to be, [AIPMT (Mains)-2012], (3) Rb, , (4) Li, , Sol. Answer (3), , GA, , The reaction is SN1. The reaction will be more favoured when there is more release of F– which depends upon, polarising power of metal. Size of Rb is largest among the given options so more release of F– will take place., , 10. Which of the following compounds undergoes nucleophilic substitution reaction most easily ?, [AIPMT (Mains)-2011], Cl, , Cl, , (2), , (1), OCH3, , Cl, , Cl, , (3), , NO2, , (4), , CH3, , Sol. Answer (3), Cl, , has electron withdrawing group NO2 which reduces the double bond character between carbon of benzene, NO2, , ring and chlorine., An Innovative Institute in Raipur (C.G) for IIT-JEE, NEET & 9 Std.- 12 Std.(PCM & PCB). Cont. @ 919993551234, 918770887703
Page 31 :
Haloalkanes and Haloarenes, , 31, , Sol. Answer (1), As in aprotic polar solvent, SN2 is favoured & DMF is aprotic polar solvent., DMF, , CH3 CH2 Br Cl , CH3 CH2 Cl Br , S 2, N, , This will occur fastest because of less steric hindrance in transition state., 18. If there is no rotation of plane polarized light by a compound in a specific solvent, thought to be chiral, it may, mean that, [AIPMT (Prelims)-2007], (1) The compound may be a racemic mixture, , (2) The compound is certainly a chiral, , (3) The compound is certainly meso, , (4) There is no compound in the solvent, , S, , Sol. Answer (3), , AL, , 19. For the following, a. I–, b. Cl–, , TU, TO, RI, , c. Br–, , The increasing order of nucleophilicity would be, (1) Br– < Cl– < I–, , [AIPMT (Prelims)-2007], , (2) I– < Br– < Cl–, , Sol. Answer (3), , (3) Cl– < Br– < l–, , (4) I– < Cl– < Br–, , The increasing order of nucleophilicity would be, Cl– < Br, , –, , < I–, , 20. Which of the following undergoes nucleophilic substitution exclusively by SN1 mechanism ?, [AIPMT (Prelims)-2005], , Sol. Answer (1), , (2) Ethyl chloride, , XY, , (1) Benzyl chloride, , (3) Chlorobenzene, , (4) Isopropyl chloride, , LA, , Br, , 21. The chirality of the compound H3C, , H is, Cl, , [AIPMT (Prelims)-2005], , (2) S, , GA, , (1) R, , C, , (3) Z, , (4) E, , Sol. Answer (1), , +, , 22. C5H11Br + NaCN, , A, , H3O, , B + NaOH, , CaO, , C, , ‘C’ has the formula C5H12 which can give four isomeric monochloro derivative. What is the structure of C5H11Br?, Br, , (1) CH3 — CH — CH2 — CH2 — Br, CH3, , (2) CH, 3, , CH 2, , CH, , CH 2, , CH3, , CH3, , (3) CH3 — CH2 — CH2— CH — CH3, , Br, , (4) CH2 — C — CH2 —Br, , CH3, , An Innovative Institute in Raipur (C.G) for IIT-JEE, NEET & 9 Std.- 12 Std.(PCM & PCB). Cont. @ 919993551234, 918770887703
Page 32 :
32, , Haloalkanes and Haloarenes, , Sol. Answer (1), Given, C is C5H12, The degree of unsaturation of C is, D° = C + 1 –, = 5 1, , H X N, 2, , 12, =6–6=0, 2, , Moreover, it forms four isomeric monochloro derivative., ∵ it must have, , Br, , S, , Hence, as per reaction sequence the structure of the compound is, , AL, , 23. CD2 = CH – CH2 – Br is subjected to SN1 and SN2 reactions separately, which of the following statement is, correct?, (1) Both SN1 and SN2 give two products, , TU, TO, RI, , (2) Both SN1 and SN2 give only one product, , (3) SN1 gives two products but SN2 gives only one product, (4) SN1 gives one product but SN2 gives two products, Sol. Answer (3), , Br, D2C, , SN 1, , SN2, , D2C, , +, , Nu, , Nu, , XY, , D2C, , Nu, , D, , D, , 24. In Finkelstein reaction when acetone is replaced by water then, , LA, , (1) Reaction occurs in forward direction via SN1 pathway, (2) Reaction occurs in forward direction via SN2 pathway, , GA, , (3) Reaction occurs in backward because NaCl formed in right hand side is soluble in water and cannot ppt., out, (4) Reaction is not possible, , Sol. Answer (3), , In Finkelstein reaction, , Acetone, , CH3 Cl NaI CH3I NaCl ppt, This reaction is in forward direction, only, H O, , 2 �, However, CH3Cl NaI ����, ���, � CH3I NaCl, Soluble, , SN2 reaction is favourable in aprotic polar solvent like acetone, DMSO, DMF. So, the reaction is SN2 pathway, in forward direction. Again, since. NaCl ppt out in acetone solvent., backward reaction is not possible, i.e.,, H3C Cl NaI CH3I NaCl , S, An Innovative Institute in Raipur (C.G) for IIT-JEE, NEET & 9 Std.- 12 Std.(PCM & PCB). Cont. @ 919993551234, 918770887703
Page 33 :
Haloalkanes and Haloarenes, , 33, , 25. Which graph is incorrect?, (2), , Rate, , Rate, , (1), , Base, , Base, For Ph3CBr + OH– Product, (3) Ea, , For (CH3)2CHBr + OH– (in acetone) Product, , (4), , P.E., , Reaction, Progress, , Reaction, Progress, , For Me2(Et) COTs + NH3 Product, , S, , For PhCHDBr + BrOH Product, , AL, , Sol. Answer (3), , The choice (3) given to us is incorrect simply because this is SN1 reaction, and the C+ thus formed is stable will not ungergo furthur rearrangement., Number of transition states = 2, , E, , TU, TO, RI, , So, number of intermediates = 1, , 26. Which will undergo fastest SN2 substitution reaction when treated with NaOH?, , CH3, C, , (1) H5C2, , CH3, , Br, , Br, , CH3, , CH3, , H, , XY, , C, , C, , (2) CH3, , H, , (3) D, , Reaction Progress , , Br, , C, , CH2 — CH2 — CH3, , Br, , LA, , C2H5, , (4) H, , Sol. Answer (4), , Obviously, for SN2, 1° substrate is always the first choice, , GA, , Hence, last option or Br, , SN2 reactivity order, , H3C – L > 1° R – L > 2° R – L > 3° R – L, , Where L = L.G., 27. Given reaction, Br, , ether, Mg, , (i) H O, , 2, X (ii) HCl, Y(main product), , Y in the reaction is, (1) Hexane, , (2) Cyclohexane, , (3) Cyclohexylcyclohexane, , (4) Cyclohexyl ether, , An Innovative Institute in Raipur (C.G) for IIT-JEE, NEET & 9 Std.- 12 Std.(PCM & PCB). Cont. @ 919993551234, 918770887703
Page 37 :
Haloalkanes and Haloarenes, , 37, , 39. Which of the following is not chiral?, (1) 2-hydroxypropanoic acid, (2) 2-butanol, (3) 2,3-dibromopentane, (4) 3-bromopentane, Sol. Answer (4), , OH, (1), , *, O, , OH, (Chiral), , Br, *, , (Chiral), , *, , (Chiral), , Br, (4), , AL, , (3), , *, , TU, TO, RI, , (2), , S, , OH, , Br, , SECTION - D, , Assertion-Reason Type Questions, , 1., , A : When chloroform is obtained from bleaching powder and ethanol then chlorine acts as oxidising agent only., , XY, , R : It oxidises ethanol into acetic acid., Sol. Answer (4), , Cl2 +, , LA, , O, , O, , OH, , (From bleaching, powder), , GA, , Cl2, OH, , –, , C, H3C, , H, , –, , CHCl3 + HCOO, , Hence, both Assertion and reason are false., , 2., , A : Dow's process is an example of nucleophilic substitution reaction., R : In this process, benzyne is formed as an intermediate., , Sol. Answer (2), , Cl, , H, , –, , OH, , (Benzyne), , OH, –, , OH, , Phenol, , Both assertion and reason are true, however the reason is not a correct explanation., An Innovative Institute in Raipur (C.G) for IIT-JEE, NEET & 9 Std.- 12 Std.(PCM & PCB). Cont. @ 919993551234, 918770887703
Page 39 :
Haloalkanes and Haloarenes, , 8., , 39, , A : Haloalkanes react with KCN to give alkyl cyanide as the main product while with AgCN they form, isocyanide as the main product., R : In KCN, K form ionic bond due to which one lone pair present on carbon, so carbon act as donor but in, AgCN, Ag form covalent bond and carbon has no lone pair so N-atom act as donor., , Sol. Answer (1), , �, AgCN, KCN, R N C , R X R CN, Because AgCN Covalent, KCN Ionic, Both the assertion and reasons are correct., A : In benzyne the hybridisation of triply bonded carbon is sp2., , S, , 9., , AL, , R : The second -bond is formed by sp2 hybrid orbital., Sol. Answer (1), 2, , 2, , (Abnormal bond), , TU, TO, RI, , sp, sp, , ∵ Both assertion and reason are correct., , 10. A : Halogen is deactivating group due to –I effect., , R : Halogen is ortho-para directing due to +M effect., Sol. Answer (2), , Halogens show (–I) effect as well as (+M)/(+R) effect., These are O/P directing because of (+M) effect., , Cl, , XY, , Cl, NO2, , is more reactive towards nucleophilic substitution reaction than, , ., , LA, , 11. A :, , NO2, , GA, , R : NO2 group is electron withdrawaing so decreases the double bond character of C–Cl bond., , Sol. Answer (3), Cl, NO2, , Cl, , >, , NO2, (ArSN), The reaction occurs via ArSN mechanism and the formation of carbanion is rate determining step (Slow step)., , Cl, 12. A :, , D, , on reaction with alcoholic KOH gives, , ., , H, R : Bond energy of C–D bond is less than that of C–H bond., An Innovative Institute in Raipur (C.G) for IIT-JEE, NEET & 9 Std.- 12 Std.(PCM & PCB). Cont. @ 919993551234, 918770887703
Page 40 :
40, , Haloalkanes and Haloarenes, , Sol. Answer (3), , Cl, KOH, , +, , D, , D, , H, , This is E2 reaction, it demands Anti-periplanar transition state., 13. A : Meso-2, 3-dibromobutane on reaction with Zn/ether gives trans but-2-ene., R : Zn/ether gives anti-elimination., , S, , Sol. Answer (1), , Br, , H, , Br, , Zn/ether, (Anti ellimination), , CH3, , (Major), , TU, TO, RI, , H, , AL, , CH3, , 14. A : The number of optically active isomers of tartaric acid is two., R : Tartaric acid contains two asymmetric carbon., Sol. Answer (2), , COOH, , COOH, , *, , OH, , HO, , *, , H, , H, , LA, , COOH, , HO, , XY, , H, , H, , OH, , COOH, , Both are optically active, , GA, , 15. A : Chlorobenzene on reaction with sodium metal in the presence of dry ether gives diphenyl., R : This reaction is called Ullmann reaction., Sol. Answer (3), , Cl + Na + Cl, Dry ether, , Biphenyl, This reaction is called Fitting reaction., , An Innovative Institute in Raipur (C.G) for IIT-JEE, NEET & 9 Std.- 12 Std.(PCM & PCB). Cont. @ 919993551234, 918770887703