Page 2 :
14.3 Proteins, , Q.82. What is the product of reaction of acetic acid with, ammonia? (Can you recall? Textbook page no. 307), (1 mark), Ans. CH,COOH + NH, ———> CH,COON’H,, Acetic acid ammonia, —*., CH,CONH, + H,O, acetamide water, *Q.83. Write the structural formula of N-methyl, acetamide. (Can you recall? Textbook page no. 307), (1 mark), , , , , , , , Ans. CH,- fi - iad, O CH,, , *Q.84. What is the name of the functional group in the, above compound. (Can you recall? Textbook page, no. 307) (1 mark), , Ans. Amido group, , *Q.85. What are the nitrogenous nutrients in human, diet? (2 marks), , Ans. (i) Proteins, *Q.86. What are the nutritional sources of proteins, (2 marks), Ans. (i) Milk (ii) Pulses (iii) nuts (iv) fish (v) meat etc., All these are nutritional sources of proteins., (2 marks), , (ii) Vitamins, , Q.87. Chemically what is a protein?, Ans. Chemically proteins are, , (i) | polyamides which are high molecular weight, polymers of a — amino acids., , 14.3.1 a - Amino acids, , Q.88. What is the expected product of complete, hydrolysis of proteins? (1 mark), , , , Ans. a - amino aicd., , , , Q.89., Ans., , (i), , Q.90., , @), (ii), Q.91., , Ans., , Q.92., , (i), (ii), , (iii), , What are a - amino acids?, , (may, , Carboxylic acid having an a amino (-NH Jn, i is the carbon ne: aoe, [Hint. a carbon is the ¢ xt to C, (carboxyl) group: e.8-: CH, -~COOH], NH,, How is glycine different from all other g ., amino aids? (1 mat, , In glycine, the a carbon is not chiral., Inall other a - amino aids, the a — carbonis chiral, , Give the Fischer projection of a - amino acid,, COOH (1 mark), , HN H, , R, , L-a-amino acid., Classify amino acids, COOH, , (1 mark), , HN H, , R, If R contains a carboxyl group (-COOH), its, acidic amino acid., IfR contains an amino (19, 29, 3° group, itis called, basic amino and, , If R contains neutral or no functional group:, called neutral amino acid., , itis, , Scanned with CamSx
Page 3 :
eee, , ay oN, LL CH,- CH- COOH, N, NH,, H, , Ans., (i) | 1-Tryprophan - neutral a-amino acid, (ii) I - Histidine - basic -amino acid., , *Q.95. Compare the molecular masses of the, following compounds and explain the observed, melting points. (2 marks), , Formula Molecular mass Melting point, CH, - cH - COOH 89 293.5°C, NH,, C,H, - NH, 87 -55°C, C,H, - COOH 88 -7.9°C, , Ans., , (i) Amino acid have both -COOH and -NH,, functional group, , (ii). Amino acids exist as zwitter ions resulting, , in strong dipole - dipole attraction., , (iii) Strong electrostatic forces exist between zwitter, ions (dipolar ions)., , (iv) Hence the o-amino acid CH, - i -— COOH, , NH,, , has a high m.p as compared to an amine and a, carboxylic acid., , Q.96. What is a zwitter ion? OR, Write a note on zwitter ion., , Ans,, , (i) | Ang-amino acid molecule contains both acidic,, carboxyl (~COOH) as well as basic (-NH,) group., , (ii) Proton transfer from acidic group to basic group, of amino acid, forms a salt., , (iii) This salt is a dipolar ion, called zwitter ion., , (2 marks), , Lone pair can, bond fo a proton, , a H ? proton trasfer ® 7 2 8, BR €-0-B Ee, R R, , caiboxyl group Zwitter ion, , can donate proton, Fig. 14.6 : Zwitter ion, Q.97. Give the three different forms of alanine. (3, marks), Ans., , , , (i), , H @, ®@, HN—|-COOH HN—+-co®, CH; CH,, 6) saab, witter ‘, oe . (No net chant, , pH=6, H, un—}-cos?, CH,, , ), Overall -1 charge, pH 2 10, , Fig. 14.7 : Three forms of alanine, , *Q.98. What does the enzyme pepsin do? (Can you, recall? Textbook page no. 309) (1 mark), Ans., , (i) Pepsin is a digestive enzyme which breaks down, proteins into smaller amino acids., , *Q.99. What are the initial and final products of, digestion of proteins? ((Can you recall? Textbook, page no. 309) (3 marks), , Ans., , (i) _ Intial - polypeptides, Final product — amino acids, , , , , , , , 14.3.2 Peptide bond and Protein, , Q.100. What is a peptide bond or Peptide linkage?, (Oct. 2015) (1 mark), , , , Ans., , (i) The bond that connects a-amino acids to eat, other is called peptide bond., , Q.101. How is peptide linkage formed?, , (July 2017) (2 marks), Ans., , (i) a-amino acids are bi-functional compounds, containing a carboxylic acid group and an amit?, group on a-carbon., , HN -CH- COOH, |, , R, , @-amino acid (R = H or alkyl or aryl group), , (2) The i ., ) pee ae of the COOH group of one molec , \ 2 8roup of the neighbouring, nea molecule forms Peptide having co", age by elimination of water., , : OLCdIIICU WILT Cain
Page 4 :
yl, / 3 : Fr, . a 157, | I| 1, [ll foaenl-N-cH-C-on AS y-du (oo-6, - it i —, Pino acid - 1) (3 amino acid - 2) ‘ . ees, Me (Peptide linkage), protein molecule~(dipeptide), , |, , How is tripeptida formed?, pith, , “ adipeptide mol, ° R,, iyo dr-f -NH- CH COOH+ NH, CHC, R, R,, |, ga RGR Ee eoio, , R,, , |, Ni, -CH103, What is a polypeptide? (1 mark), ys. When the number of o-amino acids linked by, peptide bonds is more than ten, the products are, called polypeptides., , 1. | What does 'C' terminal and 'N' terminal in, a polypeptide mean? What are the —-CHR- units, in peptide bonds called? (3 marks), Ans,, , i) The end having free carboxyl group in a, polypeptide is called ‘C' terminal, , ) The end having free amino group is called 'N’, terminal., , , , lecule combines with a third molecule of a-amino acid, a tripetide is formed, , 14.3.3 Types of proteins, , 3 4 5, (3) Above Teaction Tepeats itself to give tri, tetra,, penta and finally polypeptides (i.e. Proteins). ‘, , (Oct. 15) (2 marks), , OOH, , * |, , (iii) The -CHR- units are called amino acid residue., , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , NEL ]CH” CO-NH- —CO-NH - CH -|COOH', |, J R, x |, N - Terminal C-Terminal, amino acid, residue, Q.105. Explain the term proteins. (1 mark), , Ans. Polypeptides having more than hundred amino, acid residues linked by peptide bonds are called, proteins., , , , , , Tt, , , , ‘06, How are proteins classified? OR —, a Distinguish between Globular and Fibrous protein., , , Depending upon the molecular shape, proteins are classified into two types ee, j - eens Fibrous Proteins, Mg They have spherical shape. () They have elongated, rod lke shape —_|, " The coiling around of the polyeptide chain gives| (ii) Holding the polypetide chain of proteins parallel,, iy MRespherical shape, _ to each other gives it ent — }, Cs) “*Y are usually soluble in water. (ii) They are generally iaaublein wate !, , ©8- insulin, egg albumin (iv) Se a eat itt ponds are |, Ieeponsible for this shape], , , , OCAINICU WILIT Udll 13
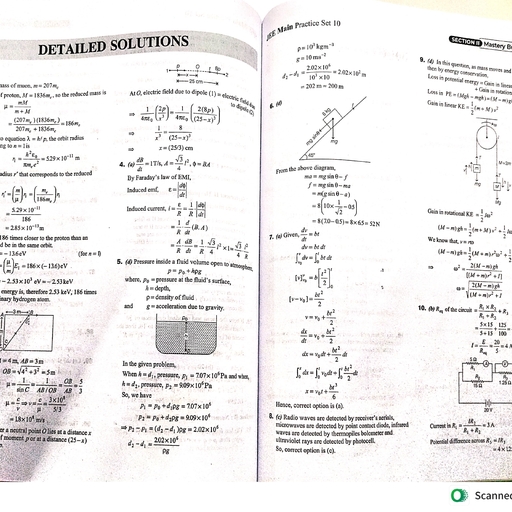
Page 5 :
Se hy,, , Q.107. Where is the protein keratin found? (1 mark), , Ans. Keratin is found in (1) Hair, (2) Nail, (3) Wool., , Q.108. Where is myosin found in living organisms, (1 mark), , Ans. Myosin is found in protein of muscles., , Q.109. Specify the function of proteins in organisms, (2 marks), , Ans., , (i) Proteins of hair, muscles and skin give shape to, the structure., , (ii) while enzymes (which are also proteins) catalyse, Physiological reactions., , , , , , , , 14.3.4 Structure of proteins, , Q.110. How can you understand the diverse functions of, proteins? OR (2 marks), Into how many levels is the structure of protein, divided. Give their names., , Ans. The diverse functions of proteins can be, understood by studying the four level structure, of proteins., , , , , , (i) Primary structure of proteins., , (ii) Secondary structure of proteins., , (iii) Tertiary structure of proteins., , (iv) Quarternary structure of proteins,, , Q.111. Write a note on the following., , — t, (1) _ Primary structure of proteins. May, Ans., , (i) The sequence of constitituent aaming .., residues linked by peptide bonds Bives, bs, primary structure of protein. Th, , (ii) | Any change in the sequence of amino acid rig, in a different protein., , (2) Representation of primary structure of prot,, , P Proteing, , Ans., , i The three letter symbols of amino acid res, are written as per their sequence in the concemej, protein., , (ii) | The symbols are separated by dash., , , , (iii) The N- terminal amino acid residue is written at the left and C-terminal amino acid at the right end., , , , oO, II, , | |, , « N-terminal, , < N-terminal R' R", , oO oO, II II, , NH - CH-C- NH- CH-C-NH-CH-C-NH-CH-C......., , R" R' C-terminal >, , (a) Representation by structural formula, , C-terminal >, , , , (b) Representation with amino acid symbols, , Fig. 14.8 : Representation of primary structure of protein, , Scanned with CamSx