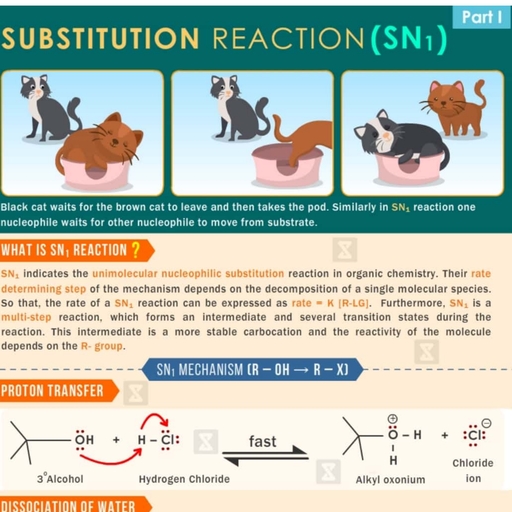
Page 2 :
289, , Amines, , Q. 3 Amongst the following, the strongest base in aqueous medium is ......... ., (a) CH3NH2, (c) (CH3) 2NH, , (b) NCCH2NH2, (d) C6H5NHCH3, , K Thinking Process, This problem is based on concept of basic strength of various types of amine depending, upon inductive effect, resonance and solvation., , Ans. (c), , Factors responsible for, basic character are, , Compound, (a), , CH3 — NH2, , Inductive effect (+ I ), , (b), , NC — CH2 — NH2, , Inductive effect (- I ), , (c), , (CH3 )2 NH, , Inductive effect (+ I )and Solvation, N, , (d), , H, CH3, , - I effect and resonance, , Since, + I effect and solvation increases basic character while -I effect and resonance, decreases basic character. Hence, correct choice is (c)., , Q., , 4 Which of the following is the weakest Bronsted base?, NH2, , NH2, , (a), , Ans. (a), , (b), , N ¾H, , (c), , (d) CH3NH2, , Aniline is weakest Bronsted base among the given four compounds due to resonance, present in case of aniline., NH2, , NH2, , NH2, , NH2, , Resonating structure of aniline, Hence, lone pair of nitrogen are less available for donation to the acid., , Q. 5 Benzylamine may be alkylated as shown in the following equation?, C6H 5CH2NH2 + R — X ¾® C6H 5CH2NHR, Which of the following alkyl halides is best suited for this reaction, through S N 1 mechanism?, (a) CH3Br, (c) C6H5 CH2Br, , (b) C6H5Br, (d) C2H5Br
Page 4 :
Ans. (d), , Source of nitrogen in Gabriel phthalimide synthesis is potassium phthalimide., O, ||, C, , CO, , NH + KOH (alc.), , –+, , –H2O, , NK, , C, ||, O, , RI, D, –KI, , CO, , Phthalimide, , CO, N—R, , +, H /H2O, D, or, –, HO /H2O, D, , COOH, , + RNH2, , CO, , COOH, , 1° amine, , Phthalic acid, , Q., , 9 Amongst the given set of reactants, the most appropriate for preparing, 2° amine is ......... ., (a) 2 °R — Br + NH3, (b) 2 °R — Br + NaCN followed by H2 / Pt, (c) 1 °R — NH2 + RCHO followed by H2 / Pt, (d) 1°R — Br(2 mol) + potassium phthalimide followed by H3 O+/ heat, , Ans. (c), Chemical transformation can be shown as, R ¾ NH2 + RCHO ¾® [R ¾ N == C — R ], |, H, H / Pt, 2, , H, |, R ¾ N¾ C ¾ R, | |, H H, 2 °amine, , While other given set of reactants give primary amine only., , Q. 10 The best reagent for converting 2-phenylpropanamide into, 2-phenylpropanamine is ......... ., (a) excess H2, (b) Br2 in aqueous NaOH, (c) iodine in the presence of red phosphorus, (d) LiAlH4 in ether
Page 8 :
Ans. (a), , Acid anhydride on reaction with primary amine produces amide as, R, , O, , O, , O, , O, , NH2 O, , RNH2, , R, , O, , R, , R, , O, , R, , R + R—COO, , R—N, H, , H, O, R + RCOOH, , R—N, H, +, , Cu/HCl, Q. 20 The reaction ArN2 Cl - ¾ ¾¾, ¾® ArCl + N2, , (a) Sandmeyer reaction, (c) Claisen reaction, , Ans. (b), , Amide, , + CuCl is named as ......... ., , (b) Gattermann reaction, (d) Carbylamine reaction, +, , N2Cl, , –, , Cl, Cu/HCl, , Benzene diazonium, chloride, , + N2 + CuCl, Chlorobenzene, , This reaction is called Gattermann reaction. In this reaction, Cl, Br and CN can be, introduced into the benzene ring by simply treating diazonium salts with HCl, HBr, KCN,, respectively in presence of copper powder instead of using Cu (I) salts., , Q. 21 Best, , method for preparing primary amines from alkyl halides without, changing the number of carbon atoms in the chain is, (a) Hofmann bromamide reaction, (c) Sandmeyer reaction, , Ans. (b), , (b) Gabriel phthalimide synthesis, (d) reaction with NH3, , Best method of preparing primary amines from alkyl halides without changing the, number of carbon atoms in the chain is Gabriel phthalimide synthesis, O, , NH, , O, , O, , O, KOH (alc.), , +, , NK, , R –—X –, , N—R, , O, , O, , NaOH/H2O, , O, + R-NH2, , OH, +, , Primary amine, , O OH, , O
Page 9 :
Q. 22 Which of the following compound will not undergo azo coupling reaction, with benzene diazonium chloride?, (a) Aniline, , Ans. (d), , (b) Phenol, , (c) Anisole, , (d) Nitrobenzene, , Nitrobenzene will not undergo azo coupling reaction with benzene diazonium chloride, while other three undergo diazo coupling reaction very easily. Diazonium cation is a, weak E + and hence reacts with electron rich compounds cotaining electron donating, group i.e., —OH1 — NH2 and —OCH3 groups and not with compounds containing, electron withdrawing group, i.e., NO 2 etc., NH2, , +, , N, , N, , N, , NH2, , N, , N, , OCH3, , N, , N, , OH, , OCH3, –, , NCl, , OH, , Q., , 23 Which of the following compounds is the weakest Bronsted base?, NH2, , (a), , Ans. (c), , Q., , NH2, , (b), , OH, , OH, , (c), , (d), , Phenol is weakest Bronsted base as phenol after loosing H+ produces least stable, conjugate acid among the compounds., Oxygen has more electronegative than N. So, O—H bond is more polar and it has, highest value of acidic character. Since, phenol is more acidic that alcohol, therefore,, phenol has the least tendency to accept a proton and hence it is weak Bronsted base., Hence, phenol is least basic among given four choices., , 24 Among the following amines, the strongest Bronsted base is ......... ., NH2, , (a), , Ans. (d), , (b) NH3, , (c), , H, , H, , N, , N, , (d), , Aniline is a weaker base than NH3 due to delocalization of lone pair of electrons of the, N-atom over the benzene ring. pyrrole is not more basic because the lone pair of, electrons on the N-atom is donated towards aromatic sextet formation., Therefore, pyrrolidine is strongest base as lone pair of nitrogen does not involved in, resonance and also due to presence of two alkyl ring residue, basic strength becomes, high among given four compounds.
Page 10 :
Q. 25 The correct decreasing order of basic strength of the following species is, ......... . H2O, NH 3 , OH - , NH2(a) NH-2 > OH- > NH3 > H2O, (c) NH3 > H2O > NH2- > OH-, , (b) OH- > NH-2 > H2O > NH3, (d) H2O > NH3 > OH- > NH-2, , Ans. (a), N, , H, , H, , OH, , H, , N, , H, , H, , Most basic, , O, , H, , H, , Least basic, , Basic strength of the above species can be explained on the basis of electronegativity, of central atom and its proton accepting tendency. Here, amide ion is most basic, among given compounds due to presence of negative charge and two pair of, electrons on nitrogen atom., , Q. 26 Which of the following should be most volatile?, I. CH 3CH2CH2NH2, CH CH, III. 3 2 NH, CH 3, (a) II, , Ans. (b), , II. (CH 3 ) 3 N, IV. CH 3CH2CH 3, (b) IV, , (c) I, , (d) III, , 1o and 2 o amines have higher boiling points due to intermolecular H-bonding but less, votatile than 3o amines and hydrocarbons of comparable molecular mass. Further,, because of polar C-N bonds, 3o amines are more polar than hydrocorbons which are, almost non-polar. Hence, due to weak dipole-dipole interactions, 3o amines have, higher boiling point (i.e., less volatile) than hydrocarbons., In other words, hydrocarbons are more volatile among given compounds as amine are, less volatile than hydrocarbon., , Q. 27 Which of the following methods of preparation of amines will give same, number of carbon atoms in the chain of amines as in the reactant?, (a) Reaction of nitrite with LiAlH4, (b) Reaction of amide with LiAlH4 followed by treatment with water, (c) Heating alkylhalide with potassium salt of phthalimide followed by hydrolysis, (d) Treatment of amide with bromine in aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide., , Ans. (a, b, c), Aliphatic and arylalkyl primary amines can be easily prepared by the reduction of the, corrsponding nitriles with LiAlH4 ., R - C º N or Ar - C º N ® LiAlH4 RCH2 NH2 or ArCH2NH2, Alkynitrile, , Arynitrile, , 1o amine, , Heating alkyl halide with Primary, secondary and tertiary amine can be prepared by, reduction of LiAlH4 followed by treatment with water., (i) LiAlH, , / ether, , 4, R - CONH2 ¾ ¾ ¾ ¾, ¾¾® R — CH2 — NH2, , 1°amide, , (ii) H 2O
Page 17 :
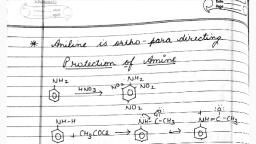
Ans., , Complete conversion can be shown as, CH3, , CH3, (i) NaNO2 + HCl,, 273-278 K, , NO2, , NO2, , NH2, , N2Cl, CH3, , 2-nitro - 4 methyl, aniline, , Cu+, , + H3PO3 + HCl + N2, , (ii) H3PO2, H2O, , NO2, 3-methyl, nitrobenzene, , Q., , 43 What is Hinsberg reagent?, , Ans., , Benzene sulphonyl chloride (C 6H5SO 2Cl) is known as Hinsberg reagent. It is used to, distinguish between primary, secondary and tertiary amine., , Q. 44 Why is benzene diazonium chloride not stored and is used immediately, after its preparation?, Ans., , Benzene diazonium chloride are highly unstable and stable for a very short time span in, solution at low temperature. Due to its instability, it is used immediately after its, preparation., , Q. 45 Why, , does acylation of ¾ NH2 group of aniline reduces its activating, , effect?, Ans., , Acylation of ¾NH2 group of aniline reduces its activity due to resonance of lone pair of, nitrogen towards the carbonyl group hence o - , p- directive influence of amino group get, disturbed., NH2, , NHCOR, , RCOCl, , N, , The resonating structure are, O, , H, , O, , C, , N, , H, , R, , C, , N, , R
Page 18 :
Q., , 46 Explain why MeNH2 is stronger base than MeOH?, , Ans., , Basicity of MeNH2 and MeOH can be explained on the basis of electronegativity of N and, O atom. MeNH2 is stronger base than MeOH because of low electronegativity value of N, it, is easy for nitrogen to loose its lone pair readily than compared to MeOH., , Q. 47 What is the role of pyridine in the acylation reaction of amines?, Ans., , Pyridine being a base, is used to remove the side product i.e., HCl from reaction mixture., NH2, , NHCOCH3, CH3COCl, , + HCl, , + HCl,, N, , N, , N, , –, , Cl, , H, , Q. 48 Under, , what reaction condition (acidic, basic) the coupling reaction of, aryl diazonium chloride with aniline is carried out?, , Ans., , In strongly basic conditions, benzenediazonium chloride is converted into diazohydroxide, and diazoate as both of which are not electrophilic and do not couple with aniline., +, , NaOH, , -, , C 6H5 N º NC l + OH SO 2 CH5 - N = N - OH S, , -, , C 6H5 - N = N - ONa +, , Diazohydroxide, , Sodium diazoate, , Similarly, in highly acidic conditions, aniline gets converted into anilinium ion. From this,, result aniline is no longer nucleophilic acid and hence will not couple with diazonium, chloride. Hence, the reaction is carried out under mild conditions, i.e., pH' -4 - 5, C 6H5NH2 + H+ ®, Aniline, , +, , C 6H5 - NH3, Anilinium ion, (coupling do not occur), , Q. 49 Predict, , the product of reaction of aniline with bromine in non-polar, solvent such as CS2 ., , Ans., , Aniline on reaction with Br2 in non-polar solvent CS2 produces 2, 4, 6 tribromo aniline., NH2, , NH2, Br, , Br, , Br2, CS2, <5°C, Aniline, , Br, 2, 4, 6 tribromo, aniline, , Aniline has high reactivity towards bromine as it gives the triply substituted product., , Q. 50 Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of dipole moment., CH3CH2CH3 , CH3CH2NH2 , CH3CH2OH, , Ans., , Dipole moment of amine, alcohol and hydrocarbon can be explained on the basis of bond, polarity of C — H, N — H and O — H bond. As the bond polarity increase, dipole moment, increases CH3CH2CH3 < CH3CH2NH2 < CH3CH2OH
Page 19 :
Q., , 51 What is the structure and IUPAC name of the compound, allyl amine?, Ans. Structural formula of allyl amine is as follows, 3, , 2, , 1, , CH2 == CH —CH2 — NH2, Prop -2-ene -1-amine (IUPAC name), , Q. 52 Write down the IUPAC name of, N(CH3)2, , CH3, , CH3, , Ans., , N, , N, N-dimthyl benzenamine, , During naming of N-substituted amine, substituted group present at N are added as suffix, on N-alkyl in IUPAC nomenclature., , Q. 53 A, , compound Z with molecular formula C 3H 9N reacts with C6H 5SO2Cl to, give a solid, insoluble in alkali. Identify ., K Thinking Process, This process is based on concept of Hinsberg test. Only amine containing replaceable H, gives Hinsberg test., , Ans., , Z(C 3H9N) is an aliphatic amine. On reaction with C 6H5SO 2Cl (Hinsberg’s reagent), it gives a, product insoluble in alkali. It means that the product does not have a replaceable H-atom, attached to the N- atom. So, compound Z is a secondary amine (ethyl methyl amine)., CH3 ¾ NH + C 6H5SO 2Cl ¾® CH3 ¾ N ¾ SO 2C 6H5, N-ethyl -N-methyl, |, benzene sulphonamide, C 2H5, (Insoluble in alkali), Ethymethylamine, [ Z = C 3H 9N ], , Q. 54 A, , primary amine, RNH2 can be reacted with CH 3 — X to get secondary, amine, R—NHCH 3 but the only disadvantage is that 3° amine and, quaternary ammonium salts are also obtained as side products. Can you, suggest a method where RNH2 forms only 2° amine?, , Ans., , KOH/CHCl 3, , RNH2 ¾ ¾ ¾ ¾¾®, RNC, Primary amine Carbylamine reaction Alkyl Iso cyanide, , H 2/ Pd, , ¾¾¾, ¾® RNHCH3, Secondary amine, , Primary amines show carbylamine reaction in which two H-atoms attached to N-atoms of, NH2 are replaced by one C-atom. On catalytic reduction, isocyanide (formed) produces, secondary amine and not tertiary or quaternary salts.
Page 27 :
Assertion and Reason, In the following questions a statement of Assertion (A) followed by a statement of, Reason (R) is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices., (a) Both assertion and reason are wrong., (b) Both assertion and reason are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation, of assertion., (c) Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement., (d) Both assertion and reason are correct statements and reason is correct explanation of, assertion., (e) Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement., , Q. 68 Assertion, , (A) Acylation of amines gives a monosubstituted product, whereas alkylation of amines gives polysubstituted product., Reason (R) Acyl group sterically hinders the approach of further acyl, groups., , Ans. (c), , Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement., Acylation of amine gives a monosubstituted product whereas alkylation of amine gives, polysubstituted product because acylation in amine takes place at N-atom and, alkylation takes place at o and p position., , Q. 69 Assertion (A) Hofmann’s bromamide reaction is given by primary amines., Reason (R) Primary amines one more basic than secondary amines., Ans. (a) Both assertion and reason are wrong., Correct Assertion Hofmanns bromamide reaction is given by amide., Correct Reason Amide on reaction with NaOX produces amine having one carbon less, than amide., , Q. 70 Assertion (A) N-ethylbenzene sulphonamide is soluble in alkali., Reason (R) Hydrogen attached to nitrogen in sulphonamide is strongly, acidic., Ans. (d), , Both assertion and reason are correct and reason is the correct explanation of, assertion., N-ethylbenzene is soluble in alkali because hydrogen attached to nitrogen in, sulphonamide is strongly acidic and forms a salt during reaction between these two., , Q. 71 Assertion (A) N, N-diethylbenzene sulphonamide is insoluble in alkali., Reason (R) Sulphonyl group attached to nitrogen atom is strong electron, withdrawing group., Ans. (d), , Both assertion and reason are correct and reason is not the correct explanation of, assertion., N, N-diethylbenzene sulphonamide is insoluble in alkali due to absence of acidic H, attached to nitrogen.
Page 28 :
Q. 72 Assertion (A) Only a small amount of HCl is required in the reduction of, nitro compounds with iron scrap and HCl in the presence of steam., Reason (R) FeCl 2 formed gets hydrolysed to release HCl during the, reaction., Ans. (d), , Assertion and reason both are correct and reason is the correct explanation of, assertion., Only small amount of HCl is required in the reduction of nitro compounds with iron, scrap and HCl in the presence of steam because FeCl 2 formed gets hydrolysed to, release HCl during the reaction., , Q. 73Assertion (A) Aromatic 1° amines can be prepared by Gabriel phthalimide, synthesis., Reason (R) Aryl halides undergo nucleophilic substitution with anion, formed by phthalimide., Ans.(a), , Both assertion and reason are wrong. Aryl 1° amine can’t be prepared by Gabriel, phthalimide reaction because aryl halide don’t undergo nucleophilic substitution with, anion formed by phthalimide., , Q. 74 Assertion (A) Acetanilide is less basic aniline., Reason (R) Acetylation of aniline results in decrease of electron density, on nitrogen., Ans. (d), , Assertion and reason both are correct and reason is the correct explanation of, assertion., Acetanilide is less basic than aniline because acetylation of aniline results in decrease, of electron density on nitrogen., , Long Answer Type Questions, Q. 75 A, , hydrocarbon ‘A’ (C 4H 8 ) on reaction with HCl gives a compound ‘B,’, (C 4H 9Cl), which on reaction with 1 mol of NH 3 gives compound ‘C,’, (C 4H 11N). On reacting with NaNO2 and HCl followed by treatment with, water, compound ‘C’ yields an optically active alcohol, ‘D’. Ozonolysis of, ‘A’ gives 2 mols of acetaldehyde. Identify compounds ‘A’ to ‘D’. Explain, the reactions involved., K Thinking Process, This problem includes conceptual mixing of ozonolysis, optical activity, ammonolysis, and diazotisation. Follow the steps to solve the problem, Analyse the overall reaction once then sequentially predict a molecule for each A,B,C, and D on the basis of information provided in the question., Fit every molecule in a flow chart made by using information provided in the question, and reach to the correct compounds.