Page 1 :
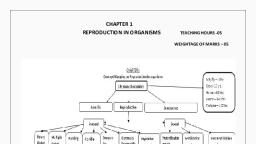
CHAPTER 1, REPRODUCTION IN ORGANISMS, , , , Life span- Is the period of time from birth to natural death of an organism, , , , , , Organism Life span, Mayfly 1day, , Butterfly 1-2 weeks, Wheat plant 6 months, Crow 15 years, Crocodile 60 years, , Man 100 years, Parrot 140 years, Tortoise 100-150 years, Banyan tree 200 years, , , , , , , , Asexual reproductive structures, , , , , , , , , , , , Zoospores Chlamydomonas, Conidia Penicillium, Gemmule Sponge, Buds Hydra, Yeast, , , , , , , , 8, , Zoospores of Chlamydomonas, , mouth, , Bud, , Buds in Hydra, , Conidia, , , , Conidia of Penicillium, , , , Gemmules in Sponges, , Asexual Reproductive Structures
Page 2 :
Differences between asexual and sexual reproduction, , , , , , , , Asexual Reproduction Sexual Reproduction, , Asingle parent is involved Two parents are involved, , There is no formation and fusion There is formation and fusion of, , of gametes gametes, , All individuals produced are genetically All individuals produced exhibit variation, identical.( Clone ), , , , , , Clone - Morphologically and genetically similar individuals formed by, asexual reproduction., , Binary fission in Amoeba, , The parent cell divides into two halves and each grows, into an adult., , , , Nucleus 1, Budding in Yeast cell, Parent cell produces lateral buds, later gets seperated s, and grows into an adult ., , _t, , , , Parent cell, , Budding in Yeast, , Daughter cells, , Budding in Hydra, Parent cell produces lateral buds, later gets seperated and grows into an adult
Page 3 :
Significance of Vegetative Propagation, , 1 Good method for multiplication of seedless plants., , 2 The plants produced by vegetative propagation will have the same characters of, their parent plant., , , , Vegetative Propagules, Runner Oxalis, Eyes Potato, Offset Water Hyacinth / Pistia, Bulbs Onion / Garlic, Rhizome Ginger / Banana, Bulbil Agave, Leaf buds Bryophyllum/ Kalanchoe, , , , , , , , Eyes, , Te, , #4, (ES, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , f r = ‘Adventitious, Eyes of Potato ——, Rhizome of Ginger, A, ‘al, iF / Adventitious, : J / buds, /, SW/, NW, 2 Leaf buds of, Bulbil of Agave Bryophyllum Offset of Water hyacinth, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , The Terror of Bengal - Water Hyacinth ( an aquatic plant ), Itis one of the most invasive weed that drains oxygen from the standing water which, leads to the death of fishes.It divides at a faster rate and spreads within a short time.
Page 4 :
Sexual Reproduction, , Oestrus Cycle - NonPrimate mammals. Eg -Cow, Sheep, dog etc, Menstrual cycle - Primate mammals. Eg: - Monkeys,Apes, Humans etc, Gametogenesis Process of formation of gametes, , Homogametes Fusing gametes are morphologically similar.(ilso gametes), Heterogametes Fusing gametes are morphologically different, , , , 6 , \, 4, }, lsogametes, of Heterogametes, Cladophora of Heterogametes, , Fucus of, Homo sapiens, , , , Male gametes---Antherozoid / Sperm, Female gamete---Egg (Ovum ), , , , , , Zygote is the vital link, that ensures continuity of species between organisms of, one generation and of the next., , Unisexual male flower : Staminate, Unisexual female flower : Pistillate, , Unisexual : Cockroach:: Bisexual ( Hermaphrodite ): Earthworm, , Monoecious : Both male and female flowers are present in same plant., , Eg :Cucurbita,Coconut, , Dioecious__: Male and female flowers are present in separate plants.Eg: Papaya,, Date palm, , , , , , , , , , , , External fertilisation Eg :- Frog Internal fetilisation Eg :- Man, , The fusion of gametes (Syngamy) occur Syngamy occurs inside the, , outside the body of organisms body of organisms., , Vulnerable to the predators, , Oviparous animals Eg :- Birds Viviparous animals Eg :- Majority, of mammals, , Egg laying animals Animals which give birth to young ones., , Eggs are protected by calcareous shell Young ones are protected inside, mothers body, , , , , , , , B-4
Page 5 :
Disadvantage of Oviparous animals, The offsprings are vulnerable to predators., , Embryogenesis : Development of embryo, , Parthenogenesis :Female gamete develops into an adult organism, without fertilisation.Eg :Honey bees, some lizards and birds, , Parthenocarpy : Development of fruits without fertilisation. Such fruits are always, seedless.|t can be induced by the application of hormones like auxins, , and gibberellins. Eg :- Banana, , Chromosome Numbers in Meiocytes (diploid, 2n ) and, , gametes (haploid, n ) of some organisms., , , , , , , , Name of organism Chromosome number|Chromosome number, in meiocyte ( 2n ) in gamete (n ), , Human beings 46 23, House fly 12 6, Rat 42 21, Dog 78 39, Cat 38 19, Fruit fly 8 4, Ophioglossum (a fern ) 1260 630, Apple 34 17, Rice 24 12, Maize 20 10, Potato 48 24, Butterfly 380 190, Onion 32 16, , , , , , , , Number of chromosomes in gametes is half the number of chromosomes in, meiocytes, , Advantages of viviparous animals, , Because of proper embryonic care and protection, the chances of survival of, young ones is greater in viviparous organisms, , Syngamy, , The process of fusion of male and female gametes., , Pollination, The transfer of pollen grains from the, , anther to the stigma. ©, , Fusion of Zygote New, gametes individual