Page 1 :
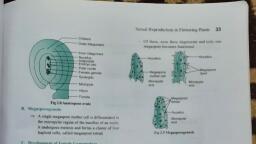
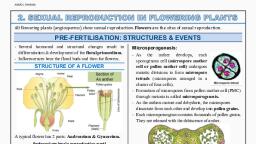
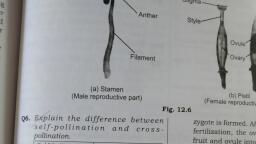
LEARNING OUTCOMES —, , When this chapter is completed, the students should be able ¢, * describe the structure of anther, as seen in a cross section,, © describe the process of microsporogenesis and formation of, © describe the structure of pollen gains., , , , , , SEXUAL REPRODUCTION IN, FLOWERING PLANTS, , pollen grains,, , * describe the structure of ovule, megasporogenesis and formation of female gametophyte, , * explain the different types of pollination,, , ® list the agents of pollination and the adaptations, the flowers have for a particular type of pollination, , * explain double fertilisation., , * explain the development of endosperm., , * explain the development of embryo from zygote along with, « describe the types of fruits., , « explain apomixis and polyembryony with suitable examples., , , , IMPORTANT TERMS AND CONCEPTS, , 2.1, FLOWERS: THE FASCINATING ORGANS OF, ANGIOSPERMS, * A flower is a shoot modified for reproduction., « Flowers bear the reproductive organs, where gametes, are produced., « Androecium is the male reproductive whorl, it consists, of stamen(s).., + Gynoecium is the female reproductive whorl; it consists, of carpel(s)., Petal, , Anther, Filament, , , , | Stamen, , |r, , , , Thalamus, ‘Ovules, , Pedicel, , Fig 2.1 L.S, of a Complete Flower, , , , diagrams,, , , , 2.2, PRE-FERTILISATION: STRUCTURES AND, EVENTS, 2.2.1, Stamen, Microsporangium, and Pollen grains, , — Atypical stamen consists of two parts:, ( along and slender stalk, called filament, (id) a terminal, bilobed structure called anther., , — The proximal end of the filament is attached to the, thalamus or the petal (epipetalous)., , Anther, Pollen sac, Lines of, dehiscence, Filament, Filament, (@ (), , Entire stamen —_ Anther cut across, , Fig 2.2 A Stamen