Page 1 :
Microbes in Human Welfare, 1 Mark Questions, 1. Give the scientific name of the source organism from which the first antibiotic was, produced., Ans. The scientific name of organism, i.e. mould from which first antibiotic was, produced is Penici Ilium notatum., 2. Which of the following is the baker’s yeast used in fermentation? Saccharum, barberi, Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Sonalika., Ans.Saccharomyces cerevisiae is the baker’s yeast used in fermentation., 3. Write the scientific name of the microbe used for fermenting malted cereals and, fruit juices., Ans. Saccharomyces cerevisiae also, commonly called brewer’s yeast is the, microbe used for fermenting malted cereals and fruit juices., 4. Mention the information that the health workers derive by measuring BOD of a, waterbody., Ans. Higher the BOD of water body, more is its polluting potential and vice-versa., BOD indicates the presence of organic matter in the water., 5. Why is sewage water treated until the BOD is reduced? Give a reason., Ans. The greater the BOD of sewage water, more is its polluting potential. So, the, sewage water is treated, till its BOD is reduced to reduce the organic matter present, in it., 6. Milk starts to coagulate when Lactic Acid Bacteria (LAB) is added to warm milk as, a starter. Mention any other two benefits LAB provides., Ans. Two benefits of LAB:, (i) They improve the nutrient quality of curd by increasing the vitamin-B12 content., (ii) LAB also check the growth of disease causing microbes in the stomach., 7. BOD of two samples of water A and B were 120 mg/L and 400 mg/L,Which, sample is more polluted?, Ans. Sample B(BOD 400 mg/L) is more polluted as higher the BOD, more is the, polluting potential, 1
Page 2 :
8. Given below are a few impurities in urban wastewater. Select two colloidal, impurities : ammonia, faecal matter, silt, bacteria, calcium., Ans. Faecal matter and silt are the colloidal impurities in urban wastewater., , 2 Marks Questions, 9.Name two groups of organisms which constitute ‘floes’. Write their influence on the, level of BOD during biological treatment of sewage., Ans. The groups of organisms that constitute mesh like structures called ‘floes’ are, bacteria and fungi., These bacterial masses associated with fungal filaments called floes, consume the, major part of organic matter present in effluent, thereby reducing the BOD of the, waste significantly during biological or secondary treatment of sewage., 10. Why is ‘starter’ added to set the milk into curd? Explain., Ans. When a small amount of curd as starter is added to fresh milk, millions of Lactic, Acid Bacteria (LAB) present in the starter grow in milk and convert it to curd. During, this process, acids are produced by LAB that coagulate and partially digest the milk, proteins (casein). LAB increases vitamin-B12 content along with other vitamins in the, curd, 11. Name the bacterium responsible for the large holes seen in swiss cheese. What, are these holes due to?, Ans. Swiss cheese is produced by the bacterium Propionibacterium shermanii. The, large holes in swiss cheese are due to the large amount of C02 production, 12. Name the source of streptokinase. How does this bioactive molecule function in, our body., or, Name the enzyme produced by Streptococcus bacterium. Explain its importance in, medical sciences., Ans. Streptokinase enzyme is produced by the bacterium Streptococcus. It is, modified by genetic engineering and is used as a clot buster for removing clots from, the blood vessels of patients who have suffered from myocardial infarction., 13. Mention the importance of lactic acid bacteria to humans other than setting milk, into curd., , 2
Page 3 :
Ans. (i)Lactic Acid Bacteria (LAB) are used to produce an acid called lactic acid that, is an important industrial product. It is also used in beverages, meat products,, confectionary, dairy products, etc., (ii) It also checks disease causing microbes in stomach., 14. Name the source of cyclosporin-A. How does this bioactive molecule function in, our body?, Ans. Cyclosporin-A is produced by the fungus Trichoderma polysporum. It is used as, an immunosuppressive agent in organ-transplant patients., 15. Name the source of statin and state its action on the human body., or, Give the scientific name of the microbes from which cyclosporin-A and statin are, obtained. Write one medical use of each one of these drugs., Ans. Statin is produced by yeast Monascus purpureus. It is used as blood, cholesterol lowering agent., It acts by competitively inhibiting the enzyme responsible for synthesis of cholesterol., or, Cyclosporin-A is produced by the fungus Trichoderma polysporum. It is used as an, immunosuppressive agent in organ-transplant patients., Statin is produced by yeast Monascus purpureus. It is used as blood cholesterol, lowering agent., It acts by competitively inhibiting the enzyme responsible for synthesis of cholesterol., 16. Why are some molecules called bioactive molecules? Give two examples of such, molecules., Ans. Bioactive molecules are produced from living organisms and are useful in other, living organisms. Examples are streptokinase, cyclosporin-A, statins., 17. How does addition of a small amount of curd to fresh milk help formation of curd?, Mention a nutritional quality that gets added to the curd., or, Explain the change fresh milk undergoes when a small amount of curd as starter is, added to it and kept at suitable temperature., 3
Page 4 :
Ans. When a small amount of curd as starter is added to fresh milk, millions of Lactic, Acid Bacteria (LAB) present in the starter grow in milk and convert it to curd. During, this process, acids are produced by LAB that coagulate and partially digest the milk, proteins (casein). LAB increases vitamin-B12 content along with other vitamins in the, curd, 18. During the secondary treatment of the primary effluent. How does the significant, decrease in BOD occur?, Ans. During the secondary treatment, the aeration allows vigorous growth of useful, aerobic microbes into floes (masses of bacterial cells in association with, fungalfilaments forming mesh-like structures). As they grow, the microbes consume, a major part of the organic matter in the effluent, so BOD is significantly reduced., 19. Identify A, B, C and D in table given below:, , Ans.A- Streptococcus, , B- Cyclosporin-A, C- Immunosuppressive agent D-Myocardial infarction, , 20. Name the blank spaces A, B, C and D in the table given below:, , Ans.A- Penicillium notatum, C- Fungus, , B- Acetic acid, D- Saccharomyces cerevisiae, , 21. Name the blank spaces A, B, C and D given in following table:, , 4
Page 5 :
Ans.A- Lactobacillus, , B- Trichoderma polysporum, C- Yeast, D-Penicillin, 22. Name the blank spaces A, B, C and D given in the following table:, , Ans., , A- Streptococcus, B- Fungus, C- Cyclosporin-A, D- Clostridium butylicum, , 23.Name the blank spaces A, B, C and D from the table given below:, , Ans., , A- Trichoderma polysporum, B- Immunosuppressive agent, C- Yeast, D- Blood cholesterol lowering agent, , 24. State the use of following enzymes/acids produced by the microbes, (i)lipase, , (ii) lactic acid, , (iii) streptokinase (iv) pectinase, Ans. The use of following products formed by microbes are:, (i) Lipase is used in detergent preparation and in removal of oil stains from clothes., (ii) Lactic acid produced by Lactobacillus converts milk into curd., 5
Page 6 :
(iii) Streptokinase is used as a ‘clot buster’ for removing blood clots from blood, vessels in patients of myocardial rction., (iv) Pactinase is used to clear (bottled) fruit juices., 25. How has fungus Trichoderma polysporum proved to be very essential to organ, transplant patients?, Ans.This fungus produces a bioactive molecule, called cyclosporin-A, which is used, as an immunosuppressive agent in organ transplant patients., , 3 Marks Questions, 26. Identify A, B, C, D, E and F in the table given below: [Foreign 2014], , Ans.The codes are identified as, A- Clot buster in patents who underwent myocardial infarction., B- Trichoderma polysporum, C- Immunosuppressive agent in organ transplantation, D- Statins, E – Blood cholesterol lowering agents, F – Lactic acid, 27. Name the two different categories of microbes naturally occurring in sewage, water. Explain their role in cleaning sewage water into usable water., Ans. Bacteria and fungi are the two categories of naturally occurring microbes in, sewage. The bacteria along with the fungal mycelia form the floes. These floes are, utilised during the secondary treatment of sewage. The primary effluent after, separation of the grit and debris is taken to the secondary treatment., Here, the effluent is passed to an aeration tank, where it is constantly agitated and, air is pumped into it. This leads to vigorous growth of bacteria and floe formation., The bacteria in these floes consume organic matter, thus decreasing the BOD of the, sewage., , 6
Page 7 :
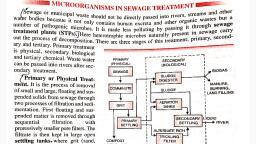
28. Explain the different steps involved in sewage treatment before it can be, released into natural water bodies., Ans.Sewage treatment includes following steps:, (i) Primary Treatment, It is a physical process of removal of small and large particles through filtration and, sedimentation., The first step is to remove the floating objects (like polythene bags) by letting the, sewage to pass through wire mesh screens of sequential smaller pore sizes., Sewage is then passed into the grit chamber, where grit is sedimented., Sewage is then allowed to pass into the settling tank, where the suspended, materials settle down to form primary sludge., Effluent is then taken for the secondary treatment., (ii)Secondary Treatment, It is a biological process in which bacteria naturally occurring in sewage are used., Effluent obtained from the primary treatment is passed into large aeration tank. Here,, it is constantly agitated and air is pumped into it., Due to this, rapid growth of aerobic bacteria occur into floes. These consume the, organic matter of the sewage and reduce the BOD., Effluent is passed into settling tank, where the floes are allowed to settle forming the, activated sludge., A small amount of activated sludge is pumped back into aeration tank as inoculum., The remaining major part of the activated sludge is pumped into anaerobic sludge, digesters, where the anaerobic bacteria digest the organic matter and produce, methane, hydrogen sulphide and carbon dioxide., Effluent is then allowed to pass into the water body., 29. Identify A, B, C, D, E and F in the table given below:, , 7
Page 8 :
Ans.A-Statins, B-They are used as blood cholesterol lowering agent, C-Penicillium, notatum, D-Penicillin, E-Trichoderma polysporum, F-Used as an immunosuppressive, agent in organ transplant patients., 30. Mention the product and its use produced by each of the microbes listed below:, Streptococcus, Lactobacillus, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Ans.(i) Streptococcus Product is streptokinase. It is used as a clot-buster for, removing the clots from the blood vessels of patients suffering from myocardial, infarction., (ii) Lactobacillus Product is lactic acid. It is used to convert milk into curd and, improves nutrient quality of curd by enriching it with vitamin-B12., (iii) Saccharomyces cerevisiae Product is ethanol and also used for bread making, and beverages., 31. Describe how biogas is obtained from the activated sludge?, Ans. Biogas formation from activated sludge:, (i) A small part of activated sludge is pumped into the aeration tank to serve as, inoculum. It grows into floes and consume organic matter to reduce BOD., (ii) The remaining major part of sludge is pumped into large tanks called anaerobic, sludge digesters., (iii) Here, anaerobic bacteria digest the organic material of the sludge., (iv) During this digestion, the bacteria produces a mixture of gases like carbon, dioxide, methane and hydrogen sulphide which form the biogas., 32., , (i) How does activated sludge get produced during sewage treatment?, (ii) Explain how this sludge is used in biogas production?, , Ans.(i) (a) The primary effluent is passed into large aeration tanks. Due to the, constant agitation floes formation occur, which are masses of bacteria associated, with fungal hyphae., (b) These microbes consumes sufficient quantity of organic matter and there by, reduce BOD., 8
Page 9 :
(c) Once, the BOD of sewage water gets reduced significantly, the effluent is passed, into a settling tank, where the bacterial floes undergo sedimentation and the, sediment is called activated sludge., (ii) Biogas formation from activated sludge:, (i) A small part of activated sludge is pumped into the aeration tank to serve as, inoculum. It grows into floes and consume organic matter to reduce BOD., (ii) The remaining major part of sludge is pumped into large tanks called anaerobic, sludge digesters., (iii) Here, anaerobic bacteria digest the organic material of the sludge., (iv) During this digestion, the bacteria produces a mixture of gases like carbon, dioxide, methane and hydrogen sulphide which form the biogas., 33. How are floes produced in the secondary treatment plant of the sewage? Explain, their role, Ans. The effluent obtained from primary treatment is passed into large aeration, tanks, where it is constantly agitated and air is pumped into it. This allows rapid, growth of aerobic microbes into floes., Floes consume organic matter of the sewage and reduce the Biochemical Oxygen, Demand (BOD). When BOD of sewage is reduced, the effluent is passed into a, settling tank, where the floes are allowed to form the activated sludge., 34. (i)Expand BOD., (ii) At a particular segment of a river near a sugar factory, the BOD is much higher, than the normal level. What is it indicative of? What will happen to the living, organism in this part of the river?, (iii) Under what conditions will the BOD be lowered in the river? How will it affect the, aquatic life?, Ans. (i) Biochemical Oxygen Demand., (ii) The higher BOD indicates high organic matter in river. Microbes involved in the, biodegradation of organic matter in water body consume a lot of oxygen., Due to this, a sharp decline occur in the amount of dissolved oxygen. This leads to, killing of fish and othe microorganisms in that part of river., (iii) BOD of water body decreases when the amount of organic matter decreases., Thus, microbes do not need oxygen for its decomposition., 9
Page 10 :
Due to the decreased BOD, aquatic life will start flourishing., , 5 Marks Questions, 35. Explain the process of sewage water treatment before it can be discharged into, natural water bodies. Why is this treatment essential, Ans. The process of sewage water treatment before being discharged into natural, water bodies., Sewage treatment includes following steps:, (i) Primary Treatment, It is a physical process of removal of small and large particles through filtration and, sedimentation., The first step is to remove the floating objects (like polythene bags) by letting the, sewage to pass through wire mesh screens of sequential smaller pore sizes., Sewage is then passed into the grit chamber, where grit is sedimented., Sewage is then allowed to pass into the settling tank, where the suspended, materials settle down to form primary sludge., Effluent is then taken for the secondary treatment., (ii)Secondary Treatment, It is a biological process in which bacteria naturally occurring in sewage are used., Effluent obtained from the primary treatment is passed into large aeration tank. Here,, it is constantly agitated and air is pumped into it., Due to this, rapid growth of aerobic bacteria occur into floes. These consume the, organic matter of the sewage and reduce the BOD., Effluent is passed into settling tank, where the floes are allowed to settle forming the, activated sludge., A small amount of activated sludge is pumped back into aeration tank as inoculum., The remaining major part of the activated sludge is pumped into anaerobic sludge, digesters, where the anaerobic bacteria digest the organic matter and produce, methane, hydrogen sulphide and carbon dioxide., Effluent is then allowed to pass into the water body, 10
Page 11 :
This sewage treatment is essential before being released into water bodies as it, leads to water pollution and as a consequence increase in water borne diseases., 36. (i) Name the category of microbes naturally occurring in sewage and making it, less polluted during the treatment., (ii) Explain the different steps involved in the secondary treatment of sewage., Ans. (i) The category of microbes naturally occurring in sewage and making it less, polluted are bacteria and fungi, wherein masses of bacteria gets associated with, filaments of fungi to form mesh like structure called floes., (ii) The different steps involved in secondary or biological treatment of sewage., Secondary Treatment, It is a biological process in which bacteria naturally occurring in sewage are used., Effluent obtained from the primary treatment is passed into large aeration tank. Here,, it is constantly agitated and air is pumped into it., Due to this, rapid growth of aerobic bacteria occur into floes. These consume the, organic matter of the sewage and reduce the BOD., Effluent is passed into settling tank, where the floes are allowed to settle forming the, activated sludge., A small amount of activated sludge is pumped back into aeration tank as inoculum., The remaining major part of the activated sludge is pumped into anaerobic sludge, digesters, where the anaerobic bacteria digest the organic matter and produce, methane, hydrogen sulphide and carbon dioxide., Effluent is then allowed to pass into the water body, , DR. NIDHI SEHGAL, PGT (BIOLOGY), , 11