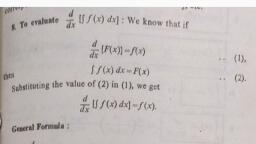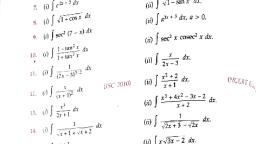Page 3 :
6. j cot(ax+b) dx = 2 log |sin (ax + b) | +c, = ~A tog |cosec (ax +) | +0, , 7. j sec(ax+b) dx "ators mea, , , , te, , (e+ x, stein (59), , , , 8. Jeminine dx, , = i log | cosec (ax + b) ~ cot (ax + b) | +c, tan( 23), , INTEGRALS OF TYPE [, , , , +c, , , , = Hiog, , , , , , dx, , asinx+bcosx, , To evaluate these type of integrals, we put, a=rcosaand b=rsin.a, where rand a are constants., » Pcostatr2sin2a = a? +b?, ©. P (costa +sin? a) = a2 +b?, , o PW) +b. 5, . Paes DH, , , , 7 Va 4b?, , After simplication using these substitutions, we, evaluate the integral., , INTEGRALS OF TYPE, , asinx +bcosx, csinx +dcosx, , ae* +b 4, , dx, Ie, , ce*+d, , To evaluate these type of integrals, we express, numerator in terms of denominator using, , , , Numerator = A (Denominator) + B 4 (Denominator),, , where A and B are constants which we find by, comparing coefficients of sin x, cos x and e*, constant., , | INTEGRALS CONTAING ODD POWERS |, , , , OF sin x OR cos x, , To evaluate integrals containing odd powers of, sin x or cos x, we separate sin x or cos x, then we, convert sin x or cos x having even power into cos x, or sin x using identity and then we substitute t for, cos x or sin x., , , , , , PHt, , , , INTEGRALS: CONTAINING EVEN, POWERS OF sin x OR cos x, , To evaluate integrals containing even powers of, sin x or cos x, we express the even powers of sin x or, cos x in the form of sin? x or cos? x and then we use, , , , sin? x = Legs, , or cos?x = digger, , , , |, , 2 f, 3. f, , INTEGRALS CONTAINING ANY POWER, OF tan x OR cot x, , To evaluate integtals containing even / odd, powers of tan x or cot x, we separate tan? x or cot? x, and then use identity.tan? x = sec? x — 1 or cot? x =, cosec? x -1 and then we substitute ¢ for tan x or cot x., , INTEGRALS CONTAINING EVEN, POWERS OF sec x OR cosec x, , To evaluate integrals containing even powers of, sec x or cosec x, we separate sec? x or cosec®.x and, then we convert remaining powers of sec x or cosec x, into tan x or cot x using identity sec? x= 1+ tan? x or, cosec? x= 1+ cot?, , , , - er emaarns, , where n is the L.C.M. of the denominators of fractional. powers., , j as = sn*(2}s0, = log| + Va? +3" [nc, , dx, va? +x?, i = log]xtvx?-a? J+e, ae 8, x -a@, , , , , , , , 4, J-= We = 1 sec” (z Jee, , , , , , , , , , , , : dx 1 “(2), 5. ==tan™'|—l+c, Pex? a 4, dx x-a, 6 l ve a 98 x4a/*°, dx _ 1, jjatx, 7. pg" te log’ stl
Page 4 :
For evaluation of above type of integrals, we use, following substitutions., , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , Expression Substitution, , ae +x? x=atan@orx=acot®, ve —x2 x=asin 0 orx=acos 0, ne? —q? x=asec 8 orx=acosec®, , = atx A, BAX or J* x=a-cos 20 or x=asin 20, a+Xx a-x We, , 2_y2 2 :, , a°-x ., , ss or | Et* | x2 =? cos 20 or x?= a? sin 24, a +x ax, , a x= asin? 0 or x=acos?0, a+x ‘, , — x=atan? 0 or x=acot? 6, xr = acos? in?, , eee a +, , bow x=acos?@+bsin?6, , , , , , , , , , , , , the coefficient nee, and dividing we tere, , expression as the sum or difference of two square, terms. Finally using appropriate formula, we, evaluate the integrals., , INTEGRALS OF TYPE, , _pttg ay, Vax? +bxte °°, , To evaluate these type of integrals, we express, , rd i, f, ax Teen, , , , the numerator in the form px +q=A 4 (ax? + bx +c) +, , B, where A and B are constants which we find by, comparing coefficients of x and constants from both, sides. Finally using appropriate formula, we evaluate, the integrals., , , , , , INTEGRALS OF TYPE f eet, , ax’ +bx+c, , WHERE 4 (x) IS A POLYNOMIAL IN x OF, , DEGREE GREATER THAN OR EQUAL TO, TWO, , ,, , , , To evaluate these type of integrals, we divide $(x), by ax? + bx + ¢ to express integrand as, 4(x), ax? +bx+c, formula, we evaluate the integral., , p(x)+ Finally using appropriate, , , , dx, INTEGRALS OF TYPE J evgdacar, , , , , , To evaluate these type of integrals, we put, ax + b = f? and then using appropriate formula,, evaluate the integral., , INTEGRALS OF TYPE, , a+bcos’ x’, (4... /—.#, a+bsin’ x’ / a+bcos’x+csin’ x, To evaluate these type of integrals, first we divide, both numerator and denominator by cos? x, then, replace sec? x if any in the denominator by 1 + tan? x., , Using substitution tan x = f, we evaluate the integral, by appropriate formula. ., , INTEGRALS OF TYPE j ft,, ae, at+bcosx+csinx, , a:, J aban’ J, , To evaluate these type of integrals, we put, , , , L (ita? (3)) dx'=2dt
Page 5 :
(1+) dx=2dt, , 2dt, 2, eke, eran, x, 2tan(3) 2, sinx= =,, 1+ tan? 5) aE, 2, 2(x, cosx 1—tan’ (3) _ 1?, 1+tan*(3) +e ., 2), , Using these, we evaluate integral by appropriate, method., , , , , ae, a+bcos2x’., , f dxf dx, , a+bsin2x’ } a+beos2x+csin2x, , , , , INTEGRALS OF TYPE j, , , , , , , , , , To evaluate these type of integrals, we put tan x=t, . sectx dx =dt, , . 2 = At, . 1+tan*x Te, , , , I-tan?x 1-2, , cos x=, l+tan?x 142?, , Using these, we evaluate integrals by appropriate, method., , INTEGRATION BY PARTS, , If wand »v are functions of x, then, du, Jude = uf vde- | (4 J vd)ax, , In general, , J fered, = FO) f 362)de- J (P(e) f e(2)ax) ax, , While using integration by parts theorem, we, choosé first function (w) and second function (v) in, the order of the letters of the word LIATE, where, L - Stands for the logarithmic function., , I - Stands for an inverse trigonometric function., A -.Stands for the algebraic function., , T - Stands for the trigonometric function., , E - Stands for an exponential function., , In the product of u and 2, if there is only one, function, then unity is taken as second function., , , , , , , , STANDARD FORMULAE, 1. [feeder = fee f gear, -f@% J (fee ax) dx, sro (J (f scrax) dx) ar-.., , é, , , , , , 2. |e“ sinbx dx = = (asinbx-beosbx)+c, a’ +b :, , 3, J et cosh a -2 (acosbx +bsin bx) +c, , . aop?, , 4. fee fandr =e f(a)re, , 5. | em( foe F(a) = Lem fiajee, , 6. fe" (m flay f'@)) di =e f(x) +e, , 2 :, 9: J a? —x? dx = gue =x? +5 sin"'(2} +c, , xadox? [+e, ctx? <a? [re, , , , , , , , j (px+q)Vax? +bx+0 dx, , To evaluate these type of integrals, we express, px+qin the form px+q= AL (ax?-+bx+0)+B, where, , A and B ate constants which we find by comparing, coefficients of x and constants from both sides. Finally, using appropriate formula, we evaluate the integrals., , { INTEGRATION BY PARTIAL FRACTION: s], f(x), , If f(x) and g (x) are two polynomials, then 3)", g (x) # 0 defines a rational algebraic function or a, rational function of x. 5 ¢, , , , , , If degree of f (x) < degree of g (zx), then ia 's, called a proper rational function., If degree of f (x) 2 degree of g (x), then a 's, , called an improper rational function.