Page 1 :
Roll No. :, Date :, , Time MM - 271, , 1.X-rays were discovered by, (a) Fermi, (b) Newton, (c) Eienstein, (d) Roentgen, Ans :, , 1, , (d), , 2. Conservation laws of charge, energy, momentum and angular momentum are applicable to, , 1, , (a) Everywhere, (b) Isolated system, (c) Non-inertial frame, (d) Some specific condition only., Ans :, , (b), , 3. Prof. Albert Einstein got noble prize in Physics for his work on, , 1, , (a) Special theory of relativity., (b) Equivalence of mass-energy., (c) Photoelectric effect., (d) Fifth state of matter BEC., Ans :, , (c), , 4. Weak nuclear force, , 1, , (a) is stronger repulsive force., (b) act between elementary particles., (c) operate beyond the range of nuclear size., (d) is conservative force., Ans :, , (b), , 5. Production of ultra high magnetic fields is based on scientific principle of, , 1, , (a) Superconductivity, (b) Radioactivity, (c) Electromagnetic induction, (d) Heating substance beyond their boiling point, Ans :, , (a), , 6.Which of the following is incorrect about strong nuclear force?, , 1
Page 2 :
(a) Strongest attraction and about 1038 times of gravitational force, (b) Short range and act between closest neighbouring nucleon., (c) Caused by exchange of π-mesons., (d) Central and conservative force., Ans :, , (d), , 7. Strongest attractive force in nature is, , 1, , (a) Frictional force on rough surface., (b) Electromagnetic force., (c) Strong nuclear force., (d) Gravitational force., Ans :, , (c), , 8. Following process is known as, , 1, , hν → e+ + e–, (a) Nuclear fission, (b) Pair production, (c) Annihilation, (d) Photoelectric effect, Ans :, , (b), , 9. Which of the following not correct about the electromagnetic force?, , 1, , (a) It obey inverse square law., (b) It is central force and conservative in nature., (c) It is independent on medium., (d) It is stronger than weak nuclear force., Ans :, , (c), , 10.Magnetic effect of current is discovered by, (a) Biot-Savart, (b) Oersted, (c) Michael Faraday, (d) Lorentz, Ans :, , 1, , (b), , 11. Elementary particle having zero rest mass and zero charge is, , 1, , (a) neutron, (b) baryons, (c) leptons, (d) neutrino, Ans :, , (d), , 12. Which of the following have same dimensions?, (a) Specific heat and latent heat, , 1
Page 3 :
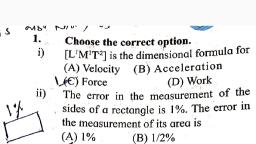
(b) Momentum and impulse, (c) Moment of inertia and moment of momentum., (d) Tension and surface tension., Ans :, , (b), , 13. Which of the following is a dimensional constant?, , 1, , (a) refractive index, (b) dielectric constant, (c) relative density, (d) gravitational constant., Ans :, , (d), , 14.The dimensional formula for latent heat is, (a) M°L2T–1, (b) ML2T–1, (c) MLT–2, (d) ML2T–2, Ans :, , 1, , (a), , 15. The length of a rod is (11.05 ± 0.05) cm. What is the total length of 2 such rods?, , 1, , (a) (22.1 ± 0.05) cm, (b) (22.10 ± 0.05) cm, (c) (22.1 ± 0.11) cm, (d) (22.1 ± 0.10) cm, Ans :, , (d), , 16. The velocity v of a particle is given in terms of time t is v = at +, , 1, , The dimensions of a, b, c are, (a) L2; TLT–2, (b) LT2; LT; L, (c) LT–2; L; T, (d) L; LT; T2, Ans :, , (c) As c is added to t, therefore, c has the dimensions of [T], As,, , =v, , ∴ b = v × t = LT–1 × T = [L], , 17. Which of the following sets cannot enter into the list of fundamental quantities in any system of, units?, , 1
Page 4 :
(a) Length, time and velocity, (b) Length, mass and velocity, (c) Mass, time and velocity, (d) Length, time and mass., Ans :, , (a) Length, time and velocity can be deduced from one another. Therefore, they cannot, enter into the list of fundamental quantities in any system, , 18., In the standard equation Snth =, , , what dimensions do you view for Snth?, , 1, , (a) M°L1T°, (b) M°L–1 T1, (c) M°L1T–1, d) M°L°T1, Ans :, , (c), , 19. Which one of the following quantities has not been expressed in proper units?, , 1, , (a) Coeff. of elasticity: N/m2, (b) Surface tension: N/m, (c) Energy: kg m/s, (d) Pressure: N/m2, (c) Energy = [M1 L2 T–2] = Kgm2 g–2, Ans :, 20. The number of significant figures in 3400 is, , 1, , (a) 3, (b) 4, (c) 2, (d) 1, Ans :, , (c), , In x = 3400, zero are not significant. Therefore, number of significant figure = 2., 21. Match List I with List II and select the correct answer:, , (a) A-3, B-4, C-2, D-1, (b) A-4, B-3, C-1, D-2, (c) A-4, B-3, C-2, D-1, (d) A-3, B-4, C-1, D-2, , 1
Page 5 :
Ans :, , (a), , Hertz = unit of frequency = [M0 L0 T–1], Joule = unit of work = [M1L2T–2], 22. The length and breadth of a metal sheet are 3.124 m and 3.002 m respectively. The area of this, sheet up to four correct significant figures is:, , 1, , (a) 9.37 m2, (b) 9.378 m2, (c) 9.3782 m2, (d) 9.378248 m2, Ans :, , (b), , As area = length × breadth, therefore, as per rules, numerical value of area has four significant digits., 23. Which of the following quantities can be written in SI units in kg2 m2 A–2 s–3?, , 1, , (a) Resistance, (b) Inductance, (c) Capacitance, (d) Magnetic flux, Ans :, , (a), , 24. If C represents capacitance and R represents resistance, then the unit of CR2 are:, (a) Henry, (b), (c) Volt/ampere, (d) Joule/ampere2, , 1
Page 6 :
Ans :, , (a, b, d), , 25.The pair(s) of physical quantities that have the same dimensions is (are):, (a) volumetric strain and coefficient of friction., (b) disintegration constant of a radioactive substance and frequency of light wave., (c) heat capacity and gravitational potential., (d) Planck’s constant and torque., Ans :, , 1, , (a, b, c), , Both have same dimensions., (c) Heat capacity is measured in cal/kg and gravitational potential is measured in, joule/kg. Both have the same dimensions [L2T–2]., 26. Which of the following combinations have the dimensions of time? L, C, R represent inductance,, capacitance and resistance respectively?, , 1, , (a) RC, (b) LC, (c) R/L, (d) C/L, Ans :, , (a, b), , We know, R = [M1L2T–3A–2], L = [M1L2T–2A–2], C = [M–1L–2T4A2], , ∴ RC = T and, , =T, , 27. The dimensions of capacitance are (where Q is the dimension of charge):, (a) M–1L–2T2Q2, (b) MLT–2Q–2, (c) M1L–1T2, (d) M–1L–2T2Q, , 1
Page 7 :
Ans :, , (a), , 28. The unit of charge is:, , 1, , (a) Ampere, (b) Coulomb, (c) Ampere/sec, (d) Ampere-second, (c, d), Ans :Unit of charge = Coulomb = Ampere × Sec, 29. The units of electrical permittivity are:, , 1, , (a) N–1m–2C2, (b) Nm–2C2, (c) C2/Nm2, (d) n/Cm2, Ans :, , (a, c), , 30. The pairs of physical quantities that have the same dimensions are:, , 1, , (a) Reynolds number and coefficient of friction, (b) Latent heat and gravitational potential, (c) Curie and frequency of light wave, (d) Planck’s constant and torque., (a, b, c), Ans :(a) Reynolds number and coefficient of friction, both are dimensionless., (b), (c) 1 curie = 3.7 × 1010 disintegrations/sec = T–1 Frequency = T–1, 31. Pressure is defined as:, (a) Momentum per unit area, (b) Momentum per unit area per unit time, (c) Momentum per unit volume, (d) Energy per unit volume, Ans :, , (b, d), , (b) Momentum per unit area per unit time, , (d) Energy per unit volume =, , 1
Page 8 :
32. Which of the following set have different dimensions?, , 1, , (a) Pressure, Young’s modulus, Stress, (b) Emf, potential difference, Electric potential, (c) Heat, Work done, Energy, (d) Dipole moment, Electric flux, Electric field, (d), Ans :Dimensions of dipole moment,, p = q × 2a = (AT) × L = [M0L1T1A1], Dimensions of electric field, , Dimensions of electric flux,, , 33. The number of significant figures in 0.06900 is, , 1, , (a) 5, (b) 4, (c) 2, (d) 3, Ans :, , (b), , Initial zero after the decimal point is not significant., 34. The sum of the numbers 436.32, 227.2 and 0.301 in appropriate significant figures is, , 1, , (a) 663.821, (b) 664, (c) 663.8, (d) 663.82, Ans :, , (b), , 436.32 + 227.2 + 0.301 = 663.821 = 664 (rounding off to three significant figures), 35.The mass and volume of a body are 4.237 g and 2.5 cm3, respectively. The density of the, material of the body in correct significant figures is, (a) 1.6048 g/cm3, (b) 1.69 g/cm3, (c) 1.7 g/cm3, (d) 1.695 g/cm3, Ans :, , (c), , = 1.6948 g/cm3 = 1.7 g/cm3, (rounding off to two significant figures), , 1
Page 9 :
36. The numbers 2.745 and 2.735 on rounding off to 3 significant figures will give, , 1, , (a) 2.75 and 2.74, (b) 2.74 and 2.73, (c) 2.75 and 2.73, (d) 2.74 and 2.74, Ans :, , (d), , In 2.745, the digit to be rounded off (i.e., 4) is even, hence it should be left unchanged and in, 2.735, the digit to be rounded off (i.e., 3) is odd, hence it should increased by 1, i.e., changed, to 4., 37. Which of the following measurements is most precise?, , 1, , (a) 5.00 mm, (b) 5.00 cm, (c) 5.00 m, (d) 5.00 km, Ans :, , (a), , It is a measurement of distance to second place of decimal in mm., 38. The mean length of an object is 5 cm. Which of the following measurements is most accurate?, , 1, , (a) 4.9 cm, (b) 4.805 cm, (c) 5.25 cm, (d) 5.4 cm, Ans :, , (a), , It is closer 5 cm and correct upto first place of decimal., 39. Young’s modulus of steel is 1.9 × 1011 N/m2. When expressed in CGS units of dynes/cm2, it will, be equal to (1N = 105 dyne, 1 m2 = 104 cm2), , 1, , (a) 1.9 × 1010, (b) 1.9 × 1011, (c) 1.9 × 1012, (d) 1.9 × 1013, Ans :, , (c), , 40.If momentum (P), area (A) and time (T) are taken to be fundamental quantities, then energy has, the dimensional formula, (a) (P1A–1T1), (b) (P2A1T1), (c) (P1A–1/2T1), (d) (P1A1/2T–1), , 1
Page 10 :
Ans :, , (d), , Let energy, E ∝ PaAbTc, or E = kPaAbTc, or [ML2T–2] = [MLT–1]a [L2]b [T]c = [MaLa+2bT–a+c], Whence, a = 1, b = 1/2 , c = –1, Dimensional formula for E is [P1A1/2T–1], 41. On the basis of dimensions, decide which of the following relation(s) for the displacement of a, particleundergoing simple harmonic motion is (are) not correct:, , 1, , (a) y = a sin 2/πt/T, (b) y = a sin vt, (c), (d), Ans :, , (b, c), , The argument of sin and cos should be dimensionless,, which is not so in case of (vt) and (t/a). More so, in (c), (a/T) is not displacement as it is, equal to amplitude/ time period., Refer to Higher order thinking Skills, 42.If P, Q, R are physical quantities, having different dimensions, which of the following, combinations (s) can never be a meaningful quantity?, (a) (P – Q)/R, (b) PQ – R, (c) PQ/R, (d) (PR – Q2)/R, (e) (R + Q)/P, Ans :, , 1, , (a, e), , (P – Q) and (R + Q), being the difference and sum of two, quantities with different dimensions, are meaningless., (b, c) : PQ may have the same dimensions as those of R., (d) : PR and Q2 may have same dimensions as those of R., 43. Photon is quantum of radiation with energy E = hν where ν is frequency and h is Planck’s, constant. The dimensions of h are the same as that of, (a) Linear impulse, (b) Angular impulse, (c) Linear momentum, (d) Angular momentum, Ans :, , (b, d), , Planck’s constant = [ML2T–1], (a) Linear impulse = Ft = [MLT–2][T] = [MLT–1], (b) Angular impulse = Iω = [ML2][T–1] = [ML2T–1], (c) Linear momentum = mv = [M] [LT–1] = [MLT–1], (d) Angular momentum = mve = [M] [LT–1][L] = [ML2T–1], , 1
Page 11 :
44. If Planck’s constant (h) and speed of light in vacuum (c) are taken as two fundamental, 1, quantities, which one of the following can, in addition, be taken to express length, mass and time in, terms of the three chosen fundamental quantities?, (a) Mass of electron (me)., (b) Universal gravitational constant (G)., (c) Charge of electron (e)., (d) Mass of proton (mp)., , Ans :, , (a, b, d), Refer to Solved Problem 19, Page 36 and Topic Based, Problems of Practice 40 and 41, Page 45., , Mass can be expressed by me and mp, 45. Which of the following ratios expresses pressure?, , 1, , (a) Force/Area, (b) Energy/Density, (c) Energy/Area, (d) Force/Volume, Ans :, , (a), , 46. Which of the following are not a unit of time?, , 1, , (a) Second, (b) Parsec, (c) Year, (d) Light year, Ans :, , (b, d), , Parsec and light year are the units of length., 47.Which of the following has metre kelvin as the unit?, (a) Rydberg constant, (b) Wein’s constant, (c) Solar constant, (d) Gas constant., , 1
Page 12 :
Ans :, , (b), , 48. Which of the following has metre kelvin as the unit?, , 1, , (a) Rydberg constant, (b) Wein’s constant, (c) Solar constant, (d) Gas constant., Ans :, , (a), , A dimensionless quantity may have a unit. For example, angle has a unit but is, dimensionless., 49. A dimensionless quantity, , 1, , (a) may have a unit, (b) never has a unit, (c) always has a unit, (d) doesn’t exist., Ans :, , 50. The physical quantities not having same dimensions are:, , 1, , (a) momentum and Planck’s constant, (b) speed and (μ0 ∈0)–1/2, (c) speed and, (d) surface tension and spring constant, Ans :, , (a), Momentum = mv = [MLT–1], , 51. The physical quantities not having same dimensions are:, (a) momentum and Planck’s constant, (b) speed and (μ0 ∈0)–1/2, (c) speed and, , 1
Page 13 :
(d) surface tension and spring constant, Ans :, , (a), Momentum = mv = [MLT–1], , 52. Which of the following systems of units is not based on units of mass, length and time alone?, , 1, , (a) S.I., (b) MKS, (c) FPS, (d) CGS, Ans :, , (a), , International system (SI) is not based on units of mass, length and time alone., 53. The length and breadth of a rectangular sheet are 16.2 cm and 10.1cm, respectively. The area of, the sheet in appropriate significant figures and error is, , 1, , (a) 164 ± 3 cm2, (b) 163.62 ± 2.6 cm2, (c) 163.6 ± 2.6 cm2, (d) 163.62 ± 3 cm2, Ans :, , (a), , As l = 16.2 cm, b = 10.1 cm, A = lb = 163.62 cm2, Since l and b contain 3 figures, i.e., A = 164 cm2, , (Rounding off to one significant figure as only the last digit in 164 is uncertain), The, A ± ∆A = (164 ± 3) cm2, 54. Which of the following pairs of physical quantities does not have same dimensional formula?, (a) Work and torque., (b) Angular momentum and Planck’s constant., (c) Tension and surface tension., (d) Impulse and linear momentum., , 1
Page 14 :
Ans :, , (c), , (a) Work = Force × Distance = [MLT–2][L] = [ML2 T–2], Torque = Force × Distance = [ML2T–2], (b) Angular momentum = mvr = [M][ML–1][L] = [ML2 T–1], , (c) Tension = force = [MLT–2], , (d) Impulse = Force × Time = [MLT–2] = [T] = [MLT–1], Momentum = Mass × Velocity = [M][LT–1] = [MLT–1], 55. Measure of two quantities along with the precision of respective measuring instrument is, , 1, , A = 2.5 m/s ± 0.5 m/s, B = 0.10 s ± 0.01 s, The value of AB will be, (a) (0.25 ± 0.08) m, (b) (0.25 ± 0.5) m, (c) (0.25 ± 0.05) m, (d) (0.25 ± 0.135) m, Ans :, , (a), Z = AB = (2.5 m/s) (0.10 s) = 0.25 m, , = 0.25 m (0.2 + 0.1), = 0.07 m = 0.08 m, 56. A stone is dropped into well in which the level of water is at a distance h below the top of well. If, v is the velocity of sound, the time T after which the splash is heard is given by, , Ans :, , 1
Page 15 :
57. The distance travelled by a body is directly proportional to the square of the time taken. Its, acceleration, , 1, , (a) increases, (b) decreases, (c) becomes zero, (d) remains constant, Ans :, , (d), , 58. Wind is blowing west to east along two parallel tracks., , 1, , Two trains moving with same speed in opposite directions have the steam track of one double, then other. The speed of each train is, (a) equal to that of wind, (b) double that of wind, (c) three times that of wind, (d) half that of wind., Ans :, , (c), , Let u and v be the speed of train and wind respectively., The speed of steam track of train moving in the direction of wind = u – v, The speed of steam track of train moving in the opposite direction of wind = u + v, As per question, (u + v) = 2(u – v) or u = 3v, 59. A particle moving with a uniform acceleration travels 24 metre and 64 metre in first two, consecutive intervals of 4 seconds each. Its initial velocity is, , 1, , (a) 1 m/s, (b) 2 m/s, (c) 5 m/s, (d) 10 m/s, Ans :, , 60. A ball is thrown up, it reaches a maximum height and then comes down. If t1(t2 > t1) are the, times that the ball takes to be at a particular height then the time taken by the ball to reach the, highest point is, (a) (t1 + t2), (b) (t1 – t2), (c) (t2 – t1)/2, (d) (t2 + t1)/2, , 1
Page 16 :
Ans :, , (d), , Let s be the height of a particular point where the ball crosses in time t1 and t2 seconds, while going upwards and coming downwards. If u is the initial velocity of projection of ball,, then, , If T is the time taken by ball to reach to its highest point then using the relation v = u + at, we, have 0 = u + (–g)T, , 61. A stone is dropped from a certain height and at the same time another stone is thrown, horizontally from the same height which one will reach the ground earlier., , 1, , (a) first stone, (b) second stone, (c) simultaneously, (d) not sure., Ans :, , Ans. (c), , Since the initial vertical velocity of both the stones is zero and both are accelerated vertically, downwards by equal acceleration, hence they reach earth simultaneously., 62. A particle is forced to move on a straight line path. It returns to the starting point after 10, 1, seconds. The total distance covered by the particle during this time is 20 m. Which of the following, statements is false regarding the motion of the particles?, (a) The average velocity of the particle is zero., (b) The displacement of the particle is zero., (c) The average speed of the particle is 2.0 ms–1., (d) The displacement of the particle is 20 m., Ans :, , (d), , When a particle while moving returns to its initial, position after a certain time, then its displacement in, that time is zero. Its average velocity ( = displacement/, time) is also zero., , 63. Select the correct statements for a particle going on a straight line:, (a) If the position and velocity are in opposite directions, the particle is moving towards the origin., , 1
Page 17 :
(b) It the acceleration and velocity are in opposite directions, the particle is slowing down., (c) If the velocity is zero for a time interval, the acceleration is zero at any moment within that time, interval., (d) If the velocity is zero at any instant, then the acceleration must also be zero at that instant., Ans :, , (a, b, c), , 64., , 1, , (a) Maximum speed of the particle is 4 units., (b) Particle further comes to rest at x = 4., (c) Particle oscillates about x = 2., (d) Particle will continuously accelerate along the x-axis., Ans :, , (b, c), , 65. Among the four graphs, there is only one graph for, , 1, , which average velocity over the time interval (0, T), can vanish for a suitably chosen T. Which one is it?, , Ans :, , (b), , When (x-t) graph is convex upward, v is decreasing and, when it is convex downward, v is increasing. Between, these two regions, the average velocity can be zero., 66. A lift is coming from 8th floor and is just about to, reach 4th floor. Taking ground floor as origin and, positive direction upwards for all quantities, which, one of the following is correct?, (a) x < 0, v < 0, a > 0, (b) x > 0, v < 0, a < 0, (c) x > 0, v < 0, a > 0, (d) x > 0, v > 0, a < 0, , 1
Page 18 :
Ans :, , (a), , When the lift is about to reach the 4th floor, it is retarding,, i.e., a is acting upward. i.e., a > 0, (fig). However,, x and v being in the downward direction are negative, i.e.,, x < 0 v < 0., , 67. In one dimensional motion, instantaneous speed v, , 1, , satisfies 0 ≤ v < v0., (a) The displacement in time T must always take non-negative values., (b) The displacement x in time T satisfies – v0T < x < v0T., (c) The acceleration is always a non-negative number., (d) The motion has no turning points., Ans :, , (b), , Since maximum distance covered in time T is v0T,, displacement in time T can have both positive and, negative values between –v0T and –v0T ., 68. The displacement of a particle is given by x = (t – 2)2, , 1, , where x is in metres and t in seconds. The distance, covered by the particle in first 4 seconds is, (a) 4 m, (b) 8 m, (c) 12 m, (d) 16 m, Ans :, , (b), , As x = (t – 2), x4 – x0 = (4 – 2)2 – (0 – 2)2, =4m+4m=8m, 69. The variation of quantity A with quantity B, plotted, in Fig. describes the motion of a particle in a straight, line. Choose the correct statement(s)., , (a) Quantity B may represent time., (b) Quantity A is velocity if motion is uniform., , 1
Page 19 :
(c) Quantity A is displacement if motion is uniform., (d) Quantity A is velocity if motion is uniformly accelerated., Ans :, , (a, b, c), , 70. For the one-dimensional motion, described by, , 1, , x = t – sin t, (a) x(t) < 0 for all t > 0., (b) v(t) > 0 for all t > 0., (c) a(t) > 0 for all t > 0., (d) v(t) lies between 0 and 2., Ans :, , (d), , 71. A man throws ball into the air one after the other., , 1, , Throwing one when other is at the highest point. How, high the balls rise if he throws twice a second?, (a) 2.45 m, (b) 1.225 m, (c) 19.6 m, (d) 4.9 m, Ans :, , (b), , The time taken by each ball to go from starting point to, highest point, t = 1/2 sec, which is equal to time taken, by each ball to fall back to starting point (= 1/2 sec)., , 72. A balloon is going upwards with velocity 12 m/sec. It, releases a packet when it is at a height 65 m from the, ground. How much time the packet will take to reach, the ground? (g = 10 m/s2), (a) 5 sec, (b) 6 sec, (c) 7 sec, (d) 8 sec, Ans :, , 1
Page 20 :
73. The position of a particle moving in the X-Y plane, , 1, , at any time t is given by; x = (3t2 – 6t) meters;, y = (t2 – 2t) meters. Select the correct statement., (a) acceleration is zero at t = 0, (b) velocity is zero at t = 0, (c) velocity is zero at t = 1 second, (d) velocity and acceleration of the particle are never zero., Ans :, , 74. A stone is thrown with an initial speed of 4.9 m/s from, , 1, , a bridge in vertically upward direction. It falls down in, water after 2 seconds. The height of the bridge is, (a) 4.9 m, (b) 9.8m, (c) 19.8 m, (d) 24.7 m, Ans :, , (b), , Taking vertical downward motion of stone, we have, u = –4.9 m/s, a = 9.8 m/s2, t = 2s, s = ?, , 75. A balloon starts rising from the ground with an, acceleration of 1.25 m/s2. After 8 seconds, a stone is, released from the balloon. The stone will, (use g = 10 m/s2)., (a) cover a distance of 40 m, (b) have displacement of 50 m, (c) reach the ground in 4 second, (d) begin to move downward after being released., , 1
Page 21 :
Ans :, , (c), , Taking upward motion of balloon for 8 seconds; we, have, u = 0; a = 1.25 m/s2; t = 8 s; v = ?; s = ?., Here v = u + at = 0 + 1.25 × 8 = 10 m/s, , Taking downward motion of released stone from balloon, at height 40 m we have,, u = –10 m/s; a = 10 m/s2; s = 40 m; t = ?, , or t2 – 2t – 8 = 0. On solving t = 4s., 76. The displacement of a particle is represented by the, , 1, , following equation s = 2t3 + 7t2 + 5t + 8 where s is in, metres and t in seconds. The acceleration of the particle, at t = 1s is, (a) 18 m/s2, (b) 32 m/s2, (c) zero, (d) 14 m/s2, Ans :, , 77. An object while moving may not have, , 1, , (a) variable speed but constant velocity., (b) variable velocity but constant speed., (c) non-zero acceleration but constant speed., (d) zero acceleration but constant velocity., Ans :, , (a), , 78. A particle moves along a straight line as, s = u(t – 2) + a(t – 2)2, (a) the acceleration of the particle is ‘a’., (b) the initial velocity of the particle is ‘v’., (c) at t = 2s, the particle is at rest., , 1
Page 22 :
(d) the acceleration of the particle is ‘2a’., Ans :, , (d), , 79. A vehicle travels half the distance L with speed V1 and, , 1, , the other half with speed V2, then its average speed is, , Ans :, , (c), , 80. The length of seconds hand of a watch is 1 cm. The change in velocity of its tip in 15 seconds in, cm/s is, , Ans :, , 1, , (d), , The angle described at the centre by the length of second hand of a watch in 15 second =, 90° = π/2 radians Figure., , 81. Five equal forces of 10 N each are applied at one point and are all lying in one plane. If the, angles between them are equal, the resultant of these forces will be, (a) Zero, (b) 10 N, (c) 20 N, (d) 10 2N, , 1
Page 23 :
Ans :, , (a), , The five forces inclined equally acting on the particle can be represented by the five sides of, a pentagon taken in the same order. Hence, their resultant is zero., 82., , 1, , (a) tan–1 (3/2), (b) tan–1 (2/3), (c) sin–1 (2/3), (d) cos–1 (3/2), Ans :, , 83. The simple sum of two forces acting at a point is 16 N and their sum is 8 N and its direction is, perpendicular to the smaller force, then the forces are:, (a) 6 N and 10 N, (b) 8 N and 8 N, (c) 4 N and 12 N, (d) 2 N and 14 N, Ans :, , 1
Page 24 :
84., , 1, , Ans :, , 85. A projectile is hurled into air from a point on the horizontal ground at an angle with the vertical., , 1, , If the air exerts a constant resistive force,, (a) the path of projectile will be parabolic path., (b) the time of ascent will be equal to time of decent., (c) the total energy of the projectile is not conserved., (d) at the highest point, the velocity of projectile is horizontal., Ans :, , (a, c, d), , 86. A cart moves with a constant speed along a horizontal circular path. From the cart, a particle is, thrown up vertically with respect to the cart, the particle will,, , 1, , (a) land outside the circular path., (b) land somewhere on the circular path., (c) follow a parabolic path., (d) follow an elliptical path., Ans :, , (a, c), , 87. A ball is bouncing elastically with a speed 1 m/s between walls of a railway compartment of size 1, 10 m in a direction perpendicular to walls. The train is moving at a constant velocity of 10 m/s, parallel to the direction of motion of the ball. As seen from the ground,, (a) the direction of motion of the ball changes every 10 seconds., (b) speed of ball changes every 10 seconds., (c) average speed of ball over any 20 second interval is fixed., (d) the acceleration of ball is the same as from the train., Ans :, , (b, c, d), , 88. Which one of the following statements is true?, (a) A scalar quantity is the one that is conserved in a process., (b) A scalar quantity is the one that can never take negative values., (c) A scalar quantity is the one that does not vary from one point to another in space., (d) A scalar quantity has the same value for observers with different orientations of the axes., Ans :, , (d) The option is self-explanatory., , 1
Page 25 :
89., , Ans :, , 1, , (b), , 90. Consider the quantities, pressure, power, energy, impulse, gravitational potential, electrical, charge, temperature, area. Out of these, the only vector quantities are, , 1, , (a) Impulse, pressure and area., (b) Impulse and area., (c) Area and gravitational potential., (d) Impulse and pressure., Ans :, , (b), Impulse, , is a vector quantity. Area of a surface is a vector which is along the normal, , to the surface in the outward direction., 91. In a two dimensional motion, instantaneous speed v0 is a positive constant. Then which of the, following are necessarily true?, , 1, , (a) The average velocity is not zero at any time., (b) Average acceleration must always vanish., (c) Displacements in equal time intervals are equal., (d) Equal path lengths are traversed in equal intervals., Ans :, , (d), , 92. In a two dimensional motion, instantaneous speed v0 is a positive constant. Then which of the, following are necessarily true?, (a) The acceleration of the particle is zero., , 1
Page 26 :
(b) The acceleration of the particle is bounded., (c) The acceleration of the particle is necessarily in the plane of motion., (d) The particle must be undergoing a uniform circular motion., Ans :, , (c), , 93., , Ans :, , 1, , (c), , 94., , 1, , Ans :, , 95. Two particles are projected in air with speed v0 at angles θ1 and θ2 (both acute) to the horizontal, 1, respectively. If the height reached by the first particle is greater than that of the second, then tick, the right choices, (a) angle of projection : q1 > q2, (b) time of flight : T1 > T2, (c) horizontal range : R1 > R2, (d) total energy : U1 > U2
Page 27 :
Ans :, , 96. A particle slides down a frictionless parabolic (y = x2 ) track (A → B → C) starting from rest at, , 1, , point A (Fig.). Point B is at the vertex of parabola and point C is at a height less than that of point A., After C, the particle moves freely in air as a projectile. If the particle reaches highest point at P, then, (a) KE at P = KE at B., (b) height at P = height at A., (c) total energy at P = total energy at A., (d) time of travel from A to B = time of travel from B to P., Ans :, , (c), , Since the parabolic track is frictionless, there is no loss of energy from A to B, B to C. Thus,, total energy at P = total energy at A., 97. Following are four different relations about displacement, velocity and acceleration for the, motion of a particle in general. Choose the incorrect one (s) :, , Ans :, , 1, , (a, c), , These relations are true only for uniform acceleration., 98. For a particle performing uniform circular motion,, choose the correct statement(s) from the following:, (a) Magnitude of particle velocity (speed) remains constant., (b) Particle velocity remains directed perpendicular to radius vector., (c) Direction of acceleration keeps changing as particle moves., (d) Angular momentum is constant in magnitude but direction keeps changing., Ans :, , (a, b, c), , 1
Page 28 :
99. A body is thrown with a velocity of 10 ms–1 at an angle of 60° with the horizontal. Its velocity at, the highest point is, , 1, , (a) zero, (b) 5 ms–1, (c) 10 ms–1, (d) 8.66 ms–1, Ans :, , (b), , At the highest point of the angular projection, the velocity of projectile has only horizontal, component velocity = u cos θ = 10 cos 60° = 5 ms–1., 100.A person moves 30 m North, then 20 m East then 30 √2 m South-West. His displacement from, the original position is, , 1, , (a) 14 m South-West, (b) 28 m South, (c) 10 m West, (d) 15 m East, Ans :, , The resultant of 30 m north will neutralise the displacement of 30 m south. Hence, the, effective displacement is the resultant of 30 m west and 20 m east = 10 m west., 101.During projectile motion the quantities that remain unchanged are, , 1, , (a) force and vertical velocity, (b) acceleration and horizontal velocity, (c) kinetic energy and acceleration, (d) acceleration and momentum., Ans :, , (b), , 102.A constant force is acting perpendicular to the velocity, of a particle. For this situation which one is correct?, (a) Velocity is constant., (b) Acceleration is constant., (c) Momentum will be constant., (d) Particle will follow elliptical path., Ans :, , (b), , When a constant force will be acting perpendicular to, the velocity, the body will describe a circular path and, its acceleration (called centripetal acceleration) will be, constant., , 1
Page 29 :
103.The x-component of the resultant of several vectors, , 1, , (a) is equal to the sum of the x-components of the vectors., (b) may be equal to the sum of the magnitudes of the vectors., (c) may be smaller than the sum of the magnitude of the vectors., (d) may be greater than the sum of the magnitude of the vectors., Ans :, , (a, b, c), , The x-component of the resultant vector can never be, greater than the sum of the magnitude of the vectors., 104., , 1, , (a) 45°, (b) 90°, (c) – 45°, (d) 180°, Ans :, , 105., , 1, , Ans :, , 106.The horizontal range of a projectile fired at an angle of 15° is 50 m. If it is fired with the same, speed at an angle of 45°, its range will be, (a) 60 m, (b) 71 m, (c) 100 m, (d) 141 m, , 1
Page 30 :
Ans :, , 107., , 1, , Ans :, , 108., , 1, , Ans :, , (c), , 109.The proper use of lubricants cannot reduce:, , 1, , (a) static friction, (b) inertia, (c) sliding friction, (d) rolling friction, Ans :, , (b), , Reaction due to a body depends on force applied, which is a function of acceleration., 110.During the motion of a lift, apparent weight of a body becomes twice its actual weight when, , 1
Page 31 :
(a) lift is moving down with acc. = g, (b) lift is moving up with acc. = g, (c) lift is moving down with uniform velocity = 9.8 ms–1, (d) lift is moving up with uniform velocity = 9.8 ms–1., Ans :, , (b), , Apparent weight = m(g ± a), Apparent weight = m(g + g) = 2mg, 111.A particle of mass m moving with a velocity v strikes a stationary particle of mass 2m and, stickes to it., , 1, , The speed of the system will be, (a) v/2, (b) 2v, (c) v/3, (d) 3v, Ans :, , (c), , Applying principle of conservation of linear momentum, (m + 2m)V = m × v + 2m × 0, V = v/3, 112.In an elevator moving vertically up with an acceleration ‘g’, the force exerted on the floor by a, passenger of mass M is, , 1, , (a) Mg, (b) 1/2 Mg, (c) zero, (d) 2 Mg, Ans :, , (d), , Force exerted by the passenger on floor, = R = M( g + a) = M(g + g) = 2 Mg, 113.For a body moving with constant speed in a horizontal circle, which of the following remains, constant?, , 1, , (a) Velocity, (b) Acceleration, (c) Centripetal force, (d) Kinetic energy, Ans :, , (d), , K.E. =, , mv2 = constant, while moving uniformly in a horizontal circle., , 114.A particle of mass 10 kg is moving in a straight line. If its displacement, x with time t is given by, x = (t3 – 2t –10)m, then the force acting on it at the end of 4 seconds is, (a) 24 N, (b) 240 N, (c) 300 N, (d) 1200 N, , 1
Page 32 :
Ans :, , (b), , 115.25 N force is required to raise 75 kg mass from a pulley. If rope is pulled 12 m, then the load is, lifted to 3m, the efficiency of pulley system will be, , 1, , (a) 25%, (b) 33.3%, (c) 75%, (d) 90%, Ans :, , 116.A light string passing over a smooth light pulley connects two blocks of masses m1 and m2, (vertically)., , 1, , If the acceleration of the system is (g/8), then the ratio of masses is:, (a) 8 : 1, (b) 9 : 7, (c) 4 : 3, (d) 5 : 3, Ans :, , (b), , In the given system,, , 117.When forces F1, F2, F3 are acting on a particle of mass m such that F2 and F2 are mutually, perpendicular, then the particle remain stationary. If the force F1 is, , 1
Page 33 :
now removed, then the acceleration of the particle is:, , Ans :, , 118.Three forces start acting simultaneously on a particle, , 1, , moving with velocity . These forces are represented, in magnitude and direction by three sides of a triangle, taken in the same order. The particle will now move with a velocity., (a) less then, (b) more than, (c) only, (d) cannot say, Ans :, , (c), , Resultant of three forces represented completely by three sides of a triangle taken in the, same order is zero. Therefore, velocity of particle remains unaffected., 119.A body of mass m collides against a wall with the, , 1, , velocity v and rebounds with the same speed. Its, change of momentum is:, (a) 2mv, (b) mv, (c) –mv, (d) zero, Ans :, , (a), , Change in momentum = m(v – u) = m(–v – v) = –2mv, 120.Physical independence of force is a consequence of, (a) Third law of motion, (b) Second law of motion, (c) First law of motion, (d) All of these laws, , 1
Page 34 :
Ans :, , (c), , Physical independence of force is a consequence of first law of motion., 121.A particle is acted upon by a force of constant magnitude which is always perpendicular to the, velocity of the particle. The motion of the particle, , 1, , takes place in a plane. It follows that, (a) its velocity is constant., (b) its acceleration is constant., (c) its KE is constant., (d) it moves in a circular path., Ans :, , (c, d), , When force of constant magnitude acts always perpendicular to the velocity of the particle,, its KE is constant and it moves in a circular path. Force is providing the necessary, centripetal force., 122.Action and reaction, , 1, , (a) act on two different objects., (b) have opposite directions., (c) have equal magnitude., (d) have zero resultant., Ans :, , (a, b, c, d), , Forces of action and reaction are equal and opposite, acting on different objects and having, zero resultant., 123.A sparrow flying in air sits on a stretched telegraph wire. If weight of the sparrow is W, which of, the following is true about the tension T produced in the wire?, , 1, , (a) T = W, (b) T < W, (c) T = 0, (d) T > W, Ans :, , 124. A neutron exerts a force on a proton which is, (a) electromagnetic, (b) nuclear, (c) gravitational, (d) weak, , 1
Page 35 :
Ans :, , (b, c), , The gravitational forces are due to their masses in addition to nuclear forces inside the, nucleus., 125.The two ends of a spring are displaced along the length of the spring. All displacements have, equal magnitudes. In which case or cases the tension of compression in the spring will have a, maximum magnitude?, , 1, , (a) The right end is displaced towards right and the left end towards left., (b) The right end is displaced towards left and the left end towards right., (c) Both ends are displaced towards right., (d) Both ends are displaced towards left., Ans :, , (c, d), , Tension/compression will be maximum when the spring is stretched/compressed from, either end., 126.A cylinder rolls up an inclined plane, reaches some height and then rolls down (without slipping, throughout these motions). The directions of frictional force acting on the cylinder are:, , 1, , (a) up the incline while ascending and down the incline while descending., (b) up the incline while ascending as well as descending., (c) down the incline while ascending and upto the incline while descending., (d) down the incline while ascending as well as descending., Ans :, , (b), , 127.Mark the correct statements:, , 1, , (a) The electron magnetic force between two protons is always greater than the gravitational, force between them., (b) The nuclear force between two protons is always greater than the electromagnetic force, between them., (c) The gravitational force between two protons may be greater than the nuclear force between them., (d) Electromagnetic force between two protons may be greater than the unclear force acting, between them., Ans :, , (a, b), , Nuclear force > electromagnetic force > gravitational force between protons., 128.A particle stays at rest as seen in a frame. We can conclude that, , 1, , (a) the frame is inertial, (b) resultant force on the particle is zero, (c) the frame may be inertial but resultant force on the particle is zero,, (d) the frame may be non-inertial but there is a non zero resultant force., Ans :, , (c, d), , Particle will be seen at rest only when frame is inertial and resultant force on particle is zero., Also, if frame is non inertial (i.e., accelerated), the particle must also possess the same, acceleration in magnitude and direction i.e., resultant force on the particle must be non zero., 129.If the tension in the cable supporting an elevator is equal to the weight of the elevator, the, elevator may be, , 1
Page 36 :
(a) going up with uniform speed., (b) going down with uniform speed., (c) going up with increasing speed., (d) going down with increasing speed., Ans :, , (a, b), , Tension = R = m(g ± a). When R = mg, a = 0 i.e., speed must be uniform. It may be upwards or, downwards., 130.A ball is travelling with uniform translatory motion. This means that, , 1, , (a) it is at rest., (b) the path can be a straight line or circular and the ball travels with uniform speed., (c) all parts of the ball have the same velocity (magnitude and direction) and the velocity is constant., (d) the centre of the ball moves with constant velocity and the ball spins about its centre uniformly., Ans :, , (c), , 131.A metre scale is moving with uniform velocity. This implies, , 1, , (a) the force acting on the scale is zero, but a torque about the centre of mass can act on the scale., (b) the force acting on the scale is zero and the torque acting about centre of mass of the scale is also, zero., (c) the total force acting on it need not be zero but the torque on it is zero., (d) neither the force nor the torque need to be zero., Ans :, , (b), , As the velocity of the metre scale is uniform, a = 0. Therefore, force (F) = 0 . Since the weight, of the scale acts through its CM, its torque about CM is zero., 132., , Ans :, , 1, , (c), , 133.Conservation of momentum in a collision between particles can be understood from, (a) conservation of energy., (b) Newton’s first law only., (c) Newton’s second law only., (d) both Newton’s second and third law., , 1
Page 37 :
Ans :, , (d), , 134.A body of mass 2 kg travels according to the law x(t)pt + qt2 + rt3, where p = 3 m/s2 or q = 4, m/s2 and r = 5 m/s3., , 1, , The force acting on the body at t = 2 seconds is, (a) 136 N, (b) 134 N, (c) 158 N, (d) 68 N, Ans :, , 135., , 1
Page 38 :
Ans :, , 136., , 1, , Ans :, , 137.In Fig., a body A of mass m slides on plane inclined at angle θ1 to the horizontal and μ1 is the, 1, coefficient of friction between A and the plane. A is connected by a light string passing over a, frictionless pulley to another body B, also of mass m, sliding on a frictionless plane inclined at angle θ2, to the horizontal. Which of the following statements are true?
Page 39 :
(a) A will never move up the plane., (b) A will just start moving up the plane when m = (sin θ2 – sin θ1)/cos θ1, (c) For A to move up the plane, θ2 must always be greater than θ1 ., (d) B will always slide down with constant speed., Ans :, , (b, c), , (b) The body A will just start moving up if, mg sin θ1 + μ mg cos θ1 = mg sin θ2, [where mg, sin θ2 is the component of weight (mg) of body B which is to pull the body A], , (c) Since m = 0, sin θ2 > sin θ1, i.e., θ2 > θ1 (True) (for the body A to move up), 138.Two billiard balls A and B, each of mass 50 g and moving in opposite directions with speed of 5 1, ms–1 each, collide and rebound with the same speed. If the collision lasts for 10–3 s, which of the, following statements are true?, (a) The impulse imparted to each ball is 0.25 kg ms–1 and the force on each ball is 250 N, (b) The impulse imparted to each ball is 0.25 kg ms–1 and the force exerted on each ball is 25 × 10–5, N., (c) The impulse imparted to each ball is 0.5 Ns., (d) The impulse and the force on each ball are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction., Ans :, , (c, d), , (c) Impulse imparted to each ball (change in momentum of each ball) on collision = 2mv =, 2(0.05 kg)(5 m/s) = 0.5 N s, (d) The option is self-explanatory., 139.A body of mass 10kg is acted upon by two perpendicular forces, 6N and 8N. The resultant, acceleration of the body is, (a) 1 m s–2 at an angle of tan–1 (4/3) w.r.t. 6N force., (b) 0.2 m s–2 at an angle of tan–1 (4/3) w.r.t. 6N force., (c) 1 m s–2 at an angle of tan–1 (3/4) w.r.t. 8N force., (d) 0.2 m s–2 at an angle of tan–1 (3/4) w.r.t. 8N force., , 1
Page 40 :
Ans :, , (a, c), , 140. A machine gun fires a bullet of mass 40 gm with a velocity 1200 m/s. The man holding it can, 1, exert a maximum force of 144N on the gun. How many bullets can he fire per second at the most?, (a) Only one, (b) Three, (c) He can fire any number of bullets, (d) 144 × 48, Ans :, , (b), , 141.Physical independence of force is a consequence of, , 1, , (a) Third law of motion, (b) Second law of motion, (c) First law of motion, (d) All of these laws., Ans :, , (c), , 142.A shell is fired from a cannon, it explodes in mid air, its total, , 1, , (a) Momentum increases., (b) Momentum decreases., (c) KE increases., (d) KE decreases., Ans :, , (c), , 143.A shell is fired from a cannon, it explodes in mid air, its total, (a) Momentum increases., (b) Momentum decreases., (c) KE increases., (d) KE decreases., , 1
Page 41 :
Ans :, , On explosion, K.E. increases, as chemical energy of explosives is converted into K.E., , 144.A ball with an initial momentum p collides normally with a rigid wall. If p′ is its linear momentum 1, after the perfectly elastic collision, then, (a) p′ = p, (b) p′ = – p, (c) p′ = 2p, (d) p′ = – 2p, Ans :, , (b), , As collision is perfectly elastic, the ball rebounces with the same velocity, , ∴ p′ = – p, 145. A 7 kg object is subjected to two forces (in Newton), , 1, , The magnitude of resulting acceleration in ms–2 will be, (a) 5, (b) 4, (c) 3, (d) 2, Ans :, , 146.A car of mass m is driven with an acceleration a along a straight level road against a constant, 1, externally resistive force R. When the velocity of the car is V, the rate at which the engine of the car, is doing work is:, (a) RV, (b) maV, (c) (R + ma)V, (d) (ma + V)R
Page 42 :
Ans :, , (c), , P = (f1 + f2)V = (R + ma)V, 147.A long spring is stretched by 2 cm. Its potential energy is V. If the spring is stretched by 10 cm,, its potential energy would be:, , 1, , (a) V/25, (b) V/5, (c) 5V, (d) 25V, Ans :, , (d), , Potential energy ∝ x2 . When x becomes 5 times, P.E. becomes 25 times., 148.A force (mv2/r) is acting on a body of mass m moving with a velocity v in a circle of radius r., What is the work done by the force in moving the body over half the circumference of the circle?, , Ans :, , 1, , (b), , Work done is zero because force is acting at 90° to the direction of motion W = Fs cos 90° =, 0., 149.Consider two observers moving with respect to each other at a speed v along a straight line., 1, They observe a block of mass m moving a distance l on a rough surface. The following quantities, will be same as observed by the two observers., (a) Work done by friction., (b) Acceleration of the block., (c) Kinetic energy of the block at time t., (d) Total work done on the bock., Ans :, , (d), , When two observers are moving with respect to each other at a speed v along a straight line,, acceleration of block, if any, will be same. Distance moved may be different. Therefore, work, done/K.E. of the block may appear different., 150.Fast neutrons can easily be slowed down by, (a) the sue of lad shield., (b) passing them through water., (c) elastic collision with heavy nuclei., (d) applying a strong electric field., Ans :, , (b), , Water is rich in hydrogen (proton). On collision, velocities of neutron and proton are, interchanged. Fast neutrons come to rest and protons move with velocity of neutrons., , 1
Page 43 :
151.If g is acceleration due to gravity on earth’s surface, the gain in potential energy of an object of, mass m raised from surface of earth to a height equal to radius R of the earth is:, , 1, , (a) (1/2) mgR, (b) 2 mgR, (c) mgR, (d) (1/4) mgR, Ans :, , (a), , 152.In which case does the potential energy decrease?, , 1, , (a) On compressing the spring., (b) On stretching a spring., (c) On moving a body against gravitational pull., (d) On the raising of an air bubble in water., Ans :, , (d), , P.E. decreases when an air bubble rises in water. Because work is done by upthrust., 153.Which of the following is not conserved in inelastic collision?, , 1, , (a) Momentum., (b) Kinetic energy., (c) Both momentum and kinetic energy., (d) Neither momentum nor kinetic energy., Ans :, , (b), , Kinetic energy is not conserved in an inelastic collision., 154.The first ball of mass m moving with the velocity v collides head on with the second ball of, 1, mass m at rest. If the coefficient of restitution is e, then the ratio of the velocities of the first and the, second ball after the collision is
Page 44 :
(a), Ans :Here, m1 = m2 = m, u1 = u, u2 = 0., Let v1, v2 be their velocities after collision. According to principle of conservation of, linear momentum., , 155.A ball of mass m moving with a velocity v collides with an identical ball at rest. After collision,, the first ball comes to rest. The speed of the other ball is, , 1, , (a) v/2, (b) 2v, (c) v, (d) zero, Ans :, , (c), , As the masses of two balls are equal, their velocities are exchanged. As first ball comes to, rest, speed of other ball = v., 156.The K.E. of a body becomes 4 times its initial value., , 1, , The new linear momentum will be, (a) same as initial value., (b) four times the initial value., (c) twice the initial value., (d) eight times the initial value., Ans :, , (c), , K.E. = p2/2m, When K.E. becomes 4 times, p2 is 4 times. Therefore, p becomes 2 times., 157.A stationary particle explodes into two particles of masses m1 and m2, which move in opposite, directions with velocities v1 and v2. The ratio of their kinetic energies, (E1/E2) is, (a) m2/m1, (b) m1/m2, (c) 1, (d) m1v2/m2v1, , 1
Page 45 :
Ans :, , (a), , According to the principle of conservation of linear momentum,, , 158.A uniform metal chain is placed on a rough table such that one end of it hangs down over the, 1, edge of the table. When one third of its length hangs over the edge, the chain starts sliding. Then, the coefficient of static friction is:, (a) 3/4, (b) 1/4, (c) 2/3, (d) 1/2, , Ans :, , (d), , The chain starts sliding, when applied force = force of friction (due to hanging part), (between chain and table), , 159.A bomb of mass 1 kg is thrown vertically upwards with a speed of 100 m/s. After 5 seconds, it 1, explodes into two fragments. One fragment of mass 400 gm is found to go down with a speed of, 25 m/s. What will happen to second fragment just after explosion? (g = 10 m/s2), (a) It will go upwards with speed 100 m/s., (b) It will go upwards with speed 40 m/s., (c) It will go upwards with speed 60 m/s., (d) It will go downwards with speed 40 m/s.
Page 46 :
Ans :, , (a), , From v = u + at = 100 – 10 × 5 = 50 m/s This is the velocity at the time of, explosion. According to principle of conservation of linear momentum,, , The second fragment will go upwards with a speed of 100 m/s., 160.One end of a light spring constant k is fixed to a wall and the other end is tied to a block placed, on a smooth horizontal surface. In a displacement, the work done by the spring is 1/2kx2. The, possible cases are:, , 1, , (a) The spring was initially compressed by a distance x and was finally in its natural length., (b) It was initially in its natural length and finally in a compressed position., (c) It was initially stretched by a distance x and finally was in its natural length., (d) It was initially in its natural length and finally in a stretched position., Ans :, , (a, c), , As work is done by the spring, therefore, there are only two possibilities: the spring was, initially compressed by a distance x and has come to its natural length or the spring was, initially stretched by distance x and finally comes to its natural length., 161.The kinetic energy of a particle continuously increases with time:, (a) The resultant force on the particle must be parallel to the velocity at all instants., (b) The resultant force on the particle must be at an angle less than 90° all the time., (c) The magnitude of its linear momentum is increasing continuously., (d) Its height above the ground level must continuously decrease., Ans :, , 1, , (b, c), As K.E. of particle is increasing continuously with time magnitude of its linear, momentum must be increasing continuously (∵ E = p2/2m) . For this resultant force on, the particle must be at an angle less than 90° all the time., , 162.A particle of mass m is attached to a light string of length l, the other end of which is fixed., Initially, the string is kept horizontal and the particle is given an upward velocity v. The particle is, just able to complete a circle., , 1, , (a) The string becomes slack when the particle reaches its highest point., (b) The velocity of the particle becomes zero at the highest point., (c) The kinetic energy of the particle in initial position was 1/2mv2 = mgl., (d) The particle again passes through the initial position., Ans :, , (a, d), , When the particle is just able to complete a circle, the string would become slack when the, particle reaches its highest point. The particle will pass again through the initial horizontal, position., 163.A heavy stone is thrown force a cliff of height h in a given direction. The speed with which it hits 1, the ground?
Page 47 :
(a) Must be larger than the speed of projection., (b) Must be independent of the speed of projection., (c) Must depend on the speed of projection., (d) May be smaller than the speed of projection., Ans :, , (a, b, d), , The speed with which it hits the ground must depend upon the speed of projection and shall, always be larger than the speed of projection, because potential energy of the body shall be, converted into kinetic energy., 164.In head on elastic collision of two bodies of equal masses, , 1, , (a) the speeds are interchanged., (b) the velocities are interchanged., (c) the faster body slows down and the slower body speeds up., (d) the momenta are interchanged., Ans :, , (a, b, c, d), , When m1 = m2; all the statements are true., 165.A ball hits a floor and rebounds after an inelastic collision. In this case, , 1, , (a) the total energy of the ball and the earth remains the same., (b) the total momentum of the ball and the earth is conserved., (c) the momentum of the ball just after the collision is same as that just before the collision., (d) the mechanical energy of the ball remains the same during the collision., Ans :, , (a, b), , As the collision is inelastic, body losses some energy, so that KE of ball does not remain the, same. However, total energy and total momentum of ball and earth remain, the same., 166.If the external forces acting on a system have zero resultant, the centre of mass, , 1, , (a) may move., (b) may accelerate., (c) must not move., (d) must not accelerate., Ans :, , (a, d), , When external forces acting on a system have zero resultant, the centre of mass may move, with a constant velocity i.e. it must not accelerate., 167.In an elastic collision,, (a) the kinetic energy remains constant., (b) the linear momentum remains constant., (c) the final kinetic energy is equal to the initial kinetic energy., (d) the final linear momentum is equal to the initial linear momentum., , 1
Page 48 :
Ans :, , (b, c, d), , In an elastic collision, KE may change but final KE = initial K.E. linear momentum is not, changed., 168.An electron and a proton are moving under the influence of mutual forces. In calculating the, 1, change in the kinetic energy of the system during motion, one ignores the magnetic force of one on, another., This is because,, (a) the two magnetic forces are equal and opposite, so they produce no net effect., (b) the magnetic forces do no work on each particle., (c) the magnetic forces do equal and opposite (but non-zero) work on each particle., (d) the magnetic forces are necessarily negligible., Ans :, , (b), , The magnetic forces which act in a direction perpendicular to the direction of motion of the, particles, do not perform work on each particle., 169.A proton is kept at rest. A positively charged particle is released from rest at a distance d in its, field. Consider two experiments; one in which the charged, , 1, , particle is also a proton and in another, a positron., In the same time t, the work done on the two moving charged particles is, (a) same as the same force law is involved in the two experiments., (b) less for the case of a positron, as the positron moves away more rapidly and the force on, it weakens., (c) more for the case of a positron, as the positron moves away a larger distance., (d) same as the work done by charged particle on the stationary proton., Ans :, , (c), , The charge on a positron is the same as that on a proton but a positron is such lighter, (1/1840 times) than a proton. However, you will have the clearer insight in Class XII., 170. A man squatting on the ground gets straight up and stand. The force of reaction of ground on, the man during the process is, , 1, , (a) constant and equal to mg in magnitude., (b) constant and greater than mg in magnitude., (c) variable but always greater than mg., (d) at first greater than mg, and later becomes equal to mg., Ans :, , (d), , In the process of getting straight up and stand from squatting position, the man exerts a, variable force (F) on the ground to set his body in motion. This force is in addition to the, force required to support his weight (mg). Once the man is in standing position, F, becomes zero., 171.During inelastic collision between two bodies, which of the following quantities always remain, conserved?, (a) Total kinetic energy., (b) Total mechanical energy., (c) Total linear momentum., (d) Speed of each body., , 1
Page 49 :
Ans :, , (c), , Total linear momentum is always conserved whether the collision is elastic or inelastic., 172.Two inclined frictionless tracks, one gradual and the other steep meet at A from where two, stones are allowed to slide down from rest, one on each track as shown in Fig., , 1, , Which of the following statement is correct?, (a) Both the stones reach the bottom at the same time but not with the same speed., (b) Both the stones reach the bottom with the same speed and stone I reaches the bottom, earlier than stone II., (c) Both the stones reach the bottom with the same speed and stone II reaches the bottom, earlier than stone I., (d) Both the stones reach the bottom at different times and with different speeds., Ans :, , (c), , 173.The potential energy function for a particle executing linear SHM is given by V(x) = 1/2kx2, where k is the force constant of the oscillator (figure)., For k = 0.5 N/m, the graph of V(x) versus x is shown in the figure. A particle of total energy E turns, back when it reaches x = ± xm . If V and K indicate the P.E. and K.E., respectively of the particle at x, = +xm, then which of the following is correct?, , (a) U = O, K = E, (b) U = E, K = O, (c) U < E, K = O, (d) U = O, K < E., Ans :, , (b), , 1
Page 50 :
174. A body of mass 0.5 kg travels in a straight line with velocity v = ax3/2, where a = 5 m–1/2s–1., The work done by the net force during its displacement from x = 0 to x = 2 m is, , 1, , (a) 1.5 J, (b) 50 J, (c) 10 J, (d) 100 J, Ans :, , Note: Distinguish between a and a, a stands for acceleration and a = 5 m–1/2 s–1., 175.A body is moving unidirectionally under the influence of a source of constant power supplying, energy. Which of the diagrams shown in Fig. correctly shows the displacement-time curve for its, motion?, , 1
Page 51 :
Ans :, , (b), , Displacement, d ∝ t3/2., 176.Which of the diagrams shown in figures most closely shows the variation in kinetic energy of, the earth as it moves once around the sun in its elliptical orbit?, , Ans :, , 1, , (d), , The velocity of the Earth in its orbit around the Sun goes on changing, it increases as it, moves towards the Sun and decreases as it moves away from the Sun, but is never zero., 177.A mass of 5 kg is moving along a circular path of radius 1 m. If the mass moves with 300, revolutions per minute, its kinetic energy would be, (a) 250 π2, (b) 100 π2, (c) 5 π2, , 1
Page 52 :
(d) 0, Ans :, , (a) 250 π2, , 178.In a shotput event an athlete throws the shotput of mass 10 kg with an initial speed of 1 m/s–1 1, at 45° from a height 1.5 m above ground. Assuming air resistance to be negligible and acceleration, due to gravity to be 10 ms2, the kinetic energy of the shotput when it just reaches the ground will be, (a) 2.5 J, (b) 5.0 J, (c) 52.5 J, (d) 155.0 J, Ans :, , (d), Initial KE of the shotput =1/2 (10 kg) (10 m/s2)(1.5 m) = 150 J, Total initial energy of the shotput = 155 J, Since air resistance is neglible and final potential of the shotput as it hits the ground (h =, 0) is zero, kinetic energy of the shotput on hitting the ground = 155 J, , 179.Which of the diagrams in figures correctly shows the change in kinetic energy of an iron sphere, falling freely in a lake having sufficient depth to impart it a terminal velocity?, , 1
Page 53 :
Ans :, , (b), , The velocity of sphere goes on increasing till it attains its terminal velocity and then, continues moving with it. Same is the case with its KE., 180.A cricket ball of mass 150 g moving with a speed of 126 km/h hits at the middle of the bat, held 1, firmly at its position by the batsman. The ball moves straight back to the bowler after hitting the, bat. Assuming that collision between ball and bat is completely elastic and the two remain in, contact for 0.001 s, the force that the batsman had to apply to hold the bat firmly at its place would, be, (a) 10.5 N, (b) 21 N, (c) 1.05 × 104 N, (d) 2.1 × 104 N, Ans :, , (c), , 181.Two blocks M1 and M2 having equal mass are free to move on a horizontal frictionless surface. 1, M2 is attached to a massless spring as shown in Fig. Initially M2 is at rest and M1 is moving toward, M2 with speed v and collides head-on with M2., , (a) While spring is fully compressed all the KE of M1 is stored as PE of spring., (b) While spring is fully compressed the system momentum is not conserved, though, final momentum is equal to initial momentum., (c) If spring is massless, the final state of the M1 is state of rest., (d) If the surface on which blocks are moving has friction, then collision cannot be elastic., Ans :, , (c, d), , (c) In a head-on elastic collision between two bodies of equal mass, the bodies exchange, their velocities during collision., (d) Since there is a loss of KE (when the surface on which the blocks move has friction), the, collision cannot be elastic.
Page 54 :
182.Two masses of 1 gm and of 4 gm are moving with equal linear momenta. The ratio of their, kinetic energies is:, , 1, , (a) 4 : 1, (b) √2 : 1, (c) 1 : 2, (d) 1 : 16, Ans :, , (a) 4 : 1, , 183.If the linear momentum is increased by 50%, then K.E. will be increased by:, , 1, , (a) 50%, (b) 100%, (c) 125%, (d) 25%, Ans :, , (c) 125%, , 184.A bulled of mass a and velocity b is fired into a large block of mass c. The final velocity of the, system is, , Ans :, , 1, , (b), , 185.No work is done by a force on an object if, , 1, , (a) the object is stationary but the point of application of the force moves on the object, (b) the object moves in such a way that the point of application of the force remains fixed, (c) the force is always perpendicular to its velocity, (d) the force is always perpendicular to its acceleration, Ans :, , (a, b, d), , W = Fs cos θ = 0, when either s = 0 or θ = 90° i.e.,, when object is stationary but the point of application of, the force moves on the object or object moves in such, a way that point of application of force remains fixed;, or force is at 90° to the acceleration., 186.A bicyclist comes to a skidding stop in 10 m. During this process, the force on the bicycle due to 1, the road is 200 N and is directly opposed to the motion. The work done by the cycle on the road is, (a) + 2000J, (b) – 200J, (c) zero, (d) – 20,000J
Page 55 :
Ans :, , (c), , The work is done by the road on the cycle and not by the cycle on the road., 187.A body is falling freely under the action of gravity alone in vacuum. Which of the following, quantities remain constant during the fall?, , 1, , (a) Kinetic energy., (b) Potential energy., (c) Total mechanical energy., (d) Total linear momentum., Ans :, , (c), , Since there is no work done against force of friction (as the body is falling in vacuum) total, mechanical energy = K + U = constant., 188.Two identical ball bearings in contact with each other and resting on a frictionless table are hit, head-on by another ball bearing of the same mass moving initially with a speed V as shown in, figure., , 1, , If the collision is elastic, which of the following figure is a possible result after collision?, , Ans :, , (b), , 189.A man, of mass m, standing at the bottom of the staircase, of height L climbs it and stands at, its top., (a) Work done by all forces on man is equal to the rise in potential energy mgL., (b) Work done by all forces on man is zero., (c) Work done by the gravitational force on man is mgL., (d) The reaction force from a step does not do work because the point of application of the force, does not move while the force exists., , 1
Page 56 :
Ans :, , (b, d), , (b) Work done on man by internal forces (muscular effort) = + mgL Work done on man by, gravity = – mgL, Work done on man by friction = 0, Thus, work done by all forces on man = + mgL – mgL = 0, 190.A constant torque acting on a uniform circular wheel changes its angular momentum from L to, 4 L in 4 seconds. The magnitude of this torque is, , 1, , (a) 3 L/4, (b) 4 L, (c) L, (d) 12 L, Ans :, , (a), , 191.Which of the following has largest moment of inertia?, , 1, , (a) Ring about its axis perpendicular to its plane, (b) Disc about its axis perpendicular to its plane, (c) Solid sphere, (d) None of the above., Ans :, , (a), , 192.A dancer on ice spins faster when she folds her arms., , 1, , This is due to:, (a) Increase in energy and increase in angular momentum, (b) Decrease in friction at the skates, (c) Constant angular momentum and increase in kinetic energy, (d) Increase in energy and decrease in angular momentum., Ans :, , (c), , On folding arms, distance K decreases,, I = MK2 decreases., As I × ω = constant,, , ∴ ω increases, , As. K.E. of rotation 1/2 Iω2, ∴ Due to decrease in I and increase in ω, there is overall increase in K.E., 193.A ring of radius r and mass m rotates about an axis passing through its centre and, perpendicular to its plane with angular velocity ω. Its K.E. is, , 1
Page 57 :
Ans :, , 194.A bomb travelling in a parabolic path explodes in mid air. The centre of mass of fragments will, , 1, , (a) move vertically upwards and then downwards,, (b) move vertically downwards, (c) move irregularly, (d) move in parabolic path, the unexploded bomb would have travelled., Ans :, , (d), , On explosion, the centre of mass of all fragments would move in a parabolic path along, which unexploded bomb would have moved., 195.A sphere cannot roll on, , 1, , (a) a smooth inclined surface, (b) a smooth horizontal surface, (c) a rough inclined surface, (d) a rough horizontal surface., Ans :, , (a), , A sphere cannot roll on a smooth inclined surface because of absence of the force of, friction which produces torque for rolling., 196.Angular momentum and areal velocity of a body of mass m are related as, (a) L = 2 m × areal velocity, (b) L = 2π × area velocity, (c) Areal velocity = 2 mL, (d) 2 m = L × areal velocity, Ans :, , 1, , (a), , From the knowledge of theory, we know that angular momentum, L = 2 m × areal velocity., 197.When sand is poured on a rotating disc, its angular velocity will:, , 1, , (a) decrease, (b) increases, (c) remain constant, (d) none of these, Ans :, , (a), , On pouring sand, mass increases and, therefore moment of inertia I increases. As (Iω) =, constant, therefore, angular velocity ω decreases., 198.A man is sitting with folded hands on a revolving table. Suddenly, he stretches his arms. Angular 1, speed of the table would, (a) increase, (b) decrease, (c) remain the same, (d) nothing can be said.
Page 58 :
Ans :, , (b), , On stretching arms, distance K increases I = MK2 increase. As Iω = constant, therefore,, angular velocity ω decreases., 199.A couple produces a, , 1, , (a) pure linear motion, (b) pure rotational motion, (c) both linear and rotational motion, (d) no motion., Ans :, , (b), , A couple has turning effect and produces pure rotational motion., 200.A body rolls down an inclined plane. If its kinetic energy of rotational motion is 40% of its kinetic 1, energy of translational motion, then the body is a, (a) ring, (b) cylinder, (c) spherical shell, (d) solid sphere., Ans :, , (d), , In case of solid sphere, K.E. of rotation = Iω2, 201.A mass m is moving with a constant velocity along a line parallel to the x-axis away from the, origin. Its angular momentum w.r.t. the origin is:, , 1, , (a) zero, (b) constant, (c) goes on increasing, (d) goes on decreasing, Ans :, , (b), , Angular momentum = Moment of momentum = Momentum × Distance = mv × r = Constant, 202.Total K.E. of a sphere of mass M rolling with velocity V is:, , 1
Page 59 :
Ans :, , (a), , 203.A cylindrical solid of mass M has radius R and length L. Its moment of inertia about a generator, is:, , Ans :, , 1, , (d), , Generator is axis touching surface of cylinder and parallel to axis of cylinder. Using theorem, of parallel axis,, , 204.The angular momentum of a system of particles is not conserved when, , 1, , (a) net external force acts on the system, (b) net external torque acts on the system, (c) net external impulse acts on the system, (d) none of the above., Ans :, , (b), , 205.When a torque acting upon a system is zero, which of the following will be constant?, (a) Force, (b) Angular momentum, (c) Linear impulse, (d) None of these, , 1
Page 60 :
Ans :, , (b), , ∴ L = constant i.e., angular momentum is constant., 206.A round disc of moment of inertia I2 about its axis perpendicular to its plane and passing, through its centre is placed over another disc of moment of inertia I1 rotating with an angular, , 1, , velocity ω about the same axis. The final angular velocity of the combination of discs is:, , Ans :, , (a), , Applying principle of conservation of angular momentum, I1ω = (I1 + I2)ω′, , 207.For a particle of a rotating rigid body, v = rω, So, , 1, , (a) ω ∝ (1/r), (b) ω ∝ v, (c) v ∝ r, (d) ω is independent of r, Ans :, , (c, d), , 208.If ar and at a represent radial and tangential acceleration, the motion of a particle will be circular 1, is, (a) ar = 0 and at = 0, (b) ar = 0 and at ≠ 0, (c) ar ≠ 0 and at = 0, (d) ar ≠ 0 and at ≠ 0, Ans :, , (c, d), , In uniform circular motion, at = 0, but in non-uniform circular motion, at ≠ 0., 209.The initial angular velocity of a circular disc of mass M is ω1. A small sphere of mass m is, attached gently on edge of the disc. The final angular velocity of the disc will be:, , 1
Page 61 :
Ans :, , (d), , As angular momentum is conserved, therefore, I2ω2 = I1ω1, (M + m)K2ω2 = MK2ω1, , 210. A circular disc X of radius R is made from an iron plate of thickness t, and another plate Y of, 1, radius 4R is made from an iron plate of thickness t/4. The ratio between moment of inertia IY /IX is, (a) 32, (b) 16, (c) 1, (d) 64, Ans :, , (d), , 211.An annular ring with inner and outer radii R1 and R2 is rolling without slipping with a uniform, angular speed. The ratio of the forces experienced by the two particles situated on the inner and, outer parts of the ring, F1/F2 is:, , Ans :, , (a), , 1
Page 62 :
212.A non-zero external force acts on a system of particles. The velocity and the acceleration of the 1, centre of mass are found to be v0 and a0 at an instant t. It is possible that, (a) v0 = 0, a0 = 0, (b) v0 ≠ 0, a0 = 0, (c) v0 = 0, a0 ≠ 0, (d) v0 ≠ 0, a0 ≠ 0, Ans :, , (c, d), , When external force is non zero, acceleration cannot be zero. However, the centre of mass, may be at rest or may be moving with some velocity., Therefore, v0 = 0 or v0 ≠ 0, but a0 ≠ 0., 213.The centre of mass of a system of particles is at the origin. It follows that, , 1, , (a) the number of particles on X-axis should be equal to the number of particles on Y-axis., (b) if there is a particle on the positive X-axis, there must be at least one particle on the negative X-axis., (c) the number of particles to the right of the origin is equal to the number of particles to the left., (d) none, Ans :, , (d) (none), , When centre of mass of a system of particles is at origin, none of the alternatives is correct., 214.If there is no external force acting on a non-rigid body, which of the following quantities must, remain constant?, , 1, , (a) linear momentum, (b) moment of inertia, (c) angular momentum, (d) kinetic energy, Ans :, , (a, c), , When no external force is acting, the linear momentum and angular momentum of the body, remain constant. As the body is non-rigid, its moment of inertia may change and hence, its, K.E. may also change., 215.A train is moving towards north. At one place, it turns towards North-East. Here we observe that: 1, (a) The radius of curvature of outer rail will be greater than that of the inner., (b) The radius of the inner rail will be greater than that of outer rail., (c) The radius of curvature of one of the rails will be greater., (d) The radius of curvature of outer and inner rails will be the same., Ans :, , (a), , 216.If I, a and τ are moment of inertia, angular acceleration and torque respectively of a body, rotating about any axis with angular velocity w, then, (a) τ = Iα, (b) τ = Iω, (c) I = τω, (d) α = τw, , 1
Page 63 :
Ans :, , (a), , 217.The moment of inertia of a body comes into play:, , 1, , (a) In motion along a curved path, (b) In linear motion, (c) In rotational motion, (d) None of the above., Ans :, , (c), , 218. A body rolls down an inclined plane without slipping. The fraction of total energy associated, with its rotation will be, , 1, , (a) (k2 + R2), (b) k2 + R2, (c) k2/(k2 + R2), (d) R2/(k2 + R2), Ans :, , 219., , (c), , A sphere can roll on a surface inclined at an angle θ if the friction coefficient is more than, , sin θ. Suppose the friction coefficient is, , g, , 1, , g sin θ, and a sphere is, , released from rest on the incline,, (a) it will stay at rest, (b) it will translate and rotate about the centre, (c) it will make pure translational motion, (d) the angular momentum of the sphere about its centre will remain constant., Ans :, , (b), , As coefficient of friction is less than the one required for rolling, therefore the sphere will slip, i.e., it will translate and rotate about the centre., 220.The moment of inertia of a disc of mass M and radius R about an axis, which is tangential to, circumference of disc and parallel to its diameter is, , 1
Page 64 :
Ans :, , 221.The radius of gyration of a uniform rod of length L, , 1, , about an axis passing through its centre of mass and, perpendicular to its length is:, , Ans :, , 222.An earth satellite is moving around the earth in a circular orbit. In such case, what is conserved? 1, (a) Velocity, (b) Linear momentum, (c) Angular momentum, (d) None of the above., Ans :, , (c), , Angular momentum is conserved, as no external torque is acting in the motion of satellites, around the earth., 223.The acceleration of a solid cylinder rolling down an inclined plane of inclination 30° is, (a) g/3, (b) g/2, (c) g, (d) g/4, , 1
Page 65 :
Ans :, , 224.A particle moves on a straight line with a uniform velocity. The angular momentum of the, particle is:, , 1, , (a) always zero., (b) zero about a point on the straight line., (c) zero about a point away from the straight line., (d) constant always about a given point not on the line., Ans :, , (b, d), , As L = mvr, therefore L = 0, when r = 0 i.e., when point lies on the straight line. When a given, point does not lie on the line, r = constant. Therefore, L = mvr = constant., 225.A sphere is rolled on a rough horizontal surface. It gradually shows down and stops. The force, of friction tries to, , 1, , (a) increase the angular velocity., (b) decreases the angular velocity., (c) increase the linear momentum., (d) decrease the linear velocity., Ans :, , (a, d), , Force of friction produces the torque for rotation. Therefore, it tries to increase the angular, velocity. However, friction opposes the motion. Therefore, it tries to decrease the linear, velocity., 226.A simple pendulum is suspended from the roof of a trolley which moves in a horizontal direction 1, with an acceleration a, then the time period is given by, , Ans :, , (d), , Bob of the pendulum is under the effect of two forces. Weight = mg acting vertically, downwards. Horizontal force = ma. Therefore, resultant force, , 227.An artificial earth satellite of mass m is circling round the earth in an orbit of radius R. If the, mass of the earth is M, then the total energy of the satellite is:, , 1
Page 66 :
Ans :, , 228.The time period of a second’s pendulum in a satellite is, , 1, , (a) zero, (b) 2, (c) infinity, (d) depends on mass of body., Ans :, , 229.The largest and shortest distance of earth from the sun are r1 and r2. Its distance from the sun, when it is perpendicular to the major axis of the orbit drawn from the sun is, , Ans :, , 1, , (c), , 230.The mean radius of the earth is R, its angular speed about its own axis is ω and the acceleration 1, due to gravity at earth surface is g. The cube of radius of orbit of ‘geostationary satellite’ will be, (a) (R2g/ω), (b) (R2ω/g), (c) (Rg/ ω2), (d) (R2g/ω2)
Page 67 :
Ans :, , 231.The distance of two planets (neptune and saturn) from sun are 1013 and 1012 m respectively., The ratio of time period of the planets is, , 1, , Ans :, , 232.The orbital speed of an artificial satellite in a circular orbit just above the earth’s surface is v. For 1, a satellite orbiting at an altitude of half the earth’s radius the orbital speed is, , Ans :, , 233.The change in potential energy, when a body of mass m is raised to a height nR from earth’s, surface is (R = radius of earth), , 1
Page 68 :
Ans :, , 234.If g is the acceleration due to gravity on the earth’s surface, the gain in the potential energy of an 1, object of mass m raised from the surface of earth to a height equal to the radius R of the earth is, , Ans :, , 235.The period of revolution of a certain planet in an orbit of radius R is T. Its period of revolution in, an orbit of radius 4R will be, , 1, , (a) 2T, (b) 2 √2 T, (c) 4 T, (d) 8 T, Ans :, , 236.If the radius of earth were to increase by 1%, its mass remaining the same, the acceleration due, to gravity on the surface of earth will, (a) increase by 1%, (b) decrease by 2%, (c) decrease by 1%, (d) increase by 2%, , 1
Page 69 :
Ans :, , 237.The escape velocity or earth is Ve. If the mass of a certain planet is 3 times and radius 3 times, than that of the earth, then the escape velocity from the planet will be, , 1, , (a) 3Ve, (b) 6Ve, (c) 3 Ve, (d) Ve, Ans :, , 238.A satellite orbits around the earth in a circular orbit with a speed v and orbital radius r. If it, losses some energy, then v and r changes as, , 1, , (a) v decreases and r increases., (b) both v and r decreases., (c) v increases and r decreases., (d) both v and r increases., Ans :, , If the satellite losses some energy, its total energy will decrease. It will be so if r, decreases. Then from (i) v increases., 239.Two spheres of masses m and M are situated in air and the gravitational force between them is 1, F. The space around the masses is now filled with liquid of specific gravity 3. The gravitational force, will now be, (a) 3F, (b) F
Page 70 :
(c) F/3, (d) F/9, Ans :, , (b), , The gravitational force between two bodies is independent of the presence of other bodies., 240.A satellite S is moving in an elliptical orbit around the earth. The mass of the satellite is very, small compared to the mass of the earth., , 1, , (a) The acceleration of S is always directed towards the centre of the earth., (b) The angular momentum of S about the centre of the earth changes in direction but its, magnitude remains constant., (c) The total energy of S varies periodically with time., (d) The linear momentum of S remains constant in magnitude., Ans :, , (a), , 241.A satellite is orbiting just above the surface of a planet of average density ρ with period T. If G, , 1, , is the universal gravitational constant, the quantity T2r is equal to, (a) 4π2G, (b) 4π2/G, (c) 4π2/G, (d) 1/G, Ans :, , 242. A satellite is moving in a circular orbit at a height 100 km above the earth’s surface. A person, inside the satellite feels weightless because, , 1, , (a) acceleration due to gravity is almost zero at such a height., (b) the earth does not exert any force on the person., (c) the centripetal force makes the satellite move in a circular orbit., (d) the forces due to earth and moon are almost compensated at such a height., (c), Ans :When a satellite is moving in a circular orbit, then centripetal force makes the satellite to, move in providing the centripetal force is balanced by centrifugal force.Due to which the, person inside the satellite feels weightlessness., 243.The density of a newly discovered planet is twice that of earth. The acceleration due to gravity, 1, at the surface of the planet is equal to that at the surface of the earth. If the radius of the earth is, surface of the earth. If the radius of the earth is R, the radius of the planet would be, (a) 2R, (b) 4R, (c) R/4
Page 71 :
(d) R/2, Ans :, , 244.Average density of the earth, , 1, , (a) is directly proportional to g., (b) is inversely proportional to g., (c) is a complex function of g., (d) does not depend on g., Ans :, , 245.In case of earth, , 1, , (a) potential is minimum at the centre., (b) potential is zero, both at centre and infinity., (c) field is zero both at centre and infinity., (d) potential is same, both at centre and infinity but no zero., Ans :, , (a, c), , 246.Which of the following statements are true about acceleration due to gravity?, , 1, , (a) ‘g’ is zero at the centre of earth., (b) ‘g’ decreases if earth stops rotating on its axis., (c) ‘g’ decreases in moving away from the centre if r > R., (d) ‘g’ decreases in moving away from the centre if r < R., Ans :, , (a, c), , 247.If two satellites of different masses are revolving in the same orbit, they have same, , 1
Page 72 :
(a) speed, (b) energy, (c) time period, (d) angular momentum, Ans :, , (a, c), , The speed and time period of revolution of a satellite is independent of mass of the satellite, but energy and angular momentum of a satellite depend upon mass of the body., 248.Choose the correct statement/(s), , 1, , (a) Weight of a body is greater on planes and less on hill tops., (b) Weight of a body is greater at the poles and less at the equator., (c) Weight of a body on the moon is less than that on the earth., (d) Weight of a body on the moon is same as that at a height, equal to radius of moon from the surface, of earth., Ans :, , (a, b, c), , Weight = Mass × Acceleration due to gravity. The acceleration due to gravity is greater on, planes than on hill top. g is greater at poles than at the equator. g is less on moon than on, the earth., 249.A ring has a total mass M but non-uniformly distributed over its circumference. The radius of, 1, the ring is R. A point mass m is placed at the centre of the ring. Work done in taking away this point, mass from centre to infinity is, , Ans :, , (b), , 250.Suppose universal gravitational constant starts to decrease, then, , 1, , (a) length of the day, on earth, will decrease., (b) length of the year will decrease., (c) earth will follow a spiral path of increasing radius., (d) kinetic energy of earth will decrease., , Ans :, , (a, c, d), , 251.The earth is an approximate sphere. If the interior contained matter which is not of the same, density everywhere, then on the surface of the earth, the acceleration due to gravity, (a) will be directed towards the centre but not the same everywhere., (b) will have the same value everywhere but not directed towards the centre., (c) will be same everywhere in magnitude directed towards the centre., (d) cannot be zero at any point., , 1
Page 73 :
Ans :, , (d), , 252.As observed from earth, the sun appears to move in an approximate circular orbit. For the, motion of another planet like mercury as observed from earth, this would, , 1, , (a) be similarly true., (b) not be true because the force between earth and mercury is not inverse square law., (c) not be true because the major gravitational force on mercury is due to sun., (d) not be true because mercury is influenced by forces other than gravitational forces., Ans :, , (c), , 253.Both earth and moon are subject to the gravitational force of the sun. As observed from the sun, 1, the orbit of the moon, (a) will be elliptical., (b) will not be strictly elliptical because the total gravitational force on it is not central., (c) is not elliptical but will necessarily be a closed curve., (d) deviates considerably from being elliptical due to influence of planets other than earth., Ans :, , (b), , 254.In our solar system, the inter-planetary region has chunks of matter (much smaller in size, compared to planets) called asteroids. They, , 1, , (a) will not move around the sun since they have very small masses compared to sun., (b) will move in an irregular way because of their small masses and will drift away into outer space., (c) will move around the sun in closed orbits but not obey Kepler’s laws., (d) will move in orbits like planets and obey Kepler’s laws., Ans :, , (d), , 255.Choose the wrong option., , 1, , (a) Inertial mass is a measure of difficulty of accelerating a body by an external force whereas the, gravitational mass is relevant in determining the gravitational force on it by an external mass., (b) That the gravitational mass and inertial mass are equal is an experimental result., (c) That the acceleration due to gravity on earth is the same for all bodies is due to the equality, of gravitational mass and inertial mass., (d) Gravitational mass of a particle like proton can depend on the presence of neighbouring, heavy objects but the inertial mass cannot., Ans :, , (d), , 256.Particles of masses 2M, m and M are respectively at points A, B and C with AB = 1/2 (BC). m is, muchmuch smaller than M and at time t = 0, they are all at rest (Fig. 8.1). At subsequent times, before any collision takes place:, , (a) m will remain at rest., (b) m will move towards M., , 1
Page 74 :
(c) m will move towards 2M., (d) m will have oscillatory motion., Ans :, , (c), , 257.If g denotes the value of acceleration due to gravity at a point distant r from the centre of earth, of radius R. If r < R, then, , 1, , (a) g ∝ r2, (b) g ∝ r, (c) g ∝ 1/r2, (d) g ∝ 1/r, Ans :, , 258.The radii of circular orbits of two satellites around the earth are in the ratio 1 : 4, then ratio of, their respective periods of revolution is:, , 1, , (a) 1 : 4, (b) 4 : 1, (c) 1 : 8, (d) 8 : 1, Ans :, , (c), , T2 ∝ R3, 259.The gravitational potential at a plane varies inversely proportional to x2(i.e., V = k/x2), then, gravitational field intensity at the place is, , 1, , (a) –k/x, (b) k/x, (c) –2k/x3, (d) 2k/x3, Ans :, , 260.If the acceleration due to gravity at earth is ‘g’ and mass of earth is 80 times that of moon and, radius of earth is 4 times that of moon, the value of ‘g’ at the surface of moon will be, (a) g, (b) g/20, (c) g/5, (d) 320/g, , 1
Page 75 :
Ans :, , (c), , Let M and R be the mass and radius of earth M ′ and R′ are mass and radius of moon. Then, R′ = R/4 and M′ = M/80 . Let g and g′ the acceleration due to gravity on the surface of earth, and moon respectively. Then, , 261.The gravitational field due to a mass distribution is I = K/r3 in the X-direction. (K is a constant)., Taking the gravitational potential to be zero at infinity, its value at a distance x is:, , 1, , (a) K/x, (b) K/2x, (c) K/x2, (d) K/2x2, Ans :, , 262.Escape velocity of a planet is ve. If radius of the planet remains same and mass becomes 4, times, the escape velocity becomes, , 1, , (a) 4 ve, (b) 2 ve, (c) ve, (d) ve/2, Ans :, , 263.The escape speed from the surface of earth is ve. The escape speed from the surface of a, planet whose mass and radius are 3 times those of the earth will be:, (a) ve, (b) 3ve, (c) 9ve, (d) 27ve, , 1
Page 76 :
Ans :, , 264.What is the weight of a 700 gm of body on a planet whose mass is 1/7th of that of earth and, radius is 1/2 of earth., , 1, , (a) 400 gm, (b) 300 gm, (c) 700 gm, (d) 500 gm, Ans :, , 265.If both the mass and the radius of the earth decreases by 1%, , 1, , (a) the escape velocity would increase., (b) the acceleration due to gravity would increases., (c) the escape velocity would decrease., (d) the acceleration due to gravity would decrease., Ans :, , 266.A body of mass m is placed on earth surface which is taken from earth surface to a height of h, = 3R, then change in gravitational potential energy is, , 1
Page 77 :
Ans :, , 267.Two satellites of masses m1 and m2(m1 > m2) are revolving round the earth in circular orbits of 1, radii r1 and r2(r1 > r2) respectively. Which of the following statements is true regarding their speeds, v1 and v2., (a) v1 > v2, (b) v1 < v2, (c) v1 = v2, (d), , Ans :, , 268.The time period of an earth satellite in circular orbit is independent of, , 1, , (a) the mass of the satellite., (b) radius of its orbit., (c) both the mass of satellite and radius of the orbit., (d) neither the mass of satellite nor the radius of the orbit., Ans :, , (a), , Time period of satellite at height h ground is, , It is independent of mass m of the satellite., 269.Which of the following is true for a satellite in an orbit?, , 1, , (a) It is a freely falling body., (b) It suffers an acceleration., (c) It does not require energy for its motion in the orbit., (d) Its speed is constant., Ans :, , (a, c, d), , A satellite in an orbit is a freely falling body. It does not require any energy for its motion in, the orbit and its speed is constant., 270.Consider a planet moving in an elliptical planet orbit round the sun. The work done on the planet 1, by the gravitational force of the sun
Page 78 :
(a) is zero in some part of the orbit., (b) is zero in no part of the motion., (c) is zero in any small part of the orbit., (d) is zero in one complete revolution., Ans :, , (c, d), , 271.Satellites orbiting the earth have finite life and sometimes debris of satellites fall to the earth., This is because,, , 1, , (a) the solar cells and batteries in satellites run out., (b) the laws of gravitation predict a trajectory spiralling inwards., (c) of viscous forces causing the speed of satellite and hence height to gradually decrease., (d) of collisions with other satellites., Ans :, , (c), , 272.(a) Show that for a projectile the angle between the velocity and the x-axis as a function of time, is given by, , 4, , (b) Show that the projection angle θ0 for a projectile launched from the origin is given by, , where the symbols have their usual meaning., Ans :, , (a) As a body is projected with a velocty u at an angle θ the horizontal component of, velocity will be u cos θ and will be constant throughout. The initial vertical velocity will be, u sin θ and will vary due to ‘g’ in the vertically downward direction., , 273.A cylinder of mass 10 kg and radius 15 cm is rolling perfectly on a plane of inclination 30°. The, co-efficient of static friction, μS = 0.25., (a) How much is the force of friction acting on the cylinder ?, (b) What is the work done against friction during rolling ?, , 4
Page 79 :
(c) If the inclination θ of the plane is increased, at what value of θ does the cylinder begin to skid,, and not roll perfectly ?, Ans :