Page 3 :
Basic properties of electaic tharge., I] Additive nature of charge., Electric charqe is additive, Similar to mass, Total charge on an object is equal to algebraic, Sum of all charges distribukd on different, poyts of Object., Q = Q1+92, Q =3C+4C, Q= 7C, +20, Q= +2+5-3, Q= +7-3, G= 4C, %3D, +5¢, +30, %3D, +4C, -3¢, * Analogy bets the additive property of charge, with that of mass,, D Mass of particles, positive. but chaxge distributed on different, parts of object may bê tre or -Ve., Si, of an object are always, ) Total mass of an object is always +ve, Reo where as total charge on object, maybe +VE, -ve, I] Quantization of charge [ Q = tne ], The charge is atways exp Yessed in tedms of, integral multiple of eleetrons, Efundamental chor, Q= tne, where n=l,2,3,-- n=.number of electrons, e = charge on electoon, 9= Charge on body., に19, charge on teleton is, 1.6710°C., it is ateo called fundamental charge., EX: number of electoons in I coulomb are, %3D, As, 18, e
Page 5 :
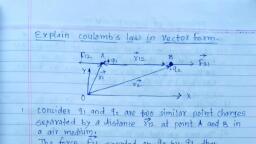
charles Augustin de coulomb in 1785]., In scalar foom 1736- 1806, 大, Coulomb's Law:-, statement :- The etectsostatic force of, attraction or yepulsion beth two point charse, at Yest is dixectly proportional to the produet, of magnitude of two'charges and inversely, proportional to square of distance bet? them., +92, consides 9, and 92 be two point charges, sepexated by distance 'x' Hhen fexce acting, bet? them is given by., And Fdte, then pa 192, 82, F = K 9,92 - 0, y2, where K'is eonstant of popoxtionality,, which depends on: D Naterre of medium, 2) system of unit used,, Fxom eqn ☺, 9,42, Nm2/ c² OB m/ farad., * S.I. unit of K'is, * Dimensions of K are [M'34I], -2, It charges aAre kept in vacuum or air medium,, where to 1s called permitivity of, free space. hence coulomb's law, K=, 4TED, belomes l, L.192, 82, 2), Vac, HITEO