Page 1 :
Chapter 8, , Electromagnetic Waves, , e Introduction Introduction, © Ampere Circuital Law and Electromagnetic waves in the form of visible light enable us to view, ites Contnadietion the world around us. Infrared waves warm our environment. Radio, waves carry our favourite TV and radio programs and the list goes on, , © Displacement Current and on. In this chapter, we will study regarding displacement current,, , © Consequences of electromagnetic waves and its various parts and their uses., Displacement Current History of EMW, © Maxwell's Equations (i) Maxwell : was the first to predict the presence of electromagnetic, wave., , e Sources of Electromagnetic, Waves (i) Hertz : produced and detected electromagnetic waves of, , Important characteristic and wavelength 6 m experimentally., , Nature of Electromagnetic (iii) J.C. Bose : produced electromagnetic wave of wavelength ranging, Waves from 5 mm to 25 mm., , e Relation Between Electric (iv) Marconi : successfully transmitted the EM waves upto a few, Field, Magnetic Field and kilometer. Marconi discovered that if one of the spark gap terminals, Speed of Light is connected to an antenna and the other terminal is earthed, the, , ¢ Intensity of Electromagnetic EM waves radiated could go upto several kilometers., Wave, , , , e Intensity due toa Point AMPERE CIRCUITAL LAW AND ITS CONTRADICTION, , Source According to Ampere circuital law, “The line integral of magnetic field along, e Electromagnetic Spectrum a closed loop is equal to j1, times the sum of steady currents threading the, , face bounded by the closed I in fre e, © Important Definition aiace y loop in free space, , © Formulae Chart GBT = jo iy + in +15), © Quick Recap, , i,’ i,, , , , , , , , , , , , Aakash Educational Services Pvt. Ltd. - Regd. Office : Aakash Tower, 8, Pusa Road, New Delhi-110005 Ph. 011-47623456
Page 2 :
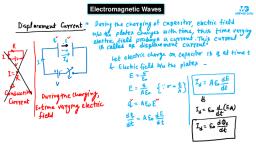
254 Electromagnetic Waves Board & Competitive Exams., , Let us consider a parallel plate capacitor which is being charged as shown in, the figure. If at an instant charge on the capacitor is Q, and the instantaneous., value of current in the connecting wire is /, then, aa, , at, Consider two surface A, and A, are bounded by a closed loop xy. The surface = +., , ', , , , , , , , , , A, lies between the two plates of capacitor and A, outside the plates. EMF Source, The area A, is pierced by the current / but area A, is not pierced by this current., , Therefore for surface A,, , GB. = trol, , For surface A, fB.di = 0, , Thus there is an apparent contradiction in applying ampere circuital law in this situation., , , , , James Clerk Maxwell (1831-1879), Born in Edinburgh, Scotland, he derived the thermal velocity distribution of, molecules in a gas and was among the first to obtain reliable estimates of, molecular parameters from measurable quantities like viscosity, etc. Maxwell's, greatest achievement was the unification of the laws of electricity and magnetism, (discovered by Coulomb, Oersted, Ampere and Faraday) into a constant set of, equations now called Maxwell's equations. From these he arrived at the most, important conclusion that light is an electromagnetic wave., , , , , , DISPLACEMENT CURRENT, , “Displacement current is a current which is produced due to the rate of change of electric flux with respect to, time”. Displacement current is given by, , d, Ig= £0 (%e) 1, , According to Maxwell, contradiction in Ampere’s law is because of some missing, term. This missing term must be such that one gets the same magnetic fields, at point P, no matter what surface is used. This missing term must be related, with changing electric field which passes through area A, between the plates - oe, of capacitor shown in the figure. EMF Source, If at an instant charge on the plates of capacitor is Q, area of plate is A then electric field between the plates is, uniform and which vanishes outside the plates is given by, , Q, E= Aey ..(i) [This field is perpendicular to area A,], The electric flux through area A,, Oe=EXA,, , =a. xA [A =A, because flux will pass through area A], , Ato, , , , , , , , , , , , %e ---(li), , £0, , Aakash Educational Services Pvt. Ltd. - Regd. Office : Aakash Tower, 8, Pusa Road, New Delhi-110005 Ph. 011-47623456
Page 3 :
Board & Competitive Exams. Electromagnetic Waves 255, , If charge on the capacitor plate changes with time then, , dQ, , p=, , doe, , So “Gt, , - 14a, £9 ot, , Me _1,,0Q, , at =f, , at, , This implies that, , This current i, (the missing term in the Ampere’s law ) passes through the surface A, and is known as Maxwell, displacement current., , Note :, , Illustration 1:, Solution :, , () For consistency of Ampere circuital law, there must be a current between the plates of, capacitor. It is called displacement (1,) current because it is produced by changing electric, field or electric displacement., , (i) The current in conductor is due to the flow of charge carrier hence called conduction current |_, , (iii) In modified Ampere circuital law, “the line integral of magnetic field along a closed loop in free, space is equal to \1, times the total current (sum of conduction and displacement) threading the, loop.”, , GB.di = poll, +14), , Show that displacement current is equal to conduction current during charging of a capacitor., , Let at an instant magnitude of charge on the plates of capacitor be Q. Area of each plate is A., Electric field between the plates of capacitor, , , , , , , , , , , , Q, E=—, , Aro -i), Flux of this field passing through the surface between the plates is, , Q, de = EX A= mene, ot ‘, , % = eo +(ii) B|, , Displacement current /, is 7 1, =e) x Te a2: 1 aa,, , fa =f0x— = °0o¢ =) = xe) dt EMF Source, , dQ, | peed ia, a ot «--(iii), 2 is the rate at which charge is reaching to positive plate of capacitor through conducting wire, therefore |, = 22 tv), From equations (iii) and (iv), lg = ts, , Aakash Educational Services Pvt. Ltd. - Regd. Office : Aakash Tower, 8, Pusa Road, New Deihi-110005 Ph. 011-47623456
Page 4 :
256 Electromagnetic Waves Board & Competitive Exams., —, , Mlustration 2: A parallel plate capacitor consists of two circular plates of radius R = 0.1 m. They are separated, by a distance d = 0.5 mm. If electric field between the capacitor plates changes as, , & =5x10"% ae Find displacement current between the plates., , xs, Solution : Area of plates A = nr? = 3.14 x (0.1)? m?, SE = 5x10, ta ~oal {ea}, = 8.85x10°'? é 3.14 (0.1)? m? x5x 10" _Y_, , Nm? mxs, , 1g = 13.9A, , , , bs If potential difference between the plates of capacitor changes with rate of 2 =10° “2, ang, capacitance of capacitor is 1 .F, then find displacement current between the plates., 2. A parallel plate capacitor consists of two circular plates of radius 0.05 m. If electric field between, , the plates is changed as & -100_V_, then find displacement current between the plates., , 3. Two circular plates of radius 0.1 m are used to form a parallel plate capacitor. If displacement, , current between the plates is 2x ampere, then find magnetic field produced by displacement, current 4 cm from the axis of the plates., , =, , CONSEQUENCES OF DISPLACEMENT CURRENT, The displacement current has far reaching consequences. Some of these are as follows., , (i) With the discovery of displacement current, the laws of electricity and magnetism become more, symmetrical than before (though still not perfectly symmetrical), , According to Faraday's law of electromagnetism, g Eg -—2¢m, ot, , This implies that magnetic field changing with time produces electric field., According to Ampere-Maxwell's law, , J8ai = Ho ic +e0 SE), , This implies that electric field changing with time produces magnetic field. Here term to SE represents, displacement current /, which produces magnetic field., , , , Aakash Educational Services Pvt. Ltd. - Regd. Office : Aakash Tower, 8, Pusa Road, New Delhi-110005 Ph. 011-47623456
Page 5 :
Board & Competitive Exams. Electromagnetic Waves 257, , , , (ii) The displacement current gives rise to magnetic effect equivalent to those produced by an ordinary conduction, current is the basis of Maxwell's electromagnetic theory of light., (iii) In all respect, displacement current has same physical effects as the conduction current., , MAXWELL’S EQUATIONS, , Maxwell's equations relate electric field E and magnetic field B and their sources which are electric charges and, current. In free space Maxwell's equations are as follows., , , , gé.ds = Tevet This equation represents Gauss's law in electrostatics, which states that net electric flux, , through any closed surface equals to 2 times the total charge enclosed by the surface. This law relates, electric field with the charge distribution’ The Gauss law is equivalent to the Coulomb's inverse square law, which has experimentally been confirmed., , (ii) g B.ds = 0. This equation is considered as Gauss’s law in magnetism. It states that net magnetic flux passing, through a closed surface is zero. It implies that number of magnetic field lines entering the closed surface is, , equal to number of magnetic line leaving the closed surface, that is magnetic field does not start or end at a, point — there is no isolated magnetic monopoles., , (iii) ged df = — Ae . This equation is Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction. This law relates electric field, , with changing magnetic flux. “Induced current in a conducting loop placed in a region in which magnetic field, is changing with respect to time confirms this equation.”, , (vy) GBdi=n, (1 +€q Se. ). This equation represents Ampere-Maxwell's law or generalised form of Ampere’s, , law. This law states that “ line integral of magnetic field along a closed loop is equal to j1, times the total, current threading the area bounded by the closed loop”. This law describes how a magnetic field can be, produced by both changing electric flux and a conduction current., , Note: (i) Maxwell's equation are as fundamental to electromagnetic phenomena as Newton's laws are, to the study of Mechanical phenomena., , () Important consequence of the Maxwell's equations is that these can be used to derive the, law of conservation of charge., , , , , Heinrich Rudolf Hertz (1857—1894) : ‘German physicist who was the first to broadcast, and receive radiowaves. He produced electromagnetic waves, sent them through space,, , and measured their wavelength and speed. He showed that the nature of their vibration,, reflection and refraction was the same as that of light and heat waves, establishing their, identity for the first time. He also pioneered research on discharge of electricity through, gases, and discovered the photoelectric effect., , , , , , SOURCES OF ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES, , “The waves that are produced by accelerated charged particles and composed of electric and magnetic field vibrating, transversely and sinusoidally perpendicular to each other and to the direction of propagation are called, electromagnetic waves or electromagnetic radiations.”, , These waves are produced in the following physical phenomena :, , (i) Anelectric charge at rest produces only electrostatic field around it., , (ii) Acharge moving with uniform velocity (i.e. steady current) produces both electric and magnetic field, here, magnetic field does not change with time hence it does not produce time varying electric field., , , , Aakash Educational Services Pvt. Ltd. - Regd. Office : Aakash Tower, 8, Pusa Road, New Dethi-110005 Ph. 011-47623456