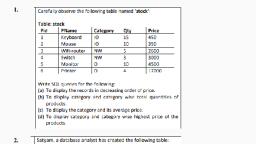
Page 3 :
CONTENTS-Learning outcomes, , QUERIES ON TABLES, , (DML Queries), , INSERT records in a table, SELECT (To display) a table content, • Select …. FROM, • Select …. DISTINCT / ALL, • Select …. FROM….WHERE, • Select …. With Relational operators, • Select …. With Logical operators, • Select …. IN / NOT IN, • Select …. IS NULL / IS NOT NULL, • Select …. BETWEEN / NOT BETWEEN, • Select …. LIKE / NOT LIKE, • Select …. Using Column Alias, • Select …. Text in Query Output, • Select .... ORDER BY (Asc/ Desc), UPDATE records in a table, DELETE records from a table
Page 5 :
INSERT QUERY, The rows (tuples/ records) are added to a table., SYNTAX, INSERT INTO <table name> [<column list>], VALUES (<value>,<value>……) ;, , Example:Insert Into student Values(105,'Dharna','2004-07-03',"Science",96,10);, , Insert Into student(Admno,Sname,DOB) Values(106,'Aman','2003-02-16');
Page 6 :
NOTE: Only, those columns, can be, ommitted that, have either, default value or, they allow, NULL values.
Page 7 :
SELECT QUERY, Select command is used to retrieve a subset of, rows or columns from one or more tables., SYNTAX, SELECT <column name> [ ,<column name>,….], FROM <table name>;, , OR, SYNTAX, SELECT <column name> [ ,<column name>,….], FROM <table name>, WHERE<condition>;, , NOTE:, , To see entire table i.e. everycolumn of the table , then *, can be substituted for a complete list of column., , (asterisk)
Page 8 :
SELECT Query without WHERE, • Select …. FROM, • Select …. DISTINCT / ALL, • Select …FROM….WHERE, • Select …. With Relational, operators, , • Select …. With Logical, operators, , • Select …. IN / NOT IN, • Select …. IS NULL /, IS NOT NULL, , • Select …. BETWEEN /, NOT BETWEEN, , • Select …. LIKE / NOT LIKE, • Select… Using Column Alias, • Select Text in Query Output, • Select .... ORDER BY, ( Asc / Desc ), , NOTE: The output will be displayed in the same order as the, order of columns given in the SELECT clause of the query
Page 9 :
SELECT Query (DISTINCT / ALL), • Select …. FROM, , • Select …. DISTINCT / ALL, • Select …FROM….WHERE, • Select …. With Relational, operators, , • Select …. With Logical, operators, , • Select …. IN / NOT IN, • Select …. IS NULL /, IS NOT NULL, , • Select …. BETWEEN /, NOT BETWEEN, , • Select …. LIKE / NOT LIKE, • Select… Using Column Alias, • Select Text in Query Output, • Select .... ORDER BY, ( Asc / Desc ), , Distinct, Keyword, eliminates, redundant, (duplicate)data, from rows of, the result of the, SELECT, statement., All keyword, keeps the, redundant, (duplicate), output rows., NOTE: If you do, not specify any, keyword,, neither distinct, nor all, it will be, treated the, same as All.
Page 10 :
SELECT Queries with WHERE clauses, • Select …. FROM, • Select …. DISTINCT / ALL, , • Select …FROM….WHERE, • Select …. With Relational, operators, , •, , Select …. With Logical, operators, , • Select …. IN / NOT IN, • Select …. IS NULL /, IS NOT NULL, , • Select …. BETWEEN /, NOT BETWEEN, , • Select …. LIKE / NOT LIKE, • Select… Using Column Alias, • Select Text in Query Output, • Select .... ORDER BY, ( Asc / Desc ), , The WHERE clause in SELECT statement specifies the criteria for selection of, rows to be returned. The query goes through the entire table one row at a, time and examines each row to determine if the given condition is true.
Page 11 :
SELECT Queries with RELATIONAL OPERATORS, • Select …. FROM, • Select …. DISTINCT / ALL, • Select …FROM….WHERE, , • Select …. With Relational, operators, , •, , Select …. With Logical, operators, , • Select …. IN / NOT IN, • Select …. IS NULL /, IS NOT NULL, , • Select …. BETWEEN /, NOT BETWEEN, , • Select …. LIKE / NOT LIKE, • Select… Using Column Alias, • Select Text in Query Output, • Select .... ORDER BY, ( Asc / Desc ), , Relational Operators are used to compare two values., The SQL has the following relational operators:, , >, < , >=, <=, = , <>, , (not equal to), , !=, , (not equal to), , The result of the comparison is either True or False.
Page 12 :
SELECT Queries with RELATIONAL OPERATORS, • Select …. FROM, • Select …. DISTINCT / ALL, • Select …FROM….WHERE, , • Select …. With Relational, operators, , • Select …. With Logical, operators, , • Select …. IN / NOT IN, • Select …. IS NULL /, IS NOT NULL, , • Select …. BETWEEN /, NOT BETWEEN, , • Select …. LIKE / NOT LIKE, • Select… Using Column Alias, • Select Text in Query Output, • Select .... ORDER BY, ( Asc / Desc )
Page 13 :
SELECT Queries with RELATIONAL OPERATORS, • Select …. FROM, • Select …. DISTINCT / ALL, • Select …FROM….WHERE, , • Select …. With Relational, operators, , • Select …. With Logical, operators, , • Select …. IN / NOT IN, • Select …. IS NULL /, IS NOT NULL, , • Select …. BETWEEN /, NOT BETWEEN, , • Select …. LIKE / NOT LIKE, • Select… Using Column Alias, • Select Text in Query Output, • Select .... ORDER BY, ( Asc / Desc ), , marks!=90
Page 14 :
SELECT Queries with RELATIONAL OPERATORS, • Select …. FROM, • Select …. DISTINCT / ALL, • Select …FROM….WHERE, , • Select …. With Relational, operators, , • Select …. With Logical, operators, , • Select …. IN / NOT IN, • Select …. IS NULL /, IS NOT NULL, , • Select …. BETWEEN /, NOT BETWEEN, , • Select …. LIKE / NOT LIKE, • Select… Using Column Alias, • Select Text in Query Output, • Select .... ORDER BY, ( Asc / Desc ), , NOTE: The more the date is recent, the greater is its value., So, more recent dates are greater and older dates are smaller., The comparison for characters are done alphabetically.
Page 15 :
SELECT Queries with Logical operators ( AND, OR, NOT ), • Select …. FROM, • Select …. DISTINCT / ALL, • Select …FROM….WHERE, • Select …. With Relational, operators, , •, , Select …. With Logical, operators, , • Select …. IN / NOT IN, • Select …. IS NULL /, IS NOT NULL, , • Select …. BETWEEN /, NOT BETWEEN, , • Select …. LIKE / NOT LIKE, • Select… Using Column Alias, • Select Text in Query Output, • Select .... ORDER BY, ( Asc / Desc ), , Logical operators in, MySQL are:, , AND(&&),, OR(II), NOT(!), Logical operators, evaluate to True(1) ,, False(0) , and NULL, values.
Page 16 :
SELECT Queries with Logical operators ( AND, OR, NOT ), • Select …. FROM, • Select …. DISTINCT / ALL, • Select …FROM….WHERE, • Select …. With Relational, operators, , •, , Select …. With Logical, operators, , • Select …. IN / NOT IN, • Select …. IS NULL /, IS NOT NULL, , • Select …. BETWEEN /, NOT BETWEEN, , • Select …. LIKE / NOT LIKE, • Select… Using Column Alias, • Select Text in Query Output, • Select .... ORDER BY, ( Asc / Desc ), , NOTE: When all the, logical operators are, used together, the, order of precedence is, , NOT (!), AND(&&), OR(!!)., Parenthesis (bracket), overrides the, precedence order.
Page 17 :
SELECT Queries with IN / NOT IN operators (condition based on a list), • Select …. FROM, • Select …. DISTINCT / ALL, • Select …FROM….WHERE, • Select …. With Relational, , For specifying a list of values, IN operator is used. The IN operator, selects values that match any value in a given list., The NOT IN operator finds row that do not match in the list., , operators, , •, , Select …. With Logical, operators, , • Select …. IN / NOT IN, • Select …. IS NULL /, IS NOT NULL, , • Select …. BETWEEN /, NOT BETWEEN, , • Select …. LIKE / NOT LIKE, • Select… Using Column Alias, • Select Text in Query Output, • Select .... ORDER BY, ( Asc / Desc ), where stream=‘Commerce’ OR stream=‘Arts’;, , where !(stream=‘Commerce’ OR stream=‘Arts’);
Page 18 :
SELECT Queries with IS NULL / IS NOT NULL, • Select …. FROM, • Select …. DISTINCT / ALL, • Select …FROM….WHERE, • Select …. With Relational, operators, , • Select …. With Logical, operators, , • Select …. IN / NOT IN, , • Select …. IS NULL /, IS NOT NULL, , • Select …. BETWEEN /, NOT BETWEEN, , • Select …. LIKE / NOT LIKE, • Select… Using Column Alias, • Select Text in Query Output, • Select .... ORDER BY, ( Asc / Desc ), , IS NULL is used in the where clause to search the NULL value in a, column., IS NOT NULL is used to search the Non-Null values in a column., Relational operators can’t be used with NULL.
Page 19 :
SELECT Queries : BETWEEN/NOT BETWEEN, • Select …. FROM, • Select …. DISTINCT / ALL, • Select …FROM….WHERE, • Select …. With Relational, , The BETWEEN operator defines a range of values that the column values, must fall into make the condition true., The NOT BETWEEN Operator is just the opposite of BETWEEN and those, rows which doesn’t satisfy the BETWEEN conditions are retrieved., , operators, , •, , Select …. With Logical, operators, , • Select …. IN / NOT IN, • Select …. IS NULL /, IS NOT NULL, , • Select …. BETWEEN /, NOT BETWEEN, , • Select …. LIKE / NOT LIKE, • Select… Using Column Alias, • Select Text in Query Output, • Select .... ORDER BY, ( Asc / Desc ), , NOTE:, BETWEEN, includes both, lower value and, upper value., , where( marks >=80 AND marks<=90);, , NOTE:, NOT BETWEEN, neither includes, lower value nor, upper value, , where( marks < 80 OR marks > 90);
Page 20 :
SELECT Queries : LIKE / NOT LIKE (Pattern matching), • Select …. FROM, • Select …. DISTINCT / ALL, • Select …FROM….WHERE, • Select …. With Relational, , LIKE is a string matching operator , for comparisons on character strings, using patterns., Two wild characters are there, , _, , (underscore symbol) matches single character, , %, , (percent symbol) matches multiple characters( any substring), , operators, , • Select …. With Logical, operators, , • Select …. IN / NOT IN, • Select …. IS NULL /, IS NOT NULL, , • Select …. BETWEEN /, NOT BETWEEN, , • Select …. LIKE / NOT LIKE, • Select… Using Column Alias, • Select Text in Query Output, • Select .... ORDER BY, (Asc / Desc), , NOTE:, All the sname, beginning, with ‘A’, , NOTE:, All the sname, ending with, ‘A’
Page 21 :
SELECT Queries : LIKE / NOT LIKE (Pattern matching), • Select …. FROM, • Select …. DISTINCT / ALL, • Select …FROM….WHERE, • Select …. With Relational, operators, , • Select …. With Logical, operators, , • Select …. IN / NOT IN, • Select …. IS NULL /, IS NOT NULL, , • Select …. BETWEEN /, , NOTE:, Second from last, letter is ‘A’., It has 1, underscore at, the end, , NOTE:, Exactly 4 characters, starting with ‘A’., It has 3 underscores at, the end, , NOT BETWEEN, , • Select …. LIKE / NOT LIKE, • Select… Using Column Alias, • Select Text in Query Output, • Select .... ORDER BY (Asc/, Desc), , NOTE:, Third letter ‘i’., It has two, underscores in, the beginning, , NOTE:, All the sname NOT, stating with ‘A’, will be retrieved.
Page 22 :
SELECT Queries : COLUMN ALIAS, • Select …. FROM, • Select …. DISTINCT / ALL, • Select …FROM….WHERE, • Select …. With Relational, operators, , •, , Select …. With Logical, , Column alias are given in Select query to display the columns with a, different name. AS is the keyword used for column alias. But, it is optional if, the alias name is of single word., , Alias means aka. Your nickname is your alias name., SYNTAX:, SELECT <columnname> AS[columnalias],[,<columnname> AS, [columnalias]], ……, FROM <tablename>;, , operators, , • Select …. IN / NOT IN, • Select …. IS NULL /, IS NOT NULL, , • Select …. BETWEEN /, NOT BETWEEN, , • Select …. LIKE / NOT LIKE, • Select.. Using Column Alias, • Select Text in Query Output, • Select .. ORDER BY, (Asc/Desc), , NOTE: COLUMN ALIAS , write in ' ' or " ", But, for a single word alias, name we can omit the quotes., AS is a keyword used for alias, name(As is optional)
Page 23 :
SELECT Queries with TEXT in Query Output, • Select …. FROM, • Select …. DISTINCT / ALL, • Select …FROM….WHERE, • Select …. With Relational, operators, , •, , Select …. With Logical, operators, , • Select …. IN / NOT IN, • Select …. IS NULL /, IS NOT NULL, , • Select …. BETWEEN /, NOT BETWEEN, , • Select …. LIKE / NOT LIKE, • Select… Using Column Alias, , • Select Text in Query, Output, , • Select .... ORDER BY (Asc/, Desc), , Text, symbols and comments can be inserted in query output to, make the OUTPUT more presentable.
Page 24 :
SELECT Queries : Sorting results using ORDER BY clause, , • Select …. FROM, • Select …. DISTINCT / ALL, • Select …FROM….WHERE, • Select …. With, Relational operators, , • Select …. With Logical, operators, , • Select …. IN / NOT IN, • Select …. IS NULL /, IS NOT NULL, , •Select …. BETWEEN /, NOT BETWEEN, , • Select …. LIKE / NOT LIKE, • Select… Using Column, Alias, , • Select Text in Query, Output, , • Select .. ORDER BY, (Asc/ Desc), , Usually, the output displayed after the execution of SELECT query is predecided., To sort the result output of a query in a specific order, we use ORDER BY clause., Sorting can be done in either ascending (asc) or descending (desc) order., If nothing is mentioned, by default it is done in the default, (ascending) order
Page 25 :
SELECT Queries : Sorting results using ORDER BY clause, , • Select …. FROM, • Select …. DISTINCT / ALL, • Select …FROM….WHERE, •Select …. With, Relational operators, , • Select …. With Logical, operators, , • Select …. IN / NOT IN, • Select …. IS NULL /, IS NOT NULL, , •Select …. BETWEEN /, NOT BETWEEN, , • Select …. LIKE / NOT LIKE, • Select… Using Column, Alias, , • Select Text in Query, Output, , • Select .. ORDER BY, (Asc/ Desc)
Page 26 :
UPDATE QUERY, UPDATE command helps in modifying the values of in an existing, row(tuple/record)., The new data value is given using the SET keyword., The new data can be a specified constant, an expression or data from, other tables., WHERE clause is used for the condition which specifies the rows to be, modified, , SYNTAX, UPDATE <table name>, SET <columnname=value>, [WHERE<condition>] ;, , NOTE:, , UPDATE query without WHERE condition will affect all the rows of the table., [WHERE condition is optional.]
Page 27 :
UPDATE QUERIES
Page 28 :
DELETE QUERY, DELETE command removes/deletes entire record(s) from a table., No field arguments required because the full row is removed, WHERE clause is used for the condition which specifies the rows to, be deleted, SYNTAX, DELETE FROM <table name>, [WHERE<condition>] ;, , NOTE:, DELETE query without WHERE condition will delete all the rows of the table., But, still the table will exist without any record., [WHERE condition is optional.]
Page 29 :
DELETE QUERIES, , Deleting record as per the, condition
Page 30 :
Display the entire table, , DELETE, command, (DML), , Delete all the records from the table, Display the entire table. Table is empty, , Vs, , DROP, command, (DDL), , Display the structure of the table. Table still exist with no records, , Remove/Drop/ Delete the entire table from the DB., , Display the entire table, Display the structure of the table.
Page 31 :
Stay safe. Stay aware. Stay healthy. Stay alert.