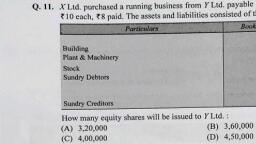
Page 1 :
CHAPTER NO. 2, MONEY, , Q.1 Explain the difficulties faced by people under Barter system., Barter system refers to the system where goods are exchanged for goods without the use of money., Following are the difficulties faced by people under barter system :, (a) Problem of double coincidence of wants :, Lack of double coincidence of wants means when two persons may not desire to purchase each other's, goods. For example Mr. Akash has wheat and want rie. So Mr. Akash has to search for another person, who wants wheat and has salt, otherwise exchange would not be possible., (b) Lack of common measure of value:, In olden times there was no common unit in terms of which the value of goods could be measured., (c) Indivisibility of certain goods: There was a problem of exchange when a person had large, commodities which could not be divided into smaller units Eg. 1 goat = 20 kg rice. If a person wanted 5, kg of rice, goat could not be cut and exchanged, (d) Difficulty in storage of goods:, It was necessary to store goods for future use but as most of the things were perishable, it was difficult, to store. For eg. Vegetables, fruits, Fish, milk etc., (e) Problem of making deferred payments:, It means payment to be made in future. E.g. taking a loan and making a payment in future was not, possible in barter system. So, to overcome these difficulties of barter system, people invented some, other kind of money., Q. 2 Explain in detail the main functions of money., According to Prof. Crowther, "Money is anything that is generally acceptable as a means of exchange, and at the same time acts as a measure and a store of value"., Functions of money can be broadly divided into following 3 groups –, (a) Primary functions, (b) Secondary functions, (c) Contingent functions., Let’s learn each function in detail :, (a) Primary Functions:, (i) Medium of exchange:
Page 2 :
The most important function of money is to make buying and selling of goods and services possible in, the market ie it serves as a medium of exchange. Thus, money facilitates sale and purchase of goods in, the market., (ii) Measure of value or Unit of account :, Price is the value of a commodity or service expressed in terms of money. Hence it becomes easier for, anyone to compare or know the value of any two or more commodities., Different countries use different currencies to express the value of their commodities. E.g. Rupee in, India, Pound in UK, Dollar in USA, etc. Thus, money as a measure of value helps in estimating cost,, revenue and profits of the business firms., (b) Secondary functions:, (i) Standard of deferred payment:, Deferred payments are the payments which are to be made at a future date. Buying and lending was, not possible in barter economy. Now this function of money develops financial and capital markets and, helps in the growth of the economy., (ii) Store of value:, Money acts as a store of value. It is a convenient form in which we can store the value or savings for, future use. According to J.M. Keynes, money is a link between the present and future., (iii) Transfer of value: Money helps to transfer values from one place to another or from one person to, another due to its general acceptability. One can sell his movable or immovable belonging at one place, and buy at another place. Values can thus be transferred. In modern times people generally use, cheques, electronic transfers, etc instead of using currency notes for transferring values., (c) Contingent Functions:, (i) Measurement of National Income:, National Income is money valuation of all the goods are services produced in an economy for the, period of one year. Country's National Income accounting is possible only because of money as a unit, of account., (ii) Basis of credit:, Modern economy is based on credit i.e. promise to pay. Hence lending and borrowing activities are, made easy by using money. Money Provides base for creation of credit money., (iii) Estimates of macro economic variables:, Macro economic variables such as Gross National Product (GNP), total investments, total savings,, taxes, etc. can be easily estimated in money terms., (iv) Imparts liquidity:, Money is the most liquid asset which can be easily converted into any other asset. For example land,, machinery, shares, etc. can be bought and sold in terms of money.
Page 3 :
Que 3. Distinguish between :, (a) Standard Coin & Token coins :, Standard coins, 1) Standard coins are those coins whose, face value is equal to its intrinsic value., , Token coins, 1) Token coins are those coins whose face value is, greater than its intrinsic value or mental value., , 2) These are made of costly metals like, gold, silver etc., , 2) These are made of cheap metals like, nickel,, aluminium etc., , Home work :, Q.1 Explain different types of Money