Page 1 :
measurement of Dispersion, , =Detailed Analysis of Lesson, , T, , Q. 1. What is dispersion? State the different measurements of dispersion., , Ans. Dispersion is a measure of the variation of the items from central value. These are, important to compare uniformity, consistency and reliability amongst variables/series., According to Dr. Bowley, “Dispersion is the measure of the variation of the items.”, , Measurement of Dispersion:, , 1. Range, , 2. Quartile Deviation, , 3. Mean Deviation, , 4, Standard Deviation, Q. 2. Explain the objectives of measures of dispersion., Ans, Following are the objectives of measuring dispersion:, , (i), , (ai), , (iii), , (iv), , 9.8 un., , To judge the reliability of an average: Measure of dispersion shows the, nature of distribution of items. It points out as to how far an average is, representative of statistical series. The greater the value of the dispersion, the, lesser will be there presentation of the central value and vice versa., , To locate the cause of variation: These measures help us to control the, variability in quantitative data. In social sciences, the measurement of inequality, in the distribution of income and wealth requires the measures of dispersion., The government canthus adopt a suitable policy to reduce economic inequalities., ith regard to their variability: The, study of variation is also useful to determine the degree of uniformity or, consistency of two or more sets of data. A high degree of variation would mean, less consistency or less uniformity as compared to the data having less variation., To facilitate statistical analysis: To facilitate the use of other statistical, Measures like regression, correlation etc. dispersion is used. We can compute, , different statistical techniques., : —_ =e 8-9 Diern nernesnes Tan, , To compare two or more series W’, , Scanned with CamScanner
Page 2 :
JAVA NANS AT) 11 Sec O, , , Aaa, , fat gfe, , Q. 1. What is standard deviation? Explain its properties/features., , Ans. Standard deviation measure of dispersion is by far the best and most widely used, measure of dispersion. Standard deviation is the square root of the arithmetic average, of the squares of all the deviations taken from mean. It was first used by Karl, Pearson. It is shortly known as root mean square deviation. It is denoted by the, small Greek letter sigma i.e., 6., , The properties/features of standard deviation are:, (i) Standard deviation is rigidly defined., (ii) It requires harder calculations., (ii) It depends on all the values of the variable., (iv) It is based on deviations from the arithmetic mean., (v) It is capable of further statistical treatment., (vi) Its value always remains in positive., Q. 2. What is coefficient of standard deviation?, , Ans. Coefficient of standard deviation is a relative measure of dispersion. It is used to, compare variation of two or more distributions expressed in different units. It is, calculated by dividing the standard deviation by the arithmetic mean of the data., , By formula: Coefficient of Standard Deviation (C.S.D.) = =,, , scanned with Camscanner
Page 3 :
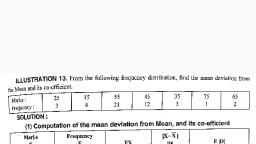
“3 -, individual Series, , ¢ are following three methods to calculat,, om ‘ sinaat Method: ate standard deviation:, , Following steps are taken under this method:, , (a) First calculate arithmetic mean i.e, X = a, , (b) Find out deviation for each item ie, d = x -X, (c) Find out the square of each deviation ie, d?, , (d) Find the sum total of squares of deviations i.e., Ld”, (ce) Use the following formula:, , SD () = [22, N, , Here, (o) = Standard Deviation, Yd? = Sum total of squares of deviations taken from mean., N = Number of Items, Coefficient of standard deviation is calculated by dividing standard deviations by the, , mean., CS.D. = =, , Example 1. Calculate standard deviation on the basis of marks obtained by 5, students in a class., Marks: 10 20 30 40 50, Solution: ‘, (1) Calculation of Standard Deviation using Direct Method:, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , Serial Number: | Marks ) | d=X- X | 7 d?, + 10 | -20 400, 2 | 20 | -10 100, { |, 3 | 30 | 0 oO, 4 \ 40 | 10 | 100, 5 { 50 oe 20 | 400, Nes | yxX=150 0 | | Xd? = 1000, __ 3K _ 150, X= N 5 = 30, Sd? 1000, Standard Deviation (6) = T 7 ao = 4200 = 14.142, 6, Co-efficient of Standard Deviation = ¥ = ae = 0.471, , Scanned with CamScanner
Page 4 :
(2) Short-cut Method:, The following steps are taken under this method:, , (a) Let any value of the X in the series as assumed mean (A)., (b) Find out deviation of the items ie., d = X - A., (c) Calculate the sum of deviations (Ld)., (d) Find square of the deviations (d?),, (e) Calculate the sum of deviations (Id?)., () Use the following formula:, xd? (xa), SD(o) = N -(), Example 2. Calculate standard deviation and its co-efficient from the following, , data:, Marks: 10 20 30 40 50, , Solution: Calculation of Standard Deviation using Short-Cut Method, , , , , , , , Serial Number Marks (X) d=X-A a2, (A = 30), , 1 10 -20 400, , 2 20 -10 100, , 3 30A 0 0, , : 40 10 100, , 5 50 20 400, _ Ya=0 Ld? = 1000, , , , , , , , , , , , (1) Standard Deviation (oc), , = 4200-0, = 14.142, (2) Coefficient of Standard Deviation = z, First, we have to calculate mean, X= A a = 30 42 = 30, 5, C.S.D. = & ~ 14149, , (3) Step-deviation Method:, The following steps are t,, aken :, (a) -Lét any valns of “1 Under this method:, of the the series as assumed mean (A), , (6) Find out deviation 0 ., f the iteme ;, ms i.e, d= X- A., , Scanned with CamScanner
Page 5 :
(c) Divide the deviations by some common factor i.e., d’, , (d) Find square of the deviations (d),, (ec) Calculate the sum of deviations (Ld),, () Use the following formula:, , Standard Deviation (a) = (Pd (2) xe, , Example 3. Calculate standard deviation on the basis of marks obtained by 5, , students in a class., , N, , af, =<., , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , ay, , , , Marks: 10 20 30 40 50, Solution: Calculation of Standard Deviation using Step-deviation Method, | | d i i, es Marks d=X-A d’= o, C= 10 d?, poe Se ee msn ee cl asa, 1 10 ~20 -2 | 4, . 20 -10 A | 1, 3 30(A) 0 0 0, 4 40 10 1 | 1, 5 50 20 2 i 4, N=5 Yd’ =0 | Yd? = 10 |, yd? (Sa’?, (1) Standard Deviation (o) = wow) ”* Cc, , 2, 0, 2-(2) x 10, = f2-0 x 10, = jg x 10 = 1.4142 x 10 = 14.142, , af c, (2) Co-efficient of Standard Deviation (C.S.D.) = =, , First, we have to find out the value of Mean., , ”, , X=aA+y * c, 0, = 80 + B x 10, 6 14.142, eae —— #£ 0.471, C.8.D. = ¥ 30, , Scanned with CamScanner