Page 1 :
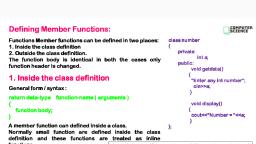
3-7, TPS Computer Science - I, TPS Computer Science-I, 3-8, (2), ...., Syntax:, if (condition), The general format of new operator is:, DataType * new DataType [size in integer];, action 1;, (3), program., else, The general format of delete operator is:, delete pointervariable;, (), For example:, action 2;, - void main (), char * str = "COMPUTER";, int len = strlen (str);, action 3;, %3D, be done., char * ptr;, = new char [len + 1];, strcpy (ptr, str);, cout << "ptr =" << ptr;, delete ptr;, 1), condition is satisfied, then default module will be executed., The switch statement :, This is a multiple branching statement., Depending on certain condition, it executes only one module out of several. If no, 2), The break statement is used to terminate switch statement., %3D, 3., 4) Expression must have int or char value, In above example, the new operator returns a pointer that point to a memory section, large enough to hold the string str plus an extra byte for null character. Then after use o, memory delete operator released memory., Syntax: switch (expression), Q. 10 What are the different selection (conditional) statements in C++? Give syntax for, case 1:, each., Ans., action 1;, The program has to be able to evaluate conditions and select alternative path in, break;, program., In C++, there are two ways in which selection may be made :, 1) The if statement, 2), The switch statement, case 2:, The if statement:, The if statement has two forms :, action 2;, break3B, i) Simple if statement, Simple if statement:, else statement, Syntax:, if (condition), action 1;, default :, action 2;, action x;, 1), direction or another., Depending on the condition value, program execution proceeds t o, If the condition is true, then action 1 will be done., 2)