Page 1 :
u, , , , § Summary of main points of quantum numbers, =, , Why is it To explain the main, | required ? lines of a spectrum, What does it (i) Main shell in, , a, {, , }, , a ppm sactgnsinmeiens within, , ; tell ?, , which the electron, resides, , (ii) Approx. distance, of the electron from, the nucleus, , (iti) Energy of th, , shell, , the: shar '), - What ar <O, symbols ?, . What are the, values ? integer, . Other K, L, M, N etc., , designations 7, , pals raed, ORO, , (iv) cn QO, elec {o in, , Azimuthual, , Magnetic Quantum, , Quantum No, (1) | @® No. (m or m), , To explain the fine, structure of the line, spectrum, , (i) No. of subshells, present in any main, shell, , asa, , (iii)Shapes of orbitals, , !, , 1, 2,3, 4 etc., i.e, any For a particular value, , of n,J=Oton—1, , 1=0, s-subshell ;, 1 = 1, p-subshell ;, 1 = 2, d-subshell ;, 1 = 3, f-subshell., , To explain, splitting of lines i, , magnetic fiel, na of nt, 1 or the, of orientaokt of each subshell, , m or m,, , For a particular value, of l,m=-lto+l, including zero, , For p-subshell m =, , — 1, 0, +1 designated, aS Py Py and p,., , \ ok plain the, Snob properties of, ned, , Direction of electron, spin, i.e., clockwise or, anti-clockwise A, , SOF m,, , For a particular value, of m,, s=+1/2,-12, Two arrows pointing, in opposite directions,, ie., T and L
Page 2 :
NUMERICAL, PR (i) Principal Quantum No. (nt) = 1, 2, 3, dy, ON Azimuthal Quantum No. (/) = 0 ton - 1 for a given value ofn, Magnetic Quantum No. (rm or m) =— {to +/ including ‘0° for a given value |, The Calculation . 1 ;, of Quantum Spin Quantum No. (s or m,) = +5» ~ 3 for a given value of ™., Numbers, (ii) Value of | Designation of sub-shell Orbitals present, Designation or 0 ' |, Orbitals 1 f 3, 2 d 5, 3 tf 7, 4 8 9, (iii) By convention, For pz "= O and for p, and py m= +1., (Generally, for p,,m=+ 1 and for py, ™=— 1), For dy) m= 0; Fot dry and da_y ym=t2;, (Generally, for 422 ,m=+2and for d,,m=— 2), 1 and for dy, ™ =— 1), , For dy, yz, = +1 (Generally, for d,.,m=+, , in a 4f orbital. What possible values for the quantum numbers, n,m |, , Problem Fl An electron is in, , and s can it have ?, , Solution. Since the electron is in a 4f orbital, the value of the principal quantum number, n = 4. |, , For the f-orbital, the secondary quantum number, / = 3., The values of the magnetic quantum (m) are — | to +I including zero. Therefore, when 1 = 3, m has seven, , values, ie, —3,-2- 1, 0, +1, +2 and 3., For each value of m, the spin quantum number,, problem PF] Write down the quantum numbers 2,, (iii) 3 d,y (iv) 4d4,,, , s has two values, i.€., $= + 1/2 ands =- 1/2., , land m for the following orbitals :, (v) 2p, (vi) 3p,, , (ii) 4d,, (i) n= 3, 1=2,m=-2, , (vi)n=3,l=1,m=t1, uantum numbers :, , NCERT Solved Example, , @ 34.5 42, (in =4,1=2,m=0, (vy)n=2,l=1,m=0, be the orbital with the following q', , Solution. (jn=3,1=2,m=+2, (iv) n=4,1=2,m=+1, , problem Rj Using s, p, d, f notations, descri, (a)n=2,1=10)n=4,120(0)n=5,1=3@)a=31=2, Solution. (a)n=2,1 = 1 means 2p orbital (b) n=4, 1 = 0 means 4s orbital, (c)n=5,1=3 means 5f orbital (d) n= 3,1 =2 means 3d orbital, Problem [J Which of the following sets of quantum numbers are not permitted ?, ) =2,/=0,m=0,s=0 (iv) n=2,/=1,m=2,s=+12, Solution. (i) This set of quantum numbers is not permitted since the value of I cannot be equal to ”., , (if) This set of quantum numbers is permitted,, (iii) This set of quantum numbers is not permitted because the value o:, , i) This f spin quantum number zero., (iv) This set of quantum numbers is also not permitted since the value at cannot be onan, preater a
Page 3 :
Free La Gre, , robler :, P em & Which of the following orbitals are not possible ?, , Solution. (i) The f Ip, 2s, 3f and 4d., 0 + (i) The first shell h 5 ied’ 2 5, qherefore, Ip orbital is not hE a8 Only one sub-shell, i.e., 1s, which has only one orbital, i.e, 18 orbital., , @ m ae sub-shell has two subshells, ie., 28 and 2p. Therefore, 28 orbitals are possible., (ii) a . ird subshell has three subshells, i.e., 3s, 3p and 3d. Therefore, 3f-orbitals are not possible., iv) The ourth shell has four Subshells, i.e., 4s, 4p, 4d and 4f. Therefore, 4d-orbitals are possible., , 1. If n is equal to 3, what are the values of quantum numbers / and m 7, , 2, How many orbitals are present in the subshells with (a)n=3,1=2(b)n=4,1=2(c)n=5,1=27, 3,, , 4, , , , "wer |, , , , . What are the values of n, J and m for 2p-orbitals ?, , Whnite the correct orbital notations for each of the following sets of quantum numbers :, (@n=1,1=0,m=0; (i) n=2,l=1,ms-1 ; and (iif) n=3,1=2,m=+1, , . What designation is given to an orbital having, @n=2,1=1, (ii) n=3,1=0, (iii) n= 5, 1=3 and (v)n=4,1=27, , Give the values of the quantum numbers for the electron with the highest energy in sodium atom., 7. Which of the following orbitals are not possible ?, , Ts, 2d, 3f and 1p, , z . «, . Which of the following sets of quantum numbers are not possible ?, (@)n=3,1=2,m=0,s=- 1/2, , (iii) n =3,1=3,m=-3,s=+1/2, : EXeWGS, , 1.1=0, 1,2 m=-2,—-1, 0, +1, +2 and s = + 1/2 and — 1/2 for each value of m, 2. Five orbitals in each case, , ., , (i) n=3,1=2,m=-2,s=-12, (iv) n=3,1=1,m=0,5=+ 1/2, , 3. For all 2p-electrons, n = 2 and / = 1, but m can have any one of three values, i.e., —1, 0 and +1, 4. @ 1s (ii) 2 py (iii) 3d, 5. (i) 2p (ii) 3s (iii) Sf (iv) 4d, 6.n=3,1=0,m=0 ands=+1/2or—1/2 7. 2d, 3f and Ip 8. (iii), , HINTS FOR DIFFICULT PROBLEMS, , 2. In each case, / = 2. Hence, m = — 2, — 1, 0, + 1, + 2, i.e., 5 values which means 5 orbitals., , 6. Electronic configuration of ,,Na = 1s 2s? 2p® 3s!. The electron with highest energy is 3s! for which n = 3, 1=0., , 8. (iii) is not possible because if n = 3, / =0, 1, 2.
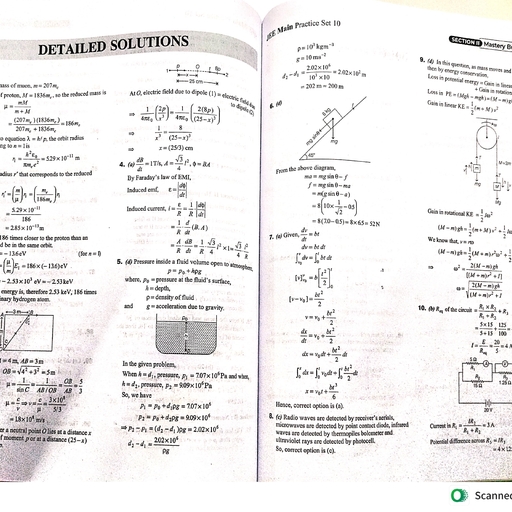
Page 4 :
¥ ! 9, Values of m by latest conventions, , Ler Retr Pree ern, d, , Pz m=0 a m=0, Px m= +1 a, m=+1, Py m=—-1 dy, . m=-1, 29 m=+2, , a, m=-2, , , , + signs are sometimes taken without any distinction, , The concept of subshells present in the main shell and the orbitals present in a sut, , 2,35., , , , , , , , FIGURE 2.35, SECOND SHELL, "s-SUBSHELL Peieee, ‘ ., s-ORBITAL p-ORBITALS, , Subshell and orbitals
Page 5 :
Write a short note on magnetic quantum number (m)., OR, , Explain the importance of magnetic quantum number. J, Magnetic quantum number (m):, , 4 : paren aera ectron, Magnetic quantum number describes the orientation of the orbitals or the distribution of el, cloud in space around the nucleus,, , Hence it is also called orientation quantum number. It is denoted by m and it has values from, +Ito-1 through zero, giving total values or total orientations equal to (2/ + 1)., , iti, These values are designated as, m=—/,...—2,—1,0,+1, +2, ...t/., , This quantum number is useful in the explanation of zeeman effect., , v., , A subshell in an atom consists of several orbitals or sub-subshells. The magnetic quantum number m, determines the orbital to which an electron belongs., , It also determines the number of orbitals in a particular shell., eg. a. s-subshell:, 1., 2., , The s subshell contains only one orbital because we have only one value of m (which is zero)., 3. Orbital contained in a s-subshell is called s-orbital., b. __ p-subshell:, , lL. For this /= 1, and m has three values, m = +1, 0, -1, 2., , Therefore p-shell has three orbitals (Px, Py and p,). They are in the direction of three, perpendicular coordinate axes x, y and z., , 1=0, hence, m= 0., , 3. In the absence of magnetic field, all the three p-orbitals are equivalent in energy and they, are three-fold degenerate or triply degenerate. In the presence of'a magnetic field, they, , have different energies and their degeneracy is removed., 4. They are represented as,, , , , , , , , , , , , , , c. — d-subshell:, , 1. For this subshell / = 2 and m has five values, m’= +2, +1, 0,-1, -2., , 2. The d-subshell has five d-orbitals designated as dy, dyz, de, d 2y2? d 2, 3. The orbitals d,,, d,., de, are planar with electron clouds in the planes specified by, subscripts in their symbols. The orbitals d 3 3 ad. are axial orbitals. d; , has cloud, ey ray?, density at the intersection of X and Y axes. ad, has electron density along the Z axis., 4. In the absence of magnetic field, all the five orbitals are equivalent in energy. They are, ; five-fold degenerate., 4 5., , These five d-orbitals are represented as,, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , dy de de dy 2d, , \ =+2 +1 0 -1 -2, ‘d. —_ f-subshell: m, , , , 1. For this subshell /= 3 and m has seven values,, m=+3,+2,+1, 0,-1,-2,-3., , 2. Therefore f-subshell has seven f-orbitals with seven different orientations., , 3 In the absence of a magnetic field, all the seven orbitals are equivalent in energy and they, are seven-fold degenerate., , 4., , They have complicated shapes and designations., , EE