Page 1 :
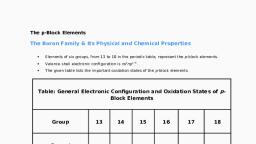
11. The p-Block Elements, Six groups (13 – 18) of p-block elements, Valence shell electronic configuration → ns°np (except for He), Difference in inner corè causes difference in physical and chemical properties., 1-6, Have all types of elements - metals, non-metals, and metalloids, In addition to group oxidation state, these elements show other oxidation states, differing from the total number of valence electrons by unit of two., * For lighter elements → Group oxidation state is the most stable., For heavier elements Lower oxidation states are progressively more stable., Non-metals and metalloids are present only in p-block., Non-metallic character decreases on moving down the, group., * Difference of the first member from the rest of the p-block elements of, their corresponding groups:, • Size and properties based on size, Unavailability of d-electrons in first member, Mation, Formation of T bonds:, Due to combined effect of size and availability of d-orbitals, Lighter elements form pTt - pT bonds while heavier elements form dn - pt or, dīt – dt bonds., Group 13 elements (The Boron family):, Valence shell electronic configuration → ns np' ., Atomic radius, increases on moving down the group, Exception: The atomic radius of Ga is less than that of Al. This is, because of poor shielding of d-electrons in Ga., Ionisation enthalpy, > A,H, <A,H, <A,H; ., > Decreases (not smoothly) on moving down the, > Exceptions : Al < Ga (Due to poor shielding by d-electron), group, In < Tl (Due to poor shielding by f-electrons), • Electronegativity, Decreases from B to Al and then increases on moving down the, group, • Physical properties, Scanned by TapScanner
Page 3 :
Na,B,0, + 2HCI + 5H,0 –→ 2NACI +, 4B OH, Orthoboric acid, H,BO,, A HBO,, do B,O,,, Metaboric, Boric oxide, acid, H., B., H., Structure of boric acid, nation, 4BF; + 3LİAIH, → 2B,H, + 3LİF + 3AIF;, * It contains two bridging hydrogen atoms between two boron atoms., * The bridging bonds are three-centre, two-electron bonds., H., H., Group 14 elements (The Carbon family):, Carbon is the most versatile element in the world., • Valence shell electronic configuration ns'np, • Covalent radius:, Increases from C to Si, but small increase from Si to Pb (due to presence of, completely filled d- and f-orbitals), • Ionisation enthalpy, > Higher than those of corresponding group 13 elements, Si, Ge, Sn, Pb, Small decrease, Slight decrease, (Due to poor shielding of d-and f alectrons), • Electronegativity, > Şlightly more electronegative than corresponding group 13 elements, Scanned by TapScanner
Page 4 :
Si, Ge, Sn, Pb, Almost same, • Physical properties, C, Si Non-metals, Ge Metalloid, Sn, Pb → Soft metals, Chemical properties, Reactivity towards oxygen, 7TW0 types of oxides- monoxide (MO) and dioxide (MO,), Reactivity towards water, C, Si, Ge, Pb Do not react, Sn+2H,O –ª_→ SnO, +2H,, > Reactivity towards halogen, > Form halides of formula MX, and MX,, CI, OH, ation, HCI, +3H;O, Si, -3HCI, Si, CI, CI, H., OH, но, OH, H., OH, CI, Anomalous behaviour of carbon:, > Due to smaller size,, → higher electronegativity, → higher ionisation enthalpy, unavailability of d orbitals, The order of catenation is, C>> Si > Ge Sn, (Pb does not undergo catenation), Allotropes of carbon:, → Diamond, → Graphite, → Fullerene, Scanned by TapScanner