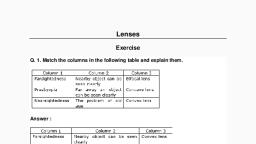
Page 1 :
EXPERIMENT 1, , Object. To siudy the parts of a compound microscope, its proper use and maintenance., , , , QUIREMENTS, , , , A compound microscope, a permanent slide, practical note book., , ompound Microscope, , Compound microscope is the most commonly used microscope in biology laboratory. It, agnifies the objects by the combination of two lens systems—(i) Objective lens lies close to, ne object and (ii) Eye piece or Ocular lens remains close to the eye., , The magnifying power of a lens is written on it as 5X, 10X, 15X, 45X etc. The magnificaion of the microscope is the combination of magnifications of the two lens systems. Thus,, Magnification of compound microscope, = Magnifying power of objective lens x Magnifying power of ocular lene:, , Parts of Microscope, , A compound microscope consists of following parts :, 1. Foot. The microscope is built around a basal foot., _ 2. Limb. It is slightly curved part of the microscope, which hold the body tube., , Bs
Page 2 :
( Ocular, eye piece, , , , , , , , Coarse _. Body tube, adjustment a, Fine adjustment EY \ Ravelvin, my ds ) evolving, / nose piece, Arm > y _ High power, y objective, Stage cli VGA, : | __ Low power, objective, Stage 2D, , ——— Cover slip, , AEE ~—— Slide, , , , , Inclination joint, Condenser, , Coins Mirror, , A | j Base, , , , Fig. 1.1. Compound microscope.
Page 3 :
&, , 5., , , , , , , Stage. A square stage is fixed to the limb with two clips to hold the slide., Mirror. A movable mirror is fixed at the lowermost part of the limb. Its plane surface’, used to direct the light over the object seen under low power and concave surface is usel, to converge the light on the object. seen under high power., , Diaphragm (Condensor). It is present under the stage to regulate the amount ol, light entering the microscope., , Body tube. It is attached to the upper end of limb and can be moved up and down bv, rack and pinion mechanism. It carries eye piece at its upper end and a revolving nos, , piece with two or three objective lenses at the lower end,, Coarse and fine adjustment. Coarse and fine adjustment Screws are present at the |, , upper end of the limb, which are used to focus with low and high power objective lenses |, , respectively,, , , , , , , , , Ny
Page 4 :
Use of the Microscope, , 1. Place the microscope in maximum diffuse light. Direct sunlight is harmful for the eyes. \, , The northern light is most suitable. If light source is artificial, filter (preferably blue |, coloured) is used. s
Page 5 :
EXPERIMENT FOR SPOTTING—1, , , , 81, , 9. Adjust the light by turning the mirror towards the source of light and also by moving, the condensor., , 3. Place the slide on the stage and adjust the object just over the stage aperture., , 4. Locate the object and focus it with a low power objective using coarse adjustment. If, higher magnification is desired, turn the nose piece to next higher power. Use only fine, adjustment at this stage., , 5. Always observe with both eyes open., ‘Care of the Microscope, , 1. Before and after use, clean all the lenses and metal part including the stage with tissue, paper, muslin cloth or soft and clean handkerchief., , 2. Keep the microscope covered when not in use., , 3. Do not remove the objective lenses from the nose piece., , 4. Handle the screw, condenser, mirror and stage clips carefully., , 5., , Care should be taken that objective lens should not touch the slide in any case.