Page 1 :
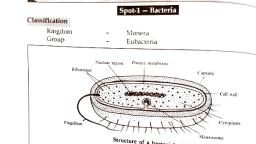
CLASS - X, BIOLOGY PRACTICALS, INSTRUCTIONS FOR STUDENTS:-, FILE WORK SHOULD BE NEAT AND CLEAN., YOU HAVE TO WRITE CLASSIFICATION ON WHITE PAGE OF FILE BY PENCIL., MAKE A DIAGRAM ON WHITE PAGE (OPPOSITE SIDE OF GIVEN SPECIMENS), DON’T USE PEN ON WHITE PAGE., USE A PAGE FOR DIVIDING EACH SECTION., YOU CAN USE COLOURS FOR HEADING., SECTION: 1, SPOTTING, IDENTIFICATION, AND, STUDY OF, PLANT & ANIMAL, SPECIMENS/ SLIDES/ MODELS, SPOT-1, AMOEBA PROTEUS, CLASSIFICATION (on white sheet of file), Phylum – Protozoa, [Single cell organism], Class – Rhizopoda (=Sacrodina), Genus – Amoeba, Species – Proteus, DIAGRAM, COMMENTS:-, It is a unicellular, microscopic organism found in ponds, ditches, lakes etc., It is irregular in shape, colourless and translucent mass of protoplasm., It constantly changes shape by putting forth and withdrawing Pseudopodia – the locomotory organelles., The body of the animal is covered by a soft and selectively permeable Plasma membrane., The protoplasm is distinguished into an outer ectoplasm and an inner endoplasm., There is a prominent nucleus in the centre., Many food vacuoles and contractile vacuole are found in the cytoplasm., SPOT-2, HYDRA, CLASSIFICATION (on white sheet of file), Phylum – Coelenterata, [Presence of coelenterons body cavity], Class – Hydrozoa, Genus – Hydra, Species – Oligactis, DIAGRAM, COMMENTS:-, The body of Hydra is a narrow, elastic, hollow cylinder which is open at one end (distal end) and closed at the other end (proximal end)., The distal end is free and has a small conical projection called oral cone or hypostome having an opening called mouth., From the base of hypostome arise 4-12 highly contractile tentacles., The tentacles bear large number of stinging cells or nematoblasts for offences defence., The proximal end is attached to some substratum and is called basal disc or foot., The body cells are arranged in to layers – an outer ectoderm and an inner endoderm (diploblastic condition)., In mature Hydra, a bud at the base and gonads (testis and ovary) in the middle are seen., SPOT – 3, FASCIOLA HEPATICA (LIVER FLUKE), CLASSIFICATION (on white sheet of file), Phylum – Platyhelminthes, [Body is flat], Class – Trematoda, Genus – Fasciola, Species – Hepatica, DIAGRAM, COMMENTS:-, It is an endoparasite in the bile passage of vertebrates like sheep; cow etc. It causes a disease called liver rot., The animal is dorso-ventrally flattened and leaf-like with a cuticle., A mouth surrounded by an oral sucker is present at the anterior end. A little below the mouth, a posterior sucker or acetabulum is present on a ventral side., On the ventral side of the body, a gonopore is present in between the two suckers., The posterior end of the body bears an excretory pore., There is no opening for faecal matter., SPOT – 4, ASCARIS LUMBRICOIDES, CLASSIFICATION (ON WHITE PAGE), Kingdom – Animalia, Phylum - Nemathelminthes, Order – Ascaroidea, Genus – Ascaris, Species- Lumbricoides, DIAGRAM:-, COMMENTS, It is a common intestinal parasite of man specially children. Occasionally it may occur in the intestine of pigs, sheep, cattle, monkey etc., It has a cylindrical body with tapering ends., The front end of body has a terminal triradiate mouth surrounded by three lips., A little behind anterior end, there is a small excretory pore., The adult worms are sexually dimorphic., Males are comparatively smaller than females. There posterior part is slightly curved. Males have two needles like penial setae or copulatory ceate which protrude out from their anus., SPOT – 5, HIRUDINARIA GRANULOSA (LEECH), CLASSIFICATION (ON WHITE PAGE), Kingdom – Animalia, Phylum – Annelida, Class – Hirudenia, Order – Gnathobdellida, Genus – Hirudinaria, Species – Granulosa, DIAGRAM:-, COMMENTS:-, It is found in ponds, lakes, rivers, swamps etc., and in the moist soils near such water bodies., It is a facultative ectoparasite of cattle and other mammals. It sucks blood (sanguinivorous) by periodically coming in contact with the body of the host., Its body is somewhat dorso-ventrally flattened and measures about 15 cm. In length but it can stretch its length upto 30cm. when required. It is olive green in colour., The body is divided in to 33 segments and each segment has superficial 2 to 5 annuli., The anterior part of body is narrower and bears a ventral triradiate mouth surrounded by a cup like anterior sucker., The posterior end bears a larger posterior sucker, and a mid-dorsal anus just in front of the sucker. The suckers help in locomotion, and in adhering to the body of host during blood meal., Leech is hermaphrodite animal but shows cross fertilization., SPOT – 6, PHERETIMA POSTHUMA (EARTHWORM), CLASSIFICATION, Kingdom – Animalia, Phylum – Annelida, Class – Oligochaeta, Order – Terricolae, Genus – Pheretima, Species – Posthuma, DIAGRAM:-, COMMENTS:-, Earthworm lives in burrows in moist soils where decaying vegetation and other organic matter are present. During rainy season they come out of their burrows as the latter get flooded by water., It has a long cylindrical and segmented body. It measures about 10 – 20cm. In length. It is quite slimy in touch and pinkish brown in colour., The dorsal surface of the body is recognised by its darker colour and ventral surface is marked by genital apertures and papillae located in anterior region of the body., The segments 14, 15 and 16 form a band called clitellum. It forms one or more egg cases or cocoons in which ova are laid and fertilized., Mouth is present at the anterior end. A fleshy lobe called Prostomium dorsally over hangs upon the mouth like a hood. Anus is present in the last segment., Each segment except the first and the last bears row of minute yellowish setae for locomotion., Earthworm is hermaphrodite animal but shows cross fertilization., SPOT – 7, PALAEMON (PRAWN), CLASSIFICATION, Kingdom – Animalia, Phylum – Arthropoda, Class – Crustacea, Order – Decapoda, Genus – Palaemon, Species – Malcolmsonii, DIAGRAM:-, COMMENTS:-, It occurs in fresh waters such as in rivers, ponds, lakes and swamps., The body is curved and is about 5 o 18 cm. Long. It is distinguished into cephalothorax and a long abdomen., The cephalothorax is dorsally covered by a hard carapace, which extends as a serrated process called rostrum., Cephalothorax bears eight pairs of segmented legs and one pair each of antennae, antennules and stalked compound eyes., Abdomen consists of six segments, with one pair of paleopod each used for swimming., Prawns are unisexual i.e. male and female sex organs occur in separate individuals., SPOT – 8, PILA GLOBOSA (APPLE SNAIL), CLASSIFICATION, Kingdom – Animalia, Phylum – Mollusca, Class – Gastropoda, Order – Prosobranchiata, Species – Globosa, DIAGRAM:-, COMMENTS:-, It is commonly found in fresh water streams, ponds, ditches, lakes, rice fields etc. Though it is aquatic but can live without water for quite some time., It has a soft and slimy body enclosed in a coiled calcarious shell. The opening of the shell is closed by a thick plate like Operculum., The body is differentiated into head, food, visceral mass and mantle., The head overhangs the foot and bears two pairs of tentacles and one pair of eyes., The foot is anterior and ventral, sole like used for creeping., Sexes are separate with slight sexual dimorphism., SPOT – 9, ASTERIAS (STAR FISH), CLASSIFICATION, Kingdom – Animalia, Phylum – Echinodermata, Class – Asterioda, Order – Forcipulata, Genus – Asterias, Species – Rubens, DIAGRAM:-, COMMENTS:-, It is a marine animal and is found crawling on rocky sea bottom in shallow water., Its body is flattered, star shaped and pentamerous with a small central disc and five short and tapering radiating arms., The oral surface directed downwards and bears pentagonal mouth in the central disc., Aboral surface bears large number of short and movable spines. Anus is present in hte centre of the disc., A narrow ambulacral groove extends from each angle of the mouth along the midline of the oral surface of each arm. Each ambulacral groove contains on eighter side two rows of tubular retractile projections called tube feetor podia. The latter are connected with water vascular system and help in locomotion, food capture and respiration., Sexes are separate without sexual dimorphism., SPOT – 10, SCOLIODON (DOG FISH), CLASSIFICATION, Kingdom – Animalia, Phylum – Chordata, Sub – phylum – Vertebrata, Class – Chondrichthyes, Genus – Scoliodon sp., DIAGRAM:-, COMMENTS:-, Dog fish commonly known as the shark, is found in the coastal waters of India., It has somewhat laterally compressed and spindle shaped or steam lined body with pointed snout. The body is differentiated into head, trunk and tail., The head is dorso – ventrally compressed, which ventrally bears the semi- circular mouth with sharp inwardly curved and pointed teeth., Two large eyes are present on the head. Five vertical gill clefts are present behind each eye., Two mid – dorsal, one mid – ventral, one caudal and two pairs of lateral (pectoral and pelvic) fins are present for swimming., Sexes are separate. The males have claspers in pelvic region. These are copulatory organs., Sharks are viviparous i.e., give birth to young ones., SPOT – 11, LABEO ROHITA (ROHU), CLASSIFICATION, Kingdom - Animalia, Phylum – Chordata, Sub-phylum – Vertebrata, Class – Osteichthyes, Genus – Labeo, Species – Rohita, DIAGRAM:-, COMMENTS:-, It is a fresh water dweller commonly called rohu fish (the Indian carp), widely used as food fish in our country., It measures about 30 to 90 cm. in length. The body is somewhat flattered and streamlined, dusky-black dorsally and laterally, but pale white ventrally. It is covered with overlapping cycloid scales., Mouth is sub-terminal and ventral. A pair each of nostrils and large lateral eyes without eyelids is present., There are five pairs of gill slits covered by an operculum., Three median (dorsal, ventral and caudal) and paired pectoral and pelvic fins are present for swimming. The tail is homocercal (i.e. caudal fin equally lobed)., Lateral line sense organs are present., Sexes are separate. The males are without claspers., SPOT – 12, COLUMBA LIVIA (PIGEON), CLASSIFICATION, Kingdom – Animalia, Phylum – Chordata, Sub-phylum – Vertebrata, Class – Aves, Genus – Columba, Species – Livia, DIAGRAM:-, COMMENTS:-, It makes its nests in scantily inhabited houses, godowns, railway stations etc., and feeds upon grains, fruits and insects., Its body is 20 to 25 cm. Long and covered with slate blue feathers. A narrow fluorescent bound occurs around the neck., It has a sub spherical head, mobile neck, thick trunk and short tail., The beak is small and slightly curved in front. The base of beak is covered by a lobe of fleshy skin called cese., The eyes are red in colour., Forelimbs are modified into feathered wings having no digits., Hindlimbs are covered with scales and each bears four clawed digits. They are adapted for perching., SPOT – 13, ORYCTOLAGUS CUNICULUS (RABBIT), CLASSIFICATION, Kingdom – Animalia, Phylum – Chordata, Sub-phylum – Vertebrata, Class – Mammalia, Order - Lagomorpha, Genus – Oryctolagus, Species – cuniculus, DIAGRAM:-, COMMENTS:-, It lives in fields, making burrows (fossorial) and feeds on vegetation (herbivorous)., Its body is divided in to head, neck and trunk and small bushy tail. The body is covered with hair of white brown or black colour., The mouth is bounded by soft and fleshy upper and lower lips. The upper lip is cleft (hair-lip) with sensory hair or wiskers on the snout., Two large movable pinnae or external ears are present behind the eyes. The eyes are pink in colour., The fore limbs are shorter and are used for borrowing. The hind limbs are long and help in leaping., Sexes are separate with sexual dimorphism. The female have mammary glands with nipples on the abdomen. The males have pair of testes in scrotal sac and a small and fleshy penis., PLANT SPOTTING, SPOT - 1, AGARICUS (Mushroom), CLASSIFICATION, Kingdom – Fungi, Division – Eumycophyta, Class – Basidiomycetes, Genus – Agaricus, Species – Compestris, DIAGRAM:-, COMMENTS:-, It is a saprophytic fungus that grows in humus rich soils, piles of straw and rotting wooden logs., It has septate mycelium under the substratum. The mycelium produces white or cream coloured umbrella shaped fruit bodies or basidiocarps above the substratum., A basidiocarp consists of a stalk like stipe and a cap like pileus., Pileus is circular, umbrella like and bears a number of vertical plates like structure called gills., The gills bear club shaped basidia on either side. The basidiospores are placed on basidia., DIAGNOSTIC FEATURES:-, The fruit body is umbrella shaped., Gills are present on the lower side of the pileus., SPOT – 2, BACTERIA, CLASSIFICATION, Kingdom – Monera, Division – Schizophyta, Order – Eubacteriales, Type – Bacteria, DIAGRAM:-, COMMENTS:-, Bacteria are microscopic, unicellular and prokaryotic organisms., Bacteria have different shapes. These are Coccus(spherical). Bacillus (rod shaped), Spirillum(Spiral shaped), Vibrio(comma shaped) and filamentous., The bacterial cell have prokaryotic organisation i.e., a distinct nucleus and membrane bound cell organelles are absent., The hereditary material is in the form of single circular chromosome, formed of a DNA alone., Bacteria reproduce by binary fission., Many bacteria also form endospores during infavourable conditions., DIAGNOSTIC FEATURES –, Microscopic and unicellular., True nucleus absent., SPOT – 3, OSCILLATORIA, CLASSIFICATION, Kingdom – Monera, Division – Cyanophyta, Class – Cyanophyceae, Genus – Oscillatoria sp., DIAGRAM:-, COMMENTS-, It occurs in stagnant water, ponds, pools, ditches etc., as bluish green scum on the surface of water., It is a filamentous blue green alga., The filaments of oscillatoria are unbranched and cylindrical. Each filament consists of a trichome made up of a row of cylindrical cells enveloped in a sheath of mucilage. The tip of trichome oscillates like pendulum., Each cell of the filament has prokaryotic organisation. The cytoplasm of a cell is differentiated into a peripheral Chromoplasm and a central centroplasm., The chromoplasm contain pigmented thylakoid lamellae and reserve food in the form of cyanophycean granules., Reproduction occurs by means of hormogonia formed due to the formation of dead cells., DIAGNOSTIC FEATURES, Bluish green in colour., Filaments unbranched and enveloped in a mucilage sheath., Each cell is prokaryotic., SPOT – 4, SPIROGYRA (Water silk or pond scum) CLASSIFICATION, Kingdom – Plantae, Division – Chlorophyta, Class – Chlorophyceae, Genus – Spirogyra sp., DIAGRAM –, COMMENTS:-, Spirogyra occurs in fresh water bodies such as ditches, ponds, lakes etc., It is commonly called water silk or pond scum because of slippery touch of its thread like filaments., It is a multicellular, filamentous green alga covered by a mucilaginous sheath., The cell wall is two layered and is made up of cellulose and pectin., Cytoplasm lies in the periphery of cell, enclosing a vacuole in the centre., One or more ribbon shaped spirally arranged chloroplasts are present in the cytoplasm. Each chloroplast bears pyrenoids., It reproduces asexually by fragmentation and sexually by conjugation., DIAGNOSTIC FEATURES:-, Unbranched, filamentous body with slimy touch., Ribbon shaped, spiral chloroplast., Nucleus suspended by cytoplasmic strands., SPOT – 5, RHIZOPUS (BREAD MOULD), CLASSIFICATION, Kingdom – Fungi, Division – Eumycophyta, Class – Zygomycetes, Genus – Rhizopus, Species – Stolonifer, DIAGRAM:-, COMMENTS:-, It commonly grows on stale bread, decaying vegetables and fruits., Its body is made up of interwoven mass of white cottony threads or hyphae, and is known as mycelium., The hyphae of the mycelium are branched, unseptate and multinucleate (coenocytic hyphae)., Each sporangiophore bears a globular sporangium at its tip. The sporangium contains black coloured spores, which give black colour to the mycelium in reproductive phase., Asexual reproduction occurs by spores and sexual reproduction occurs by conjugation., DIAGNOSTIC FEATURES:-, Mycelium is unceptate and multinucleate (coenocytic)., Sporangiophores arise in the form of tufts., SPOT – 6, SACCHAROMYCES (YEAST), CLASSIFICATION, Kingdom – Fungi, Division – Eumycophyta, Class – Ascomycetes, Genus – Saccharomyces sp., DIAGRAM –, COMMENTS:-, It is commonly found growing in sugary medium such as fruit surfaces, nector, cane juice etc., It is a unicellular but may form a pseudomycelium by repeated budding., The cytoplasm has a large central vacuole with a nucleus on its side. Dark strands over vacuole from the nucleus., Volutin granules and glycogen droplets are present as reserve food in the cytoplasm., Asexual reproduction takes place by budding and sexual reproduction occurs by the formation of ascospores., DIAGNOSTIC FEATURES_, Unicelluar., Presence of nuclear vacuole., Reproduction by budding., SPOT – 7, MARCHANTIA (LIVERWORT), CLASSIFICATION, Kingdom – Plantae, Division – Bryophyta, Class – Hepaticae, Genus – Marchantia sp., DIAGRAM:-, COMMENTS:-, It commonly grows on moist, shady and damp places on hills., The thallus is dorsiventrally flattened and dichotomously branched with notched apex., Cup shaped bodies called gemma cups are present on the median groove on dorsal surface of the thallus. The gemma cups contain gammae for vegetative propogaion., Multicellular purple coloured scales and unicellular rhizoids are present on the ventral surface of the thallus., Antheridia and archegonia are present on special erect gametophores called antheridiophores and archegoniophores respectively born on separate thallai., Sporophyte is produced on the archegoniophore after fertilization. It is differentiated into foot, seta and capsule., SPOT – 8, FUNARIA HYGROMETRICA (MOSS), CLASSIFICATION, Kingdom – Plantae, Division – Bryophyta, Class – Musci, Genus – Funaria, Species – hygrometrica, DIAGRAM –, COMMENTS:-, It is commonly grows on moist, shady and damp soils, walls of houses, creoices of rocks., The plant body is gametophyte. It is green, erect and is differentiated into rhizoids, axis (stem) and leaves., Rhizoids are multicellular and branched with oblique septa., The main axis bears antheridia at its apex and is called male shoot. A lateral branch called female shoot bears archegonia at its tip., After fertilisation a partially dependent sporophyte develops on the female shoot., The sporophyte is differentiated into foot, seta and capsule. The capsule encloses spore sac that contains spores., The spores germinate into filamentous protonema., SPOT – 9, DRYOPTERIS (MALE FERN), CLASSIFICATION, Kingdom – Plantae, Division – Pteridophyta, Class – Filicinae, Genus – Dryopteris, DIAGRAM –, COMMENTS:-, Dryopteris commonly called male fern is a perennial land plant. It grows in cool, shady and moist places., The plant body is sporophyte and is differentiated into root, stem (underground rhizome) and pinnately compound leaves (fronds)., The mature leaves bear kidney shaped sori. Such leaves are called sporophyllus. The sori bear sporangia that contain spores., The spores are haploid which give rise to heart shaped membranous gametophyte called prothallus., The prothallus is monoceious i.e., bears both antherida and archegonia., SPOT – 10, PINUS ROXBURGHII (CHIR), CLASSIFICATION, Kingdom – Plantae, Division – Spermatophyta, Class – Gymnospermae, Genus – Pinus, Species – roxburgii, DIAGRAM:-, COMMENTS:-, The plant body is sporophyte. It is a evergreen tall tree differentiated into root, stem and leaves., Root has tap root system and often associated with mycorrhizae., Stem is covered with bark and bears two types of branches long shoots and dwarf shoots., The leaves are of two types :, A). Scale leaves are thin, membranous non-photosynthetic and protective in function., B). Foliage leaves are long, acicular, green and photosynthetic in function. Dwarf shoot with its leaves is called spur shoot., Pinus tree is monoecious and bears both male and female cones in spring season., Male cone is ovoid, brown in colour, narrow at the base and broad at the apex. A number of membranous microsporophylls are arranged spirally around its axis., Female cone is cone shaped and bears large and woody megasporophyllus., SPOT – 11, BRASSICA CAMPESTRIS (MUSTARD), CLASSIFICATION, Kingdom – Plantae, Division – Spermatophyta, Class – Angiospermae, Sub–class – Dicotyledonae, Genus – Brassica, Species – campestris, DIAGRAM:-, COMMENTS:-, It is a cultivated annual herb., It has a tap root system., The stem is soft green with distinct nodes and internodes., The leaves are alternate, sessile, and simple with lobed margin and reticulate venation., It bears yellow colour flowers for reproduction. Each flower is bisexual and bimerous with cruciform corolla., The seeds are enclosed within the fruit., The seed contains an embryo with two cotyledons., SPOT – 12, SPHODELOUS TENEUFOLIUS (PIAZI), CLASSIFICATION, Kingdom – Plantae, Division – Spermatophyta, Class – Angiospermae, Sub-class – Dicotyledonae, Genus – Asphodelus, Species – teneufolius, DIAGRAM:-, COMMENTS:-, It bears adventitious root system., The stem is reduced and lies under the soil., Leaves are borne in cluster. Each leaf is cylindrical, hollow and has parallel venation., Floral axis grows out of the soil and bears trimerous flowers., The seeds are produced within the fruits., The seed enclosed an embryo with only one cotyledon., SPOT – 13, LICHENS (A symbiotic association), DIAGRAM:-, COMMENTS:-, Lichens are composite organisms representing a symbiotic association between a fungus and an alga., Lichens grow on lands, rocks, tree trunks and walls of houses, like dry vegetation., The thallus of lichen resembles neither alga nor fungus., Lichens occur in three forms:-, A). Crustose lichens are thin, membranous, found attached to the substratum in the form of a crust., B). Foliose lichens have flat, lobed and leaf like thallus., C). Fruticose lichens have branched and small bushy thallus attached to the substratum by means of a disc., Lichens reproduce vegetatively by fragmentation, asexually by soredia and isidia and sexually by forming sex organs like those formed in Ascomycetes (sac fungi)., SECTION 2: STUDY AND DESCRIPTION OF THE FLOWER, TYPE1: PETUNIA ALBA – PETUNIA, CLASSIFICATION (on white page of file), Division – Angiospermy, Class – Dicotyledonae, Family – Solanaceae, Genus – Petunia, Species – Alba, 1 Vegetative character:-, Root- Tap root, branched, Stem- Herbaceous, erect, hairy, Leaf – Alternative, opposite in the floral region, petiolate, simple, ovate, hairy, 2 Floral characters:-, Inflorescence – Solitary, axillary., Flower – Ebracteate, pedicellate, complete, bisexual, actinomorphic, pentamerous, hypogynous., Calyx – Sepals 5, gamosepalous, valvate aestivation, persistent, inferior, green, hairy., Corolla – petals 5, gamopetalous, infundibuliform, valvate aestivation, white or purplish in colour., Androecium – stamens 5, alternipetalous, epipetalous, anther bithecous, basifixed., Gynoecium – Bicarpellary, syncarpous, ovary superior, obliquely placed, bilocular with axile placentation, swollen placenta, style long, stigma bifid., Floral formula – Ebr, Reasons for identification:-, Persistent sepals., Corolla Infundibuliform., Stamen epipetalous., Ovary obliquely placed placentation axile with swollen placenta., TYPE 2:- LATHYRUS ODORATUS – SWEET PEA (MATAR), CLASSIFICATION (on white pg), Division – Angiospermae, Class – Dicotyledonae, Family – Fabaceae, Genus – Lathyrus, Species – Odoratus, Vegetative character:, Root: - Tap root, branched with root nodules containing nitrogen fixing bacteria., Stem: - Herbaceous, weak, hollow climbing., Leaf: - Alternate, petiolate, stipulate, stipules leafy. Compound, the upper leaflets modified into tendrils., Floral character:, Flower: - Bracteate(bract caduceus), pedicellate, complete, bisexual, Zygomorphic slightly perigynous, pentamerous, variously coloured., Calyx: - Sepals 5, gamosepalous, valvate, odd sepal anterior, persistent, inferior, green., Corolla: - Petals 5, polypetalous, corolla papillionaceous, vexillary aestivation, variously coloured, inferior., Androecium: - Stamens 10, Diadelphous 1 +(9), 9 stamens united to form a tube, tenth stamen is free, basifixed inferior., Gynoecium: - Monocarpellary, ovary superior, unilocular, marginal placentation, style curved and hairy, style flattened., Floral formula: - Br ††, Reasons for identification:, Flower zygomorphic with papilionaceous corolla., Odd sepal anterior., Stamens diadelphous., Monocarpellary gynoecium, ovary unilocular with marginal placentation., TYPE 3: ALLIUM CEPA – ONION, CLASSIFICATION, Division- Angiospermi, Class – Monocotyledonae, Family- Liliaceae, Genus – Allium, Species- Cepa, Vegetative character:, Root:- Adventitious, fibrous., Stem:- Underground bulb, inner scales fleshy outer dry membranous and brown., Leaf:- Radical, cylindrical, sheathing., Inflorescence:- Umbellate cyme., Floral character:, Flower:- Bracteate, pedicillate, incomplete, bisexual, actinomorphic, hypogynous, trimerous., Perianth:- Tepals 6, arranged in two whorls of 3 each, slightly gamophyllous at the base, petaloid, white in colour, each tepal is marked with a brown midrib., Androecium:- Stamens 6, polyandrous, arranged in two whorls of 3 each, antiphyllous, epiphyllous, anther bithecous, basifixed., Gynoecium:- Tricarpellary, syncarpous, ovary superior, trilocular eachlocule with two ovule, axile placentation, style short, stigma trilobed., Floral formula:- Br, Reasons for identification:, Flower trimerous., Petaloid perianth in two whorls of 3 each, epiphyllous., Stamens six in two whorls of 3 each, epiphyllous., Ovary tricarpellary, trilocular with axile placentation.