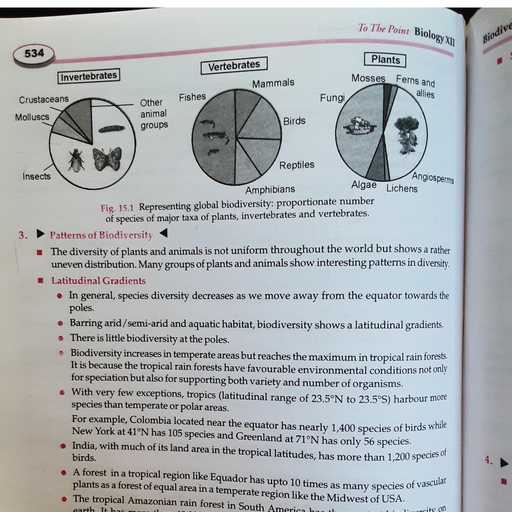
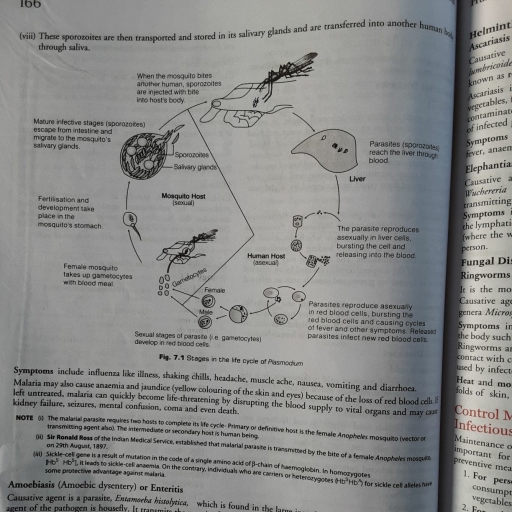
Page 1 :
Thus, CO, assimilation during photosynthesis is of two types:, G) C. pathway- in which the first product is a C, acid (PGA) and the primary acceptor, of CO, is a 5C compound, ribulose biphosphate (RUBP)., G) C. pathway – in which the first product is a C, acid (OAA) and the primary acceptor, of CO, is a 3C compound, phosphoenol pyruvate (PEP)., . However, Calvin cycle (calvin pathway) occurs in all photosynthetic plants; it does not, matter whether they have C, or C (or any other) pathways of photosynthesis (Fig. 13.8)., -, Atmosphere, Ribulose-1,, 5-bisphosphate, Co, + H,0, ADP, 1 Carboxylation, Regeneration 3, 3-phosphoglycerate, ATP +, NADPH, ATP, 2 Reduction, Triose, ADP +, phosphate, P, + NADP*, Sucrose, starch, Fig. 13.8. Calvin cycle., The Calvin Cycle (C, pathway), Calvin cycle proceeds in three stages as follows:, (a) Carboxylation, – Carboxylation is the fixation of CO, into a stable organic intermediate., -, -, - CO, combines with a 5C compound, ribulose 1, 5-biphosphate to form 2 molecules, 2., of 3PGA in presence of enzyme RUBP carboxylase., – This enzyme has an oxygenation activity, hence commonly called RUBP, carboxylase-oxygenase (RUBISCO)., -, (b) Reduction, - It involves a series of reactions that lead to the formation of carbohydrate (glucose), and utilises 2 molecules of ATP and 2 molecules of NADPH for reduction per, CO, molecule fixed., - For the formation of one molecule of glucose 6 molecules of CO, and 6 turns of, the cycle are required., (c) Regeneration, -, – To continue the cycle, the CO, acceptor molecule RUBP is formed from triose, phosphate with the utilisation of one molecule of ATP., – Hence, for each CO, molecule, a total of 3 molecules of ATP and 2 of NADPH are, required., -, -