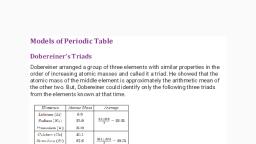
Page 1 :
s of Newland’s Law of Octaves, , was applicable only upto, eighth element did, , Limitation, (1) The Law of Octaves, calcium, as afte! calcium ever y ean, not possess properties similar to that of the t's, ned that only 56 elements, and no more elements would be, Rut, later on, several new, properties did, , Newlands assut, existed in nature, discovered In the future. |, nts were discovered, whose, e Law of Octaves., , nts into his Table, Newlands, same slot, but also, same note,, , (2), , eleme, not fit into th, In order to fit eleme, adjusted two elements In the, put some unlike elements under the, , (3), , Example:, e Cobalt and nickel are in the s, these are placed in the same, , ame slot and, column as, , fluorine, chlorine and bromine which have very, , different properties than these olameants, , ® lron, which resembles cobalt and nickel In, properties, has been placed far away from, these elements, (4) Newlands’ Law of Octaves worked well with, lighter elaments only, , Example 2. Did Débereiner's triads also exist In, , the columns of Newlands’ Octaves? Compare and, , find out,, , Ans. Yos, triads exists in the, columns of Newlands’ Octaves, For example, Li,, Na and K form Débereiner’s triads and thay also, exist in Newland’s octaves under the same note, or column, , Débereiner's also, , | TOPIC 2 |, MENDELEEV'S PERIODIC TABLE, , The main credit for classifying elements goes to Dmitri, lvanovich Mendeléev, a Russian chemist. He was the, most important contributor to the early development, of a Periodic Table of elements wherein the elements, were arranged on the basis of their fundamental, property, the atomic mass, and also on the similarity, of chemical properties., , (1) When Mendeléev started his work, 63 elements, were known., , He examined the relationship between the atomic, masses of the elements and their physical and, chemical properties., , Among chemical properties, | Mendeléev, concentrated on the compounds formed by, elements with oxygen and hydrogen., , (2), , (3), , , , , , elements. The formulae of the hydrides and, oxides formed by an element were treated as, one of the basic properties of an element for its, classification., , He then took 63 cards and on each card he wrote, down the properties of one element., , He sorted out the elements with similar properties, and pinned the cards together on a wall., , He observed that most of the elements got a, place in a Periodic Table and were arranged in the, order of their increasing atomic masses., , It was also observed that there occurs a periodic, recurrence of elements with similar physical and, chemical properties., , Mendeléev Periodic Law: ‘The properties of elements, are the periodic function of their atomic masses., , (8), , vill, , , , (4) He selected hydrogen and oxygen as they are, very reactive and formed compounds with most, , eM Me NA, , Oxide RO RO R203 RO2, Hydride ee Ree ie _ RH) ‘ A x RH3 RH3, , |Peods |A BIA BIA BIA 'B, , | |, , 11 H, , | |1.008 |, , + 7, , 2 | Li Be B G, , | |6939 |9.012 | 1081 | 12011, , {3 Na /Mg Al Si, , | | 22.99 | 2431 | 2998 | 28.09, , 4 First | K Ca Sc Ti, series: | 39.102 | 40.08 4496! 47,90, Second | Cul Zn Ga Ge, series | 6354) 65,37 69.72 | 72.59, , , , , , , , we eho” Vi | Vil, RROMMMERC, | R207 |, | ieee ea. | RA |, A BIA BLA B Transition sries, |, N O F, 14.007 | 15999 | 18998, P s ict, 30.974 |3206 /|35.453 | |, } |, Vv Cr Mn | Fe Co Ni, 47.90 50.94 $4.94 | 55.85 5893 58.71 |, As Se | Br | |, | 7AGa 7896 | 79,909 | |, , TS