Page 1 :
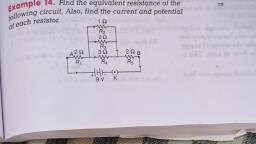
Aim, To determine the focal length of concave mirror by obtaining the image of a distant object., Theory, The rays of light coming from a distant object such as the sun or a distant tree can be, considered parallel to each other., , When parallel rays of light fall on a concave mirror along its axis, the rays meet at a, point in front of the mirror known as focus F and the image formed of the object is, real, inverted and very small in size., The distance between the principal axis P of the concave mirror and the focus F is the focal, length of the concave mirror, , Procedure, 1. Select a distant object from the laboratory window., 2. Fix the concave mirror on the mirror stand placed on the table, facing the, distant object., 3. Place the screen in front of the reflecting surface of the mirror. Move the screen, back and forth until a clear, sharp image of the distant object is obtained on the, screen., 4. Measure the distance between the concave mirror and the screen with a metre, scale. This distance is the focal length of the given concave mirror. Record the, focal length., 5. Repeat the above procedure twice and record the readings. Take three, readings and calculate the average focal length., , Observation Table
Page 2 :
Focal length, S.No. Position of concave mirror (M), , Position of screen (S), [ = (M – S)] cm, , 1., , ……… cm, , ……….. cm, , ……… cm, , 2., , ……… cm, , ………..cm, , ………. cm, , 3., , ……… cm, , ……… cm, , ……….. cm, , Calculation, Mean value of focal length of concave mirror =, , Result, The focal length of the given concave mirror = ……… cm, , Precautions, 1. The distant object must be well illuminated to produce a well illuminated and, distinct image., 2. Always place the concave mirror near an open window., 3. The polished surface of the concave mirror must face the distant object., 4. There should be no obstacle or hurdle in the path of rays of light from the, distant object, incident on the concave mirror., 5. The base of the stands of the concave mirror and screen should be parallel to, the measuring scale., 6. The mirror holder along with the mirror should be kept perpendicular to the, measuring scale for precise measurements.
Page 3 :
Aim, To determine the focal length of convex lens by obtaining the image of a distant, object., Theory, , , When a parallel beam of light falls on a convex lens, the rays, after refraction, converge at a point on its other side., If the parallel beam of light comes from a distant object, a real, inverted image, of very small size is formed at the focus of the lens., The distance between the optical centre of lens ‘O’ and the principal focus ‘F’, of the lens is called focal length of a lens, ‘f’ is the representation of focal, length., Materials Required, Wooden bench, convex lens, a lens holder, a screen fixed to a stand, a measuring scale;, etc., , Procedure, 1. Arrange the wooden bench capable of holding the lens and screen horizontally, on a table, so that the lens and screen are not disturbed., 2. Keep the lens in a holder facing a distant object say tree branches., 3. Fix the screen on another holder and keep it on the bench., 4. Adjust the position of the screen in such a way that a sharp image of the given, distant object falls on it., 5. Note down the position of the lens in the table and the screen, and find the, differences and record the same. The difference will give the focal length of the, given convex lens., 6. Focus the lens towards various distant objects and repeat the experiment to, find the position of sharp image and thereby the focal length., 7. Add all the focal lengths found out and find the mean value of the focal length, of the convex lens
Page 4 :
Observation Table, Focal length, S.No., , Position of convex lens (L), , Position of screen (S), [= (L – S) cm], , 1., , …. cm, , …. cm, , f1 = …. cm, , 2., , …. cm, , …… cm, , f2 = …. cm, , 3., , ….. cm, , …. cm, , f3 = …. cm, , Calculation, Mean value of focal length of convex lens =, Result, The focal length of the given convex lens = …… cm, Precautions, 1. Convex lens should be placed vertically., 2. There should be no obstacle or hurdle in the path of rays of light from the, distant object incident on the common lens., 3. In order to get a well illuminated and distinct image, it must be ensured that the, distanct object is well illuminated., 4. The base of the stands of the convex lens and screen should be parallel to the, measuring scale.