Page 1 :
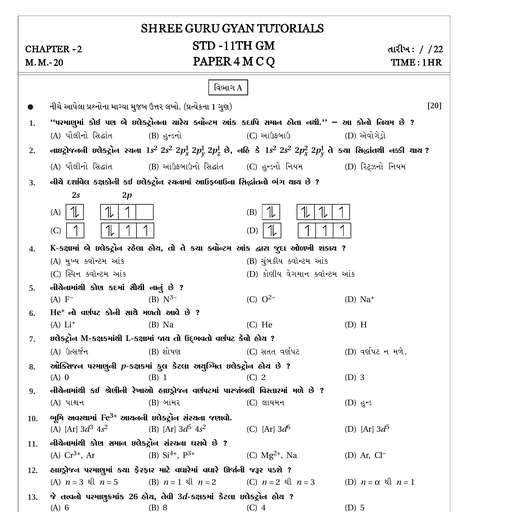
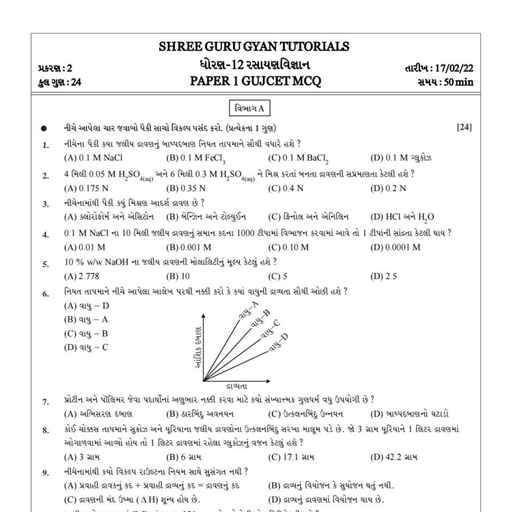
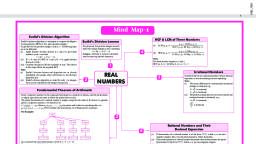
SHREE GURU GYAN PHTUTORIALS, -8980322383/9898553283, , A polynomials in one variable x is an algebraic expression of the form, p (x) = an xn + an–1 xn–1 + an–2 xn–2 + ... +a2 x2 + a1x + a0,, where a0, a1, a2 ... an are constants and these are also called coefficients of polynomial and an≠ 0., , If p(x) and g (x) are any two polynomials with g (x)¹0, then, we can find polynomials q (x) and r (x) such that, p (x) = g (x) × q (x) + r (x), i.e. Dividend = (Divisor × Quotient) + Remainder, where, r (x) = 0 or degree of r (x) < degree of g (x)., , The exponent of the highest degree term in a polynomial, is, known as degree of polynomial., , Zero Polynomial A polynomial of degree zero, is called zero, polynomial., , Linear Polynomial Zero of the linear polynomial ax + b is, b, Constant term, – — = – ———————, a, Coefficient of x, , Quadratic Polynomial Let α and β be the zeroes of the, quadratic polynomial p (x) = ax2 + bx + c, a ≠ 0, then, Sum of zeroes,, b, Coefficient of x, α + β = – — = – ———————, a, Coefficient of x 2, Product of zeroes,, c, Coefficient term, αβ = — = ———————, a, Coefficient of x 2, , Cubic Polynomial Let α, β and γ be the zeroes of the cubic, polynomial ax 3 + bx 2 + cx + d, a ≠ 0, then, b, Coefficient of x 2, α + β + γ = – — = – ———————, a, Coefficient of x 3, c, Coefficient of x, αβ + βγ + γα = — = ———————, a, Coefficient of x 3, d, Constant term, αβγ = – — = – ———————3, a, Coefficient of x, , Formation of Quadratic and Cubic Polynomial, (i) If α and β are the zeroes of a quadratic polynomial, then, quadratic polynomial will be k [x 2 – (sum of zeroes)x +, product of zeroes] i.e. k [x 2 – (α + β)x + αβ], where k is, a real number., (ii) If α, β and γ are the zeroes of a cubic polynomial, then, cubic polynomial will be, k [x 3 – (α + β + γ) x 2 + (αβ + βγ + γα) x – αβγ], where, k is a real number., , SGGTC, , SHAILESHPRAJAPATI, , or, A polynomial which contains only constant term is called, zero polynomial or constant polynomial., Linear Polynomial A polynomial of degree one is called, linear polynomial., Quadratic Polynomial A polynomial of degree two is called, quadratic polynomial., Cubic Polynomial A polynomial of degree three is called, cubic polynomial., Biquadratic Polynomial A polynomial of degree four is, called biquadratic polynomial., , Value of a Polynomial at a Given Point, If p(x) is a polynomial in x and α is a real number, then the, value obtained by putting x = α in p(x), is called the value, of p(x) at x = α., , Zero of a Polynomial, A real number k is said to be a zero of a polynomial f(x), if, f(k) = 0., , Linear Polynomial The linear polynomial ax + b, a ≠ 0 has, exactly one zero, namely, the x-coordinate of the point,, where the graph of y = ax + b intersect the X-axis., Quadratic Polynomial The zeroes of a quadratic, polynomial ax 2 + bx + c, a ≠ 0 are precisely the, x-coordinates of the point, where it intersect the X-axis., Case I If the graph intersect the X-axis at two points, then, quadratic polynomial has two zeroes., Case II If the graph intersects or touches the X-axis at, exactly one point, then quadratic polynomial has, one zero or two equal zeroes., Case III If the graph is either completely above or below the, X-axis (i.e. not intersect), then quadratic polynomial, has no zero.