Page 1 :
INDEX, Sl. No., , Unit Name, , 1, , Arithmetic Progression, , 2-12, , 12-15, , 2, , Triangles, , 3, , Pair of Linear equations in two variables, , 4, , Circles, , 16-25, , 25-29, , 5, , Constructions, , 6, , Coordinate Geometry, , 7, , Quadratic Equations, , 8, , Trigonometry, , 9, , Applications of Trigonometry, , 10, , Statistics, , 11, , Page No., , 30-32, , 33-40, , 40-47, , 47-52, , 53-58, , 59-63, , Surface area and volume, 1, , 64-73
Page 2 :
OFFICE OF D.D.P.I , KOLAR DISTRICT, KOLAR, Unit 1: Arithmetic Progression, I. Multiple choice questions., 1) The nth term of an A.P whose first term ‘a’ and common difference ‘d’ is, A) a+(n+1) d, B) a+(n−1)d, C) a−(n+1)d, D) a−(n−1)d, 2) Which of the following list of numbers is an A.P?, A) 1,3,6,8---- B) 1,4,9----, , C) 2,4,8,16---- D) 1,3,5,7---- (common difference is 2), , 3) The common difference of the A.P 2, 0, −2, −4,---A) 0, , C) −2, , B) 2, , D) −4, , (0-2=-2-0=-4+2=-2), , 4) The sum of first ‘n’ natural numbers of an A.P is, A), , 𝒏(𝒏+𝟏), , B), , 𝟐, , 𝒏(𝒏−𝟏), , C) n2, , 𝟐, , D) n(n+1), , 5) The value of ‘x’ if 7, x, 23 are in A.P is, A) 30, , B) 18, , C) 15, , D) 9, , (X=7+15/2=30/2=15), , 6) If the nth term of an A.P is an= 8−3n, then its common difference is, A) −5, , B) −3, , C) 3, , D) 5, , 7) The 13th term of an A.P whose first term and common difference respectively are, A), , 𝟔, , B), , 𝟓, , 𝟏𝟏, , C), , 𝟐, , 𝟏𝟕, , D), , 𝟐, , 𝟑, 𝟐, , 𝟐, , and 𝟑 is, , 𝟏𝟗, 𝟐, , 8) The result obtained on making half the sum of 7th and 9th term of an A.P is, A) 6th term, , B) 8th term, , C) 10th term, , D) common difference, , 9) In an A.P the first term is ‘m’ and common difference is 2m then its 5 th term is, A) 5m, , B) 8m, , C) 9m, , D) 10m, , (a5=a+4d=m+4x2m=m+8m=9m), , 10) In an A.P first term is ‘a’ and common difference is ‘d’ the correct relation in the following is, A) a6 = a4 + 4d, , B) a8 = a5 + 3d, , C) a10 = a3 + 4d, , D) a5 = a3 + d, , II. One mark questions., 1)In an A.P if S10 = 35 and S9 = 28 find a10., Ans:- a10=Sn-Sn-1=S10-S10-1=S10-S9=35-28=7, 2) Find the sum of first 25 odd natural numbers., Ans:-The number series 1, 3, 5, 7, 9,. . . . 49., The first term a = 1, , Sn = n/2 x (a + an), = 25/2 x (1 + 49), , The common difference d = 2, Total number of terms n = 25, , = (25 x 50)/ 2, = 1250/2= 625, 2
Page 3 :
3) Find the common difference of the A.P 1, −1, −3, −5 -----, , Ans:- d=a2-a1=-1-1=-2, , 4) Write the formula used to find the sum of first ‘n’ terms of the A.P whose first term ‘a’ and common, difference ‘d’., Ans:- sn=n/2{a+(n-1)d}, 5) Find the 20th term of the A.P 12, 7, 2-------, , • Hence , The 20th term of A.P. is -83., 6) In an A.P first term is ‘K’ and common difference is ‘m’. Find its (n−3)rdterms., Ans:-k+(n-4)m, 7) The interior angles of a triangle are in A.P in which the first term and common differences are equal., Find the measure of bigger angle if the smaller one is 30 o., Ans:- sum of all n interior angles of triangle = 180°, the angles are in A. P. with the smallest angle = 30°, Common difference = d=a=300 the angles are a, a + d and a+2d, The bigger angle=a+2d=30+2x30=30+60=900, 8) Find the sum of first 10 terms of an A.P in which the half of the sum of first and last term is 80., , Ans:- (a+l)/2 =80, a+l =160, S10 = n/2(a+l)=10/2(a+l) =5x160 =800, , III. Two mark questions., 1) Which term of the A.P 3,8,13,18,------- is 78 ., a = 3, d = 8 – 3 = 5, an = 78, n =?, an = a + (n – 1) d, 78 = 3+(n—1)(5) = 3 + 5n – 5 = 5n – 2, 5n = 78 + 2 ∴ n = 80/5 ∴ n = 16, , 2) How many two-digit numbers which are divided by 3., We know, first two digit number divisible by 3 is 12 and last two digit number divisible by 3 is 99. Thus, we get, 12,15,18,...,99 which is an AP, Here, a=12,d=3, Let there be n terms. Then,, 3
Page 4 :
an=99, a+(n−1)d=99, 12+(n−1)3=99, n=29+1=30, Therefore, two digit numbers divisible by 3 are 30., 3) Find the 20th term from the last term of the A.P 3,8,13 ----253., an=253, d=−5, ∴a20=253+19d=253−19(5)=253−95=158., 4) Find the sum of first 20 terms of the A.P 1,4,7 --Sn=n/2*2a+(n−1)d+, S24=24/2*2(5)+(24−1)3+=12*10+23×3+=948, 5) Find the sum of first 15 terms of the A.P having the nth term is 3+4n., nth term = 3+4 n, 1st term = 3+4(1)=7, 2nd term = 3+4(2)=11, 3rd term 3+4(3)=15, 7, 11, 15 ……………., a=7,, d=4, n=15, Sn=n/2*2a+(n−1)d+, S15=15/2[2(7)+14(4)]=15/2x2[7+28]=525, 6) Find the sum of first 15 positive integers are divisible by 6 ( using formula ), First forty positive integers which are divisible by 6 are, 6,12,18,24,.... to 40 terms, Here, a=6,d=12−6=6, and n=40., S40=n/2*2a+(n−1)d+, =40/2*2×6+(40−1)×6+=20*12+39+6+=20*12+234+=20×246=4920., 7) The angles of a triangle are in an A.P. The smallest angle is 30 o. Find all the angles of a triangle., It is given that the smallest angle is 300., Then other angle are 300+d and 300+2d., Since, in a triangle, the sum of three interior angles is 1800, therefore,, 300+300+d +300+2d=1800, ⇒900+3d=1800⇒3d=1800−1500⇒3d=300⇒d=100, Now, the other angles are:, a=300, 300+d=300+300=600, and 300+2d=300+2(300) = 300+600= 900, 8) The sum of 20 terms of an A.P is 820. If the first term is 3. Find the common difference., Sn= n/2[2a+(n-1)d], Sn=820,n=20,a=3, 820=20/2[2×3+(20-1)d], 820=10[6+19d] =6+19d =82-6=19d, 76=19d, d=4, 9) If 2x, x + 10, 3x + 2 are in an A.P. Find the value of x., 2x, x+10, 3x+2 are in A.P, => (x+10) - 2x = (3x+2) - (x+10), , [ the common difference! ], , => -x + 10 = 2x - 8, 4
Page 5 :
=> 3x = 18, => x = 6, IV. Three mark questions., 1) Find the A.P whose third term is 16 and 7th term exceeds the 5th term by 12., Now , a₃ = 16, a + 2d = 16 ------ equation 1, Also ,, , a₇ = a + 6d, , a₅ = a + 4d, , ▶ Now , it is given that 7th term exceeds the 5th term by 12 ., ➡ a₇ - a₅ = 12, ➡ a + 6d - (a + 4d) = 12, ➡ a + 6d - a - 4d = 12, ➡2d = 12 = 12/2d = 6, ☯ Substitute the values in equation 1 now ,, ➡ a + 2 × 6 = 16, ➡ a + 12 = 16 = 16 - 12 = 4, A.P. = 4, 10, 16 , 22, ..., 2) If 10 times the 10th term of an A.P is equal to 15 times the 15th term. Show that 25th term of the A.P is, zero., 10a10 = 15a15, 10[a + (10 – 1)d] = 15[a + (15 – 1)d], [an = a + (n - 1)d], 10[a + 9d] = 15[a + 14d], 2[a + 9d] = 3[a + 14d], [Dividing by 5 on both sides], 2a + 18d = 3a + 42d, 2a - 3a = 42d - 18d, - a = 42d – 18d, -a = 24d, a = - 24d …………..(1), 25th term :, an = a + (n - 1)d, a25 = a + (25 - 1)d = a + 24d = -24d + 24d [From eq 1], a25 = 0 (zero), 3) How many terms of the A.P 1,4,7 ----- should be taken so that their sum is 51., 5
Page 6 :
a=1,, d=3, Sn=51, Sn=n/2 {2a+(n-1) d}, =>51=n/2 {2.1+(n-1) 3}=n/2 {3n-1}, =>3n2 -n=102, => 3n2-n-102=0, 3n2-18n+17n-302=0, 3n(n-6)+17(n-6)=0, (n-6)=0 or(3n-17)=0, n=6 or n=-17/3, but n =-17/3 is not possible, so n=6, 4) The first term of an A.P is 5, the last term is 45 and the sum is 400. Find the number of terms and, common difference., a = 5,, , l = 45 and, , Sn = 400, , Sn = n/2 [a + l], 400 = n/2 [5 + 45] = n/2 [5 + 45], 400 = n/2 × 50, 400 = 25n, n = 400/25, n = 16,, , a16 = 45, , a + (16 - 1)d = 45, a + 15d = 45, 5 + 15d = 45, 15d = 45 - 5, 15d = 40, d = 40/15, d = 8/3, 5) The sum of three terms of an A.P is 12 and their product is 48. Find the terms, Let the three consecutive terms be a-d , a , and a+d, Sum of 3 consecutive terms = 12, ➙ (a - d) + a + (a + d ) = 12, ➙ a + a + a - d + d = 12, ➙ 3a = 12 = 12/3 = 4, Product of 3 consecutive terms = 48, ➙ (a - d) × a × (a + d) = 48, we know that (a + b)(a - b) = a² - b², then, ➙ (4² - d²) × 4 = 48, ➙ d = ±√4, , ➙ 16 - d² = 48/4, , ➙ (a² - d²) × a = 48, ➙ 16 - d² = 12, , ➙ -d² = 12 - 16 = -4, , ➙ d = ±2, , three consecutive terms when d = +2 are (a - d) = 4 -2 = 2, 6, , a=4, , (a + d) = 4 + 2 = 6
Page 7 :
three consecutive terms , when d = -2, , (a - d) = 4 -(-2) = 6, , a=4, , (a + d) = 4 - 2 = 2, , 6) In an A.P if an = 5 – 2n. Find the sum of first 30 terms., a1=5–2(1)=5-2=3, , a2=5-2(2)=5-4=1, , a3=5-2(3)=5-6= -1, , a=3, d=1-3= -2, S30=n/2[2a+(n-1)d], =30/2[2(3)+29(-2)]=15[6-58]=15x-52= -780, V. 4 mark questions., 1) The third term of an A.P is 8 and the 9th term of the A.P exceeds three times the third term by 2. Find, the sum of its first 19 terms., a3=8, a₁ + 2d = 8 -----(1), a₉ = 3 × a3 + 2, a₉ = 3 × 8 + 2, a₉ = 24 + 2, a₉ = 26, a₁ + 8d = 26 ------(2), ➟ Solving equation 1 and equation 2 by elimination method,, a₁ + 8d = 26, a₁ + 2d = 8, 6d = 18, d = 18/6= 3, a₁ + 2 × 3 = 8, a₁ + 6 = 8, a₁ = 8 - 6 =2, , S₁₉ = 19/2 ( 2 × 2 + (19 - 1) × 3), S₁₉ = 9.5 × (4 + 54) = 551, 2) Find three numbers of the A.P whose sum is 24 and sum of their squares is 200., a' be middle term and 'd' be common difference, (a-d)+a+(a+d)=24, 3a=24⇒a=8, and (a-d)²+a+(a-d)²=200, i.e,3a²+2d²=200⇒3×64+2d=200, ⇒2d²=8 ⇒d=2, 7
Page 8 :
i.e, the numbers are 6,8,10, 3) Divide 32 into four parts which are in A.P such that the product of extremes to the product of means is, 7:15. Find the four parts., Let 32 be divided into four parts such as,, (a-3d),(a-d),(a+d),(a+d) and (a+3d)., (a-3d)+(a-d)+(a+d) +(a+3d)=32, 4a = 32, Now According to the question,, , So here the extremes are (a-3d)×(a+3d)., Means are (a-d) ×(a+d)., Therefore,, , By putting the value of a =8,we get, , The four parts are 2,6,10 and 14 respectively., 4) In an A.P whose first term is 2. The sum of first five terms is one fourth of the sum of the next five, terms. Show that a20 = – 112., a=2, [a1 + a2 + a3 + a4 + a5] = 1/4 [ a6 + a7 + a8 + a9 + a10], {(a) + (a + d) + (a + 2d) + (a + 3d) + (a + 4d)} = 1/4 {(a+5d) + (a+6d) + (a+7d) + (a+8d) + (a+9d)}, 5a + 10d = 1/4 ( 5a + 35d), 20a + 40d = 5a + 35d, 15a = -5d, 15 ( 2 ) = -5d., d = 30 / -5= -6, a20=a + 19d = 2 + 19 ( -6 ) = 2 - 114 = -112, 5) In an A.P, the sum of first term, third term and fifth term is 39 and the sum of second, fourth and sixth, terms is 51. Find the 10th term of the A.P., a1 + a3+ a5= 39-------------- (1), a2+ a4 + a6 = 51------------ (2), In equation (1), 8
Page 10 :
a = 8/2 = 4, a = 4, d = 3, 2) The sum of three terms of an A.P is 21 and the product of the first and third term exceeds the second, term by 6. Find the sum of 20 terms of the A.P., Sum of three terms of an A.P. is 21, Let the three terms in AP are (a - d), a, (a + d), (a – d) + a + (a + d) = 21, 3a = 21, a = 21/3, a = 7 ………..(1), (a – d) (a + d) = a + 6, a² – d² = a + 6, 7² – d² = 7 + 6, [From eq.1, a = 7], 49 – d² = 13, d² = 36, d = √36, d = ±6, If d = 6 , then, First term ( a – d) = 7 – 6 = 1 Third term (a + d) = 7 + 6 = 13, , Second term a = 7, , If d = - 6 , then, First term, ( a – d) = 7 – (-6) = 7 + 7 = 13 Third term (a + d) = 7 + (-6) = 7 - 6 = 1 Second term a = 7, 3) In an A.P the sum of first 9 terms is 14 more than 5 times the 8 th term, 8th and 2nd terms are in the ratio, 11:2. Find the sum of first 20 terms of the A.P., , Now, we know that,, 10
Page 11 :
Now, from the given condition,, , Now, we know that,, Now,, , Now, by substituting d = 3a in equation ( 2 ), we get,, , Now, we know that,, , 11
Page 12 :
∴ The sum of the first 20 terms of the AP is 1180., , OFFICE OF D.D.P.I , KOLAR DISTRICT, KOLAR, Unit 2: Triangles, I. Multiple choice questions., 1) Sides of two similar triangles are in the ratio 4:9 then areas of these triangles, are in the ratio., A) 2 : 3, B) 4 : 9, C) 81 : 16, D) 16 : 81, 2) At a certain time of the day, a man 6 feet tall casts his shadow 8 feet long,, then the length of the shadow cast by a building 45 feet high at the same, time which is next to the man is, A) 60 feet, B) 45 feet, C) 48 feet, D) 90 feet, 3) In the adjoining figure ∆ ABN ~ ∆ AMC. The ratio of sides AM and AN is, 2:5 then CM : BN is, A) 5 : 2, B) 2 : 5, C) 1 : 2, D) 2 : 3, 4) The measures representing the sides of a right angled triangle are, A) 2,3,5, B) 6,8,10, C) 8,4,6, D) 6,8,9, , 10 cm, , II. One mark questions., 1) Write the statement of Basic proportionality theorem., Ans:- If a line is drawn parallel to one side of a triangle to intersect the other two sides in distinct points,, the other two sides are divided in the same ratio., 2) Write the statement of converse of Basic proportionality theorem., Ans:- If a line divides any two sides of a triangle in the same ratio, then the line is parallel to the third side., 3) Write the statement of Pythagoras theorem., Ans:- In a right angled triangle the square on the hypotenuse is equal to the squares of the other two, sides., 4) In a right angles triangle ABC, ∠B = 90o, AC = 17 cm and AB = 8 cm find the length of BC., Ans:- In, ABC ∠B=900, A, AB2+BC2=AC2, 82+BC2=172, 17, 16+BC2=289, cm, BC2=289-64, C, B, =225, ?, , 12
Page 16 :
2) State and prove “Pythagoras theorem”., , OFFICE OF D.D.P.I , KOLAR DISTRICT, KOLAR, Unit-3:- Pair of linear equations in two variables, I. Multiple choice questions., 𝒂𝟏 𝒃𝟏, 1. If two equations have exactly one solution and are in the form 𝒂𝟐 ≠ 𝒃𝟐 then they are, a. Coincident lines, , b. Intersecting lines, , c. Transversal lines d. Parallel lines, , 2. If two equations have no solutions and are in the form, a. Coincident lines, , b. Intersecting lines, , 𝒂𝟏, , 𝒃𝟏, , 𝒄𝟏, , = 𝒃𝟐 ≠ 𝒄𝟐 then they are, 𝒂𝟐, , c. Parallel lines, , d. All of the above, , 3. In the general form of pair of linear equations a1x+b1y+c1=0 and a2x+b2y+c2=0 where a1, a2, b1, b2, and c1, c2 are, a. Whole numbers, , b. Real numbers, , c. Integers, , d. Co-primes, , c. Intersect, , d. None of the above, , 4. x+2y-4=0 and 2x+4y-12=0 then the lines are, a. Coincide, , b. Parallel, , 5. If the lines 3x+2ky-2=0and 2x+5y+1=0 are parallel then the value of k is, 𝟒, , a.𝟏𝟓, , b., , 𝟏𝟓, , c., , 𝟒, , 𝟒, 𝟓, , d., , 𝟓, 𝟒, , 6. The solution of the equations x-y=2 and x+y=4 are, a. 3,1, , b. 4,3, , c. 5,1, , d. -1, -3, , II. One mark questions., 1. The coach of a cricket team buys 3 bats and 6 balls for Rs 3900. Later, she buys another bat and 2, more balls of the same kind for Rs 1300. Represent this situation algebraically., Ans:- 3x+6y=3900, x+2y=1300, 2. Check whether the pair of equations x + 3y = 6 and 2x – 3y = 12 is consistent., The given pair can be written as, x+3y−6=0 and 2x−3y−12, Herea1=1,b1=3,c1=−6...........eq1, , and, , a2=2,b2=−3,c2=−12.........eq2, , 16
Page 19 :
x, y, , 0, , 1, , 3, , x, , 0, , 1, , 2, , 6, , 4, , 0, , y, , 2, , 4, , 6, , 6. x-y=1, , and, , x–y=1, , 2x+y=8, 2x + y = 8, y = 8 – 2x, , y = x -1, x, , 0, , 1, , 2, , x, , 3, , 4, , 2, , y, , -1, , 0, , 1, , y, , 2, , 0, , 4, , 7. 2x-y-2=0, , and, , 2x – y – 2 = 0, Y = 2x – 2, , 4x-3y-24=0, 4x – 3y – 24 = 0, 3y = 4x – 24, y=, , 𝟒𝒙−𝟐𝟒, 𝟑, , x, , 0, , 1, , x, , 0, , 6, , y, , -2, , 0, , y, , -8, , 0, , 8. x+y=3, , and, , x+y=3, , 2x+5y=12, 2x+5y=12, , y=3–x, , y=, , 𝟏𝟐−𝟐𝒙, 𝟓, , x, , 0, , 1, , 3, , x, , 1, , -4, , 6, , y, , 3, , 2, , 0, , y, , 2, , 4, , 0, , 19
Page 20 :
9. x+y=6, , and, , x-y=6, , x+y=6, , x–y=6, , y=6–x, , y=x–6, , x, y, , 0, , 6, , 3, , x, , 0, , 6, , 3, , 6, , 0, , 3, , y, , -6, , 0, , -3, , V. For the pair of linear equations find their solution by elimination method., 1. 3x-5y=-1, , and, , x-y=-1, , 3x-y=-1, 3x-3y=-3, 3x-5y=-1, 3x-3y=-3, -. + +, ___________, -2y=2, y=-1, substituting y=-1 in eq 1, 3x-5(-1)=-1, 3x+5=-1, 3x=-6, 20
Page 21 :
x=-2, 2. x+2y=-1, , and, , 2x-3y=12, , Multiply eq-(1) by 2*, We get,, →2x+4y+2=0-(3), Now,, Add Eq-(3)&(2)*, we get, y=2-(4), •Using eq-(4) in eq-(1) or eq(2)•, *I prefer using in eq-(1)*, →x+2(2)=-1, →x=-1-4, →x=-5, x=-5ʻand, y=2, 3. 2x+3y=9 and, 2x+3y=9, , 3x+4y=5, , 3x+4y=5, Eliminate y, multiply (1)by -4, Multiply (2) by 3, -8 x -12 y = -36, 9 x +12 y = 15, Add the two equations, 1 x = -21, x = -21, put value of x in (1), 2x+3y=9, -42 + 3 y = 9, 3 y = 9 + 42, 3 y = 51, y = 17, 4. x-y+1=0, , and, , 3x+2y-12=0, , Solve these equations:-), , 21
Page 22 :
Multiply equation (1) by 3., , Now, Substract in equation (2) and (3)., 3x + 2y = 12., 3x - 3y = -3., (-)...(+)......(+)., __________, => 5y = 15., ↪➡ Put the value of ‘ y’ in equation (1)., => x - 3 = -1., => x = -1 + 3., , 5. x-y=1, x-y=1, , and, 2x+y=8, .....(1), , 2x + y = 8, , .....(2), , Adding (1) and (2),, x - y + 2x + y = 1 + 8, → 3x = 9, →x=9‚3=3, , .....(3), , From (3) in (1),, 3-y=1, →y=3-1=2, 6. x+y =6, and, x+y=6 ----------(1), , x-y=6, , x-y=6 -----------(2), add both equation, x + y=6, x -y=6, _______, 2x=12, x= 12/2, x=6, putting the value of x in question 1st, x+y=6, 6+y=6, y=6-6, 22
Page 23 :
y=0, Ans- X=6, y=0, 7. x-y=1, x-y=1, , and, 2x+y=8, .....(1), , 2x + y = 8, , .....(2), , Adding (1) and (2),, x - y + 2x + y = 1 + 8, → 3x = 9, →x=9‚3=3, , .....(3), , From (3) in (1),, 3-y=1, →y=3-1=2, , VI. Solve the following by constructing linear equation., 1. The sum of a two-digit number and the number obtained by reversing the digits is 66. If, the digits of the number differ by 2, find the number. How many such numbers are there?, Let the two numbers be 10x+y and 10y+x where x and y are positive integers., Adding the two numbers we get, 11x+11y=66., x+y=6.....1, Also, difference of the two digits it 2 so,, x-y=2.....2, Adding eq. 1 and 2,, 2x=8, x=4, Substituting x,, 4-y=2, y=2, So the number can be 10x+y or 10y+x., So the required numbers are 24 and 42., So there are two such numbers., 2. Ritu can row downstream 20 km in 2 hours, and upstream 4 km in 2 hours. Find herspeed of rowing, in still water and the speed of the current., Ans. Let the speed of Ritu in still water and the speed of stream be x km/h and y km/h respectively., Speed of Ritu while rowing Upstream = (x – y) km/h, Downstream = (x + y) km/h, 2(x + y) = 20, ⇒ x + y = 10 ... (i), 23
Page 24 :
2(x – y) = 4, ⇒ x – y = 2 ... (ii), Adding equation (i) and (ii), we get x=6, Putting this equation in (i), we get, y=4, Hence, Ritu’s speed in still water is 6 km/h and the speed of the current is 4 km/h., 3. 2 women and 5 men can together finish an embroidery work in 4 days, while 3women and 6 men can, finish it in 3 days. Find the time taken by 1 woman alone and also time taken by 1man alone., Ans. Let the number of days taken by a woman and a man be x and y respectively., Therefore, work done by a woman in 1 day = 1/x, According to the question,, 4(2/x + 5/y) = 1, 2/x + 5/y = 1/4, 3(3/x + 6/y) = 1, 3/x + 6/y = 1/3, Putting 1/x = p and 1/y = q in these equations, we get, 2p + 5q = 1/4, By cross multiplication, we get, p/–20 – (–18) = q/–9 – (–18) = 1/144 – 180, p/–2 = q/–1 = 1/–36, p/–2 = – 1/36 and q/–1 = 1/–36, p = 1/18 and q = 1/36, p = 1/x = 1/18 and q = 1/y = 1/36, x = 18 and y = 36, Hence, number of days taken by a woman = 18 and number of days taken by a man = 36, 4. The coach of a cricket team buys 3 bats and 6 balls for Rs 3900. Later, he buys another bat and 2, more balls of the same kind for Rs 1300. Find the cost of each ball and bat separately., let the cost of bat be x, and the cost of ball be y., acc. to the Question:, 3x+6y= 3900----------------(1), x +3y = 1300-----------------(2). {×2], => 2x+ 6y = 2600, now by elimination method we get ,, 3x+6y= 3900, - 2x + 6y = 2600, _______________, x =1300, from (2) we get,, 1300 +3y= 1300, 3y= 1300-1300, y= 0, therefore , the value of x& y is 1300 and 0 respectively., 5. The larger of two supplementary angles exceeds the smaller by 18 degrees. Find them., Ans. Let the first angle be= x, 24
Page 25 :
And the second angle be = y, As both angles are supplementary so that sum will 180, x + y = 180, x = 180 – y ... (i), Given; difference is 18 degree, Therefore, x – y = 18, Putting the value of x we get, 180 – y – y = 18, – 2y = – 162, y = – 162/–2, y = 81, Putting the value back in equation (i), we get, x = 180 – 81 = 99 Hence, the angles are 99° and 81°., 6. Five years ago, hari was thrice as old as ramu. Ten years later hari, will be twice as old as ramu. How old ar ehari and ramu., Let the present age of hari be = x, Let the present age of ramu be = y, According to the given information,, (x – 5) = 3(y – 5), x – 3y = – 10 ... (i), (x + 10y) = 2(y + 10), x – 2y = 10 ... (ii), Subtracting equation (i) from equation (ii), we get, y = 20 ... (iii), Putting this value in equation (i), we get, x – 60 = – 10, x = 50, Hence, age of hari = 50 years and age of ramu = 20 years., , OFFICE OF D.D.P.I , KOLAR DISTRICT, KOLAR, UNIT -4:- CIRCLES, I. Multiple choice questions., 1. Maximum number of tangents drawn to a circle from an external point is, A. 2, B. 3, C. 4, D. 5, 2. A straight which intersects a circle at two distinct points is, A. Tangent, B. Chord, C. Secant, D. Diameter, 3. The angle between a tangent to a circle and the radius through the point of contact is, A. 60°, B. 90° C. 120°, D. 180°, 4. Number of tangents can be drawn at any point on a circle is, A. 1, B. 2, C. 3, D. Many, 5. The lengths of tangents drawn from an external point to the circle are, A. Equal, B. Not equal C. sometimes are equal D. none, 6. Tangents drawn at extremities of the diameter of a circle are, A. Perpendicular, B. parallel, C. Equal, D. Not equal, 7. A line through point of contact and passing through the centre of circle is known as, A. Tangent, B. Secant, C. Chord, D. Segment, 25
Page 26 :
8. If the angle between the two tangents to a circle is 400 , then the angle between the radii is, A. 900, B. 1000, C. 1400, D. 1800, 9. Distance between two parallel tangents of a circle of radius 3.5cm is, A. 3.5cm, B. 7cm, C. 10cm, D. 14cm., II. VSAQ (one mark questions)., 1. How many tangents can a circle have?, , Ans:-Infinetely many, , 2.What is called the intersecting point of a circle and a tangent?, , Ans:-Point of Contact, , 3. How many parallel tangents at most a circle can have?, , Ans:-2, , 4. What is angle between a tangent of a circle and its radius?, , Ans:-90°, , 5. What is the name of line intersecting a circle in two points?, , Ans:-Secant, , 6. What is the name of two circles having a common centre?, , Ans:-Concentric Circles, , 7.How many lines passes through a point on the circle ?, , Ans:-One, , 8 . How many tangents can be drawn at the ends of diameter of a circle?, , Ans:-Two, , III. 2 marks questions., 1. PA is a tangent to the circle with center O. If BC = 3 cm, AC = 4 cm, and ΔACB~ΔPAO then find OA, 𝑂𝑃, and 𝐴𝑃, , IN ∆𝑨𝑩𝑪, ∠ACB = 90° (Angle in semi circle ), 𝑨𝑩𝟐 = 𝑨𝑪𝟐 + 𝑩𝑪𝟐 ( Pythagoras theorem ), 𝑨𝑩𝟐 = 𝟒𝟐 + 𝟑𝟐, AB = 𝟏𝟔 + 𝟗 = 𝟐𝟓 = 5cm, ∴OA =, , 𝑨𝑩, 𝟐, , 𝟓, , 𝒅, , = 𝟐 = 2.5cm (r=𝟐), , 𝜟ACB ~𝜟PAO ( Given), 𝑶𝑷, , =, , 𝑨𝑩, , 𝑨𝑷 𝑨𝑪, 𝑶𝑷 𝟓, 𝑨𝑷, , =𝟒, , 2. The length of common chord of two intersecting circles is 30 cm. If the diameters of these two, circles are 50 cm and 34 cm, then calculate the distance between their centers., Data: ∠SQR= 38° PQ and PR are tangents, In Quadrilateral PQOR,∠Q=∠R =90°, (Radius ⊥ Tangent at touching point ), ∠O =90° ( Data ), ∠O + ∠R + ∠Q + ∠P = 360°, 90° + 90° + 90° + ∠QPR =360°, ∠QPR = 360° - 270° = 90°, In ∆PQR, PQ = PR ( tangents drawn from an external point ), 26
Page 27 :
∴∠PQR = ∠PRQ = x opposite angles of equal sides, ∴ x + x ∠QPR = 180° ( Sum of ∠’s of ∆ ), 2x + 90° = 180°, 𝟗𝟎°, x = 𝟐 = 45°, ∴∠PQR = 45°&∠PRQ = 45°, 3 . PQ and PRare tangents at Q and R, respectively. If ∠SQR = 38°, then find ∠QPR, ∠PRQ,, ∠QSR and ∠PQR, , In ∆QSR, ∠QRS = 90° ( Angle in semi circle ), ∠SQR + ∠QRS+ ∠QSR = 180°, 38° + 90° + ∠QSR = 180°, ∠QSR = 180° - 128° = 52°, 4. In the adjoining figure, an isosceles ΔABC with AB = AC, circumscribes a circle. Prove, that point of contact P bisects the base BC., , AB = AC ------ (1) (Data), AR = AQ ------ (2) (tangents drawn from an external point), (1) – (2) →AB – AR = AC – AQ, BR = QC ------ (3), BR = BP & QC = PC (Axiom 1), 5.Prove that in two concentric circles, the chord of the larger circle, which touches the, smaller circle, is bisected at the point of contact., , Data :𝑪𝟏 &𝑪𝟐 are concentric circles with centre ‘O’,AB is the Chord of 𝑪𝟐 touches 𝑪𝟏 ., To Prove : - AP = PB, Proof :- OP ⊥ AB ( Radius ⊥ Tangent at touching point ), ∴AP = PB ( line drawn from center of a circle ⊥ ly bisects Chord ), 6 . In two concentric circles, a chord of the larger circle touches the smaller circle. If the length, of this chord is 8 cm and the diameter of the smaller circle is 6 cm, then find the diameter of the larger, , circle., Data :𝑪𝟏 &𝑪𝟐 are concentric circles, OP ⊥ AB-----------------1, (Radius ⊥ Tangent at touching point), AP = PB = 4cm, (⊥from center of a circle to its Chord bisects it)., ∴ In ΔOPB , ∠P = 90° ( from 1 ), 27
Page 29 :
In Quadrilateral ORDS,∠R = ∠S = 90° ( radius ⊥ tangent at a point of contact, ∠D = 90° Data, ∠O = 90° sum of ainterior angles in Quadrilateral is 360° ), OR = OS (radii of same circle), ∴ ORDS is a square., ∴ OS = OR = DR, OS = OR = 15cm (from (1)), ∴Radius of given circle is 15cm., 4. A circle touches the side BC of a ΔABC at P and AB and AC when produced at Q and R respectively, as shown in the figure. Show that AQ = ½ (Perimeter of ΔABC), , AQ = AR ---------(1) ( tangents drawn from an external point ), Similarly BQ = BP, PC =CR ---------(2), Perimeter of ΔABC = AB + BC + AC = AB + BQ + CR+ AC (from(2)), = AQ + AR = AQ + AQ (from(1)), = 2AQ, 𝟏, (perimeter of ΔABC) = AQ, 𝟐, 5.A circle touches all the four sides of a quadrilateral ABCD. Prove that AB+CD = BC+DA, , AP = AS, BP = BQ, SD = DR, CQ = CR-------------------- 1, ( tangents drawn from an external point are equal ), L.H.S, AB + CD = AP + PB + DR + RC, = AS + BQ + SD + CQ (from (1)), = AS + SD + BQ + CQ, AB + CD = AD + BC = R.H.S, 6. Prove that the angle between two tangents drawn from an external point to a circle is, supplementary to the angle subtended by the line segment joining the points of contact at the, center., , Data :- AP and BP are tangents to a circle with center ‘O’, To prove that :- ∠AOB + ∠APB = 180°, Proof :- In Quadrilateral OAPB ∠A = ∠B = 90°, ∠A + ∠B + ∠O + ∠P = 360° sum of angles in a Quadrilateral, 29, , .
Page 30 :
90° + 90° +∠O + ∠P = 360°, ∠O + ∠P = 360° - 180° = 180, ∠AOB + ∠APB = 360°, , OFFICE OF D.D.P.I , KOLAR DISTRICT, KOLAR, , UNIT -5:- Constructions, I. Two marks questions., 1. Draw a line segment of length 8.6 cm and divide it in the ratio 4:7 and measure the parts., , 2. Draw a circle of radius 3 cm and construct a tangent at a point ‘P’ on the circle., , 3. Draw a circle of radius 3 cm, construct a tangent which is 7 cm away from the centre of the circle., Measure the length of the tangent and verify., , 30
Page 31 :
4. Draw a circle of radius 3.5 cm, construct two tangents from an external point which is 5.5 cm away from, the circle., , 5. Draw a circle of radius 4 cm and draw two radii which inclines an angle of 600. Construct tangents at the, ends of radii to the circle., , 6. Draw a circle of radius 3 cm and a chord 5 cm, construct a tangent at one end of the chord., , 31
Page 32 :
II. Three marks questions., 1. Construct a triangle of sides 4 cm, 6 cm and 7 cm and then construct a triangle similar to it whose, sides are ⅔ of the corresponding sides of the first triangle., , 3.Draw a triangle ABC given BC=7cm, ∟B=450, ∟A=1050 then construct a triangle whose sides, are, , 𝟒, , 𝟑times, , the corresponding sides of the triangle ABC., , 4. Draw a right angled triangle in which the sides other than the hypotenuse are of lengths 4 cm, and 3 cm. Then construct another triangle whose sides are 𝟑 𝟓times the corresponding sides, 32
Page 33 :
of the given triangle., , OFFICE OF D.D.P.I , KOLAR DISTRICT, KOLAR, UNIT -6:- Co-ordinate Geometry, I. Choose the correct answer for the fallowing questions., 1. The Coordinates of the origin is, A) (1,1), , B) (0,0), , C) (0,1), , D) (1,0), , 2. Area of the triangle formed by three collinear points is, A) 0 sq.units, , B)1 sq.units, , C)2 sq.units, , D)4 sq.units, , 3. The perpendicular distance of point P (3,-5) from x axis is, A) 4 units, , B) 1 Unit, , C) 3 units, , D) 5 units, , 4. If the distance between origin and the point p (x, y) is, A) x + y, , B) x + y, , C) 𝒙𝟐 − 𝒚𝟐 D) 𝒙𝟐 + 𝒚𝟐, , 5. The coordinates of the point P in the given graph is, , A) (1,3), , B) (-3,-1), , C) (0,-3), , 6. The coordinates of a point P on the x-axis is, A) (x,0), , B) (0,y), , C) (0,0), , D) (0,-y), , II. one - mark questions., , 33, , D) (-3,0)
Page 41 :
𝑨), , 𝒃, 𝟐𝒂, , =, , 𝟐𝒄, , 𝒃, , B) b2 + 4ac = 0, , 𝒃, , 𝒃, , C) 𝟐𝒂 =, , D) a = b, , 𝟐𝒄, , 2., , If one root of px2 + qx + r =0 is reciprocal of the other root then,, , A), , p=q, , 3., , The sum of the roots of 3x2 + 6x + 3 = 0 is, , A), , 2, , 4., , If one root of 2x2 + kx + 4 = 0 is -2, then the value of k is, , A), , 12, , 5., , The nature of the roots of 2x2 – 4x - 3 = 0 is, , A), , Real & distinct, , 6., , The roots of quadratic equation 3x2 – 6x = 0 are, , A), , (0,2), , 7., , The sum of the squares of two consecutive natural numbers is 20. Representing this statement in, , B) q = r, , C) p = r, , B) -3, , D) p = q = r, , C) 1, , B) -6, , B) real & equal, , B) (3,6), , D) -2, , C) 6, , D) -12, , C) no real roots, , D) imaginary roots, , C) (0,-2), , D) (0,6), , the form of quadratic equation is,, A), , X2 + (x + 1)2=20, , B) x2 – (x – 1)2 = 20, , C) (x + 1)2 – x2 =20, , D) x2+(x+1)2+20=0, , II. One mark questions., 8.Write the standard form of quadratic equation., , Ans:-ax2 + bx + c =0, −𝒃 ± (𝐛 𝟐 − 𝟒𝒂𝒄, , 9.Write the formula to find the roots of ax2 + bx + c =0., , Ans:-x =, , 10. The quadratic equation whose roots are x = 2 & x = -3., , Ans:-x2+x-6=0, , 11.If the roots of 6x2 – 24x + c = 0 are equal, then find the value of c., , Ans:- 24, , 12.Determine whether -3 is a root of the equation 3x2 + 5x – 8 = 0., , III. Two mark questions., 13. Check whether, y(y+7) + 9 = (y+7)(y-7) form a quadratic equation., , 14.If the roots of 9x2 - 3kx + 4 = 0 are equal, then find the value of k, 9 x² - 3 k x + k = 0, a=9, , b=-3 k, , c=k., 41, , Ans:- No, , 𝟐𝐚
Page 42 :
b² = 4 a c, ( - 3 k )² = 4 ( 9 ) ( k ), ⇒ 9 k² = 36 k, ⇒ k² = 36 k / 9, ⇒ k² = 4 k, ⇒k=4, The value of k is 4 ., 15.Find the roots of 3x2 +11x + 8=0 by factorization method., 3x2+11x+8=0, 3x2+8x+3x+8=0, 3x(x+8)+3(x+8)=0, (3x+3) (x+8)=0, 16.Check the nature of the roots of 2x2 + 5x + 5 = 0., ⇒ 2x² + 5x + 5., ⇒∆ = discriminant Or b² - 4ac., ⇒= (5)² - 4(2)(5) = 25 - 40 = -15., ⇒∆< 0 Roots are imaginary., 17.A chess board contains 64 equal squares & the area of each square is 6.25 cm 2. A border around the, board is 2cm wide. Find the length of each side of the chess board., we know that a chess board contains 64 equal squares., given the area of one square = 6.25cm², total area of 64 equal squares = 64 × 6.25 = 400cm², therefore side × side = 400cm², ==> side² = 400cm², ==> side = √400, ==> side = 20cm, the side of the board is 20cm., ATQ, the width of the border around the board is 2cm., hence, the length of the side of the chess board Along with the border is = 20 + 2 + 2 (as border is all around so the, length will increase from both sides), = 24cm, , 18. Find the quadratic equations whose roots are 2 𝟑 and - 2, Let the quadratic equation be, ax²+bx+c=0, a≠0 and, , 42
Page 43 :
Therefore,, The quadratic equation is ax²+bx+c =0 is, , 19.The area of a triangular plot is 156cm2. The base of the plot is 2cm more than twice its height. Form a, quadratic equation., Let the breadth of the plot be x metres, It is given that the length of the plot is one more than twice its breadth, Length=(2x+1) metres, Now. Area of the plot =528m2, Length× Breadth=528m2, ⇒(2x+1)×x=528, ⇒2x2+x−528=0, This is the required quadratic equation, 20.Solve by using formula:, a) 3x2 – 7x – 6 = 0, , 43
Page 44 :
IV. Three mark questions., 21. If one root of the equation x2 + px + 12= 0 is 4, while the equation x2 + px + q has equal roots. Find the, value of q., , Substitute x = 4 in the equation, we get, Divide each term by 4, we get, , Now,, , Given roots are equal, , 22.The perimeter of a right triangle is 60 cm. Its hypotenuse is 25 cm. Find the area of the triangle., , , Perimeter = 60cm, , , , hypotenuse = 25cm, Let ABC be the Given right angled triangle, Let , Base = Xcm, hypotenuse = 25cm, Perimeter = 60cm, AB+BC+AC = 60, ➺ AB +x+25=60, ➺ AB =35-x, By Pythagoras theorem, h²= p²+b², ➺ 25²= (35-x)²+x², 44
Page 45 :
➺ 2x²-70x+600=0, ➺ x²-35x+300=0, ➺ x²-20x-15x+300=0, ➺ x(x-20)-15(x-20)=0, ➺ (x-20)(x-15)=0, x=20 or x=15, If x= 20 Then,, AB = 35-x = 35-20 = 15, BC = x = 20, Area = 1/2XbXh, =1/2 × 20×15= 1/2 × 300, = 150cm², 23.Sum of the areas of two squares is 468 m2. I f the difference of their perimeter Is 24 m, find the sides, of two squares., Let the sides of the two squares are x m and y m., so, their perimeter will be 4x and 4yrespectively and their areas will be x² and y²respectively., [as you know perimeter of square = 4 × side length and area of square = (side length)²], It is given that 4x − 4y = 24 [Difference of perimeter], or x − y = 6, x = y + 6.........(1), Also, x² + y² = 468 [sum of squares is 468], => (6+y)² +y² = 468 [ put eq (1) ], => 36 + y²+12y + y² = 468, => 2y² + 12y – 432 = 0, => y² + 6y – 216 = 0, => y² +18y – 12y – 216 = 0, => y(y + 18)(y – 12) = 0, => y = - 18 or 12., However, side of a square cannot be negative., Hence, the sides of the squares are 12 m and (12 + 6) m = 18 m, 25.The sum of the squares of two consecutive natural numbers is 365. Find the numbers., Let the first number = x, Then the second number = x+1, According to the question ,, (x)²+(x+1)²= 365, x²+x²+1+2x = 365, 2x²+2x+1 = 365, 2x²+2x = 364, 45
Page 46 :
2x²+2x-364 = 0, 2x²-26x +28 x - 364 = 0, 2x(x-13)+ 28(x-13), (x-13)(2x+28) = 0, x-13 => x = 13, 2x+28 => x = -28/2, But the value of x can't be negative so x = 13, x+1 = 13+1 = 14, The required numbers are = 13 and 14, 24.The perimeter of rectangular field is 28 cm and its area is 48 cm 2. Find its length and breadth., P=28cm, A=42 cm2, , Area= lxb, , b=6 0r b=8, , Perimeter= 2(l+b), , 48= (14-b)b ( from 1), , substitute b=6 in eq. 1, , 28= 2(l+b), , 48=14b-b2, , l= 14-6=8, , l+b=14, , b2-14b+48=0, , l=8 and b=6, , l=14-b --------------1, , b2-8b-6b+48=0, b(b-8)-6(b-8)=0, , 25.The sum of the ages of a father and his son is 45 years. Five years ago the product of their, age was 124. Determine their present ages., Let father's age be x years. Then, ➼ Present age of son = (45 – x), [ 5 years ago their ages were ], Father's age = (x – 5) years, Son's age = (45 – x – 5) = (40 – x) years, Product of ages is 124., (x – 5) (40 – x) = 124, x(40 – x) –5(40 – x) = 124, 40x – x² – 200 + 5x = 124, 45x – x² = 124 + 200, 45x – x² = 324, x² – 45x + 324=0, Now, break this by middle term splitting method., x² – 45x + 324=0, x² – 36x – 9x + 324=0, x (x – 36) –9 (x – 36)=0, (x – 9) (x – 36)=0, ➱ (x – 9) = 0 or, (x – 36) = 0, x = 9 or x = 36, Father's age cannot be 9 years so we will take x = 36 years., So,➬ Father's age = x = 36 years➬ Son's age = 45 – x = 45 – 36 = 9 years., 46
Page 53 :
tan θ=tan450∴θ=450, 2. A tower stands vertically on the ground from a point on the ground which is 15 m away from the foot of, the tower, the angle of elevation of the top of the tower is found to be 60 0. Find the height of the tower., Ans:- θ= angle of elevation=600, tan θ=, , AB= height of the tower=?, A, , 𝐀𝐁, , 𝑩𝑪, , tan600=, , 𝐀𝐁, , 𝟏𝟓, , 𝟑 =, , 𝐀𝐁, , 𝟏𝟓, , B, , C, , ∴AB=50 𝟑m, , 3. An observer 1.5 m tall is 28.5 m away from a chimney. The angle of elevation of the top of the chimney, from her eyes is 450. What is the height of the chimney?, Ans:- AB=1.5 m= CY, , BY= 28.5 m, , X, , 0, , θ= angle of elevation=45, In triangle ACY, tan θ=, , 𝐗𝐂, , 𝑨𝑪, , 0, , tan45 =, , A, , 𝐗𝐂, , 28.5 m, , 1.5, , 𝟐𝟖.𝟓, , 𝐗𝐂, , 1= 𝟐𝟖.𝟓, , Y, , B, , XC= 28.5 m, , C, , Height of chimney XY = XC + CY= 28.5+1.5=30 m, , 4. The angle of elevation of the top of a tower from a point on the ground, which is 30 m away from the, A, foot of the tower is 300. Find the height of the tower., Ans:- θ= angle of elevation=300, AB= height of the tower=?, tan θ=, , 𝐀𝐁, , C, , 𝑩𝑪, , tan300=, , B, , 𝐀𝐁, , 𝟑𝟎, , 𝟏, , =, , 𝐀𝐁, , 𝟑 𝟑𝟎, , 30= 𝟑AB, AB=, , 𝟑𝟎, , 𝟑, , =, , 𝟑𝐱𝟏𝟎, , 𝟑, , =, , 𝟑𝐱 𝟑𝐱𝟏𝟎, , 𝟑, , = 10 𝟑 m, , 5. A tower stands vertically on the ground from a point on the ground which is 50 m away from the foot of, the tower, the angle of elevation of the top of the tower 600. Find the height of the tower., θ= angle of elevation=600, 53
Page 59 :
5. A 1.2 m tall girl spots a balloon moving with the wind in a horizontal line at a height of 88.2.m from the, ground. The angle of elevation of the balloon from the eyes of the girl at that instant is 60 0. After some, time the angle of elevation reduces to 300. Find the distance travelled by the balloon during the interval., Ans:- In triangle ABE, , tan θ=, , 𝐀𝐁, , In triangle BEF, tan θ=, , 𝑩𝑬, , 𝟖𝟖.𝟐, , tan600=, 𝟑 =, BE=, , tan300=, , 𝑩𝑬, , 𝟖𝟖.𝟐, , 𝟏, , 𝑩𝑬, , 𝟑, , BF=, , 𝟑, 𝟐𝟗.𝟒𝐱𝟑, 𝟑, , A, , 𝑩𝑬, , 𝐁𝐅, , F, , 𝟐𝟗.𝟒 𝟑, , 𝟖𝟖.𝟐, , =, , 𝐁𝐅, , = 29.4 𝟑, , 𝟐𝟗.𝟒 𝟑, 𝟑, , =, , D, , 𝐁𝐅, , 𝟐𝟗.𝟒 𝟑, , = 𝟐𝟗. 𝟒 𝟑m, , X, , distance travelled by the balloon= 88.2 -29.4=58.8 m, , OFFICE OF D.D.P.I , KOLAR DISTRICT, KOLAR, Unit -10:-Statistics, I. Multiple choice questions :1. The mean value of scores 3,4,8,6,9,12 is, a. 7, , b. 8, , c. 9, , d. 42, , 2. If the mean of 10,15,19,20 and m+1 is 20, then ‘m’ is, a. 30, , b. 35, , c. 65, , d.100, , 3. The median of scores 81,95,106,38,95,104 and 28 is, a. 106, , b.81, , c. 104, , d. 95, , c. 12, , d. 10, , 4. The midpoint of interval (10-20) is, a.15, , b. 14, , 5. The practical relation between mean, median and mode is written as, a. median= mode – mean, , b. mode=mean + 2 median, , c. 3 median=mode+2 mean, , d. 2 mean= 3 mode – median, , II. One mark questions:1. Write the formula to find the mean of classified data in direct method., Ans:- Mean =, , 𝚺𝒇𝒙, 𝑵, , OR Mean =, , 𝚺𝒇𝒊𝒙𝒊, 𝒇𝒊, , 2. Write the formula to find the mode of a classified data., 59, , B, , Y
Page 60 :
Ans:- Mode = l + [, , 𝒇𝟏−𝒇𝟎, 𝟐𝒇𝟏−𝒇𝟎−𝒇𝟐, , ]xh, , 3. Find the mode of the data 8, 12, 9, 3, 5, 12., Ans:- 3,5,8,9,12,12, Mode = 12, 4. Find the class interval from this distribution which contains mode., C.I., f, Ans:- 15-20, , 0-5, 3, , 5-10, 8, , 10-15, 4, , 15-20, 9, , 20-25, 2, , 5. The mean and median of a distribution are 10 and 11 respectively. Find the mode., Ans:- 3 median=mode+2 mean, 3x11=mode+2x20, 33= mode +20, Mode= 33-20 = 13, III. Two Mark questions:1. Find the mean for the data by direct method, , C.I., f, , 1-5, 2, , 5-9, 3, , 9-13, 5, , 13-17, 3, , 17-21, 2, , Ans:C.I, 1-5, 5-9, 9-13, 13-17, 17-21, , fi, 2, 3, 5, 3, 2, 𝚺fi=15, , xi, 3, 7, 11, 15, 19, , fixi, 6, 21, 55, 45, 38, 𝚺𝐟𝐢𝐱𝐢 = 𝟏𝟔𝟓, , 2., , Ans:, , xi, 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, , fi, 1, 2, 3, 2, 2, 𝚺fi=10, , fixi, 10, 40, 90, 80, 100, 𝚺𝐟𝐢𝐱𝐢 = 𝟑𝟐𝟎, , Mean =, 𝟏𝟔𝟓, , =11, , Find the mean for the, following frequency, distribution table., , Mean =, , 𝚺𝒇𝒊𝒙𝒊, 𝒇𝒊, , 𝟑𝟐𝟎, , IV. Three marks questions:1. Find the mode for the frequency distribution table given below., 4-10, 4, , 10-16, 5, , 16-22, 3, , 22-28, 6, , 28-34, 2, , l=22, 60, , 𝒇𝒊, , = 𝟏𝟓, , = 𝟏𝟎 = 32, , C.I., f, , 𝚺𝒇𝒊𝒙𝒊, , 34-40, 1, , x, f, , 10, 1, , 20, 2, , 30, 3, , 40, 2, , 50, 2
Page 61 :
Mode = l + [, , h=6, , 𝒇𝟏−𝒇𝟎, 𝟐𝒇𝟏−𝒇𝟎−𝒇𝟐, , ]xh, , f1=6, , = 22+ [, , 𝟔−𝟑, 𝟐 𝟔 −𝟑−𝟐, , f0=3, , = 22 +[, , 𝟑, 𝟏𝟐−𝟓, , f2=2, , = 22 + [𝟕] x6 = 22 +[ [ 𝟕 ] = 24.57, , ]x6, , ] x6, , 𝟑, , 𝟏𝟖, , 2. calculate the median for the given data., C.I., f, , 1-4, 6, , C.I., l=7 1-4, 4-7, 7-10, n=100, 10-13, 13-16, 16-19, , 4-7, 30, , 7-10, 40, , 10-13, 16, , 13-16, 4, Ans:-, , f, c.f.𝒏−𝒄𝒇, Median, = l + [6 𝟐 𝒇 ] xh, 6, 30, 36, 𝟓𝟎−𝟑𝟔, 40, = 7 + [ 76𝟒𝟎 ] x3, 16, 92, 4, 96, 4, 100, N=100, , 16-19, 4, , n/2=50, 𝟏𝟒, , h= 3, , = 7 + 𝟒𝟎 x3, 𝟐𝟏, , cf=36, f=40, , = 7 + 𝟐𝟎 = 7+1.05=8.05, , 3. The following table gives the age of 300 people in a village. Find the arithmetic mean of their ages., , Ans:-, , Age (in years), No. of people, , 10-20, 20, , C.I, 10-20, 20-30, 30-440-50, 50-60, 60-70, , xi, 15, 25, 35, 45, 55, 65, , fi, 20, 50, 80, 120, 20, 10, 𝚺fi=300, , 20-30, 50, , 30-40, 80, , fixi, 300, 1250, 2800, 5400, 1100, 650, 𝚺𝐟𝐢𝐱𝐢 = 𝟏𝟏𝟓𝟎𝟎, , 40-50, 120, , 50-60, 20, , Mean =, , 60-70, 10, , 𝚺𝒇𝒊𝒙𝒊, 𝒇𝒊, , 𝟏𝟏𝟓𝟎𝟎, , =, , 𝟑𝟎𝟎, , = 38.33 years ≈ 𝟑𝟖 𝒚𝒆𝒂𝒓𝒔, , 4. Draw a ‘more than’ type of ogive for the data given below., C.I., f, , 0-3, 9, , 3-6, 3, , 6-9, 5, , 9-12, 3, , 12-15, 1, , Ans:C.I., 0-3, 3-6, 6-9, 9-12, 12-15, , f, 9, 3, 5, 3, 1, , c.f., 21, 12, 9, 4, 1, , Points, (0,21), (3,12), (6,9), (9,4), (12,1), , 61, , Scale:- X-axis :- 1cm=3 units, Y-axis:- 1cm= 2 units
Page 62 :
5. Following table shows that 60 mens weekly expenditure. Draw a ‘less than’ type of ogive for the data, given below., Expenditure, Less than 100, Less than 150, Less than 200, Less than 250, Less than 300, Less than 350, Less than 400, , No. of men, 3, 18, 25, 30, 43, 52, 60, , Expenditure, Less than 100, Less than 150, Less than 200, Less than 250, Less than 300, Less than 350, Less than 400, , No. of men, 3, 18, 25, 30, 43, 52, 60, , Scale:- X-axis :- 1cm= 50, Y-axis:- 1cm= 10, , Points, (100,3), (150,18), (200,25), (250,30), (300,43), (350,52), (400,60), , 62
Page 63 :
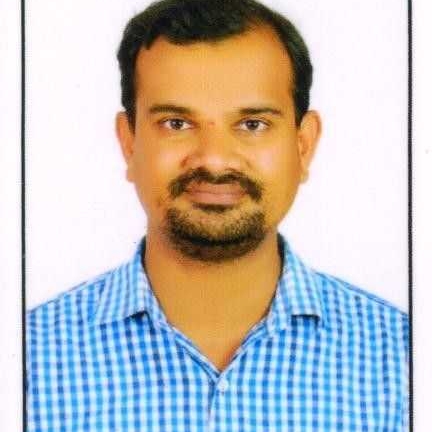
OFFICE OF D.D.P.I , KOLAR DISTRICT, KOLAR, Unit -11:-SURFACE AREA AND VOLUME, I. Multiple choice questions one mark each., 1) The height of the cylinder is 20 cm and radius is 7cm the volume of a cylinder is., A) 3080 cm3 B) 3080 cm2, , C) 3080 cm, , D) 3080 cm4, , 2) A rectangular tank is 25 m long and 9.5m deep. If 600 m3 of water to be drawn off the tank the level of water, goes down by 1.5 m then the width of the tank is., A) 18m, , B) 17m, , C) 16m, , D) 19m, , 3) The volume of one sphere is 27 times that of another sphere. Calculate the ratio of their radii., A) 1:27, , B) 3:27, , C) 9:81, , D) 3:9, , 4) A cylindrical pencil sharpened at one end it is a combination of., 63
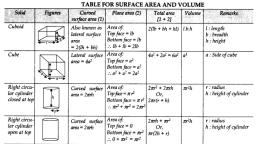
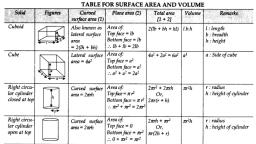
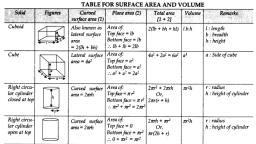
Page 64 :
A) Two cylinders B) Hemisphere and cylinder C) Cone and cylinder D) Frustum of a cone and cylinder, 5) The total surface area of a hemispherical solid having 7 cm radius is., A) 462 cm2, , B) 294 cm2, , C) 588 cm2, , D) 154 cm2, , 6) The surface area of a sphere is 616cm2 its radius is., A) 7 cm, , B) 14 cm, , C) 21 cm, , D) 28 cm, , 7) A cylinder and cone are of same base radius and of same height. The ratio of their volumes is., A) 2:1, , B) 3:1, , C) 2:3, , D) 3:2, , 8) If two solid hemispheres of same radius are joined together along their bases. Then surface area of this new, solid is., A) 𝟑𝝅𝒓𝟐 B) 4𝝅𝒓𝟐 C) 5𝝅𝒓𝟐 D) 6𝝅𝒓𝟐, , II. ONE MARK QUESTIONS., 1) How many balls each of radius 3 cm can be made by melting a bigger ball whose diameter is 48 cm?, , Radius of small ball - 3cm , vol - x, radius of bigger ball 24 cm , vol = x, , x3=4, x 24 =32, , no. of small balls can be created =, , =, , = 8 balls, , 2) A spherical ball of lead has been melted and made in to identical smaller balls with radius equal to half the, radius of the original one. How many such balls can be made?, , Let the radius of big ball be 'r' cm, ∴ Radius of smaller ball = r/2 cm., ➻ Volume of sphere = 4/3 πr³, ➻ Volume of big spherical ball = 4/3 πr³, ➻ Volume of smaller spherical ball = 4/3 π(r/2)³, = Volume of big ball/Volume of smaller ball, = (4/3 πr³)/*4/3 π (r³/8)+, = (4/3 πr³)/*πr³/6+, = (4/3)/(1/6), *Cancelling πr³+, = (4/3) × 6, =4×2, =8, ∴ Number of balls can be made = 8, , 64
Page 65 :
3) Volume and surface area of a solid hemisphere are numerically equal. What is the diameter of the given, hemisphere?, , Let ‘r’ be the radius of the hemisphere., Volume of hemisphere = Surface area of hemisphere, (2/3)πr³= 3πr², (2/3)πr³ / r² = 3π, (2/3)r = 3, Radius of hemisphere, r = 3 × 3/2, Radius of hemisphere, r = 9/2, Radius of hemisphere,r = 9/2 units, Diameter = 2 × Radius, Diameter of hemisphere = 2 × (9/2), Diameter of hemisphere = 9 units., III. TWO MARK QUESTIONS., 1)How many litters of water flows out of a pipe of crass section area 5cm 2 in one minute if the speed of, the water in the pipe is 30 cm/s. (1 litter=1000 cm3), Area of cross section of pipe = 5 cm², Speed of water flowing out of the pipe = 30 cm/sec, Volume of the water flows in 1 minute = Area of the cross section × 30 × 60, = 5 × 30 × 60 = 9000 cm³, Since, 1000 cm³ = 1 litre, , Then, 9000 cm³ = 9 litres, , Hence, 9 litres of water flows out from a pipe., 2) The surface area of sphere is 2464 cm2 find its volume., Surface area of sphere=, Surface area=2464cm square, , Volume= 4/3×𝝅×r3, 4/3×22/7×14×14×14, =11498.66 cm3, 3) Eight metallic spheres each of radius 2 mm are melted and recast in to a single sphere. Calculate the radius of the, new sphere., , Radius= 2mm, 65
Page 66 :
volume if one metallic sphere = 4/3 πr³, = 4/3 × 3.14 × 2³, = 4/3 × 3.14 × 8 = 33.49 mm³, Volume of eight metallic sphere having radius 2mm = 33.49 × 8 = 267.94 mm³, Since eight spheres are melted and casted into single sphere., That means single sphere has same volume as that of volume of eight spheres, •°• Volume of new sphere = 267.94mm³, 4/3 πr³ = 267.94, 4/3 × 3.14 × r³ = 267.94, r³ = 267.94/4.18, r³ = 64.100 ≈64, r³ = 64, r³=43, r = 4mm, Therefore, radius of new sphere is 4mm, 4) A right circular con of radius 3cm has a curved surface area 47.1 cm2. Find the volume of cone (𝝅 = 𝟑. 𝟏𝟒), , Radius of cone ( r ) = 3 cm,, Curved surface area of a cone= 47.1 cm², Curved surface area of a cone= πrl, 47.1 = πrl, 47.1 = 3.14 × 3 × l, l = 47.1 / (3.14 × 3), l = 15.7 / 3.14= 1570/314= 5 cm, slant height (l) = 5 cm, Height of a cone (h) = (𝐥²) − (𝐫²), h = (𝟓²) − (𝟑²), h = (𝟐𝟓 − 𝟗= 𝟏𝟔 = 4 cm, h = 4 cm, Volume of cone= ⅓(πr²h), = ⅓(3.14 × 3 × 3 × 4), = 3.14 × 12= 37.68 cm³, Hence, the volume of a cone is 37.68 cm³., 5) The volume of a sphere is 38808 cm3 find its diameter and surface area., volume of the sphere = 38808cm³, formula to find the volume of a sphere is 4/3πr³, therefore 4/3πr³ = 38808cm³, ➡ 4/3 × 22/7 × r³ = 38808cm³, ➡ 88/21 × r³ = 38808cm³, ➡ r³ = 38808/1 × 21/88, 66
Page 67 :
➡ r³ = 441 × 21, ➡ r³ = 9261, ➡r=, , 𝟑, , 𝟐𝟏 × 𝟐𝟏 × 𝟐𝟏= 21cm, , Diameter d= 2r= 2x21=42cm, now, it's curved surface area = 4πr², = 4 × 22/7 × 21 × 21= 88/7 × 441= 88 × 63= 5544cm², hence, the curved surface area of the sphere is 5544cm², 6) A cylinder ,cone and a hemisphere have the same base and the same height. Find the ratio between, their volumes., Volume of hemisphere = 2/3 π r³ = V1, Volume of cylinder = π r²H = V2, Volume of Cone = ⅓ π r² H = V3, We know that radius of hemisphere is its height which means that radius of all given solids are equal, to their height since their radius are also given equal., V1/V2/V3=2/3*π H³ (since r=h) / π H³ / 1/3*π H³, => 2/3 /1 / 1/3, =>2/3:1:1/3, => 1:1/3:2/3, Multiplying by 3, => 3:1:2 is the ratio of volumes of cylinder : Cone : hemisphere, IV. THREE MARK QUESTIONS., 1) The ratio between the radius of the base and the height of the cylinder is 2: 3. If its volume is 1617, cm3, the total surface area of the cylinder is?, , , Ratio between the radius of the base and the height of the cylinder is 2: 3., , , , volume is 1617 cm³., , , , Total surface area of the cylinder = ?, Let the radius of the base and the height of the cylinder be 2x and 3x respectively., Now,, Volume of Cylinder = πr²h, =) 1617 = π× (2x)² × (3x), =) 1617 × 7/22 = 4x² × 3x, =) 514.5 = 12x³, =) x³ = 514.5/12, =) x³ = 42.875, 67
Page 68 :
𝟑, , =) x = 𝟒𝟐. 𝟖𝟕𝟓), =) x = 3.5, , , Radius = 2x = 2×3.5 = 7 cm., , , , Height = 3x = 3 × 3.5 = 10.5 cm., Total Surface Area of Cylinder = 2πr ( h + r), =) T.S.A. of Cylinder = 2 × (22/7) × 7 ( 10.5 + 7 )= 44 ( 17.5 )= 770 cm³., 2) A solid cone of a base radius 10 cm is cut into two parts through the midpoint of its height by a plane, parallel to its base. Find the ratio of the volume of the two parts of the cone., , Let r & R be the radius of the lower part of the frustum., Height of a cone , AB’ = 10 cm, Height of a Smaller cone, AB = 5 cm, [Cut through the midpoint of its height], From the figure,, AB = h = 5, AB’ = 2h = 10, BC = r, B'C = R, In ∆ABC & ∆AB’C’ ,, ∠ABC = ∠AB’C’ (each 90°), ∠ACB = ∠AC’B’ (corresponding angles), ∆ABC ∼ ∆AB’C’ [By AA Similarity], BC/B'C’ = AB/AB’, [Corresponding sides of a similar triangles are proportional], r/R = 5 /10, r/R = ½, R = 2r, Volume of the upper part (Smaller cone) = ⅓ πr²h, Volume of solid cone = ⅓ π R²2h, = ⅓ π (2r)² 2h = ⅓ π × 4r² × 2h = 8/3πr²h, Volume of lower part (frustum) = volume of solid cone - volume of Smaller cone = 8/3πr²h - ⅓ πr²h = 7/3, πr²h, Volume of lower part (frustum) = 7/3 πr²h, Volume of the upper part (Smaller cone)/ Volume of lower part (frustum) =, 68
Page 69 :
⅓ πr²h / 7/3 πr²h= 1/7, Hence, the ratio of volume of two parts of the cone is 1 : 7 ., , 3) A solid metallic sphere of diameter 8 cm is melted and drawn into a cylindrical wire of uniform width if, the length of the wire is 12 m find its width., Diameter of sphere = 8m, Radius of sphere = Diameter/2 = 8/2 =4 m, Volume of sphere =, =, =, Length of wire is 12 m, Since wire is in the shape of cylinder, Volume of wire =, =, Since Sphere is melted to make wire so, volume will remain same ., , Radius of wire = 2.66m, Width = Diameter = Radius x2 = 2.66x2 =5.32 m, Hence the width of the wire is 5.32 m, V. FOUR MARK QUESTIONS., 1) The sum of the radius of base and height of a solid right circular cylinder is 37 cm. If the total surface, area of cylinder is 1628 cm2 find the volume of the cylinder., , 69
Page 70 :
TSA = 2πr(h+r), 1628 = 2πr × 37 ( from q ), 814 = 22/7 × 37 × r, 814×7/22 = 37r, 37 × 7 = 37r, r = 7 cm, So h = 37-7 = 30 cm, Volume of cylinder= πr²h, V = 22 / 7 × 7 × 7 × 30= 22 × 7 × 30= 4620 cm³, 2) A vessel is in the form of a hemispherical bowl is surmounted by a hallow cylinder of same diameter., The diameter of the hemispherical bowl is 14 cm and the total height of the vessel is 13 cm. Find the inner, total surface area of the vessel., => Diameter of hemisphere = Diameter of cylinder = 14 cm., => Radius of hemisphere = Radius of cylinder = 7 cm., => Height of cylinder = Total height - radius of hemisphere, => 13 - 7 = 6 cm., => Curved surface area of cylinder = 2πrh, => Curved surface area of hemisphere = 2πr², Curved surface area of cylinder = 2πrh, , Now, Curved surface area of hemisphere = 2πr², , ∴ Inner surface area of vessel = Curved surface area of cylinder + curved surface area of hemisphere, => 264 + 308, => 572 cm², So, the inner surface area of vessel = 572 cm², 3) 504 cones each of diameter 3.5 cm and height 3 cm are melted and recast into a metallic sphere. Find, the diameter of the sphere and also find the surface area., Number of cones = 504, Diameter of cone = 3.5cm, , Radius of cone = 1.75cm, , Volume of each cone, =, =1/3 x 22/7 x 1.75x1.75 x3, = 22x0.25x1.75= 9.625 cm3, 70, , Height = 3cm
Page 71 :
Volume of all cones = 504 x9.625= 4851 cm3, After melting,, Volume of sphere = Volume of cones, Volume of sphere = 4851, , r3= 1157.625, r= 10.5 cm, Diameter of sphere = 2*Radius, = 2x10. 5= 21 cm, VI. FIVE MARK QUESTIONS., 1) A vessel in the form of an inverted cone is filled with water to the brim. Its height is 32 cm and, diameter of the base is 25.2 cm. six equal solid cones are dropped in it, so that they are fully, submerged. As a result one fourth of water in the original cone over flows. What is the volume of, each of the solid cones submerged?, Height of Cone = 32 cm, Diameter of Cone = 25.2 cm, Radius of Cone = 12.6 cm, Now if we will find the Volume of Cone in Liters then we will be able to find the Volume of each cone., Volume of Cone = πr²h/3, V = π (12.6)(12.6)(32)/3 cm³, V = 1693.44π cm³, Converting cm³ to Liters., V = 1.69344π L, Now, As given one-fourth over flow., Volume of small cones =1/4Volume of water×1/6, V = 1/24 × 1.69344, V = 0.07056 L, Again, Converting L to cm³ V = 70.56 cm³, Volume of each cone = V = 70.56 cm³, 2) From a solid cylinder of height 36 cm and radius 14 cm, a conical cavity of radius 7 cm and height 24 cm, drilled out. Find the volume and the total surface area of the remaining solid., Vol. 20944 cm3 , S.A. 4796 cm2, Vol. of Cylinder = 22/7x Radius2 x Height , Total SURFACE AREA OF CYLINDER = 2x(22/7)xRADIUS(radius +, height ), Vol. of cone = (1/3) (22/7) (Radius2 ) x Height, Lateral Surface area of cone = (22/7)x radius x slant height, Vol. of Cylinder= (22/7) x 14 x 14 x36, Vol of Cone = (1/3) (22/7) x7x7x24, Vol. of cylinder- Vol. of cone = (22/7) (14x14x36 - (7x7x24/3), 71
Page 72 :
= 22/7( 7056- 392), = 22/7X6664, =20944 cm3, Tsa of remaining solid = 44/7X14(14+36) + 22/7x7x25 - (22/7 x 7 x7 ), =4400- 154 + 550, = 4796 cm2, l = 𝐡𝟐 + 𝐫𝟐, l = 𝟔𝟐𝟓= 25 cm, 3) A circus tent is cylindrical to a height of 4m and conical above it. If its diameter is 105 m and its slant, height is 80 m. calculate the total surface area of canvas required. Also find the total cast of canvas, used at rate of Rs 15 per meter of the width is 1.5 m., , For cylinder, Diameter is 105 m, then radius is 105/2m, Now height=4 m, For cone,, l=80 m and r= 105/2, Total surface area of the tent is the sum of lateral suface of cone and cylinder, =2πrh+πrl, =1320+13200=14520m², Width of canvas used = 1.5 m, Length of canvas = 14520/1.5 = 9680m, Therefore, total cost of canvas at the rate of rupees 15 per metre = 9680 × 15 = ₹145200, 4) Bucket open at the top is in the form of a frustum of a cone with a capacity of 12308.8 cm 3. The radius, of the top and bottom circular ends are 20 cm and 12 cm respectively. Find the height of the bucket, and the area of metal sheet used the making the bucket. (use 𝝅=3.14), , Bucket is in the form of the frustum of a cone., 72
Page 73 :
Capacity of Frustum of a cone = volume of the frustum of a cone = 12308.8 cm³, Bigger radius (r1) = 20 cm, Smaller radius (r2) = 12 cm, Volume of Frustum of cone =(⅓ π)h ( r1² + r2² + r1r2), 12308.8 = (π/3)h ( 20×20 + 12×12 + 20×12), 12308.8× 3 = π h( 400 + 144+240), 12308.8×3 = 22/7 h(784), h = 12308.8×3 ×7 / (22 × 784), h = 12308.8×3 / (22 × 112), h = 6,154.4 × 3 / 11× 112, h= 18,463.2/1232 = 14.99, h=15 (approximately), Height of Frustum of cone (h) = 15 cm, Slant height (l) of a frustum cone = 𝐡² + (𝐫𝟏 − 𝐫𝟐)², l = 𝟏𝟓² + (𝟐𝟎 − 𝟏𝟐)² = 𝟐𝟐𝟓 + (𝟖)² = 𝟐𝟐𝟓 + (𝟔𝟒 ) = 𝟐𝟖𝟗 =17 cm, Surface area of a frustum cone = πl (r1 + r2), = π × 17 (20+12), = 22/7 × 17(32), = 11968/7 = 1,709.7cm², Cost of making 1 cm² = ₹10, Cost of making 1709.7 cm² = ₹(1709.7 × 10) = ₹ 17097, Cost of making 1709.7 cm² = ₹ 17097, Hence, the height of the bucket is 15 cm and the cost of making the bucket is ₹ 17097., , 73