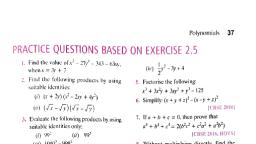Page 1 :
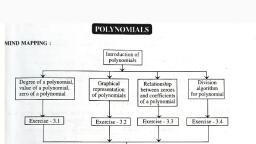
Key Notes, Chapter-02, Polynomials, •, •, •, •, , •, •, •, •, , •, , An algebraic expression of the form a0 x n + a1 x n −1 + a2 x n − 2 + ... + an −1 x + an , where a0 , a1 , a2 ...an, are real numbers, n is a non-negative integer and a0 ≠ 0 is called a polynomial of degree n., Degree: The highest power of x in a polynomial p(x) is called the degree of polynomial., Polynomials of degrees 1, 2 and 3 are called linear, quadratic and cubic polynomials, respectively., Types of Polynomial:, (i), Constant Polynomial: A polynomial of degree zero is called a constant polynomial, and it is of the form p(x) = k., (ii), Linear Polynomial: A polynomial of degree one is called linear polynomial and it is of, the form p(x) = ax + b where a, b are real numbers and a0 ≠ 0 ., (iii) Quadratic Polynomial: A quadratic polynomial in x with real coefficient is of the, 2, form ax + bx + c , where a, b, c are real numbers with a ≠ 0 ., (iv) Cubical Polynomial: A polynomial of degree three is called cubical polynomial and is, of the form p(x) = ax3 + bx 2 + cx + d where a, b, c, d are real numbers and a ≠ 0 ., (v), Bi-quadratic Polynomial: A polynomial of degree four is called bi-quadratic, polynomial and it is of the form p ( x) = ax 2 + bx3 + cx 2 + dx + e , where a, b, c, d, e are, real numbers and a ≠ 0 ., The zeroes of a polynomial p(x) are precisely the x–coordinates of the points where the, graph of y = p(x) intersects the x-axis i.e. x = a is a zero of polynomial p(x) if p(a) = 0., A polynomial can have at most the same number of zeros as the degree of polynomial., b, c, For quadratic polynomial ax 2 + bx + c (a ≠ 0) Sum of zeros = − Produce of zeros =, a, a, The division algorithm states that given any polynomial p(x) and polynomial g(x), there are, polynomials q(x) and r(x) such that: p ( x ) = g ( x ) .q ( x ) + r ( x ) , g ( x ) ≠ 0 where r(x) = 0 or, degree of r(x) < degree of g(x), The division algorithm states that given any polynomial p(x) and polynomial g(x), there are, polynomials q(x) and r(x) such that: p(x) = g(x). q (x) + r(x), g(x) = 0 where r(x) = 0 or degree, of r(x) < degree of g(x).