Page 1 :
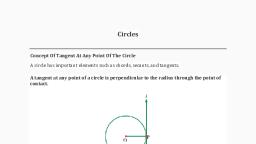
СHAPТER 10, CIRCLE, ONE MARK QUESTIONS, equals., (а) 30°, (b) 45°, (c) 60°, (d) 90°, MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS, Ans :, [Board 2020 Delhi Basic], Let O be the centre of the circle. As per given, 1., From an external point Q, the length of tangent to a, information we have drawn the figure below., P, circle is 12 cm and the distance of Q from the centre, of circle is 13 cm. The radius of circle (in cm) is, (a) 10, (b) 5, (c) 12, (d) 7, Ans :, [Board 2020 Delhi Basic], Let O be the centre of the circle. As per given, information we have drawn the figure below., We know that, the radius and tangent are perpendicular, at their point of contact., Now, in isosceles triangle POQ we have, Z POQ+ 2 OPQ+ 2 0QP, 180°, 13 сm, Equal sides subtend equal angles in isosceles triangle., Thus, 22OQP+ 90°, 180°, P, 12 cm, ZOQP = 45°, We have, OQ = 13 cm, Thus (b) is correct option., and, РQ — 12 cm, 3. A chord of a circle of radius 10 cm, subtends a right, angle at its centre. The length of the chord (in cm) is, Radius is perpendicular to the tangent at the point, of contact., (a) 2, (b) 5/2, Thus, ОP I PQ, In A OPQ, using Pythagoras theorem,, (c) 10/2, (d) 10/3, OP + PQ, OQ, Ans :, [Board 2020 OD Basic], As per given information we have drawn the figure, OP + 122, = 13?, below., OP = 132 – 122, = 169 – 144, = 25, Thus, ОР — 5 сm, 10 cm, Thus (b) is correct option., B', QP is a tangent to a circle with centre O at a point, P on the circle. If A OPQ is isosceles, then Z OQR, 2., Using Pythagoras theorem in A ABC, we get, 10 cm
Page 2 :
Chap 10, Circle, Page 305, BC, = AB + ACe, cm, then the length of AP (in cm) is, A, = 102+ 102, = 100 + 100 = 200, ВС — 10/2 cm, BA, Thus (c) is correct option., PA, (а) 15, (b) 10, (c) 9, (d) 7.5, Ans :, [Board 2020 Delhi Basic], In figure, O is the centre of circle. PQ is a chord and, PT is tangent at P which makes an angle of 50° with, РQZ POQ is, 4., Due to tangents from external points,, BP = BR, CR = CQ, and AP= AQ, Perimeter of A ABC,, АВ+ ВС+ АС, T-, = AB+ BR+ RC+ AC, 5+4+6 = AB+ BP+ CQ+ AC, P, 15 = AP+ AQ, 15 = 2AP, 15, Thus, AP = = 7.5 cm, %3D, Thus (d) is correct option., (a) 130°, (b) 90°, 6. In figure, on a circle of radius 7 cm, tangent PTis, drawn from a point P such that PT = 24 cm. If O is, the centre of the circle, then the length of PR is, (c) 100°, (d) 75°, Ans :, [Board 2020 OD Basic], Due to angle between radius and tangent,, R, ZOPT = 90°, P, ZOPQ = 90° - 50° = 40°, Also,, ОP — 0Q, [Radii of a circle], Since equal opposite sides have equal opposite angles,, (а) 30 сm, (b) 28 сm, ZOPQ = 2OQP = 40°, (c) 32 cm, (d) 25 cm, ZPOQ = 180° – ZOPQ - Z OQP, Ans :, [Board 2020 Delhi Basic], Tangent at any point of a circle is perpendicular to, the radius at the point of contact., = 180° – 40° – 40° = 100°, Thus (c) is correct option., Thus, OT I PT, 5. In figure, AP, AQ and BC are tangents of the circle, with centre O. If AB = 5 cm, AC= 6 cm and BC= 4, Now in right-angled triangle PTO, OP = OT + PT
Page 3 :
Page 306, Circle, Chap 10, Ans :, = (7) + (24), = 49 + 576, = 625, Thus, ОP — 25 сm, Since OR = OT because of radii of circle,, PR = OP+ OR = 25 + 7 = 32 cm, Thus (c) is correct option., 7., Two chords AB and CD of a circle intersect at E such, that AE = 2.4 cm, BE= 3.2 cm and CE = 1.6 cm., The length of DE is, (a) 1.6 cm, (b) 3.2 сm, Since C is the mid-point of AB,, (с) 4.8 сm, (d) 6.4 ст, AC = 12, Ans : (c) 4.8 cm, AO = 37, and, АО, — 20, CO = V372 – 122 = 35, CO, = V202 – 12?, = 16, B, O, 02 = 35 + 16 = 51, Thus (b) is correct option., 10. In the adjoining figure, TP and TQ are the two, tangents to a circle with centre O. If ZPOQ = 110°,, then PTQ is, Applying the rule,, AE X EB = CE X ED, T, 2.4 x 3.2 = 1.6 x ED, ED = 4.8 cm, Thus (c) is correct option., If a regular hexagon is inscribed in a circle of radius r,, then its perimeter is, 8., (а) 3г, (b) 6т, (b) 70°, (d) 90°, (а) 60°, (с) 9т, (d) 12г, (c) 80°, Ans :, Ans :, Side of the regular hexagon inscribed in a circle of, radius r is also r, the perimeter is 6r., Here OP 1 PT and OQ 1 QT,, In quadrilateral OPTQ, we have, ZPOQ+ 2OPT+ ZPTQ+ ZOQT= 360°, Thus (b) is correct option., 110° + 90° + PTQ+ 90° = 360°, 9., Two circles of radii 20 cm and 37 cm intersect, in A and B. If O and O, are their centres and, AB = 24 cm, then the distance O O2 is equal to, Z PTQ = 70°, Thus (b) is correct option., (а) 44 ст, (b) 51 сm, (с) 40.5 сm, (d) 45 cm, 11. AB and CD are two common tangents to circles
Page 4 :
Chap 10, Circle, Page 307, which touch each other at a point C. IfD lies on AB, such that CD = 4 cm then AB is, (а) 12 ст, (b) 8 сm, (с) 4 сm, (d) 6 cm, Ans :, AD = CD and BD = CD, B, AB = AD+ BD = CD+ CD, = 2CD = 2 × 4 = 8 cm, A, D B, Thus, OC I PT, ZOCP = 90°, Thus (b) is correct option., Given,, ZACP = 118°, ZACO = L ACP- LOCP, = 118° – 90°= 28°, ZACO = 28°, Since O is the circumcentre, thus OA = 0C (radius), ZOAC = ACO, x = 28°, 12. In the adjoining figure, PT is a tangent at point C, of the circle. O is the circumference of A ABC. If, ZACP = 118°, then the measure of Zx is, Thus (a) is correct option., 13. In the given figure, a circle touches all the four sides, of quadrilateral ABCD with AB = 6 cm, BC=7 cm, and CD = 4 cm, then length of AD is, R, B, A, P, В, (а) 3 сm, (b) 4 сm, (c) 5 cm, (d) 6 сm, Ans :, (a) 28°, (b) 32°, Four sides of a quadrilateral ABCD are tangent to a, (c) 42°, (d) 38°, circle., Ans :, AB+ CD = BC+ AD, We join OC as shown in the below figure. Here OC is, the radius and PT is the tangent to circle at point C., 6 +4 = 7+ AD
Page 5 :
Page 308, Circle, Chap 10, AD = 10 – 7 = 3 cm, 15. Two concentric circles are of radii 10 cm and 8 cm,, then the length of the chord of the larger circle which, Thus (a) is correct option., touches the smaller circle is, 14. Two concentric circles of radii a and b where a > b,, The length of a chord of the larger circle which touches, the other circle is, (а) 6 сm, (b) 12 сm, (c) 18 cm, (d) 9 cm, Ans :, (a) Va+ b, (c) Va – b, (b) 2va+ b?, Let O be the centre of the concentric circles of radii, (d) 2ya - 6, 10 cm and 8 cm, respectively. Let AB be a chord of, the larger circle touching the smaller circles at P., Ans :, Then,, AP = PB and OP 1 AB, In A OAL,, OA? = OĽ + AL, a? = OĽ + b², OL =, Va? – b², 10 cmo, 8 cm, Length of chord,, 2AL = 2/a² – 6?, A, B, P, B., a, Applying Pythagoras theorem in A OPA, we have, OA? = OP? + AP?, 100 = 64 + AP?, АР? — 100 -64 — 36 > АР — 6 сm, AB = 2AP = 2 x 6 = 12 cm, Thus (d) is correct option., Thus (b) is correct option., 16. In the given figure, PA is a tangent from an external, point P to a circle with centre O. If ZPOB = 115°,, then perimeter of ZAPO is, 115°, B., (а) 25°, (b) 20°, (c) 30°, (d) 65°, Ans :, Since tangent at a point to a circle is perpendicular, to the radius,, ZOAP = 90°