Page 2 :
Based on the above information, answer the following questions., , (i) Ifthe roots of the quadratic equation are 2, -3, then its equation is, , , , , , , , (a) x°-2x+3=0 (b) x7+x-6=0 (c) 2x7-3x+1=0 (d) °-6x-1=0, (ii) If one root of the quadratic equation 2x? + kx + 1 =O is -1/2, then k =, , (a) 3 (b) -5 (c) =3 (d) 5, (iii) Which of the following quadratic equations, has equal and opposite roots?, , (a) *-4=0 (b), 16x7-9=0 (©) 3x°+5x-5=0 — (d) Both (a) and (b), (iv) Which of the following quadratic equations can be represented as (x — 2)? + 19 = 0?, , (a) x2+4x#15=0 (b) 2 -4x+15=0 (c) x7-4x+23=0 (d) x7+4x+23=0, (iv) If one root of a quadratic equation is = , then its other root is, , = -1+V5 -1-45, fa) a ) 6 o= @ = =, , ¢—____—, Formation of Quadratic Equation, , Quadratic equations started around 3000 B.C. with the Babylonians. They were one of the world’s first civilisation,, and came up with some great ideas like agriculture, irrigation and writing. There were many reasons why, Babylonians needed to solve quadratic equations. For example to know what amount of crop you can grow on, the square field., , Based on the above information, represent the following questions in the form of quadratic equation., , (i) The sum of squares of two consecutive integers is 650., (a) x7 +2x-650=0 (b) 2x7 4+2x-649=0 — (c) x°-2x-650=0 = (d) 2x* + 6x-550=0, , (ii) The sum of two numbers is 15 and the sum of their reciprocals is 3/10., (a) x2+10x-150=0 — (b) 15x*-x+150=0 = (c) x*-15x4+50=0 § (d) 3x?- 10x + 15=0, , (iii) Two numbers differ by 3 and their product is 504., , (a) 3x7 -504=0 (b) x? -504x+3=0 (c) 504x74+3=x (d) x2 +3x-504=0, (iv) A natural number whose square diminished by 84 is thrice of 8 more of given number., (a) x7 +8x-84=0 (b) 3x7-84x+3=0 = (c) x°-3x-108=0 = (d) x°-11x+ 60=0, , (v) A natural number when increased by 12, equals 160 times its reciprocal., (a) x°-12x+160=0 = (b) x*-160x+12=0 (Cc) 12x*-x-160=0 (d) x7 +12x-160=0, , Factorization Method, , Amit is preparing for his upcoming semester exam. For this, he has to practice the chapter of Quadratic, , Equations. So he started with factorization method. Let two linear factors of ax? + bx+cbe (px + q) and (rx +s)., ax? + bx + c= (px + q) (rx + s) = prx? + (ps + qr)x + qs., , Now, factorize each of the following quadratic equations and find the roots., , (i) 6x7 +x-2=0, , 1-2 1-1 3, (a) 1,6 (b) 3 (c) oO (d) 7?
Page 3 :
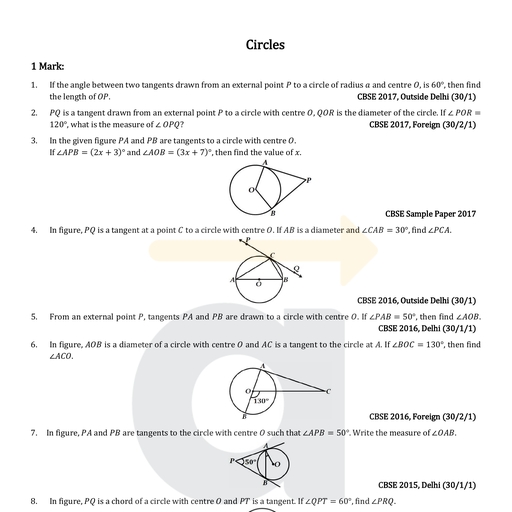
(ii) 2x? + x -300=0, , 2 2 -25, (a) 30,5 (b) 60, (c) 12,- (d) None of these, (iii) x7 - 8x + 16 =0, (a) 3,3 (b) 3,-3 () 4,-4 (d) 4,4, (iv) 6x? - 13x+5=0, @ 2,3 () -2 2 © 13 (@ 1,5, 5 3 275 2’3, (v) 100x? - 20x+1=0, 14 1 -1 -1, 327 b) -10,-10 -10, — d =, =, (a) 1a° 1G (b) -1 (c) -1 0 (d) 10” 10, , Concept of Quadratic Equation, If p(x) is a quadratic polynomial i.e., p(x) = ax’ + bx+c,a#0, then p(x) = 0 is called a quadratic equation., Now, answer the following questions., , (i) Which of the following is correct about the quadratic equation ax? + bx +c =02, , (a) a, band care real numbers, c 40 (b) a, band care rational numbers, a +0, (c) a, band care integers, a, b and c #0 (d) a, band care real numbers, a+ 0, (ii) The degree of a quadratic equation is, (a) 1 (b) 2 (c) 3 (d) other than 1, (iii) Which of the following is a quadratic equation?, (a) x(x+3)+7=5x-11 (b) (x- 1)? -9 = (x- 4)(x +3), (c) 7(2x+1)-4=5x7-10 (d) x(x —1)(x +7) = x(6x - 9), , (iv) Which of the following is incorrect about the quadratic equation ax? + bx + c= 0?, (a) Ifac? + ba +c=0, then x = —« is the solution of the given quadratic equation., , (b) The additive inverse of zeroes of the polynomial ax” + bx + c is the roots of the given equation., (c) If isa root of the given quadratic equation, then its other root is -c., (d) All of these, , (v) Which of the following is not a method of finding solutions of the given quadratic equation?, (a) Factorisation method (b) Completing the square method, (c) Formula method (d) None of these, , (GL eS, , 1. (i) (a):To have no real roots, discriminant (a) D=1?-4(1)(-1)=1+4=5, whichis nota perfect, , (D = b? - 4ac) should be < 0. square., (a) D=7? -4(-4)(-4) = 49 - 64 =-15<0 (b) D=(-5)? -4(1)(6) = 25 - 24= 1, which isa perfect, (b) D=7) -4(-4)(-2) = 49 -32=17>0 square., (c) D=5° - 4(-2)(-2) = 25- 16=9>0 (c) D=(-3)? - 4(4)(-2) = 9 + 32 = 41, which is nota, , (d) D=6 - 4(3)(2) = 36 - 24=12>0 perfect square., , (ii) (b): To have rational roots, discriminant (d) D=(-1)? - 4(6)(11) = 1 - 264 = -263, which is not, (D = b — 4ac) should be > 0 and also a perfect square. _a perfect square.
Page 4 :
(iii) (Cc): To have irrational roots, discriminant, (D = b? — 4ac) should be > 0 but nota perfect square., (a) D=2?-4(3)(2)=4-24=-20<0, , (b) D = (-7)? - 4(4)(3) = 49 - 48 = 1 > O and alsoa, perfect square., , (c) D=(-3)? - 4(6)(-5) = 9 + 120 = 129 > Oand nota, perfect square., , (d) D = 3? - 4(2)(-2) = 9 + 16 = 25 > 0 and alsova, perfect square., , (iv) (d):To have equal —_roots,, (D = b? - 4ac) should be = 0., , (a) D=(-3)?- 4(1)(4)=9-16=-7 <0, (b) D=(-2)? ~4(2)(1) =4-8=-4<0, (c) D=(-10)? - 4(5)(1) = 100 - 20 = 80 >0, (d) D=6 - 4(9)(1) = 36 - 36=0, , (v) (a): To have two distinct real roots, discriminant, (D = b? - 4ac) should be > 0., , (a) D=3?-4(1)(1)=9-4=5>0, , (b) D=3?-4(-1)(-3) =9-12=-3<0, , (c) D=8? - 4(4)(4) = 64 - 64=0, , (d) D= 6? - 4(3)(4) = 36 - 48 =-12 <0, , 2., ss ‘ The required quadratic equation is, , (x -2)(x +3) =03 x7 +x-6=0, (ii) (a): We have, 2x? + kx + 1=0, , Since, -1/2 is the root of the equation, so it will satisfy, the given equation., , (-4 uj }1=0=1-kr 2-0 kas, 2 2, , (iii) (d): If the roots of the quadratic equations are, opposites to each other, then coefficient of x (sum of, roots) is 0., , So, both (a) and (b) have the coefficient of x = 0., , (iv) (c): The given equation is (x - 2° +19=0, , = x -4x4+4419=0 = x7 -4x4+23=0, , (v) (b):If one root of a quadratic equation is, irrational, then its other root is also irrational and also, its conjugate i.e., if one root is p+ Ja , then its other, root is p-Va., , 3. (i) (b): Let two consecutive integers be x, x + 1., Given, x? + (x + 1)? = 650, , = 2x7+2x+1-650=0, , => 2x7 +2x-649=0, , (ii) (c): Let the two numbers be x and 15 - x., 1 3, , 15—x 10, , discriminant, , (i) (b): Roots of the quadratic equation are 2 and, , , , ‘i 1, Given, — +, x, , => 10(15-x+x) =3x(15-x), => 50=15x-x = x-15x+50=0, , (iii) (d): Let the numbers be x and x + 3., Given, x(x + 3) =504, => x+3x-504=0, , (iv) (c): Let the number be x., According to question, x°- 84 = 3(x + 8), => °-84=3x+24 = °-3x-108=0, , (v) (d): Let the number be x., , 60, According to question, x +12 = 10, , = x +12x-160=0 *, , 4. (i) (b):We have, 6x7+ x-2=0, => 6x -3x+4x-2=0, = (3x+2)(2x-1)=0, => x=>,—, 23, , (ii) (c): 2x? + x - 300=0, => 2x - 24x + 25x-300=0, = (x-12)(2x+25)=0, , —25, => x=12,—, , 2, (iii) (d): x? - 8x + 16 =0, => (x-4)=0 = (x-4)(x-4)=0 = x=4,4, , (iv) (d): 6x? - 13x+5=0, => 6x°-3x-10x+5=0, = (2x-1)(3x-5)=0, 15, => x=-,2 3, , (v) (a): 100x? - 20x + 1 =0, 1, , 1, Ox-1?=0 > x=—,, = (10x-1)°=0 10’ 10, , 5. (i) (d) (ii) (b), , (iii) (a): x(x + 3) +7 =5x-11, , => x2 43x+7=5x-11, , = x? — 2x + 18 = 0 is a quadratic equation., (b) (x-1)?- 9 =(x-4)(x + 3), , => 2-2x-8=x'-x-12, , = x-4=0is nota quadratic equation., (c) x7°(2x +1) -4=5x7- 10, , => Ix+x-4=5x7-10, , => 2x) - 4x? + 6 = 0 is not a quadratic equation., (d) x(x - 1)(x + 7) = x(6x - 9), , => + 6x7 -7x = 6x? - 9x, , => x°+2x=0is not a quadratic equation., , (iv) (d) (vy) (dd)