Page 1 :
Assignments in Mathematics Class X (Term II), 5. Arithmetic Progressions, IMPORTANT TERMS, DEFINITIONS AND RESULTS, , •, , If a is the first term and d the common difference, of an AP, then the general form of the AP is, a, a + d, a + 2d, ..., , N, , First term : a – 3d, common difference = 2d, Their sum = �a – 3d + a – d + a + d + a, + 3d = 4a, , A, , •, , Let a be the first term and d be the common, difference of an AP, then, its nth term or general, is given by, , SH, , •, , Remember the following while working with, consecutive terms in an AP., (i) Three consecutive terms in an AP., a – d, a, a + d, First term = a – d, common difference = d, Their sum = a – d + a + a + d = 3a, (ii) Four consecutive terms in an AP., a – 3d, a – d, a + d, a + 3d, , (iii) Five consecutive terms in an AP., a – 2d, a – d, a, a + d, a + 2d, First term = a – 2d, common difference = d, , tn = a + (n – 1) d, , •, , •, , The sum Sn up to n terms of an AP whose first, term is a and common difference d is given by, n, S n = [2a + (n − 1)d ], 2, , PR, , A, , If l is the last term of the AP, then nth term from, the end is the nth term of an AP, whose first term, is l and common difference is – d., \ nth term from the end = Last term , + (n – 1) (– d), ⇒ nth term from the end = l – (n – 1) d, • If a, b, c, are in AP, then, (i) (a + k), (b + k), (c + k) are in AP., (ii) (a – k), (b – k), (c – k) are in AP., (iii) ak, bk, ck, are in AP., , A, , •, , •, , Some numbers arranged in a definite order, according, to a definite rule, are said to form a sequence., A sequence is called an arithmetic progression, (AP), if the difference of any of its terms and the, preceding term is always the same., i.e., tn + 1 – tn = constant., The constant number is called the common, difference of the A.P., , K, , •, , If the first term and the last term of an AP are t1, and tn, then, , ER, , S, , •, , TH, , O, , a b c, , , are in AP (k ≠ 0), k k k, , •, , n, n, (t1 + tn ) = (first term + last term), 2, 2, , If t1 = a, the first term and tn = l, the last term,, n, then S n = (a + l ), 2, Sn – Sn – 1 = tn, , L, , B, , R, , (iv), , Sn =, , YA, , Summative Assessment, , O, , MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS, , [1 Mark], , G, , A. Important Questions, 4. An A.P. whose first term is 10 and common, difference is 3, is :, (a) 10, 13, 16, 19, ... (b) 5, 7, 9, 11, ..., (c) 8, 12, 16, 20, ..., (d) all of these, 5. The common difference of the A.P. –5, –1, 3, 7,, ... is :, (a) 2, (b) 3, (c) – 4, (d) 4, 6. Which of the following list of numbers does form, an A.P. ?, , 1. The common difference of the A.P. 3, 1, –1, –3, ... is :, (a) –2, , (b) 2, , (c) –1, , (d) 3, , 2. The general form of an A.P. is :, (a) a, a – d,a – 2d, a – 3d, ..., (b) a, a + d,a + 2d, a + 3d, ..., (c) a, 2d, 3d, 4d, ..., , (d) none of these, , 3. The common difference of the A.P. 8, 11, 14, 17,, 20, ... is :, (a) 2, , (b) –2, , (c) 3, , (a) 2, 4, 8, 16, ..., , (d) –3, 1, , 5 7, (b) 2, ,3 ....., 2 2
Page 2 :
22. The sum of first 5 multiples of 3 is :, , (c) 0.22, 0.22, 0.222, 0.2222, ..., (d) 1, 3, 9, 27, ..., , (a) 45, , 7. The 10th term of the A.P. 5, 8, 11, 14, .... is :, (c) 38, , (d) 185, , 8. The list of numbers – 10, – 6, – 2, 2 .... is :, , (a) 0, , (a) an A.P. with a = – 16, (d) not an A.P., , (b) 3, , (c) 4, , (b) 8.5, , (c) 103.5, , (a) – 10, , (a) 56, , S, , (c) – 5, (d) 10, 5, 5, 14. The 11th term of the A.P. −5, − , 0, ,... is :, 2, 2, (a) – 20, (b) 20, (c) – 30, (d) 30, , TH, , O, , (c) 22nd, , (d) 38, , 17. If the numbers a, b, c are in A.P., then :, , O, , (c) a – b = b – c, , (b) b + a = c + b, , (c) 45, , (b) 9th, , (c) 10th, , (a) 10, , (b) Newton, , (c) Gauss, , (d) Euclid, , (a) 7, , (b) 320, , (d) 30, , (b) 137, , (c) 143, , (d) – 143, , (b) – 8, , (c) 4, , (d) – 4, , (b) 33, , (c) 37, , (d) 38, , (b) 20, , (c) 30, , (d) 40, , (b) 11, , (c) 18, , (d) 0, , 35. What is the sum of all natural numbers from 1, to 100?, (a) 4550, , 21. The sum of first 16 terms of the A.P. 10, 6, 2, ..., is :, (a) – 320, , (c) 25, , 34. If 11 times the 11th term of an A.P. is equal to 7, times its 7th term, then its 18th term will be :, , (d) 11th, , 20. The famous mathematician associated with finding, the sum of first 100 natural numbers is :, (a) Pythagoras, , (b) 20, , 33. How many numbers of 2-digits are divisible by 3?, , (d) 49, , 19. Which term of the A.P. 72, 63, 54, .... is 0?, (a) 8th, , (a) 5, , (a) 30, , G, , (b) 55, , (d) – 2, – 4, – 8, – 16, , 32. If 2nd term of an A.P. is 13 and the 5th term is, 25, then its 7th term is :, , (d) none of these, , 18. How many terms are there in the A.P. 7, 10, 13,, ..., 151?, (a) 50, , (c) – 2, – 4, – 6, – 8, , (a) 8, , YA, , (a) b – a = c – b, , (b) – 2, 4, – 8, – 16, , 31. Two A.P.s have the same common difference. The, first term of one of these is – 2 and that of the, other is – 10. The difference between their 10th, terms is :, , R, , B, , (c) 36, , L, , (b) 30, , (a) – 2, 0, 2, 4, , (a) 17, , (d) 16th, , 16. How many terms are there in the A.P. 1, 3, 5, ...., 73, 75?, (a) 28, , (d) 50, , 30. The first two terms of an A.P. are – 3 and 4. The, 21st term of the A.P. will be :, , 15. Which term of the A.P. 4, 9, 14, 19, ... is 109?, (b) 18th, , (c) 46, , 29. If the common difference of an A.P. is 5, then, what is t18 – t13?, , ER, , (b) – 10, , (a) 14th, , (d) 10, , 28. The first four terms of an A.P. whose first term, is – 2 and the common difference is – 2, are :, , 13. If first term of an A.P. is 2 and common difference, is – 2, then t7 is :, (a) – 8, , (b) 41, , K, , (d) 2n – 3, , (c) 7, , A, , (c) 3n – 2, , (b) – 7, , PR, , (b) 2n – 1, , (d) 42, , 27. The first term of an A.P. is 6 and its common, difference is 5. What will be its 11th term?, , (d) 150, , 12. The nth term of the A.P. 2, 5, 8, ... is :, (a) 3n – 1, , (c) 38, , N, , (d) 28, , 11. In an A.P., if a = 8.5, d = 0, n = 57, then tn will, be :, (a) 0, , (b) 21, , 25. The sum of first n natural numbers is :, , (d) 5, , (c) 20, , (d) 15, , A, , (b) 7, , (c) 6, , (a) n2, (b) n(n + 1), n(n − 1), n(n + 1), (c), (d), 2, 2, 26. If 4th term of an A.P. is 14 and its 12th term is, 70, what is its first term?, , 10. In an A.P., if tn = 4, d = – 4, and n = 7, then a, is :, (a) 6, , (b) 5, , (a) 19, , 9. In an A.P., if a = – 7.2, d = 3.6 and tn = 7.2, then, n is :, (a) 1, , (d) 75, , 24. In an A.P., if a = 1, tn = 20 and Sn = 399, then, n is :, , (b) an A.P. with a = – 4, (c) an A.P. with a = 4, , (c) 65, , SH, , (b) 35, , A, , (a) 32, , (b) 55, , 23. The first term of an A.P. is – 5 and the common, difference is 2. The sum of first 6 terms of this, A.P. is:, , (b) 4780, , (c) 5050, , (d) 5150, , 36. 51 + 52 + 53 + ... + 100 = ?, (a) 3775, , (c) – 352 (d) – 400, 2, , (b) 4025, , (c) 4275, , (d) 5050
Page 3 :
37. If the sum of p terms of an A.P. is q and the sum, of q terms is p, then the sum of (p + q) terms, will be:, , (a) 4n – 3 (b) 3n – 4 (c) 4n + 3 (d) 3n + 4, 41. If the first term of an A.P. is 2 and common, difference is 4, then the sum of its 40 terms is:, , (b) p – q, , (a) 3200, , (d) – (p + q), , (b) 3, , (c) 1, , (a) 1625, , 39. If the sum of n terms of an A.P. be 3n2 + 5n,, then which of its terms is 164?, (b) 27th, , (c) 28th, , (d) none of these, , (d) 2800, , (b) 1525, , (c) 1725, , (d) 1650, , 43. The sum of first n positive integers is given by:, n(2n + 1), n(n − 1), (a), (b), 2, 2, n(n + 1), (c), (d) none of these, 2, 44. The sum of first n even integers is given by :, , (d) 4, , (a) 26th, , (c) 200, , 42. 25 + 28 + 31 + .... + 100 = ?, , 38. If the sum of n terms of an A.P. be 3n2 – n and, its common difference is 6, then its first term, is:, (a) 2, , (b) 1600, , n(n + 1), 2, (c) (n + 1)(n – 1) (d) none of these, , (a) n(n + 1), , (b), , SH, , 40. If the sum of n terms of an A.P. is 2n2 + 5n, then, its nth term is :, , N, , (c) p + q , , A, , (a) 0 , , A, , B. Questions From CBSE Examination Papers, , 9. Which term of the A.P. 92, 88, 84, 80, .... is 0?, , (c) 10th, , A, , (b) 9th, , (d) 12th, , 2. Which term of the A.P. 2, –1, –4, .......... is –70?, (b) 18th, , [2011 (T-II)], , (c) 25th, , (d) 30th, , (b) 40, , (c) 43, , (d) 58, , TH, , (a) 37, , R, , O, , 4. Which term of the A.P. 21, 42,, 63 ..................., is 210?, [2011 (T-II)], (a) 9th, (b) 10th, (c) 12th, (d) 11th, , (c) 4, , L, , (b) –8, , B, , 5. What is the common difference of the A.P. in, which a18 – a14 = 32 ?, [2011 (T-II)], (a) 8, , (d), , (a) –3, (b) –2, (c) 3, (d), 2, 13. If an A.P. has a = 1, tn = 20 and Sn = 399, then, value of n is :, [2011 (T-II)], , –4, , (a) 20, (b) 32, (c) 38, (d) 40, 14. If a + 1, 2a + 1, 4a – 1 are in A.P., then the, value of a is :, [2011 (T-II)], , 27, 48, 75 , .... is :, [2011 (T-II)], , O, , 105 (b) 107 (c) 108 (d) 147, 7. Which term of the A.P. 100, 90, 80....... is zero?, , G, , (a), , YA, , 6. The next term of the A.P., , , (a) 5th, , (b) 6th, , (c) 10th, , (b) –9, , ER, , 3. The 4th term from the end of A.P. –11, –8, –5,, ................... 49 is :, [2011 (T-II)], , (a) 9, , [2011 (T-II)], , (c) 18, (d) 23, 3+ n, 11. If the nth term of an A.P. is, , then its 8th, 4, term is :, [2011 (T-II)], 11, (a) 11, (b), (c) 11, (d) 22, 4, 2, 12. If a, a – 2 and 3a are in A.P., then the value of, a is :, [2011 (T-II)], , S, , (a) 15th, , [2011 (T-II)], , (a) 23, (b) 32, (c) 22, (d) 24, 10. For an A.P. if a25 – a20 = 45, then d equals to :, , PR, , (a) 8th, , K, , 1. Which term of the A.P. 24, 21, 18, ..................., is the first negative term?, [2011 (T-II)], , (a) 1, (b) 2, (c) 3, (d) 4, 15. The sum of the first n terms of an A.P. is 2n2 + 5n., Then its nth term is :, [2011 (T-II)], , [2011 (T-II)], , (d) 11th, , (a) 4n + 3, , 8. Which of the following is not an A.P., , (b) 4n – 3, , (c) 3n – 4, (d) 3n + 4, 16. For what value of p are 2p + 1, 13, 5p – 3, three, consecutive terms of an A.P.?, [2011 (T-II)], , [2011 (T-II)], , (a) 13, 8, 3, –2, –7, –12, , (a) 2, (b) –2, (c) 4, (d) –4, 17. Which term of the A.P., 113, 108, 103, ..............., is the first negative term?, [2011 (T-II)], , (b) 10.8, 11.2, 11.6, 12, 12.4, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, (c) 8 ,18 , 28 , 48 ,58, 7, 7, 7, 7, 7, 3, 6, 9, 12, (d) 8 ,11 ,14 ,17, 23, 23, 23, 23, 3, , (a) 22nd term, , (b) 24th term, , (c) 26th term, , (d) 28th term
Page 4 :
18. 15th term of the A.P., x – 7, x – 2, x + 3,....is :, , (c) x + 83, (d) x + 53, 19. If p –1, p + 3, 3p – 1 are in A.P., then p is equal, to:, [2011 (T-II)], (a) 4, (b) – 4, (c) 2, (d) – 2, , [2011 (T-II)], , (a) x + 63, , (b) x + 73, , SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS, , [2 Marks, , a. important Questions, 1. For the A.P. – 3, – 7, – 11, ... can we find directly, t30 – t20 without actually finding t30 and t20? Give, reasons for your answer., , 10. Is 0 a term of the A.P. 31, 28, 25, ... ? Justify, your answer., 11. If the numbers of x – 2, 4x – 1, and 5x + 2 are, in A.P find the value of x., , 2. Is 68 a term of the A.P. 7, 10, 13, ...?, , 12. Verify that each of the following is an A.P. :, , N, , 3. The 4th term of an A.P. is three times the first, term and the 7th term exceeds twice the third, term by 1. Find the first term and the common, difference., , A, , (a) x + y, (x + 1) + y, (x + 1) + (y + 1), ..., , SH, , (b) x, 2x + 1, 3x + 2, 4x + 3, ..., 13. Find a, b and c, if the numbers a, 7, b, 23, c are, in A.P.., 14. Find the number of terms of the A.P. 17, 14.5,, 12, .... – 38., , 5. The nth term of an A.P. cannot be m2 + 1. Justify, your answer., , 15. The sum of n terms of a sequence is 3n2 + 4n., Find the nth term and show that it is an A.P.., , PR, , A, , K, , A, , 4. Shonal deposited Rs 1000 at compound interest, at the rate of 10% p.a. The amounts at the end, of first year, second year, third year .... form an, A.P. Justify your answer., [HOTS], , 16. The sum of first n terms of an A.P. is given by, 3n2 – n. Determine the A.P. and its 25th term., 11, 17. How many terms of the A.P. −6 − , −5... are, 2, needed to give the sum – 25?, , ER, , S, , 6. Write the expression tn – tm for the A.P. a, a + d,, a + 2d, ..... Hence, find the common difference of, the A.P. for which 11th term is 5 and 13th term, is 79., , 7. Show that x – y, x and x + y form consecutive, terms of an A.P., , TH, , 18. Find the sum of first n odd natural numbers., 19. Show that the sum of all odd integers between 1 and, 100 which are divisible by 3 is 83667. [HOTS], , 9. Which term of the A.P. 32, 29, 26, ... is first, negative term?, , 20. If tn = 3 – 4n, show that t1, t2, t3, ... form an A.P., Also, find S20., [HOTS], , B, , R, , O, , 8. Justify whether it is true to say that 2n – 3 is the, nth term of an A.P., , L, , B. Questions From CBSE Examination Papers, 8. If the nth term of an A.P. is (2n + 1), find the, sum of first n terms of the A.P., [2011 (T-II)], , 2. Calculate how many multiples of 7 are there, between 100 and 300. [2011 (T-II)], , 9. The 8th term of an A.P. is 37 and its 12th term, is 57. Find the A.P., [2011 (T-II)], , G, , O, , YA, , 1. Which term of the A.P., 6, 13, 20, 27, ..............., is 98 more than its 24th term ? [2011 (T-II)], , 3. If Sn denotes the sum of n terms of an AP whose, common difference is d and first term is a, find, Sn – 2Sn–1 + Sn–2. , [2011 (T-II)], , 10. Which term of the A.P. 3, 15, 27, 39,............. is, 132 more than its 54th term?, [2011 (T-II)], , 5. Determine the 2nd term of an A.P. whose 6th, term is 12 and 8th term is 22., [2011 (T-II)], , 12. For an A.P. show that a p + a p + 2 = 2a p + q, , 11. In an A.P. the first term is – 4, the last term is, 29 and the sum of all its terms is 150.Find the, common difference of the A.P., [2011 (T-II)], , 4. Find the sum of all two digit positive numbers, divisible by 3., [2011 (T-II)], , [2011 (T-II)], , 6. Find the sum of first 10 terms of the sequence, {an} where an = 5 – 6n, where n is a natural, number., [2011 (T-II)], , 13. Find the common difference of an A.P. whose first, 1, term is, and the 8th term is 17 . Also write its, 2, 6, 4th term., [2011 (T-II)], , 7. Find the sum of the first 50 odd natural, numbers., [2011 (T-II)], 4
Page 5 :
14. Find the sum of first twelve multiples of 7., , 23. If the sum of first n terms of an A.P. is given by, Sn = 4n2 – 3n, find the nth term of the A.P., [2004C], 24. If the sum of first n terms of an A.P. is given by, Sn = 2n2 + 5n, find the nth term of the A.P., [2004C], 25. Find the number of terms of the A.P. 54, 51, 48,, .... so that their sum is 513., [2005], 26. Find the sum of the first 51 terms of the A.P., whose 2nd term is 2 and 4th term is 8. [2005C], 27. The sum of the first n terms of an A.P. is given, by Sn = 3n2 – n. Determine the A.P. and its 25th, term., [2005C], 28. The sum of three numbers in A.P. is 27 and their, product is 405. Find the numbers., [2005C], 29. How many terms are there in an A.P. whose first, term and 6th term are – 12 and 8 respectively, and sum of all its terms is 120?, [2006], 5n 2 3n, 30. In an A.P. the sum of first n terms is, + ., 2, 2, Find its 20th term., [2006C], 31. The first term, common difference and last term, of an A.P. are 12, 6 and 252 respectively. Find, the sum of all terms of this A.P., [2007], , [2011 (T-II)], , 15. Find the sum of the 25 terms of an A.P. whose, nth term is given by tn = 7 – 3n. [2011 (T-II)], 16. How many terms are there in A.P., 7, 16, 25, .........., 349?, , [2011 (T-II)], , 17. Find the number of terms of the series:, – 5 + (– 8) + (– 11) + ............. + (– 230), , , , [2011 (T-II)], , 18. Which term of the arithmetic progression 3, 10,, 17.......... will be 84 more than its 13th term ?, , [2011 (T-II)], , N, , 19. Find the number of all 2 digit numbers divisible, by 3., [2011 (T-II)], , SH, , A, , 20. Find the value of p, if the numbers x, 2x + p,, 3x + 6, are three consecutive terms of an A.P. , [2011 (T-II)], , A, , 21. If 6th term of an A.P. is –10 and its 10th term, is –26, then find the 15th term of the A.P., , K, , [2011 (T-II)], , PR, , S, , SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS, , A, , 22. If 8th term of an A.P. is 31 and 15th term is 16, more than 11th term, find the A.P. [2011 (T-II)], , [3 Marks], , ER, , A. Important Questions, 10. The sum of first three terms of an A.P. is 33. If, the product of the first and the third terms exceeds, the second term by 29, find the A.P., a + b 3a − 2b 5a − 3b, 11. Find the sum =, +, +, + ... to, a−b, a+b, a+b, 11 terms., , TH, , 1. Determine the A.P. whose 5th term is 19 and the, difference of the eight term from the thirteeth term, is 20., , R, , O, , 2. The sum of first three terms of an A.P. is 21 and, their product is 231. Find the numbers. [Imp.], 3. What are the middle most terms of the A.P. – 11,, – 7, – 3, ... 49?, , B, , 12. If Sn denotes the sum of first n terms of an A.P.,, prove that S12 = 3(S8 – S4)., , L, , 4. The 26th, 11th and the last term of an A.P. are, 1, 0, 3 and − respectively. Find the common, 5, difference and the number of terms., , YA, , 13. If the numbers a, b, c, d, e, form an A.P., then, find the value of a – 4b + 6c – 4d + e., , O, , 14. In an A.P. if the first term is 22, the common, difference is – 4 and the sum of n terms is 64,, find n., , G, , 5. If the 9th term of an A.P. is zero, prove that its, 29th term is twice its 19th term., , 15. Split 207 into three parts such that these are in, A.P. and the product of the two smaller parts is, 4623., , 6. The sum of first 6 terms of an A.P. is 42. The, ratio of the 10th term to the 30th term is 1 : 3., Find the first term and the 11th term of the A.P., , 16. How many terms of the A.P. – 15, – 13, – 11, ..., are needed to make the sum – 55? Explain the, reason for the double answer., [HOTS], , 7. If the nth terms of two A.Ps. 9, 7, 5, ... and, 24, 21, 18, ... are same, find the value of n. Also,, find that term., , 17. The sum of first n terms of an A.P. whose first, term is 8 the common difference is 20 is equal, to the sum of first 2n terms of another A.P. whoe, first term is – 30 and the common difference is, 8. Find n., , 8. How many numbers lie between 10 and 30 which, when divided by 4 leave a remainder 3?, 9. If (m + 1)th term of an A.P. is twice the (n + 1), th term, prove that (3m + 1)th term is twice the, (m + n + 1)th term., 5
Page 6 :
18. If a, b, c are in A.P., show that (a – c)2 = 4, (b2 – ac)., , 21. The pth term of an A.P is q and qth term is p., Find its (p + q)th term., 22. If a, b, c are in A.P., show that, 1 1 1, , ,, are in A.P., (i), bc ca ab, (ii) a2 (b + c), b2(c + a), c2(a + b) are in A.P., , 19. Reshma saves Rs 32 during the first month, Rs 36, in the second month and Rs 40 in the third month., If she continues to save in this manner, in how, many months will she save Rs 2000? [HOTS], 20. A manufacturer of radio sets produced 800 units, in the third year and 700 units in the seventh year., Assuming that the product increases uniformly by, a fixed number every year, find, (i) the production in the first year, (ii) the production in the 10th year., , A, , B. questions From CBSE Examination Papers, , N, , 23. If a 2 , b 2 , c 2 are in A.P., then prove that, 1, 1, 1, ,, ,, are in A.P., [HOTS], b+c c+a a+b, 24. If the sum of m terms of an A.P. is the same, as the sum of n terms, show that the sum of its, (m + n) terms is 0., [HOTS], , 14. The ticket receipts at the show of a film amounted, to Rs 6,500 on the first day and showed a drop of, Rs 110 every succeeding day. If the operational, expenses of the show are Rs 1000 a day, Find on, which day the show ceases to be profitable., [2011 (T-II)], , SH, , 1. Which term of the A.P. : 3, 15, 27, 39, ...... will, be 120 more then its 21st term ? [2011 (T-II)], , K, , A, , 2. The sum of the first n terms of an A.P. is 5n 2 - 3n., Find the A.P. and hence find its 12th term., [2011 (T-II)], , A, , 3. The angles of a triangle are in A.P. The greatest, angle is twice the least. Find all angles of the, triangle., [2011 (T-II)], , PR, , 15. Find the sum of all the two-digit natural numbers, which are divisible by 4., [2011 (T-II)], 16. Determine ‘a’ so that 2a + 1, a 2 + a + 1 and, 3a 2 - 3a + 3 are consecutive terms of an A.P., [2011 (T-II)], , S, , 4. Find the sum of all natural numbers between 200, and 1000 exactly divisible by 6. [2011 (T-II)], 5. Find the value of the middle most term(s) of the, arithmetic progression :, [2011 (T-II)], , ER, , 17. If the sum of first m terms of an A.P. is n and, the sum of first n terms in m, then show that the, sum of its first (m + n) terms is – (m + n)., [2011 (T-II)], , TH, , – 11, – 7, – 3, ............49., , 6. The sum of first six terms of an arithmetic, progression is 42. The ratio of its 10th term to its, 30th term is 1 : 3. Find the first and the thirteenth, term of the A.P., [2011 (T-II)], , R, , O, , 18. How many terms of the A.P. – 6, –11/2, –5, ....., are needed to give the sum – 25 ? [2011 (T-II)], 19. If the sum of all the terms of an A.P. 1, 4, 7, 10,, ........., x. is 287, find x., [2011 (T-II)], , B, , 7. How many terms of the A.P. 9, 17, 25, ....., must, be taken to get a sum of 450 ?, [2011 (T-II)], , 20. How many terms of the A.P. 78, 71, 64, ..... are, needed to give the sum 465 ? Also find the last, term of this A.P., [2011 (T-II)], , YA, , L, , 8. Find the sum of all two digit odd positive, numbers., [2011 (T-II)], 9. If the sum of first fourteen terms, of an AP is, 1050 and its first term is 10, find its 20th term., [2011 (T-II)], , G, , O, , 21. The 4th term of an A.P. is equal to 3 times the, first term and the 7th term exceeds twice the 3rd, term by 1. Find the first term and the common, difference., [2011 (T-II)], , 10. If the sum of first n terms of an A.P. is 4n2 – n,, find the 12th term., [2011 (T-II)], , 22. Find three numbers in A.P. whose sum is 15 and, whose product is 105., [2011 (T-II)], , 11. The sum of first three terms of an A.P. is 33. If, the product of the first and third term exceeds the, second term by 29, find the A.P. [2011 (T-II)], , 23. The sum of the 5th and 7th terms of an A.P. is, 52 and its 10th term is 46. Find the A.P., [2011 (T-II)], , 12. Which term is the first negative term in the given, 1, A.P. : 23, 21 , 20, ........ ?, [2011 (T-II)], 2, 13. In an A.P. the first term is –4, the last term is, 29 and the sum of all its term is 150. Find its, common difference., [2011 (T-II)], , 24. Sum of the first n terms of an A.P. is 5n2 – 3n., Find the A.P. and also find its 16th term., [2011 (T-II)], 25. Find the sum of all three digit numbers which, leave the same remainder 2 when divided by 5., [2011 (T-II)], 6
Page 7 :
29. The sum of first six terms of an A.P. is 42. The, ratio of its 10th term to its 30th term is 1 : 3., Calculate the first and the thirteenth terms of the, A.P., [2009], , 26. For what value of n are the nth terms of two A.P., 63, 65, 67 ... and 3, 10, 17 ... equal ?, [2008], 27. If the sum of first 7 terms of an A.P. is 49 and, that of first 17 terms is 289, find the sum of first, n terms., [2008C], , 30. The sum of the first sixteen terms of an A.P. is, 112 and the sum of its next fourteen terms is 518., Find the A.P., [2010], , 28. If the 8th term of an A.P. is 37 and the 15th term, is 15 more than the 12th term, find the A.P. Hence, find the sum of the first 15 terms of the A.P., [2008C], , LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS, , [4 Marks], , A. Important Questions, 7. An A.P. consists of 37 terms. The sum of three, middle most terms is 225 and the sum of the last, three is 429. Find the A.P., 1, 8. If mth term of an A.P. is 1 and the nth term is, ,, m, n, 1, show that the sum of its mn terms is (mn + 1) ., 2, 9. If S1, S2, S3 be the sums of n, 2n and 3n terms, respectively of an A.P, prove that S3 = 3(S2 – S1)., , A, , K, , A, , SH, , A, , N, , 1. The sum of four consecutive numbers in an A.P., is 32 and the ratio of the product of the first and, the last terms to the product of the two middle, terms is 7 : 15. Find the numbers., 1 1 1, 2. If , , are in A.P., show that :, a b c, b+c c+a a+b, (i), are in A.P., ,, ,, a, b, c, (ii) bc, ca, ab are in A.P., , PR, , 10. Prove that no matter what the real numbers a, and b are, the sequence with nth term a + nb is, always an A.P. What is the common difference?, What is the sum of the first 20 terms? [HOTS], , 3. Find the sum of those integers :, , S, , (a) between 1 and 500 which are multiples of 2 as, well as of 5., , 11. A contractor employed 150 labourers to finish a, piece of work in a certain number of days. 4 workers, went away the second day, 4 more workers went, away the third day and so on. If it took 8 more, days to finish the work, find the number of days, in which the work was completed., [HOTS], , ER, , (b) from 1 to 500 which are multiples of 2 as well, as of 5., , TH, , (c) from 1 to 500 which are multiples of 2, or 5., , O, , 4. If pth, qth and rth terms of an A.P. are a, b and, c respectively, then show that :, , R, , 12. The students of a school decided to beautify the, school on the annual day by fixing colourful flags, on the straight passage of the school. They have, 27 flags to be fixed at interval of every 2m. The, flags are stored in the position of the middle, most flag. Ruchi was given the responsibility of, placing the flags. Ruchi kept her books where the, flags were stored. She could carry only one flag, at a time. How much distance did she cover in, completing this jobs and returning back to collect, her books? What is the maximum distance she, travelled carrying a flag?, [HOTS], , B, , (a) a(q – r) + b(r – p) + c(p – q) = 0 , (b) (a – b)r + (b – c)p + (c – a)q = 0, , L, , 5. Solve the equation, , YA, , 1 + 4 + 7 + 10 + .... + x = 287., , G, , O, , 6. The sums of x terms of three A.P.s are S1, S2, and S3. The first term of each is unity and the, common differences are 1, 2 and 3 respectively., Prove that S1 + S3 = 2S2., , B. Questions From CBSE Examination Papers, 1. In an A.P. the sum of first ten terms is –80 and the, sum of next ten terms is –280. Find the A.P., , instalment of 1000. He increases the instalment, by Rs 100 every month. What amount will be, paid by him in the 30th instalment? What amount, of loan does he still have to pay after the 30th, [2011 (T-II)], instalment?, , , [2011 (T-II)], 2. The sum of first 7 terms of an A.P. is 49 and that, of first 17 terms is 289. Find the sum of first n, terms., [2011 (T-II)], 3. Kartik repays his total loan of Rs. 1,18,000, by paying every month starting with the first, , 4. In an A.P., the sum of first n terms is given by, 3n 2 5n, Sn =, +, . Find the 25th term of the A.P., 2, 2, 7
Page 8 :
5. A contractor on construction job specifies a penalty, for delay of completion beyond a certain date, as follows : Rs 200 for the first day, Rs 250 for, the second day, Rs 300 for the third day etc. the, penalty for each succeeding day being Rs 50 more, than for the preceding day. How much money the, contractor has to pay as penalty if he has delayed, the work by 30 days ?, [2011 (T-II)], , as shown in the figure. what is the total length, of such spiral made up of thirteen consecutive, 22, semicircles? (Take π = ), [2011 (T-II)], 7, , 6. If a, b and c be the sums of first p, q and r terms, respectively of an AP, show that, a, b, c, (q − r ) + (r − p) + ( p − q) = 0 [2011 (T-II)], p, q, r, , 7. In November 2009, the number of visitors to a zoo, increased daily by 20. If a total of 12300 people, visited the zoo in that month, find the number of, visitors on 1st November 2009., [2011 (T-II)], , A, , N, , 15. A manufacturer of T.V. sets produced 600 sets in, the third year and 700 sets in the seventh year., Assuming that the production increases uniformly, by a fixed number every year, find, , SH, , 8. For what value of n, the nth terms of the A.P., 63, 65, 67, .... and 3, 10, 17, ......... are equal?, [2011 (T-II)], Also find that term., , (a) The production in the first year, , A, , (b) The production in the 10th year, , 9. A ladder has rungs 25 cm apart. The rungs decrease, uniformly in length from 45 cm at the bottom, to 25 cm at the top (see figure). If the top and, bottom rungs are 2.5 m apart, what is the length, of the wood required for the rungs? [2011 (T-II)], , A, , K, , (c) The total production in first 7 years, , , [2011 (T-II)], , ER, , S, , PR, , 16. The houses of a row are numbered consecutively, from 1 to 49. There is a value of x such that the, sum of the numbers of the houses preceding the, house numbered x is equal to the sum of the, number of the houses following it. Find this value, of x., [2011 (T-II)], , O, , TH, , 17. Show that the sum of all odd integers between 1, and 1000 which are divisible by 3 is 83667., , [2011 (T-II)], , B, , R, , 18. The 4th term of an A.P. is equal to 3 times the, first term and the 7th term exceeds twice the 3rd, term by 1. Find the A.P., [2011 (T-II)], , 10. Find the sum of the first 31 terms of an A.P. whose, 2, nth term is given by 3 +, n., [2011 (T-II)], 3, 11. The sum of the third and seventh term of an A.P., is 6 and their product is 8. Find the sum of the, first sixteen terms of the A.P., [2011 (T-II)], , YA, , L, , 19. Find the sum of all multiples of 9 lying between, 300 and 700., [2011 (T-II)], , G, , O, , 20. A woman takes up a job of Rs 8000 per month, with an annual increment of Rs 100. What will, she earn over a period of 10 years ? [2011 (T-II)], 21. 228 logs are to be stacked in a store in the, following manner: 30 logs in the bottom, 28 in, the next row, then 26 and so on. In how many, rows can these 228 logs be stacekd? How many, logs are there in the last row?, [2011 (T-II)], , 12. A sum of Rs 2700 is to be used to give eight cash, prizes to students of a school for their overall, academic performance. If each prize is Rs 25, more than its preceding prize find the value of, each of the prizes., [2011 (T-II)], , 22. Neera saves Rs 1600 during the first year, Rs 2100, in the second year, Rs 2600 in the third year. If, she continues her savings in this pattern, in how, many years will she save Rs 38500? [2011 (T-II)], , 13. In an A.P., prove that am +n + am - n = 2am , where aa, denotes nth term of the A.P., , [2011 (T-II)], , 14. A spiral is made up of successive semicircles,, with centres alternatively at A and B, starting with, centre at A of radii 0.5 cm, 1 cm, 1.5 cm, 2 cm...., , 23. If m times the mth term of an A.P. is equal to n, times its nth term, show that the (m+n)th term of, the A.P. is zero (m ≠ n)., [2011 (T-II)], 8
Page 9 :
Formative Assessment, Activity-1, , Observations :, , Objective : To verify that the given sequence is an, arithmetic progression by paper cutting and pasting, method., , 1. For figure 1:, The difference between the heights of first and, second strips = 3 cm., , Materials Requried : Squared paper, colour pencils,, geometry box, etc., , The difference between the heights of second and, third strips = 3 cm., , Procedure :, , The difference between the heights of third and, fourth strips = 3 cm., , Case 1. Let the given sequence be 1, 4, 7, 10, 13, ..., , The difference between the heights of fourth and, the fifth strips = 3 cm., , N, , 1. Take a squared paper. Using a colour pencil,, colour 1 square (1 is the first term of the given, sequence)., , A, , 2. If we consider figure 1 as a ladder, then we can say, that the difference between the heights of adjoining, steps of this ladder is constant, which is 3 cm., , SH, , 2. Using a different colour pencils, colour 4, squares vertically (4 is the 2nd term of the given, sequence)., , A, , 3. For figure 2 :, , The difference between the heights of first and, second strips = 2 cm., , 4. Colour 10 squares vertically (10 is the 4th term of, the sequence) and so on., , The difference between the heights of second and, third strips = 3 cm., , O, , TH, , ER, , S, , PR, , A, , K, , 3. Colour 7 squares vertically (7 is the 3rd term of the, sequence)., , The difference between the heights of fourth and, fifth strips = 2 cm., , 4. If we consider figure 2 as a ladder, then we can say, that the difference between the heights of adjoining, steps of this ladder is not constant., , B, , R, , Conclusion : Squence 1 is an AP, as the difference, between its consecutive terms is constant. Sequence 2 is, not an AP, as the difference between its consecutive terms, is not constant., , L, , Activity-2, , YA, O, , G, , Figure 1, , The difference between the heights of third and, fourth strips = 2 cm., , Objective : To verify that the sum of first n natural, n ( n + 1), numbers is, by activity method., 2, , Figure 2, , Materials Required : Squared paper, colour pencils,, geomety box, a pair of scissors, white sheets of paper,, gluestick, etc., , Case 2. Let the sequence be 1, 3, 6, 8, 10, 12, …, 1. Take a squared paper. Using a colour pencil, colour, 1 square (1 is the first term of the sequence)., , Procedure : Let us find the sum of first 12 natural, numbers, ie, 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + … + 12., , 2. Using a different colour pencil, colour 3 squares, vertically (3 is the second term of the sequence)., , 1. Take a squared paper of size 12 cm × 12 cm. With, the help of colour pencils, shade rectangles of length, 1 cm, 2 cm, 3 cm, 4 cm, … 12 cm and of width 1, cm each, as shown in figure 3. Mark the rectangles, as 1, 2, 3, … 12 respectivety from top to bottom., , 3. Next colour 6 squares vertically (6 is the third term, of the sequence)., 4. Colour 8 squares vertically (8 is the fourth term of, the sequence) and so on., 9
Page 10 :
Observations :, 1. The area of the shaded region in figure 3, = (1×1 + 1×2 + 1×3 + 1×4 + … + 1×12) cm2, = (1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + … + 12) cm2, 2. The area of the shaded region in figure 4, = (1×1 + 1×2 + 1×3 + 1×4 + … + 1×12) cm2 = (1 +, 2 + 3 + 4 + … + 12) cm2, 3. Since, figure 5 is comprised of shaded regions of, figures 1 and 2 so, area of figure 5, = 2 (1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + … + 12) cm2, , N, , 4. But, figure 5 is a rectangle of dimensions 12 cm × 13, cm or 12 cm × (12 + 1) cm, So, its area = 12(12 + 1) cm2, , A, , Figure 3, , A, , K, , A, , SH, , 5. From 3 and 4 above, 2 (1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + … + 12) = 12, × (12 + 1), 12 × (12 + 1), ⇒ 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + … + 12 =, ., 2, 12(12 + 1), ., ⇒ sum of first 12 natural numbers =, 2, , S, , PR, , �So, sum of first n natural numbers = 1 + 2 + 3 + …, n(n + 1), ., +n=, 2, Do Yourself :, , TH, , ER, , Repeat the above activity by considering the sum of first, 20 natural numbers., , Figure 4, , Activity-3, , 2. Take another squared paper of size 12 cm ×12 cm., Shade rectangles of length 1 cm, 2 cm, 3 cm, …, 12 cm and of width 1 cm each, in riverse order as, shown in figure 4. Mark the rectangles as 1, 2, 3,, … 12 respectivety from bottom to top., 3. Now, cut out the coloured portions of figures 3 and, 4 and paste them together on a white sheet of paper, as shown in figure 5., , R, , O, , Objective : To verify that the sum of first n odd natural, numbers is given by n2 by an activity method., , YA, , L, , B, , Materials Required : Squared paper, colour pencils,, white sheets of paper, a pair of scissors, geometry box,, gluestick, etc., Procedure :, , G, , O, , 1. Take a squared paper of size 10 cm × 10 cm. Using, a colour pencil, shade its top left square., 2. Colour the three squares adjacent to the above, square, using a different colour., 3. Colour the five squares, which are adjacent to the, previous squares using a different colour., 4. Colour seven squares which are adjacent to the, previous squares, using a different colour., 5. Continue this process till you shade all the, squares., , Figure 5, , 10
Page 11 :
Procedure :, , Let the AP be 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20., Here, a = 4, d = 2, and t9 = 20, , A, , N, , 1. Take a squared paper of dimensions 9 cm × 20, cm., 2. Shade 4 squares of all the 9 rows as shown in, figure 7., , Figure 7, , Figure 6, , SH, , 3. Shade 1 × 2 = 2 more squares of second row using, different colour as shown in the figure 8., , Observations :, , ER, , S, , PR, , A, , K, , A, , 1. Area of the square shaded in step 1 = 1 cm2, 2. Total area of the squares shaded in steps 1 and 2, = (1 + 3) cm 2, 3. But, the squares shaded in steps 1 and 2 together, form another square of side 2 cm., So, its area = 22 cm2., 4. So, from 2 and 3 above, 1 + 3 = 22., 5. Area of squares shaded in steps 1, 2, and 3 = (1 +, 3 + 5) cm2., , TH, , 6. But, the squares shaded in steps 1, 2 and 3 together, form another square of side 3 cm., So, its area = 32 cm2., , Figure 8, , 4. Shade 2 × 2 = 4 more squares of third row as shown, in figure 9., , O, , 7. So, from 5 and 6 above, 1 + 3 + 5 = 32., , B, , R, , 8. Area of the squares shaded in steps 1, 2, 3 and 4 =, (1 + 3 + 5 + 7) cm2., , YA, , L, , 9. But, the squares shaded in steps 1, 2, 3 and 4, together form another square of side 4 cm., So, its area = 42 cm2., , 10. From 8 and 9 above, 1 + 3 + 5 + 7 = 42., , O, , Figure 9, , 11. Similarly, we can say that 1 + 3 + 5 + 7 + 9 + 11 +, 13 + 15 + 17 + 19 = 102, , G, , 5. Shade 3 × 2 = 6 more squares of fourth row., Continue this process up to the 9th row as shown, below., , or 1 + 3 + 5 + … up to 10 terms = 102, , , or 1 + 3 + 5 … up to n terms = n2, , Conclusion : From the above activity, we can say that the, sum of first n odd natural numbers is n2., , Activity-4, Objective : To find the formula for nth term of an, arithmetic progression., Materials Required : Squared paper, colour pencils,, geometry box, etc., , Figure 10, , 11
Page 12 :
Observations :, , is given by Tn = a + (n – 1)d., Do Yourself :Find the formula for nth term of an AP by, activity method taking the following AP’s, , 1. In figure 10,, the first row represents T1 = a = 4, the second row represents T2 = a + d = 4 + 2, the third row represents T3 = a + 2d = 4 + 2 × 2, the fourth row represents T4 = a + 3d = 4 + 3 × 2, the fifth row represents T5 = a + 4d = 4 + 4 × 2, the sixth row represents T6 = a + 5d = 4 + 5 × 2, the seventh row represents T7 = a + 6d = 4 + 6 × 2, the eighth row represents T8 = a + 7d = 4 + 7 × 2, the ninth row represents T9 = a + 8d = 4 + 8 × 2, 2. From 1 above, we have, T1 = a, T2 = a + d = a +, (2 – 1)d,, T3 = a + 2d = a + (3 – 1)d, ... T9 = a + 8d = a +, (9 – 1)d, If we continue the pattern, we can write Tn= a +, (n – 1)d, Conclusion : From the above activity, we find the nth term, of an AP whose first term is a and common difference d, , (i) 5, 8, 11, 14, 17, …, , Activity-5, Objective : To find the formula for the sum of n terms of, an arithmetic progression., Materials Required : Squared paper, colour pencils,, geometry box, a pair of scissors, white sheets of paper,, gluestick, etc., , N, , Procedure : Let us take the AP 1, 4, 7, 10, 13, 16, …, , A, , Here a = 1, d = 3, , K, , A, , SH, , 1. Take a squared paper of size 16 cm × 6 cm. With the, help of colour pencils, shade rectangles of length 1, cm, 4 cm, 7 cm, 10 cm, 13 cm, 16 cm and of width, 1 cm each as shown in the figure., , A, , T1 = 1, , PR, , T2 = 1 + 3 = 4, T3 = 1 + 2 × 3 = 7, , S, , T4 = 1 + 3 × 3 = 10, , ER, , T5 = 1 + 4 × 3 = 13, , TH, , T6 = 1 + 5 × 3 = 16, , Figure 11, , Observations :, , 2. Take another squared paper of size 16 cm × 6 cm., Shade rectangles of length 1 cm, 4 cm, 7 cm, 10, cm, 13 cm, 16 cm and of width 1 cm each in the, reverse order as shown in figure 12., , O, , 1. The area of the shaded region in the figure 11, , B, , R, , = (1×1 + 1×4 + 1×7 + 1×10 + 1×13 + 1×16) cm2, = (1 + 4 + 7 + 10 + 13 + 16) cm2, 2. The area of the shaded region in the figure 12, , YA, , L, , = (1×1 + 1×4 + 1×7 + 1×10 + 1×13 + 1×16) cm2, = (1 + 4 + 7 + 10 + 13 + 16) cm2, 3. Since, figure 13 is made up of the shaded regions, of figures 11 and 12, so area of figure 13, , O, G, , (ii) 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, …, , = 2 (1 + 4 + 7 + 10 + 13 + 16) cm2, , Figure 12, , 4. But, figure 13 is a rectangle of dimensions , 6 cm × 17 cm, So, its area = (6 × 17) cm2, 5. From 3 and 4 above we have,, 6, 6, 1 + 4 + 7 + 10 + 13 + 16 = × 17 = (1 + 16) =, 2, 2, 6, [1 +(1 + 5 × 3)] [ T6 = 16 = 1 + 5 × 3], 2, 6, 6, [2 + 5 × 3] = [2 +(6 – 1) 3], =, 2, 2, ⇒ T1 + T2 + T3 + T4 + T5 + T6 , , 3. Now, cut the coloured portions of figures 11 and 12, and paste them on a white sheet of paper as shown, in figure., , Figure 13, , 12
Page 13 :
=, , 6, [2a + (6 – 1)d], 2, [Replacing 1 by a and 3 by d], , ⇒ S6 = T1 + T2 + T3 + T4 + T5 + T6 =, [2a + (6 – 1)d], , 6, ⇒ T1 + T2 + T3 + T4 + T5 + T6 =, (1 + 16), 2, 6, = (T1 + T6), 2, n, 6, ⇒ S6 = (T1 + T6) ⇒ Sn = [T1 + Tn], 2, 2, [Extending the same pattern for n terms], , 6, 2, , n, [2a + (n – 1)d], 2, [Extending the pattern for n terms], , ⇒ Sn = T1 + T2 + T3 + … Tn =, , Conclusion :, 1. From the above activity, it is verified that, (a) the sum of first n terms of an AP whose first, term is a and common difference is d, is given, n, [2a + (n – 1)d], by Sn =, 2, , 6. From figure 13, the area of first row = 1 × (1 + 16), cm2, There are 6 rows in figure 13. So, area of firure , 13 = 6 × (1 + 16) cm2, , N, , (b) the sum of first n terms of an AP whose first, term is T1 and the last term is Tn, is given by, n, Sn = [T1 + Tn], 2, , A, , 7. From 3 and 6, we have , , A, , 6, (1+16), 2, , G, , O, , YA, , L, , B, , R, , O, , TH, , ER, , S, , PR, , A, , K, , ⇒ 1 + 4 +7 + 10 + 13 + 16 =, , SH, , 2(1 + 4 + 7 + 10 + 13 + 16) = 6 (1 + 16), , 13
Page 14 : Class X, , Chapter 5 – Arithmetic Progressions, , Maths, , Exercise 5.1, Question 1:, In which of the following situations, does the list of numbers involved, make as arithmetic progression and why?, (i) The taxi fare after each km when the fare is Rs 15 for the first km, and Rs 8 for each additional km., (ii) The amount of air present in a cylinder when a vacuum pump, removes, , of the air remaining in the cylinder at a time., , (iii) The cost of digging a well after every metre of digging, when it, costs Rs 150 for the first metre and rises by Rs 50 for each subsequent, metre., (iv)The amount of money in the account every year, when Rs 10000 is, deposited at compound interest at 8% per annum., Answer:, (i) It can be observed that, Taxi fare for 1st km = 15, Taxi fare for first 2 km = 15 + 8 = 23, Taxi fare for first 3 km = 23 + 8 = 31, Taxi fare for first 4 km = 31 + 8 = 39, Clearly 15, 23, 31, 39 … forms an A.P. because every term is 8 more, than the preceding term., (ii) Let the initial volume of air in a cylinder be V lit. In each stroke,, the vacuum pump removes, , of air remaining in the cylinder at a time., Page 1 of 70, , Website: www.vidhyarjan.com, , Email:
[email protected], , Mobile: 9999 249717, , Head Office: 1/3-H-A-2, Street # 6, East Azad Nagar, Delhi-110051, (One Km from ‘Welcome Metro Station)
Page 15 : Class X, , Chapter 5 – Arithmetic Progressions, , In other words, after every stroke, only, , Maths, , part of air will, , remain., , Therefore, volumes will be, Clearly, it can be observed that the adjacent terms of this series do, not have the same difference between them. Therefore, this is not an, A.P., (iii) Cost of digging for first metre = 150, Cost of digging for first 2 metres = 150 + 50 = 200, Cost of digging for first 3 metres = 200 + 50 = 250, Cost of digging for first 4 metres = 250 + 50 = 300, Clearly, 150, 200, 250, 300 … forms an A.P. because every term is 50, more than the preceding term., (iv) We know that if Rs P is deposited at r% compound interest per, , annum for n years, our money will be, , after n years., , Therefore, after every year, our money will be, , Clearly, adjacent terms of this series do not have the same difference, between them. Therefore, this is not an A.P., , Question 2:, Write first four terms of the A.P. when the first term a and the, common difference d are given as follows, Page 2 of 70, Website: www.vidhyarjan.com, , Email:
[email protected], , Mobile: 9999 249717, , Head Office: 1/3-H-A-2, Street # 6, East Azad Nagar, Delhi-110051, (One Km from ‘Welcome Metro Station)
Page 16 : Class X, , Chapter 5 – Arithmetic Progressions, , Maths, , (i) a = 10, d = 10, (ii) a = − 2, d = 0, (iii) a = 4, d = − 3, (iv) a = − 1 d =, (v) a = − 1.25, d = − 0.25, Answer:, (i) a = 10, d = 10, Let the series be a1, a2, a3, a4, a5 …, a1 = a = 10, a2 = a1 + d = 10 + 10 = 20, a3 = a2 + d = 20 + 10 = 30, a4 = a3 + d = 30 + 10 = 40, a5 = a4 + d = 40 + 10 = 50, Therefore, the series will be 10, 20, 30, 40, 50 …, First four terms of this A.P. will be 10, 20, 30, and 40., (ii) a = −2, d = 0, Let the series be a1, a2, a3, a4 …, a1 = a = −2, a2 = a1 + d = − 2 + 0 = −2, a3 = a2 + d = − 2 + 0 = −2, a4 = a3 + d = − 2 + 0 = −2, Therefore, the series will be −2, −2, −2, −2 …, First four terms of this A.P. will be −2, −2, −2 and −2., (iii) a = 4, d = −3, Page 3 of 70, Website: www.vidhyarjan.com, , Email:
[email protected], , Mobile: 9999 249717, , Head Office: 1/3-H-A-2, Street # 6, East Azad Nagar, Delhi-110051, (One Km from ‘Welcome Metro Station)
Page 17 : Class X, , Chapter 5 – Arithmetic Progressions, , Maths, , Let the series be a1, a2, a3, a4 …, a1 = a = 4, a2 = a1 + d = 4 − 3 = 1, a3 = a2 + d = 1 − 3 = −2, a4 = a3 + d = − 2 − 3 = −5, Therefore, the series will be 4, 1, −2 −5 …, First four terms of this A.P. will be 4, 1, −2 and −5., (iv) a = −1, d =, Let the series be a1, a2, a3, a4 …, , Clearly, the series will be, …………., First four terms of this A.P. will be, , ., , (v) a = −1.25, d = −0.25, Let the series be a1, a2, a3, a4 …, a1 = a = −1.25, a2 = a1 + d = − 1.25 − 0.25 = −1.50, a3 = a2 + d = − 1.50 − 0.25 = −1.75, Page 4 of 70, Website: www.vidhyarjan.com, , Email:
[email protected], , Mobile: 9999 249717, , Head Office: 1/3-H-A-2, Street # 6, East Azad Nagar, Delhi-110051, (One Km from ‘Welcome Metro Station)
Page 18 : Class X, , Chapter 5 – Arithmetic Progressions, , Maths, , a4 = a3 + d = − 1.75 − 0.25 = −2.00, Clearly, the series will be 1.25, −1.50, −1.75, −2.00 …….., First four terms of this A.P. will be −1.25, −1.50, −1.75 and −2.00., , Question 3:, For the following A.P.s, write the first term and the common, difference., (i) 3, 1, − 1, − 3 …, (ii) − 5, − 1, 3, 7 …, (iii), (iv) 0.6, 1.7, 2.8, 3.9 …, Answer:, (i) 3, 1, −1, −3 …, Here, first term, a = 3, Common difference, d = Second term − First term, = 1 − 3 = −2, (ii) −5, −1, 3, 7 …, Here, first term, a = −5, Common difference, d = Second term − First term, = (−1) − (−5) = − 1 + 5 = 4, (iii), Here, first term,, Common difference, d = Second term − First term, Page 5 of 70, Website: www.vidhyarjan.com, , Email:
[email protected], , Mobile: 9999 249717, , Head Office: 1/3-H-A-2, Street # 6, East Azad Nagar, Delhi-110051, (One Km from ‘Welcome Metro Station)
Page 19 : Class X, , Chapter 5 – Arithmetic Progressions, , Maths, , (iv) 0.6, 1.7, 2.8, 3.9 …, Here, first term, a = 0.6, Common difference, d = Second term − First term, = 1.7 − 0.6, = 1.1, , Page 6 of 70, Website: www.vidhyarjan.com, , Email:
[email protected], , Mobile: 9999 249717, , Head Office: 1/3-H-A-2, Street # 6, East Azad Nagar, Delhi-110051, (One Km from ‘Welcome Metro Station)
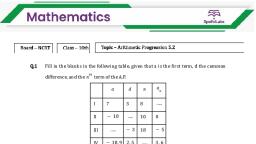
Page 20 : Class X, , Chapter 5 – Arithmetic Progressions, , Maths, , Exercise 5.2, Question 1:, Fill in the blanks in the following table, given that a is the first term, d, the common difference and an the nth term of the A.P., a, , d, , n, , an, , I, , 7, , 3, , 8, , …..., , II, , − 18, , ….., , 10, , 0, , III, , ….., , −3, , 18, , −5, , IV, , − 18.9, , 2.5, , ….., , 3.6, , V, , 3.5, , 0, , 105, , ….., , Answer:, I. a = 7, d = 3, n = 8, an = ?, We know that,, For an A.P. an = a + (n − 1) d, = 7 + (8 − 1) 3, = 7 + (7) 3, = 7 + 21 = 28, Hence, an = 28, II. Given that, a = −18, n = 10, an = 0, d = ?, We know that,, Page 7 of 70, Website: www.vidhyarjan.com, , Email:
[email protected], , Mobile: 9999 249717, , Head Office: 1/3-H-A-2, Street # 6, East Azad Nagar, Delhi-110051, (One Km from ‘Welcome Metro Station)
Page 21 : Class X, , Chapter 5 – Arithmetic Progressions, , Maths, , an = a + (n − 1) d, 0 = − 18 + (10 − 1) d, 18 = 9d, , Hence, common difference, d = 2, III. Given that, d = −3, n = 18, an = −5, We know that,, an = a + (n − 1) d, −5 = a + (18 − 1) (−3), −5 = a + (17) (−3), −5 = a − 51, a = 51 − 5 = 46, Hence, a = 46, IV. a = −18.9, d = 2.5, an = 3.6, n = ?, We know that,, an = a + (n − 1) d, 3.6 = − 18.9 + (n − 1) 2.5, 3.6 + 18.9 = (n − 1) 2.5, 22.5 = (n − 1) 2.5, , Hence, n = 10, Page 8 of 70, Website: www.vidhyarjan.com, , Email:
[email protected], , Mobile: 9999 249717, , Head Office: 1/3-H-A-2, Street # 6, East Azad Nagar, Delhi-110051, (One Km from ‘Welcome Metro Station)
Page 22 : Class X, , Chapter 5 – Arithmetic Progressions, , Maths, , V. a = 3.5, d = 0, n = 105, an = ?, We know that,, an = a + (n − 1) d, an = 3.5 + (105 − 1) 0, an = 3.5 + 104 × 0, an = 3.5, Hence, an = 3.5, , Question 2:, Choose the correct choice in the following and justify, I. 30th term of the A.P: 10, 7, 4, …, is, A. 97 B. 77 C. − 77 D. − 87, II 11th term of the A.P., , is, , A. 28 B. 22 C. − 38 D., Answer:, I. Given that, A.P. 10, 7, 4, …, First term, a = 10, Common difference, d = a2 − a1 = 7 − 10, = −3, We know that, an = a + (n − 1) d, a30 = 10 + (30 − 1) (−3), a30 = 10 + (29) (−3), a30 = 10 − 87 = −77, Page 9 of 70, Website: www.vidhyarjan.com, , Email:
[email protected], , Mobile: 9999 249717, , Head Office: 1/3-H-A-2, Street # 6, East Azad Nagar, Delhi-110051, (One Km from ‘Welcome Metro Station)
Page 23 : Class X, , Chapter 5 – Arithmetic Progressions, , Maths, , Hence, the correct answer is C., II. Given that, A.P., First term a = −3, Common difference, d = a2 − a1, , We know that,, , Hence, the answer is B., , Question 3:, In the following APs find the missing term in the boxes, I., II., III., IV., , Page 10 of 70, Website: www.vidhyarjan.com, , Email:
[email protected], , Mobile: 9999 249717, , Head Office: 1/3-H-A-2, Street # 6, East Azad Nagar, Delhi-110051, (One Km from ‘Welcome Metro Station)
Page 24 : Class X, , Chapter 5 – Arithmetic Progressions, , Maths, , V., Answer:, I., For this A.P.,, a=2, a3 = 26, We know that, an = a + (n − 1) d, a3 = 2 + (3 − 1) d, 26 = 2 + 2d, 24 = 2d, d = 12, a2 = 2 + (2 − 1) 12, = 14, Therefore, 14 is the missing term., II., For this A.P.,, a2 = 13 and, a4 = 3, We know that, an = a + (n − 1) d, a2 = a + (2 − 1) d, 13 = a + d (I), a4 = a + (4 − 1) d, 3 = a + 3d (II), On subtracting (I) from (II), we obtain, Page 11 of 70, Website: www.vidhyarjan.com, , Email:
[email protected], , Mobile: 9999 249717, , Head Office: 1/3-H-A-2, Street # 6, East Azad Nagar, Delhi-110051, (One Km from ‘Welcome Metro Station)
Page 25 : Class X, , Chapter 5 – Arithmetic Progressions, , Maths, , −10 = 2d, d = −5, From equation (I), we obtain, 13 = a + (−5), a = 18, a3 = 18 + (3 − 1) (−5), = 18 + 2 (−5) = 18 − 10 = 8, Therefore, the missing terms are 18 and 8 respectively., III., For this A.P.,, , We know that,, , Page 12 of 70, Website: www.vidhyarjan.com, , Email:
[email protected], , Mobile: 9999 249717, , Head Office: 1/3-H-A-2, Street # 6, East Azad Nagar, Delhi-110051, (One Km from ‘Welcome Metro Station)
Page 26 : Class X, , Chapter 5 – Arithmetic Progressions, , Therefore, the missing terms are, , Maths, , and 8 respectively., , IV., For this A.P.,, a = −4 and, a6 = 6, We know that,, an = a + (n − 1) d, a6 = a + (6 − 1) d, 6 = − 4 + 5d, 10 = 5d, d=2, a2 = a + d = − 4 + 2 = −2, , Page 13 of 70, Website: www.vidhyarjan.com, , Email:
[email protected], , Mobile: 9999 249717, , Head Office: 1/3-H-A-2, Street # 6, East Azad Nagar, Delhi-110051, (One Km from ‘Welcome Metro Station)
Page 27 : Class X, , Chapter 5 – Arithmetic Progressions, , Maths, , a3 = a + 2d = − 4 + 2 (2) = 0, a4 = a + 3d = − 4 + 3 (2) = 2, a5 = a + 4d = − 4 + 4 (2) = 4, Therefore, the missing terms are −2, 0, 2, and 4 respectively., V., For this A.P.,, a2 = 38, a6 = −22, We know that, an = a + (n − 1) d, a2 = a + (2 − 1) d, 38 = a + d (1), a6 = a + (6 − 1) d, −22 = a + 5d (2), On subtracting equation (1) from (2), we obtain, − 22 − 38 = 4d, −60 = 4d, d = −15, a = a2 − d = 38 − (−15) = 53, a3 = a + 2d = 53 + 2 (−15) = 23, a4 = a + 3d = 53 + 3 (−15) = 8, a5 = a + 4d = 53 + 4 (−15) = −7, Therefore, the missing terms are 53, 23, 8, and −7 respectively., , Page 14 of 70, Website: www.vidhyarjan.com, , Email:
[email protected], , Mobile: 9999 249717, , Head Office: 1/3-H-A-2, Street # 6, East Azad Nagar, Delhi-110051, (One Km from ‘Welcome Metro Station)
Page 28 : Class X, , Chapter 5 – Arithmetic Progressions, , Maths, , Question 4:, Which term of the A.P. 3, 8, 13, 18, … is 78?, Answer:, 3, 8, 13, 18, …, For this A.P.,, a=3, d = a2 − a1 = 8 − 3 = 5, Let nth term of this A.P. be 78., an = a + (n − 1) d, 78 = 3 + (n − 1) 5, 75 = (n − 1) 5, (n − 1) = 15, n = 16, Hence, 16th term of this A.P. is 78., , Question 5:, Find the number of terms in each of the following A.P., I. 7, 13, 19, …, 205, II., Answer:, I. 7, 13, 19, …, 205, For this A.P.,, a=7, d = a2 − a1 = 13 − 7 = 6, Let there are n terms in this A.P., Page 15 of 70, Website: www.vidhyarjan.com, , Email:
[email protected], , Mobile: 9999 249717, , Head Office: 1/3-H-A-2, Street # 6, East Azad Nagar, Delhi-110051, (One Km from ‘Welcome Metro Station)
Page 29 : Class X, , Chapter 5 – Arithmetic Progressions, , Maths, , an = 205, We know that, an = a + (n − 1) d, Therefore, 205 = 7 + (n − 1) 6, 198 = (n − 1) 6, 33 = (n − 1), n = 34, Therefore, this given series has 34 terms in it., II., For this A.P.,, , Let there are n terms in this A.P., Therefore, an = −47 and we know that,, , Page 16 of 70, Website: www.vidhyarjan.com, , Email:
[email protected], , Mobile: 9999 249717, , Head Office: 1/3-H-A-2, Street # 6, East Azad Nagar, Delhi-110051, (One Km from ‘Welcome Metro Station)
Page 30 : Class X, , Chapter 5 – Arithmetic Progressions, , Maths, , Therefore, this given A.P. has 27 terms in it., , Question 6:, Check whether − 150 is a term of the A.P. 11, 8, 5, 2, …, Answer:, For this A.P.,, a = 11, d = a2 − a1 = 8 − 11 = −3, Let −150 be the nth term of this A.P., We know that,, , Clearly, n is not an integer., Page 17 of 70, Website: www.vidhyarjan.com, , Email:
[email protected], , Mobile: 9999 249717, , Head Office: 1/3-H-A-2, Street # 6, East Azad Nagar, Delhi-110051, (One Km from ‘Welcome Metro Station)
Page 31 : Class X, , Chapter 5 – Arithmetic Progressions, , Maths, , Therefore, −150 is not a term of this A.P., , Question 7:, Find the 31st term of an A.P. whose 11th term is 38 and the 16th term, is 73, Answer:, Given that,, a11 = 38, a16 = 73, We know that,, an = a + (n − 1) d, a11 = a + (11 − 1) d, 38 = a + 10d (1), Similarly,, a16 = a + (16 − 1) d, 73 = a + 15d (2), On subtracting (1) from (2), we obtain, 35 = 5d, d=7, From equation (1),, 38 = a + 10 × (7), 38 − 70 = a, a = −32, a31 = a + (31 − 1) d, = − 32 + 30 (7), = − 32 + 210, Page 18 of 70, Website: www.vidhyarjan.com, , Email:
[email protected], , Mobile: 9999 249717, , Head Office: 1/3-H-A-2, Street # 6, East Azad Nagar, Delhi-110051, (One Km from ‘Welcome Metro Station)
Page 32 : Class X, , Chapter 5 – Arithmetic Progressions, , Maths, , = 178, Hence, 31st term is 178., , Question 8:, An A.P. consists of 50 terms of which 3rd term is 12 and the last term, is 106. Find the 29th term, Answer:, Given that,, a3 = 12, a50 = 106, We know that,, an = a + (n − 1) d, a3 = a + (3 − 1) d, 12 = a + 2d (I), Similarly, a50 = a + (50 − 1) d, 106 = a + 49d (II), On subtracting (I) from (II), we obtain, 94 = 47d, d=2, From equation (I), we obtain, 12 = a + 2 (2), a = 12 − 4 = 8, a29 = a + (29 − 1) d, a29 = 8 + (28)2, a29 = 8 + 56 = 64, Therefore, 29th term is 64., Page 19 of 70, Website: www.vidhyarjan.com, , Email:
[email protected], , Mobile: 9999 249717, , Head Office: 1/3-H-A-2, Street # 6, East Azad Nagar, Delhi-110051, (One Km from ‘Welcome Metro Station)
Page 33 : Class X, , Chapter 5 – Arithmetic Progressions, , Maths, , Question 9:, If the 3rd and the 9th terms of an A.P. are 4 and − 8 respectively., Which term of this A.P. is zero., Answer:, Given that,, a3 = 4, a9 = −8, We know that,, an = a + (n − 1) d, a3 = a + (3 − 1) d, 4 = a + 2d (I), a9 = a + (9 − 1) d, −8 = a + 8d (II), On subtracting equation (I) from (II), we obtain, −12 = 6d, d = −2, From equation (I), we obtain, 4 = a + 2 (−2), 4=a−4, a=8, Let nth term of this A.P. be zero., an = a + (n − 1) d, 0 = 8 + (n − 1) (−2), 0 = 8 − 2n + 2, 2n = 10, Page 20 of 70, Website: www.vidhyarjan.com, , Email:
[email protected], , Mobile: 9999 249717, , Head Office: 1/3-H-A-2, Street # 6, East Azad Nagar, Delhi-110051, (One Km from ‘Welcome Metro Station)
Page 34 : Class X, , Chapter 5 – Arithmetic Progressions, , Maths, , n=5, Hence, 5th term of this A.P. is 0., , Question 10:, If 17th term of an A.P. exceeds its 10th term by 7. Find the common, difference., Answer:, We know that,, For an A.P., an = a + (n − 1) d, a17 = a + (17 − 1) d, a17 = a + 16d, Similarly, a10 = a + 9d, It is given that, a17 − a10 = 7, (a + 16d) − (a + 9d) = 7, 7d = 7, d=1, Therefore, the common difference is 1., , Question 11:, Which term of the A.P. 3, 15, 27, 39, … will be 132 more than its 54th, term?, Answer:, Given A.P. is 3, 15, 27, 39, …, a=3, d = a2 − a1 = 15 − 3 = 12, a54 = a + (54 − 1) d, Page 21 of 70, Website: www.vidhyarjan.com, , Email:
[email protected], , Mobile: 9999 249717, , Head Office: 1/3-H-A-2, Street # 6, East Azad Nagar, Delhi-110051, (One Km from ‘Welcome Metro Station)
Page 35 : Class X, , Chapter 5 – Arithmetic Progressions, , Maths, , = 3 + (53) (12), = 3 + 636 = 639, 132 + 639 = 771, We have to find the term of this A.P. which is 771., Let nth term be 771., an = a + (n − 1) d, 771 = 3 + (n − 1) 12, 768 = (n − 1) 12, (n − 1) = 64, n = 65, Therefore, 65th term was 132 more than 54th term., Alternatively,, Let nth term be 132 more than 54th term., , Question 12:, Two APs have the same common difference. The difference between, their 100th term is 100, what is the difference between their 1000th, terms?, Answer:, Let the first term of these A.P.s be a1 and a2 respectively and the, common difference of these A.P.s be d., For first A.P.,, a100 = a1 + (100 − 1) d, Page 22 of 70, Website: www.vidhyarjan.com, , Email:
[email protected], , Mobile: 9999 249717, , Head Office: 1/3-H-A-2, Street # 6, East Azad Nagar, Delhi-110051, (One Km from ‘Welcome Metro Station)
Page 37 : Class X, , Chapter 5 – Arithmetic Progressions, , Maths, , All are three digit numbers which are divisible by 7 and thus, all these, are terms of an A.P. having first term as 105 and common difference, as 7., The maximum possible three-digit number is 999. When we divide it, by 7, the remainder will be 5. Clearly, 999 − 5 = 994 is the maximum, possible three-digit number that is divisible by 7., The series is as follows., 105, 112, 119, …, 994, Let 994 be the nth term of this A.P., a = 105, d=7, an = 994, n=?, an = a + (n − 1) d, 994 = 105 + (n − 1) 7, 889 = (n − 1) 7, (n − 1) = 127, n = 128, Therefore, 128 three-digit numbers are divisible by 7., , Question 14:, How many multiples of 4 lie between 10 and 250?, Answer:, First multiple of 4 that is greater than 10 is 12. Next will be 16., Therefore, 12, 16, 20, 24, …, , Page 24 of 70, Website: www.vidhyarjan.com, , Email:
[email protected], , Mobile: 9999 249717, , Head Office: 1/3-H-A-2, Street # 6, East Azad Nagar, Delhi-110051, (One Km from ‘Welcome Metro Station)
Page 38 : Class X, , Chapter 5 – Arithmetic Progressions, , Maths, , All these are divisible by 4 and thus, all these are terms of an A.P. with, first term as 12 and common difference as 4., When we divide 250 by 4, the remainder will be 2. Therefore, 250 − 2, = 248 is divisible by 4., The series is as follows., 12, 16, 20, 24, …, 248, Let 248 be the nth term of this A.P., , Therefore, there are 60 multiples of 4 between 10 and 250., , Question 15:, For what value of n, are the nth terms of two APs 63, 65, 67, and 3,, 10, 17, … equal, Answer:, 63, 65, 67, …, a = 63, d = a2 − a1 = 65 − 63 = 2, nth term of this A.P. = an = a + (n − 1) d, an= 63 + (n − 1) 2 = 63 + 2n − 2, Page 25 of 70, Website: www.vidhyarjan.com, , Email:
[email protected], , Mobile: 9999 249717, , Head Office: 1/3-H-A-2, Street # 6, East Azad Nagar, Delhi-110051, (One Km from ‘Welcome Metro Station)
Page 39 : Class X, , Chapter 5 – Arithmetic Progressions, , Maths, , an = 61 + 2n (1), 3, 10, 17, …, a=3, d = a2 − a1 = 10 − 3 = 7, nth term of this A.P. = 3 + (n − 1) 7, an = 3 + 7n − 7, an = 7n − 4 (2), It is given that, nth term of these A.P.s are equal to each other., Equating both these equations, we obtain, 61 + 2n = 7n − 4, 61 + 4 = 5n, 5n = 65, n = 13, Therefore, 13th terms of both these A.P.s are equal to each other., , Question 16:, Determine the A.P. whose third term is 16 and the 7th term exceeds, the 5th term by 12., Answer:, =a3 = 16, a + (3 − 1) d = 16, a + 2d = 16 (1), a7 − a5 = 12, [a+ (7 − 1) d] − [a + (5 − 1) d]= 12, (a + 6d) − (a + 4d) = 12, 2d = 12, Page 26 of 70, Website: www.vidhyarjan.com, , Email:
[email protected], , Mobile: 9999 249717, , Head Office: 1/3-H-A-2, Street # 6, East Azad Nagar, Delhi-110051, (One Km from ‘Welcome Metro Station)
Page 40 : Class X, , Chapter 5 – Arithmetic Progressions, , Maths, , d=6, From equation (1), we obtain, a + 2 (6) = 16, a + 12 = 16, a=4, Therefore, A.P. will be, 4, 10, 16, 22, …, , Question 17:, Find the 20th term from the last term of the A.P. 3, 8, 13, …, 253, Answer:, Given A.P. is, 3, 8, 13, …, 253, Common difference for this A.P. is 5., Therefore, this A.P. can be written in reverse order as, 253, 248, 243, …, 13, 8, 5, For this A.P.,, a = 253, d = 248 − 253 = −5, n = 20, a20 = a + (20 − 1) d, a20 = 253 + (19) (−5), a20 = 253 − 95, a = 158, Therefore, 20th term from the last term is 158., , Page 27 of 70, Website: www.vidhyarjan.com, , Email:
[email protected], , Mobile: 9999 249717, , Head Office: 1/3-H-A-2, Street # 6, East Azad Nagar, Delhi-110051, (One Km from ‘Welcome Metro Station)
Page 41 : Class X, , Chapter 5 – Arithmetic Progressions, , Maths, , Question 18:, The sum of 4th and 8th terms of an A.P. is 24 and the sum of the 6th, and 10th terms is 44. Find the first three terms of the A.P., Answer:, We know that,, an = a + (n − 1) d, a4 = a + (4 − 1) d, a4 = a + 3d, Similarly,, a8 = a + 7d, a6 = a + 5d, a10 = a + 9d, Given that, a4 + a8 = 24, a + 3d + a + 7d = 24, 2a + 10d = 24, a + 5d = 12 (1), a6 + a10 = 44, a + 5d + a + 9d = 44, 2a + 14d = 44, a + 7d = 22 (2), On subtracting equation (1) from (2), we obtain, 2d = 22 − 12, 2d = 10, d=5, From equation (1), we obtain, Page 28 of 70, Website: www.vidhyarjan.com, , Email:
[email protected], , Mobile: 9999 249717, , Head Office: 1/3-H-A-2, Street # 6, East Azad Nagar, Delhi-110051, (One Km from ‘Welcome Metro Station)
Page 42 : Class X, , Chapter 5 – Arithmetic Progressions, , Maths, , a + 5d = 12, a + 5 (5) = 12, a + 25 = 12, a = −13, a2 = a + d = − 13 + 5 = −8, a3 = a2 + d = − 8 + 5 = −3, Therefore, the first three terms of this A.P. are −13, −8, and −3., , Question 19:, Subba Rao started work in 1995 at an annual salary of Rs 5000 and, received an increment of Rs 200 each year. In which year did his, income reach Rs 7000?, Answer:, It can be observed that the incomes that Subba Rao obtained in, various years are in A.P. as every year, his salary is increased by Rs, 200., Therefore, the salaries of each year after 1995 are, 5000, 5200, 5400, …, Here, a = 5000, d = 200, Let after nth year, his salary be Rs 7000., Therefore, an = a + (n − 1) d, 7000 = 5000 + (n − 1) 200, 200(n − 1) = 2000, (n − 1) = 10, n = 11, Page 29 of 70, Website: www.vidhyarjan.com, , Email:
[email protected], , Mobile: 9999 249717, , Head Office: 1/3-H-A-2, Street # 6, East Azad Nagar, Delhi-110051, (One Km from ‘Welcome Metro Station)
Page 43 : Class X, , Chapter 5 – Arithmetic Progressions, , Maths, , Therefore, in 11th year, his salary will be Rs 7000., , Question 20:, Ramkali saved Rs 5 in the first week of a year and then increased her, weekly saving by Rs 1.75. If in the nth week, her week, her weekly, savings become Rs 20.75, find n., Answer:, Given that,, a=5, d = 1.75, an = 20.75, n=?, an = a + (n − 1) d, , n−1=9, n = 10, Hence, n is 10., , Page 30 of 70, Website: www.vidhyarjan.com, , Email:
[email protected], , Mobile: 9999 249717, , Head Office: 1/3-H-A-2, Street # 6, East Azad Nagar, Delhi-110051, (One Km from ‘Welcome Metro Station)
Page 44 : Class X, , Chapter 5 – Arithmetic Progressions, , Maths, , Exercise 5.3, Question 1:, Find the sum of the following APs., (i) 2, 7, 12 ,…., to 10 terms., (ii) − 37, − 33, − 29 ,…, to 12 terms, (iii) 0.6, 1.7, 2.8 ,…….., to 100 terms, (iv), , ,………, to 11 terms, , Answer:, (i)2, 7, 12 ,…, to 10 terms, For this A.P.,, a=2, d = a2 − a1 = 7 − 2 = 5, n = 10, We know that,, , (ii)−37, −33, −29 ,…, to 12 terms, For this A.P.,, a = −37, d = a2 − a1 = (−33) − (−37), = − 33 + 37 = 4, Page 31 of 70, Website: www.vidhyarjan.com, , Email:
[email protected], , Mobile: 9999 249717, , Head Office: 1/3-H-A-2, Street # 6, East Azad Nagar, Delhi-110051, (One Km from ‘Welcome Metro Station)
Page 45 : Class X, , Chapter 5 – Arithmetic Progressions, , Maths, , n = 12, We know that,, , (iii) 0.6, 1.7, 2.8 ,…, to 100 terms, For this A.P.,, a = 0.6, d = a2 − a1 = 1.7 − 0.6 = 1.1, n = 100, We know that,, , (iv), , . …….. , to 11 terms, , For this A.P.,, , Page 32 of 70, Website: www.vidhyarjan.com, , Email:
[email protected], , Mobile: 9999 249717, , Head Office: 1/3-H-A-2, Street # 6, East Azad Nagar, Delhi-110051, (One Km from ‘Welcome Metro Station)
Page 46 : Class X, , Chapter 5 – Arithmetic Progressions, , Maths, , n = 11, , We know that,, , Question 2:, Find the sums given below, (i) 7 +, , + 14 + ………… + 84, , (ii) 34 + 32 + 30 + ……….. + 10, (iii) − 5 + (− 8) + (− 11) + ………… + (− 230), Answer:, (i)7 +, , + 14 + …………+ 84, , For this A.P.,, Page 33 of 70, Website: www.vidhyarjan.com, , Email:
[email protected], , Mobile: 9999 249717, , Head Office: 1/3-H-A-2, Street # 6, East Azad Nagar, Delhi-110051, (One Km from ‘Welcome Metro Station)
Page 47 : Class X, , Chapter 5 – Arithmetic Progressions, , Maths, , a=7, l = 84, , Let 84 be the nth term of this A.P., l = a + (n − 1)d, , 22 = n − 1, n = 23, We know that,, , (ii)34 + 32 + 30 + ……….. + 10, For this A.P.,, a = 34, d = a2 − a1 = 32 − 34 = −2, l = 10, Let 10 be the nth term of this A.P., , Page 34 of 70, Website: www.vidhyarjan.com, , Email:
[email protected], , Mobile: 9999 249717, , Head Office: 1/3-H-A-2, Street # 6, East Azad Nagar, Delhi-110051, (One Km from ‘Welcome Metro Station)
Page 48 : Class X, , Chapter 5 – Arithmetic Progressions, , Maths, , l = a + (n − 1) d, 10 = 34 + (n − 1) (−2), −24 = (n − 1) (−2), 12 = n − 1, n = 13, , (iii)(−5) + (−8) + (−11) + ………… + (−230), For this A.P.,, a = −5, l = −230, d = a2 − a1 = (−8) − (−5), = − 8 + 5 = −3, Let −230 be the nth term of this A.P., l = a + (n − 1)d, −230 = − 5 + (n − 1) (−3), −225 = (n − 1) (−3), (n − 1) = 75, n = 76, And,, , Page 35 of 70, Website: www.vidhyarjan.com, , Email:
[email protected], , Mobile: 9999 249717, , Head Office: 1/3-H-A-2, Street # 6, East Azad Nagar, Delhi-110051, (One Km from ‘Welcome Metro Station)
Page 49 : Class X, , Chapter 5 – Arithmetic Progressions, , Maths, , Question 3:, In an AP, (i) Given a = 5, d = 3, an = 50, find n and Sn., (ii) Given a = 7, a13 = 35, find d and S13., (iii) Given a12 = 37, d = 3, find a and S12., (iv) Given a3 = 15, S10 = 125, find d and a10., (v) Given d = 5, S9 = 75, find a and a9., (vi) Given a = 2, d = 8, Sn = 90, find n and an., (vii) Given a = 8, an = 62, Sn = 210, find n and d., (viii) Given an = 4, d = 2, Sn = − 14, find n and a., (ix) Given a = 3, n = 8, S = 192, find d., (x)Given l = 28, S = 144 and there are total 9 terms. Find a., Answer:, (i) Given that, a = 5, d = 3, an = 50, As an = a + (n − 1)d,, ∴ 50 = 5 + (n − 1)3, 45 = (n − 1)3, 15 = n − 1, n = 16, , Page 36 of 70, Website: www.vidhyarjan.com, , Email:
[email protected], , Mobile: 9999 249717, , Head Office: 1/3-H-A-2, Street # 6, East Azad Nagar, Delhi-110051, (One Km from ‘Welcome Metro Station)
Page 50 : Class X, , Chapter 5 – Arithmetic Progressions, , Maths, , (ii) Given that, a = 7, a13 = 35, As an = a + (n − 1) d,, ∴ a13 = a + (13 − 1) d, 35 = 7 + 12 d, 35 − 7 = 12d, 28 = 12d, , (iii)Given that, a12 = 37, d = 3, As an = a + (n − 1)d,, a12 = a + (12 − 1)3, 37 = a + 33, a=4, , Page 37 of 70, Website: www.vidhyarjan.com, , Email:
[email protected], , Mobile: 9999 249717, , Head Office: 1/3-H-A-2, Street # 6, East Azad Nagar, Delhi-110051, (One Km from ‘Welcome Metro Station)
Page 51 : Class X, , Chapter 5 – Arithmetic Progressions, , Maths, , (iv) Given that, a3 = 15, S10 = 125, As an = a + (n − 1)d,, a3 = a + (3 − 1)d, 15 = a + 2d (i), , On multiplying equation (1) by 2, we obtain, 30 = 2a + 4d (iii), On subtracting equation (iii) from (ii), we obtain, −5 = 5d, d = −1, From equation (i),, 15 = a + 2(−1), 15 = a − 2, a = 17, a10 = a + (10 − 1)d, a10 = 17 + (9) (−1), Page 38 of 70, Website: www.vidhyarjan.com, , Email:
[email protected], , Mobile: 9999 249717, , Head Office: 1/3-H-A-2, Street # 6, East Azad Nagar, Delhi-110051, (One Km from ‘Welcome Metro Station)
Page 52 : Class X, , Chapter 5 – Arithmetic Progressions, , Maths, , a10 = 17 − 9 = 8, (v)Given that, d = 5, S9 = 75, ,, , As, , 25 = 3(a + 20), 25 = 3a + 60, 3a = 25 − 60, , an = a + (n − 1)d, a9 = a + (9 − 1) (5), , (vi) Given that, a = 2, d = 8, Sn = 90, As, , ,, , 90 = n [2 + (n − 1)4], 90 = n [2 + 4n − 4], Page 39 of 70, Website: www.vidhyarjan.com, , Email:
[email protected], , Mobile: 9999 249717, , Head Office: 1/3-H-A-2, Street # 6, East Azad Nagar, Delhi-110051, (One Km from ‘Welcome Metro Station)
Page 53 : Class X, , Chapter 5 – Arithmetic Progressions, , Maths, , 90 = n (4n − 2) = 4n2 − 2n, 4n2 − 2n − 90 = 0, 4n2 − 20n + 18n − 90 = 0, 4n (n − 5) + 18 (n − 5) = 0, (n − 5) (4n + 18) = 0, Either n − 5 = 0 or 4n + 18 = 0, n = 5 or, However, n can neither be negative nor fractional., Therefore, n = 5, an = a + (n − 1)d, a5 = 2 + (5 − 1)8, = 2 + (4) (8), = 2 + 32 = 34, (vii) Given that, a = 8, an = 62, Sn = 210, , n=6, an = a + (n − 1)d, 62 = 8 + (6 − 1)d, 62 − 8 = 5d, 54 = 5d, , Page 40 of 70, Website: www.vidhyarjan.com, , Email:
[email protected], , Mobile: 9999 249717, , Head Office: 1/3-H-A-2, Street # 6, East Azad Nagar, Delhi-110051, (One Km from ‘Welcome Metro Station)
Page 54 : Class X, , Chapter 5 – Arithmetic Progressions, , Maths, , (viii) Given that, an = 4, d = 2, Sn = −14, an = a + (n − 1)d, 4 = a + (n − 1)2, 4 = a + 2n − 2, a + 2n = 6, a = 6 − 2n (i), , −28 = n (a + 4), −28 = n (6 − 2n + 4) {From equation (i)}, −28 = n (− 2n + 10), −28 = − 2n2 + 10n, 2n2 − 10n − 28 = 0, n2 − 5n −14 = 0, n2 − 7n + 2n − 14 = 0, n (n − 7) + 2(n − 7) = 0, (n − 7) (n + 2) = 0, Either n − 7 = 0 or n + 2 = 0, n = 7 or n = −2, However, n can neither be negative nor fractional., Therefore, n = 7, From equation (i), we obtain, Page 41 of 70, Website: www.vidhyarjan.com, , Email:
[email protected], , Mobile: 9999 249717, , Head Office: 1/3-H-A-2, Street # 6, East Azad Nagar, Delhi-110051, (One Km from ‘Welcome Metro Station)
Page 55 : Class X, , Chapter 5 – Arithmetic Progressions, , Maths, , a = 6 − 2n, a = 6 − 2(7), = 6 − 14, = −8, (ix)Given that, a = 3, n = 8, S = 192, , 192 = 4 [6 + 7d], 48 = 6 + 7d, 42 = 7d, d=6, (x)Given that, l = 28, S = 144 and there are total of 9 terms., , (16) × (2) = a + 28, 32 = a + 28, a=4, , Question 4:, How many terms of the AP. 9, 17, 25 … must be taken to give a sum, of 636?, Answer:, Let there be n terms of this A.P., Page 42 of 70, Website: www.vidhyarjan.com, , Email:
[email protected], , Mobile: 9999 249717, , Head Office: 1/3-H-A-2, Street # 6, East Azad Nagar, Delhi-110051, (One Km from ‘Welcome Metro Station)
Page 56 : Class X, , Chapter 5 – Arithmetic Progressions, , Maths, , For this A.P., a = 9, d = a2 − a1 = 17 − 9 = 8, , 636 = n [9 + 4n − 4], 636 = n (4n + 5), 4n2 + 5n − 636 = 0, 4n2 + 53n − 48n − 636 = 0, n (4n + 53) − 12 (4n + 53) = 0, (4n + 53) (n − 12) = 0, Either 4n + 53 = 0 or n − 12 = 0, or n = 12, n cannot be, , . As the number of terms can neither be negative nor, , fractional, therefore, n = 12 only., , Question 5:, The first term of an AP is 5, the last term is 45 and the sum is 400., Find the number of terms and the common difference., Answer:, Given that,, a=5, , Page 43 of 70, Website: www.vidhyarjan.com, , Email:
[email protected], , Mobile: 9999 249717, , Head Office: 1/3-H-A-2, Street # 6, East Azad Nagar, Delhi-110051, (One Km from ‘Welcome Metro Station)
Page 57 : Class X, , Chapter 5 – Arithmetic Progressions, , Maths, , l = 45, Sn = 400, , n = 16, l = a + (n − 1) d, 45 = 5 + (16 − 1) d, 40 = 15d, , Question 6:, The first and the last term of an AP are 17 and 350 respectively. If the, common difference is 9, how many terms are there and what is their, sum?, Answer:, Given that,, a = 17, l = 350, d=9, Let there be n terms in the A.P., l = a + (n − 1) d, 350 = 17 + (n − 1)9, , Page 44 of 70, Website: www.vidhyarjan.com, , Email:
[email protected], , Mobile: 9999 249717, , Head Office: 1/3-H-A-2, Street # 6, East Azad Nagar, Delhi-110051, (One Km from ‘Welcome Metro Station)
Page 58 : Class X, , Chapter 5 – Arithmetic Progressions, , Maths, , 333 = (n − 1)9, (n − 1) = 37, n = 38, , Thus, this A.P. contains 38 terms and the sum of the terms of this A.P., is 6973., , Question 7:, Find the sum of first 22 terms of an AP in which d = 7 and 22nd term is, 149., Answer:, d=7, a22 = 149, S22 = ?, an = a + (n − 1)d, a22 = a + (22 − 1)d, 149 = a + 21 × 7, 149 = a + 147, a=2, , Page 45 of 70, Website: www.vidhyarjan.com, , Email:
[email protected], , Mobile: 9999 249717, , Head Office: 1/3-H-A-2, Street # 6, East Azad Nagar, Delhi-110051, (One Km from ‘Welcome Metro Station)
Page 59 : Class X, , Chapter 5 – Arithmetic Progressions, , Maths, , Question 8:, Find the sum of first 51 terms of an AP whose second and third terms, are 14 and 18 respectively., Answer:, Given that,, a2 = 14, a3 = 18, d = a3 − a2 = 18 − 14 = 4, a2 = a + d, 14 = a + 4, a = 10, , = 5610, , Question 9:, If the sum of first 7 terms of an AP is 49 and that of 17 terms is 289,, find the sum of first n terms., Answer:, Given that,, S7 = 49, , Page 46 of 70, Website: www.vidhyarjan.com, , Email:
[email protected], , Mobile: 9999 249717, , Head Office: 1/3-H-A-2, Street # 6, East Azad Nagar, Delhi-110051, (One Km from ‘Welcome Metro Station)
Page 60 : Class X, , Chapter 5 – Arithmetic Progressions, , Maths, , S17 = 289, , 7 = (a + 3d), a + 3d = 7 (i), Similarly,, , 17 = (a + 8d), a + 8d = 17 (ii), Subtracting equation (i) from equation (ii),, 5d = 10, d=2, From equation (i),, a + 3(2) = 7, a+6=7, a=1, , Page 47 of 70, Website: www.vidhyarjan.com, , Email:
[email protected], , Mobile: 9999 249717, , Head Office: 1/3-H-A-2, Street # 6, East Azad Nagar, Delhi-110051, (One Km from ‘Welcome Metro Station)
Page 61 : Class X, , Chapter 5 – Arithmetic Progressions, , Maths, , = n2, , Question 10:, Show that a1, a2 … , an , … form an AP where an is defined as below, (i) an = 3 + 4n, (ii) an = 9 − 5n, Also find the sum of the first 15 terms in each case., Answer:, (i) an = 3 + 4n, a1 = 3 + 4(1) = 7, a2 = 3 + 4(2) = 3 + 8 = 11, a3 = 3 + 4(3) = 3 + 12 = 15, a4 = 3 + 4(4) = 3 + 16 = 19, It can be observed that, a2 − a1 = 11 − 7 = 4, a3 − a2 = 15 − 11 = 4, a4 − a3 = 19 − 15 = 4, i.e., ak + 1 − ak is same every time. Therefore, this is an AP with, common difference as 4 and first term as 7., , Page 48 of 70, Website: www.vidhyarjan.com, , Email:
[email protected], , Mobile: 9999 249717, , Head Office: 1/3-H-A-2, Street # 6, East Azad Nagar, Delhi-110051, (One Km from ‘Welcome Metro Station)
Page 62 : Class X, , Chapter 5 – Arithmetic Progressions, , Maths, , = 15 × 35, = 525, (ii) an = 9 − 5n, a1 = 9 − 5 × 1 = 9 − 5 = 4, a2 = 9 − 5 × 2 = 9 − 10 = −1, a3 = 9 − 5 × 3 = 9 − 15 = −6, a4 = 9 − 5 × 4 = 9 − 20 = −11, It can be observed that, a2 − a1 = − 1 − 4 = −5, a3 − a2 = − 6 − (−1) = −5, a4 − a3 = − 11 − (−6) = −5, i.e., ak + 1 − ak is same every time. Therefore, this is an A.P. with, common difference as −5 and first term as 4., , Page 49 of 70, Website: www.vidhyarjan.com, , Email:
[email protected], , Mobile: 9999 249717, , Head Office: 1/3-H-A-2, Street # 6, East Azad Nagar, Delhi-110051, (One Km from ‘Welcome Metro Station)
Page 63 : Class X, , Chapter 5 – Arithmetic Progressions, , Maths, , = −465, , Question 11:, If the sum of the first n terms of an AP is 4n − n2, what is the first, term (that is S1)? What is the sum of first two terms? What is the, second term? Similarly find the 3rd, the10th and the nth terms., Answer:, Given that,, Sn = 4n − n2, First term, a = S1 = 4(1) − (1)2 = 4 − 1 = 3, Sum of first two terms = S2, = 4(2) − (2)2 = 8 − 4 = 4, Second term, a2 = S2 − S1 = 4 − 3 = 1, d = a2 − a = 1 − 3 = −2, an = a + (n − 1)d, = 3 + (n − 1) (−2), = 3 − 2n + 2, = 5 − 2n, Page 50 of 70, Website: www.vidhyarjan.com, , Email:
[email protected], , Mobile: 9999 249717, , Head Office: 1/3-H-A-2, Street # 6, East Azad Nagar, Delhi-110051, (One Km from ‘Welcome Metro Station)
Page 64 : Class X, , Chapter 5 – Arithmetic Progressions, , Maths, , Therefore, a3 = 5 − 2(3) = 5 − 6 = −1, a10 = 5 − 2(10) = 5 − 20 = −15, Hence, the sum of first two terms is 4. The second term is 1. 3rd, 10th,, and nth terms are −1, −15, and 5 − 2n respectively., , Question 12:, Find the sum of first 40 positive integers divisible by 6., Answer:, The positive integers that are divisible by 6 are, 6, 12, 18, 24 …, It can be observed that these are making an A.P. whose first term is 6, and common difference is 6., a=6, d=6, S40 =?, , = 20[12 + (39) (6)], = 20(12 + 234), = 20 × 246, = 4920, , Question 13:, Find the sum of first 15 multiples of 8., Answer:, , Page 51 of 70, Website: www.vidhyarjan.com, , Email:
[email protected], , Mobile: 9999 249717, , Head Office: 1/3-H-A-2, Street # 6, East Azad Nagar, Delhi-110051, (One Km from ‘Welcome Metro Station)
Page 65 : Class X, , Chapter 5 – Arithmetic Progressions, , Maths, , The multiples of 8 are, 8, 16, 24, 32…, These are in an A.P., having first term as 8 and common difference as, 8., Therefore, a = 8, d=8, S15 =?, , = 960, , Question 14:, Find the sum of the odd numbers between 0 and 50., Answer:, The odd numbers between 0 and 50 are, 1, 3, 5, 7, 9 … 49, Therefore, it can be observed that these odd numbers are in an A.P., a=1, d=2, l = 49, Page 52 of 70, Website: www.vidhyarjan.com, , Email:
[email protected], , Mobile: 9999 249717, , Head Office: 1/3-H-A-2, Street # 6, East Azad Nagar, Delhi-110051, (One Km from ‘Welcome Metro Station)
Page 66 : Class X, , Chapter 5 – Arithmetic Progressions, , Maths, , l = a + (n − 1) d, 49 = 1 + (n − 1)2, 48 = 2(n − 1), n − 1 = 24, n = 25, , = 625, , Question 15:, A contract on construction job specifies a penalty for delay of, completion beyond a certain date as follows: Rs. 200 for the first day,, Rs. 250 for the second day, Rs. 300 for the third day, etc., the penalty, for each succeeding day being Rs. 50 more than for the preceding day., How much money the contractor has to pay as penalty, if he has, delayed the work by 30 days., Answer:, It can be observed that these penalties are in an A.P. having first term, as 200 and common difference as 50., a = 200, d = 50, Penalty that has to be paid if he has delayed the work by 30 days =, S30, Page 53 of 70, Website: www.vidhyarjan.com, , Email:
[email protected], , Mobile: 9999 249717, , Head Office: 1/3-H-A-2, Street # 6, East Azad Nagar, Delhi-110051, (One Km from ‘Welcome Metro Station)
Page 67 : Class X, , Chapter 5 – Arithmetic Progressions, , Maths, , = 15 [400 + 1450], = 15 (1850), = 27750, Therefore, the contractor has to pay Rs 27750 as penalty., , Question 16:, A sum of Rs 700 is to be used to give seven cash prizes to students of, a school for their overall academic performance. If each prize is Rs 20, less than its preceding prize, find the value of each of the prizes., Answer:, Let the cost of 1st prize be P., Cost of 2nd prize = P − 20, And cost of 3rd prize = P − 40, It can be observed that the cost of these prizes are in an A.P. having, common difference as −20 and first term as P., a=P, d = −20, Given that, S7 = 700, , a + 3(−20) = 100, a − 60 = 100, , Page 54 of 70, Website: www.vidhyarjan.com, , Email:
[email protected], , Mobile: 9999 249717, , Head Office: 1/3-H-A-2, Street # 6, East Azad Nagar, Delhi-110051, (One Km from ‘Welcome Metro Station)
Page 68 : Class X, , Chapter 5 – Arithmetic Progressions, , Maths, , a = 160, Therefore, the value of each of the prizes was Rs 160, Rs 140, Rs 120,, Rs 100, Rs 80, Rs 60, and Rs 40., , Question 17:, In a school, students thought of planting trees in and around the, school to reduce air pollution. It was decided that the number of trees,, that each section of each class will plant, will be the same as the class,, in which they are studying, e.g., a section of class I will plant 1 tree, a, section of class II will plant 2 trees and so on till class XII. There are, three sections of each class. How many trees will be planted by the, students?, Answer:, It can be observed that the number of trees planted by the students is, in an AP., 1, 2, 3, 4, 5………………..12, First term, a = 1, Common difference, d = 2 − 1 = 1, , = 6 (2 + 11), = 6 (13), = 78, Therefore, number of trees planted by 1 section of the classes = 78, , Page 55 of 70, Website: www.vidhyarjan.com, , Email:
[email protected], , Mobile: 9999 249717, , Head Office: 1/3-H-A-2, Street # 6, East Azad Nagar, Delhi-110051, (One Km from ‘Welcome Metro Station)
Page 69 : Class X, , Chapter 5 – Arithmetic Progressions, , Maths, , Number of trees planted by 3 sections of the classes = 3 × 78 = 234, Therefore, 234 trees will be planted by the students., , Question 18:, A spiral is made up of successive semicircles, with centres alternately, at A and B, starting with centre at A of radii 0.5, 1.0 cm, 1.5 cm, 2.0, cm, ……… as shown in figure. What is the total length of such a spiral, , made up of thirteen consecutive semicircles?, , Answer:, Semi-perimeter of circle = πr, I1 = π(0.5), I2 = π(1) = π cm, I3 = π(1.5) =, Therefore, I1, I2, I3 ,i.e. the lengths of the semi-circles are in an A.P.,, , Page 56 of 70, Website: www.vidhyarjan.com, , Email:
[email protected], , Mobile: 9999 249717, , Head Office: 1/3-H-A-2, Street # 6, East Azad Nagar, Delhi-110051, (One Km from ‘Welcome Metro Station)
Page 70 : Class X, , Chapter 5 – Arithmetic Progressions, , Maths, , S13 =?, We know that the sum of n terms of an a A.P. is given by, , = 143, Therefore, the length of such spiral of thirteen consecutive semi-circles, will be 143 cm., , Question 19:, 200 logs are stacked in the following manner: 20 logs in the bottom, row, 19 in the next row, 18 in the row next to it and so on. In how, many rows are the 200 logs placed and how many logs are in the top, row?, , Page 57 of 70, Website: www.vidhyarjan.com, , Email:
[email protected], , Mobile: 9999 249717, , Head Office: 1/3-H-A-2, Street # 6, East Azad Nagar, Delhi-110051, (One Km from ‘Welcome Metro Station)
Page 71 : Class X, , Chapter 5 – Arithmetic Progressions, , Maths, , Answer:, It can be observed that the numbers of logs in rows are in an A.P., 20, 19, 18…, For this A.P.,, a = 20, d = a2 − a1 = 19 − 20 = −1, Let a total of 200 logs be placed in n rows., Sn = 200, , 400 = n (40 − n + 1), 400 = n (41 − n), 400 = 41n − n2, n2 − 41n + 400 = 0, n2 − 16n − 25n + 400 = 0, n (n − 16) −25 (n − 16) = 0, (n − 16) (n − 25) = 0, Either (n − 16) = 0 or n − 25 = 0, n = 16 or n = 25, an = a + (n − 1)d, Page 58 of 70, Website: www.vidhyarjan.com, , Email:
[email protected], , Mobile: 9999 249717, , Head Office: 1/3-H-A-2, Street # 6, East Azad Nagar, Delhi-110051, (One Km from ‘Welcome Metro Station)
Page 72 : Class X, , Chapter 5 – Arithmetic Progressions, , Maths, , a16 = 20 + (16 − 1) (−1), a16 = 20 − 15, a16 = 5, Similarly,, a25 = 20 + (25 − 1) (−1), a25 = 20 − 24, = −4, Clearly, the number of logs in 16th row is 5. However, the number of, logs in 25th row is negative, which is not possible., Therefore, 200 logs can be placed in 16 rows and the number of logs, in the 16th row is 5., , Question 20:, In a potato race, a bucket is placed at the starting point, which is 5 m, from the first potato and other potatoes are placed 3 m apart in a, straight line. There are ten potatoes in the line., , A competitor starts from the bucket, picks up the nearest potato, runs, back with it, drops it in the bucket, runs back to pick up the next, potato, runs to the bucket to drop it in, and she continues in the same, way until all the potatoes are in the bucket. What is the total distance, the competitor has to run?, , Page 59 of 70, Website: www.vidhyarjan.com, , Email:
[email protected], , Mobile: 9999 249717, , Head Office: 1/3-H-A-2, Street # 6, East Azad Nagar, Delhi-110051, (One Km from ‘Welcome Metro Station)
Page 73 : Class X, , Chapter 5 – Arithmetic Progressions, , Maths, , [Hint: to pick up the first potato and the second potato, the total, distance (in metres) run by a competitor is 2 × 5 + 2 ×(5 + 3)], Answer:, , The distances of potatoes are as follows., 5, 8, 11, 14…, It can be observed that these distances are in A.P., a=5, d=8−5=3, , = 5[10 + 9 × 3], = 5(10 + 27) = 5(37), = 185, As every time she has to run back to the bucket, therefore, the total, distance that the competitor has to run will be two times of it., Therefore, total distance that the competitor will run = 2 × 185, = 370 m, Alternatively,, The distances of potatoes from the bucket are 5, 8, 11, 14…, , Page 60 of 70, Website: www.vidhyarjan.com, , Email:
[email protected], , Mobile: 9999 249717, , Head Office: 1/3-H-A-2, Street # 6, East Azad Nagar, Delhi-110051, (One Km from ‘Welcome Metro Station)
Page 74 : Class X, , Chapter 5 – Arithmetic Progressions, , Maths, , Distance run by the competitor for collecting these potatoes are two, times of the distance at which the potatoes have been kept. Therefore,, distances to be run are, 10, 16, 22, 28, 34,………., a = 10, d = 16 − 10 = 6, S10 =?, , = 5[20 + 54], = 5 (74), = 370, Therefore, the competitor will run a total distance of 370 m., , Page 61 of 70, Website: www.vidhyarjan.com, , Email:
[email protected], , Mobile: 9999 249717, , Head Office: 1/3-H-A-2, Street # 6, East Azad Nagar, Delhi-110051, (One Km from ‘Welcome Metro Station)
Page 75 : Class X, , Chapter 5 – Arithmetic Progressions, , Maths, , Exercise 5.4, Question 1:, Which term of the A.P. 121, 117, 113 … is its first negative term?, [Hint: Find n for an < 0], Answer:, Given A.P. is 121, 117, 113 …, a = 121, d = 117 − 121 = −4, an = a + (n − 1) d, = 121 + (n − 1) (−4), = 121 − 4n + 4, = 125 − 4n, We have to find the first negative term of this A.P., , Therefore, 32nd term will be the first negative term of this A.P., , Question 2:, The sum of the third and the seventh terms of an A.P is 6 and their, product is 8. Find the sum of first sixteen terms of the A.P., Answer:, We know that,, , Page 62 of 70, Website: www.vidhyarjan.com, , Email:
[email protected], , Mobile: 9999 249717, , Head Office: 1/3-H-A-2, Street # 6, East Azad Nagar, Delhi-110051, (One Km from ‘Welcome Metro Station)
Page 77 : Class X, , Chapter 5 – Arithmetic Progressions, , Maths, , Question 3:, , Page 64 of 70, Website: www.vidhyarjan.com, , Email:
[email protected], , Mobile: 9999 249717, , Head Office: 1/3-H-A-2, Street # 6, East Azad Nagar, Delhi-110051, (One Km from ‘Welcome Metro Station)
Page 78 : Class X, , Chapter 5 – Arithmetic Progressions, , Maths, , A ladder has rungs 25 cm apart. (See figure). The rungs decrease, uniformly in length from 45 cm at the bottom to 25 cm at the top. If, the top and bottom rungs are, , m apart, what is the length of the, , wood required for the rungs?, [Hint: number of rungs, , ], , Answer:, It is given that the rungs are 25 cm apart and the top and bottom, rungs are, , m apart., , ∴ Total number of rungs, , Page 65 of 70, Website: www.vidhyarjan.com, , Email:
[email protected], , Mobile: 9999 249717, , Head Office: 1/3-H-A-2, Street # 6, East Azad Nagar, Delhi-110051, (One Km from ‘Welcome Metro Station)
Page 79 : Class X, , Chapter 5 – Arithmetic Progressions, , Maths, , Now, as the lengths of the rungs decrease uniformly, they will be in an, A.P., The length of the wood required for the rungs equals the sum of all the, terms of this A.P., First term, a = 45, Last term, l = 25, n = 11, , Therefore, the length of the wood required for the rungs is 385 cm., , Question 4:, The houses of a row are number consecutively from 1 to 49. Show that, there is a value of x such that the sum of numbers of the houses, preceding the house numbered x is equal to the sum of the number of, houses following it., Find this value of x., [Hint Sx − 1 = S49 − Sx], Answer:, The number of houses was, 1, 2, 3 … 49, It can be observed that the number of houses are in an A.P. having a, as 1 and d also as 1., Let us assume that the number of xth house was like this., , Page 66 of 70, Website: www.vidhyarjan.com, , Email:
[email protected], , Mobile: 9999 249717, , Head Office: 1/3-H-A-2, Street # 6, East Azad Nagar, Delhi-110051, (One Km from ‘Welcome Metro Station)
Page 80 : Class X, , Chapter 5 – Arithmetic Progressions, , Maths, , We know that,, Sum of n terms in an A.P., Sum of number of houses preceding xth house = Sx − 1, , Sum of number of houses following xth house = S49 − Sx, , It is given that these sums are equal to each other., , However, the house numbers are positive integers., Page 67 of 70, Website: www.vidhyarjan.com, , Email:
[email protected], , Mobile: 9999 249717, , Head Office: 1/3-H-A-2, Street # 6, East Azad Nagar, Delhi-110051, (One Km from ‘Welcome Metro Station)
Page 81 : Class X, , Chapter 5 – Arithmetic Progressions, , Maths, , The value of x will be 35 only., Therefore, house number 35 is such that the sum of the numbers of, houses preceding the house numbered 35 is equal to the sum of the, numbers of the houses following it., , Question 5:, A small terrace at a football ground comprises of 15 steps each of, which is 50 m long and built of solid concrete., Each step has a rise of, , m and a tread of, , m (See figure) calculate, , the total volume of concrete required to build the terrace., , Answer:, , Page 68 of 70, Website: www.vidhyarjan.com, , Email:
[email protected], , Mobile: 9999 249717, , Head Office: 1/3-H-A-2, Street # 6, East Azad Nagar, Delhi-110051, (One Km from ‘Welcome Metro Station)
Page 82 : Class X, , Chapter 5 – Arithmetic Progressions, , Maths, , From the figure, it can be observed that, 1st step is, , m wide,, , 2nd step is 1 m wide,, 3rd step is, , m wide., , Therefore, the width of each step is increasing by, whereas their height, , m each time, , m and length 50 m remains the same., , Therefore, the widths of these steps are, , Volume of concrete in 1st step, Volume of concrete in 2nd step, , Page 69 of 70, Website: www.vidhyarjan.com, , Email:
[email protected], , Mobile: 9999 249717, , Head Office: 1/3-H-A-2, Street # 6, East Azad Nagar, Delhi-110051, (One Km from ‘Welcome Metro Station)
Page 83 : Class X, , Chapter 5 – Arithmetic Progressions, , Maths, , Volume of concrete in 3rd step, It can be observed that the volumes of concrete in these steps are in, an A.P., , Volume of concrete required to build the terrace is 750 m3., , Page 70 of 70, Website: www.vidhyarjan.com, , Email:
[email protected], , Mobile: 9999 249717, , Head Office: 1/3-H-A-2, Street # 6, East Azad Nagar, Delhi-110051, (One Km from ‘Welcome Metro Station)