Page 1 :
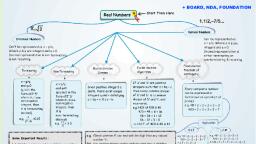
10th maths study material for slow learners, Day1, 1. Write Euclid’s division algorithm?, , A. Given positive integers a and b ,there exists, unique pair of integers q and r satisfying, a=bq+r, where 0≤ r < b., , ………………………………………………………, , 2. Use Euclid’s division algorithm to find the, HCF of 96 and 72?, A. a = b q + r, 96 = 72x1+24, 72 = 24x3 + 0, HCF(96,72) = 24., , ………………………………………………..., 3. Use Euclid’s division algorithm to find the, HCF of 900 and 270?, A. a = b q + r, 900 = 270x3+ 90, 270 = 90x3 + 0, HCF(96,72) = 90., …………………………………………………, 4. State The Fundamental Theorem Of Arithmetic?, A. Every composite number can be expressed as, a product of primes., …………………………………………………., 5. Find the LCM and the HCF of 72,108?, A., 72 = 2x36, 108 = 2x54, = 2x2x18, =2x2x27, =2x2x2x9, = 2x2x3x9, =2x2x2x3x3, = 2x2x3x3x3, = 23 x 32, = 22 x 33, LCM(72,108) = 23 X 33 =8x27 =216, HCF(72,108) = 22 x 32 = 4x9 =36., …………………………………………………., Day 2, 6.Show that 5-√ is irrational.?, A. let 5-√ be rational, ⇒5-√ =, ⇒ -√ =, , -5, , ALLA SUBBARAO, SA(MATHS)-9963529677, , ⇒-√ =, , ⇒ √, , −, , =, , −, , ⇒ √ = rational, ⇒ this is contradiction., Hence 5-√ is irrational., …………………………………………………., 7. Show that 3√ is irrational.?, A. let 3√ be irrational., ⇒3√ =, ⇒ √ =, , ⇒√ = rational, ⇒ this is contradiction., Hence 3√ is irrational ., …………………………………………………, 8. Expand log, , A. log, , ?, , = log 343 – log 125, , = log 73 - log 53, = 3log7 - 3 log5., ……………………………………………….., 9. Expand log, A. log, , ?, , = log 128 – log 625, , = log 27 - log 54, = 7log2 - 4 log5., ……………………………………………….., 10. Determine log, ?, A. log, = log, = 9 log, = 9x1, = 9., ………………………………………………, Day3, 11. write {3,6,9,12} in set – builder form?, A. {3,6,9,12} = {3(1), 3(2), 3(3),3(4)}, = {3x/ x � N, x ≤ 4}, ………………………………………………, , Page 1
Page 2 :
12. write {5,25,125,625} in set – builder form?, A. {5,25,125,625} = {51,52,53,54}, = {5x / x � N, x ≤ 4}, …………………………………………………., 13. Write the following in roster and set builder forms., (i) The set of all natural numbers which divide 42., (ii) The set of natural numbers which are less than 10., A. let A be set of all natural numbers which divide 42., , A = {1,2,3,6,7,14,21,42}, A = { x/ x is natural numbers which divide 42}, Let B set of natural numbers which are less than 10., B = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9}, , B = {x : x is a natural number less than 10}, ……………………………………………………., 14. B = {x : x + 5 = 5} is not an empty set. Why?, , A., , x+5=5, x = 5-5, x= 0, B = {0} is not an empty set, ………………………………………………..., 15. List all the subsets of {x, y, z}?, A. { }, {x},{y},{z},{x,y},{y,z},{z,x},{x,y,z}, …………………………………………………, Day4, 16. List all the subsets of {1,4,9,16}?, A. { },{1},{4},{9},{16},{1,4},{1,9},{1,16},, {4,9},{4,16},{9,16},{1,4,9},{1,9,16},{4,9,16},, {1,4,16},{1,4,9,16}., …………………………………………………, 17. Let A = {2, 5, 6, 8} and B = {5, 7, 9, 1}., Find A ∪ B and B ∪ A.?, A. A ∪ B = {2, 5, 6, 8} U {5, 7, 9, 1}, = { 1,2,5,6,7,8,9}, B ∪ A = {5, 7, 9, 1} U {2, 5, 6, 8}, = { 1,2,5,6,7,8,9}, Hence A ∪ B = B ∪ A, ……………………………………………….., 18. Find A ∩ B and B ∩ A when A = {5, 6, 7, 8}, and B = {7, 8, 9, 10} ?, A. A ∩ B = {5, 6, 7, 8} ∩ {7, 8, 9, 10}, = { 7,8}, B ∩ A = {7, 8, 9, 10} ∩ {5, 6, 7, 8}, = { 7,8}, Hence A ∩ B = B ∩ A ., ……………………………………………………., 19. A={1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10}; B ={2,3,5,7}., Find A ∩ B and show that A ∩ B = B. ?, , A. A ∩ B ={1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9}∩ {2,3,5,7}, ALLA SUBBARAO, SA(MATHS)-9963529677, , = {2,3,5,7}, = B., ………………………………………………….., 20. If A = {2, 3, 5}, find A ∪ φ and φ ∪ A and, compare.?, A. A ∪ φ = {2, 3, 5} U { }, = {2, 3, 5}, = A., φ ∪ A = { } U {2, 3, 5}, = {2, 3, 5}, = A., ………………………………………………, Day5, 21. If A = {1, 2, 3, 4 ,5}; B = {4, 5, 6, 7}then, find A – B and B – A. Are they equal?, A. A – B = {1, 2, 3, 4 ,5} - {4, 5, 6, 7}, = {1,2,3}, B – A = {4, 5, 6, 7} - {1, 2, 3, 4 ,5}, = {6,7}, Hence A – B ≠ B – A, …………………………………………………, 22. A = {0, 2, 4}, find A ∩ φ and A ∩ A. Comment., A. A ∩ φ = {0, 2, 4} ∩ { }, ={ }, =φ, A ∩ A = {0, 2, 4} ∩ {0,2,4 }, = {0, 2, 4}, = A., …………………………………………………….., 23. Check whether the given pair of equations, , represent intersecting, parallel or coincident, lines. 2x + y - 5 = 0 and 3x - 2y - 4 = 0?, A.. 2x + y - 5 = 0 and 3x - 2y - 4 = 0, , =, Since, , =, ≠, , −, , =, , −, −, , therefore they are intersecting lines ., hence, they have unique solution., …………………………………………………., 24.write the general form of linear equation in, two variables?, A. ax + by + c =0., , Page 2
Page 3 :
25. Check whether the following pair of equations is, consistent. 3x + 4y = 2 and 6x + 8y = 4.?, A. 3x + 4y - 2 = 0, 6x+8y - 4 = 0, , =, , =, , Since, , =, =, , =, , =, , =, , −, , =, , −, , They are coincident lines., They have infinitely many solutions., ……………………………………………………., Day6, 27. Check whether the equations 2x-3y = 5 and 4x6y = 15 are consistent?, A. 4x-6y - 15 = 0, 2x-3y - 5 = 0, , =, , =, , Since, , =, , −, −, , =, , ≠, , =, , =, , −, , −, , =, , They are parallel lines., They have no solutions., ………………………………………………………, 28. For what value of 'p' the following pair of, equations has a unique solution. 2x + py = - 5 and 3x, + 3y = - 6?, A. 2x + py = - 5 and 3x + 3y = - 6, , ≠, , We have, , ≠, p ≠, , x3, , p ≠ 2, …………………………………………………., 29. Find the value of 'k' for which the pair of, equations 2x - ky + 3 = 0, 4x + 6y - 5 =0 represent, parallel lines.?, A. 2x - ky + 3 = 0, 4x + 6y - 5 =0, We have, , =, =, , −�, , k = x -6, k = -3, ………………………………………………….., 30. For what value of 'k', the pair of equation 3x + 4y, + 2 = 0 and 9x + 12y + k = 0 represent coincident, lines.?, A. 3x + 4y + 2 = 0 and 9x + 12y + k = 0, We have, , =, , =, , �, , k = 2x, k = 6, …………………………………………………., Day 7, 31. Find the 10th term of the AP : 5, 1, –3, –7 . . .?, , A. Here, a = 5, d = 1 – 5 = – 4 and n = 10., We have an = a + (n – 1) d, a10 = 5 + (10 – 1) (–4), = 5 – 36, = –31, ……………………………………………………., 32.Which term of the AP : 21, 18, 15, . . . is – 81?, A.Here, a = 21, d = 18 – 21 = – 3, an = – 81, a + ( n – 1) d = -81, 21 + (n – 1)(– 3) = -81, 24 – 3n = -81, – 3n = -81-24, – 3n = -105, −, n = −, n = 35., …………………………………………………….., 33. In a flower bed, there are 23 rose plants in the, first row, 21 in the second, 19 in the third, and so on., There are 5 rose plants in the last row. How many, rows are there in the flower bed?, A. 23, 21, 19, . . ., 5, AP., Then a = 23, d = 21 – 23 = – 2,, an = 5, a + (n – 1) d = 5, 23 + (n – 1)(– 2) = 5, (n – 1)(– 2) = 5 – 23, (n – 1) = -18/-2, n = 9+1, n = 10., So, there are 10 rows in the flower bed., …………………………………………………….., 34. Find the distance between two points A(4, 2) and, B(8, 6)?, A. x1 = 4, x2 = 8, y1 = 3, y2 = 6, AB = √, −, +, −, =√ −, +, −, =√ +, =√ +, =√, = 5 units., ………………………………………………………, , =, , ALLA SUBBARAO, SA(MATHS)-9963529677, , Page 3
Page 4 :
35. Find the centroid of the triangle whose vertices, are (3, −5), (−7, 4), (10, −2) respectively.?, − +, − + −, A. G = (, ,, ), , Day9, 40.Write the properties of the similar triangles?, A. Two triangles are similar if, (i) All the corresponding angles are equal and, −, = (, ,, ), (ii) All the corresponding sides are in the same ratio., = ( 2 , -1), ……………………………………………………, ………………………………………………………. 41. State Basic Proportionality theorem?, Day8, A. If a line is drawn parallel to one side of a triangle, 36. Find the area of a triangle whose vertices are to intersect the other two sides in distinct points, then, (1, −1), (−4, 6) and (−3, −5).?, the other two sides are divided in the same ratio., − −, …………………………………………………….., A. ∆ = |, |, −, −, −, 42. State the converse of Basic Proportionality, = |, − −, −, + −, −, − −, +, theorem?, A. If a line divides two sides of a triangle in the same, −, −, −, − |, ratio, then the line is parallel to the third side., = | − +, +, + + |, …………………………………………………….., = x 48, 43. State Pythagoras theorem?, A. In a right triangle, the square of hypotenuse is, = 24 sq.units., ………………………………………………………. equal to the sum of the squares of the other two, 37. The end points of a line are (2, 3), (4, 5). Find the sides., ………………………………………………………, slope of the line.?, 44. State the converse of Pythagoras theorem?, A. Here x1 = 2 , y1 = 3 , x2 = 4 , y2 = 5, −, A. In a triangle if square of one side is equal to the, Slope m = −, sum of squares of the other two sides, then the angle, −, = −, opposite to the first side is a right angle and the, triangle is a right angled triangle., =, …………………………………………………….., = 1., Day10, ………………………………………………………, 45. A ladder 25m long reaches a window of building, 38. Determine x so that 2 is the slope of the line, 20m above the ground. Determine the distance of the, through P(2, 5) and Q(x, 3)?, foot of the ladder from the building.?, A. Here x1 = 2 , y1 = 5 , x2 = x , y2 = 3, A., A, −, Slope m = − = 2, −, 20, 25, = 2, −, , -2 = 2 (x-2), −, = x-2, -1+2 = x, x =1, ……………………………………………………, 39. The points (3, −2) (−2, 8) and (0, 4) are three, points in a plane. Show that these points are, collinear.?, −, A. ∆ = |, |, −, −, − −, −, + −, −, +, = |, |, −, −, =, − − − + −, , = x0, = 0 sq.units., Hence the three points are collinear., , ALLA SUBBARAO, SA(MATHS)-9963529677, , C, B, In ΔABC, ∠C = 90°, ⇒ AB2 = AC2 + BC2 (by Pythagoras theorem), 252 = 202 + BC2, BC2 = 625 − 400 = 225, BC = √, = 15m, ……………………………………………………., 46. ABC is an isosceles triangle right angled at C., Prove that AB2 = 2AC2.?, A. In ΔABC, ∠C = 90° and AC=BC, ⇒ AB2 = AC2 + BC2 (by Pythagoras theorem), ⇒ AB2 = AC2 + AC2, ⇒ AB2 = 2AC2, …………………………………………………, , Page 4
Page 5 :
47. Two poles of heights 6m and 11m stand on a, =√, −, plane ground. If the distance between the feet of the, =√, poles is 12m find the distance between their tops.?, = 12cm., A., A, ………………………………………………………, Day11, 5, 51. Prove that the tangents to a circle at the end, points of a diameter are parallel.?, A., B, 12, C, l, A, 6, , D, , 12, , E, , In ΔABC, ∠B = 90°, ⇒ AC2 = AB2 + BC2 (by Pythagoras theorem), ⇒AC2 = 52 + 122, ⇒AC2 = 25 + 144, ⇒AC2 = 169, ⇒AC = 13m., ………………………………………………………, 48. ΔABC ~ ΔDEF and their areas are respectively, 64cm2 and 121 cm2. If EF = 15.4 cm., then find BC., A. ΔABC ~ ΔDEF, ⇒, , ⇒, , ⇒, , Δ, , Δ, , OOO, , 6, , =, =, =, , ., , ., , ⇒, BC =, X 15.4, ⇒, BC =, . cm, ……………………………………………………., 49. Find the length of the tangent to a circle with, centre ‘O’ and radius = 6 cm. from a point P such, that OP = 10 cm.?, A. Given r = 6 cm, d = 10cm, The length of the tangent = √� − �, =√, −, =√, −, =√, = 8cm., ………………………………………………………., 50. Calculate the length of tangent from a point 15, cm. away from the centre of a circle of radius 9 cm.?, A.Given, r = 9cm, d = 15cm, The length of the tangent = √� − �, =√, −, ALLA SUBBARAO, SA(MATHS)-9963529677, , m, B, Given AB is a diameter., l , m are tangents at A and B., There fore l ⊥ AB and m ⊥ AB, Hence l ‖ m., …………………………………………………, 52. prove that The lengths of tangents drawn from, an external point to a circle are equal.?, A., A, , O, , P, , B, Given PA and PB are tangents to a circle., In triangles AOP , BOP, AO = BO (radii), PO = PO (common), ∠A = ∠B = 900, Hence ∆AOP ≡ ∆BOP, Hence PA = PB (cpct), ………………………………………………….., 53. Two concentric circles are radii 5 cm and 3cm, are drawn. Find the length of the chord of the larger, circle which touches the smaller circle.?, , A., , O, A, , P, , B, , Given OA = 5cm ,, OP = 3cm, Since ∆AOP is right triangle,, AP2 = OA2 - OP2, Page 5
Page 6 :
AP2 = 52 – 32, AP2 = 25 – 9 = 16, AP = 4cm, Since OP bisects AB,, , AP = PB, AB = AP+PB, AB = 2AP, AB = 2X4 = 8cm., …………………………………………………, 54. Find the probability of getting a head when a, coin is tossed once. Also find the probability of, getting a tail.?, A. S = { H, T} ⇒ n(S) = 2, ⇒ n(H) = 1, ⇒ n(T) = 1, n, ∴ P(H) =, =, n, , 58. A box contains 3 blue, 2 white, and 4 red, marbles. If a marble is drawn at random from the, box, what is the probability that it will be (i) white?, (ii) blue? (iii) red?, A. S= { 3blue, 2white, 4 red marbles}, n(S) = 3+2+4 = 9, n(white) = 2, n(blue) = 3, n(red) = 4, n w, p(white) = n, =, p(blue) =, p(red) =, , n bl, , n, n r, n, , =, , =, , ……………………………………………………., 59. A bag contains 3 red balls and 5 black balls. A, ball is drawn at random from the bag. What is the, probability that the ball drawn is (i) red ? (ii) not, red?, n, =, ∴ P(T) =, A. n(S) = 3+5=8, n, …………………………………………………….., n ( R) = 3 and n(B) =5, n, 55. A bag contains a red ball, a blue ball and an, p (R) =, =, n, yellow ball, all the balls being of the same size., p (notR) = 1 - p (R), Manasa takes out a ball from the bag without, = 1looking into it. What is the probability that she takes, a (i) yellow ball? (ii) red ball? (iii) blue ball?, =, A. S = { R, B, Y} ⇒ n(S) = 3, ………………………………………………………, ⇒ n(R) = 1, 60. A box contains 5 red marbles, 8 white marbles, ⇒ n(B) = 1, and 4 green marbles. One marble is taken out of the, ⇒ n(Y) = 1, box at random. What is the probability that the, n, ∴ P(R) = n, =, marble taken out will be (i) red? (ii) white ? (iii) not, n, green?, =, ∴ P(B) = n, A. n(S) = 5+8+4=17, n Y, n ( R) = 5 , n(W) =8, n ( G) = 4, ∴ P(Y) = n, =, n, =, p (R) = n, ……………………………………………………, Day 12, n W, p (W) = n, =, 56.If P(E) = 0.05, what is the probability of 'not E'?, n, A. Given P(E) = 0.05, p (G) = n, =, P(not E) = 1 - P(E), p (not G) = 1- p (G) = 1=, = 1 - 0.05, = 0.95, …………………………………………………….., ……………………………………………………., Day13, 57. A bag contains lemon flavoured candies only. 61. write formula for mean of grouped data by StepMalini takes out one candy without looking into the deviation method.?, bag. What is the probability that she takes out (i) an A. Mean = a + � � � x h, � �, orange flavoured candy? (ii) a lemon flavoured, a, =, assumed, mid value, candy?, �� = i th class frequency, A. The probability of an orange flavoured candy is, h = size of the class, 0, because this is impossible event., −, �� = �ℎ, The probability of a lemon flavoured candy is 1 ,, because this is sure event., � = class mark., ………………………………………………………. ………………………………………………………, , ALLA SUBBARAO, SA(MATHS)-9963529677, , Page 6
Page 7 :
62. The wickets taken by a bowler in 10 cricket, Surface area of conical tent = πrl, matches are as follows: 2, 6, 4, 5, 0, 2, 1, 3, 2, 3., = x 7x 12.2, Find the mode of the data.?, = 22 x 12.2, A. Given 0, 1, 2,2,2,3,3,4,5,6, = 268.4 sq.m, Mode = 2., the width of the canvas = 2m, …………………………………………………….., Length of canvas = � ℎ, 63.Write the formula for mode ?, ., −, =, A. Mode = � + − − x h, = 134.2m, Where l = lower boundary of the modal class,, ………………………………………………………, h = size of the modal class interval,, 67. A sphere, a cylinder and a cone are of the same, f1 = frequency of the modal class,, f0 = frequency of the class preceding the modal class, radius and same height. Find the ratio of their curved, f2 = frequency of the class succeeding the modal surface areas?, A., class., ………………………………………………………., 64. Write the formula for median?, A. Median = � +, , �, , −, , xh, , Where l = lower boundary of median clas,, n = number of observations,, cf = cumulative frequency of class preceding the, median class,, f = frequency of median class,, h = class size, ……………………………………………………, 65. Define “ogive”?, A. we plot the lower boundaries on the X-axis, and the corresponding greater than cumulative, frequencies on the Y-axis. Then we plot the points, (lower boundaries, corresponding cumulative, frequency), on a graph paper, and join them by a free, hand smooth curve. The curve we get is a greater, than cumulative frequency curve, or an ogive (of the, more than type)., (or), we plot the upper boundaries on the X-axis, and the corresponding less than cumulative, frequencies on the Y-axis. Then we plot the points, (upper boundaries, corresponding cumulative, frequency), on a graph paper, and join them by a free, hand smooth curve. The curve we get is a less than, cumulative frequency curve, or an ogive (of the less, than type)., ……………………………………………………., Day 14, 66. The radius of a conical tent is 7 meters and its, height is 10 meters. Calculate the length of canvas, used in making the tent if width of canvas is 2m.?, A. Given r = 7m, h = 10m, ∴ � = √� + ℎ, = √ +, = √, = 12.2m, ALLA SUBBARAO, SA(MATHS)-9963529677, , Radius of sphere = r and h = 2r, Radius of cylinder = r and h = 2r, Radius of cone = r and h = 2r, Slant height l = √� + ℎ, = √� + � = √ �, The ratio of their curved surface areas =, 4π r2 : 2πrh : πrl, = 4π r2 : 2πr(2r) : πr(√ �, = 4 : 4 : √, ……………………………………………………, 68. Find the volume and surface area of a sphere of, radius 2.1cm?, A. Surface area of sphere = 4πr2, = 4x x 2.1x2.1, = 55.44sq.cm, 3, Volume of sphere = πr, = x x 2.1x2.1x2.1, = 38.808 cm3, …………………………………………………….., 69. Find the volume and the total surface area of a, hemisphere of radius 3.5 cm.?, A. Given r = 3.5 = cm, Volume of hemisphere = πr3, = x, x, = 89.83cm3, Total surface area = 3πr2, =3x x, = 115.5 cm2, , Page 7
Page 8 :
= { 1,3,5,7…………………..}, D = {x : x is a prime number}, = { 2,3,5,7,………………}, A ∩ B = { 2,4,6,8,…………………}, A ∩ C = { 1,3,5,7…………………..}, ⇒ √2 q = p, A ∩ D = { 2,3,5,7,………………}, ⇒ √2 q)2 = p2, B∩C= { }, 2, 2, B ∩ D = { 2}, ⇒ q =p, 2, C ∩ D = { 3,5,7,………………}, ⇒ divides p, ……………………………………………………., ⇒ divides p, 4. If A = {3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21}; B = {4, 8, 12,, ⇒ let p = r, 2, 2, 16, 20} C = {2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16}; D =, ⇒ q = (2r), 2, 2, {5, 10, 15, 20} find (i) A – B (ii) A – C (iii), ⇒ q = 4r, 2, 2, A, – D (iv) B – A (v) C – A (vi) D – A (vii) B, ⇒ q = 2r, 2, – C (viii) B – D (ix) C – B (x) D – B?, ⇒2 divides q, A., A, = {3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21};, ⇒ divides q, B = {4, 8, 12, 16, 20}, Hence p and q have common factor 2, C = {2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16};, It is contradiction because p,q are coD = {5, 10, 15, 20}, primes, A – B = {3, 6, 9, 15, 18, 21}, Hence √2 is irrational ., A – C = {3, 9, 15, 18, 21}, …………………………………………….., A – D = {3, 6, 9, 12, 18, 21}, 2. Prove that √3 is irrational.?, B – A = {4, 8, 16, 20}, A. Let √3 be rational., C – A = {2, 4, 8, 10, 14, 16}, ⇒ √3 = ( p,q are co-primes), D – A = {5, 10, 20}, B – C = { 20}, ⇒ √3 q = p, 2, 2, B – D = {4, 8, 12, 16, }, ⇒ √3 q) = p, C – B = {2, 6, 10, 14, }, ⇒ q2 = p 2, D – B = {5, 10, 15, }, ⇒ divides p2, ………………………………………………………., ⇒ divides p, Day 17, ⇒ let p = r, 5. Find the zeroes of the quadratic polynomial x2 +, ⇒ q2 = (3r)2, 7x + 10, and verify the relationship between the, ⇒ q2 = 9r2, zeroes and the coefficients.?, ⇒ q2 = 3r2, A. Given x2 + 7x + 10 = x2 + 2x + 5x + 10, ⇒ divides q2, = x(x+2) + 5(x+2), ⇒ divides q, = (x+2)(x+5), Hence p and q have common factor 3, ∴ -2,-5 are zeroes of x2 + 7x + 10 ., It is contradiction because p,q are coHere a = 1, b = 7, c = 10 and, primes, = -2 ,, = -5., Hence √3 is irrational ., −, −, =, ∴ + = -2 -5 = -7 =, …………………………………………….., Day16, ∴ . = -2 x -5 = 10 =, =, 3. If A = {x : x is a natural number}, ……………………………………………………., B = {x : x is an even natural number}, 6.Find a quadratic polynomial, the sum and product, C = {x : x is an odd natural number}, of whose zeroes are – 3 and 2, respectively.?, D = {x : x is a prime number}, A. Given + = -3 and . = 2, Find A ∩ B, A ∩ C, A ∩ D, B ∩ C, B ∩ D, C ∩ D.?, Required quadratic polynomial is, A. A = {x : x is a natural number}, = x2 + ( + ) x + ., = { 1,2,3,4,……………….}, = x2 -3x + 2., B = {x : x is an even natural number}, ………………………………………………………, = { 2,4,6,8,…………………}, C = {x : x is an odd natural number}, , Day15, 1. Prove that √2 is irrational.?, A. Let √2 be rational., ⇒ √2 = ( p,q are co-primes), , ALLA SUBBARAO, SA(MATHS)-9963529677, , Page 8