Page 1 :
Heredity, , Genes, •, •, •, , Gene is the functional unit of heredity., Every gene controls one or several particular characteristic features in living organisms., A gene is a small portion of the DNA, with codes for a particular polypeptide or a protein. In other words, it is the, functional unit of the DNA. It is also responsible for the transmission of hereditary characters from the parents to the, offspring., Heredity, • The process by which the features of an organism is passed on from one generation to another is called heredity., • The process is done by genes, which define the characters the organism., Mendel’s work, • Gregor Johann Mendel, known as ‘Father of Genetics’, was an Austrian Monk who worked on Pea plants to understand, the concept of heredity., • His work laid the foundation of modern genetics., • He made three basic laws of inheritance –, 1. The Law of Dominance,, 2. The Law of Segregation and, 3. The Law of Independent Assortment., Law of Dominance, • This is also called as Mendel’s first law of inheritance. According to the law of dominance, hybrid offsprings will only, inherit the dominant trait in the phenotype., • The alleles that are suppressed are called as the recessive traits while the alleles that determine the trait are known as the, dormant traits., Law of Segregation, • The law of segregation states that during the production of gametes, two copies of each hereditary factor segregate so that, offspring acquire one factor from each parent. In other words, allele (alternative form of the gene) pairs segregate during, the formation of gamete and re-unite randomly during fertilization. This is also known as Mendel’s third law of, inheritance., Law of Independent Assortment, , 1
Page 2 :
•, •, Traits, •, , Also known as Mendel’s second law of inheritance, the law of independent assortment states that a pair of trait, segregates independently of another pair during gamete formation., As the individual heredity factors assort independently, different traits get equal opportunity to occur together., , Traits are characteristic features of an organism, manifested in a physical form that is visible or in a physiological aspect, of the organism, Dominant traits, • Dominant traits are always expressed when the connected allele is dominant, even if only one copy exists, • Dominant allele is denoted by a capital letter, • The traits that express themselves in an organism in every possible combination and can be seen are called Dominant traits., • In Mendel’s experiment, we see that tall trait in pea plants tends to express more than the short trait., • Therefore, the tall trait of the plant is said to be dominant over the short trait., • Eg: V-shaped hairline, Almond-shaped eyes, Right handedness, Detached earlobes, Dark hair, Brown eyes, Recessive traits, • A trait which is not expressed in presence of a dominant allele is known as recessive., • Recessive traits are expressed only if both the connected alleles are recessive. If one of the alleles is dominant, then the, associated characteristic is less likely to manifest, • Recessive allele is denoted by a small letter, • So, recessive character/trait is present in an organism but cannot be seen if a dominant allele exists., • Eg: Straight hairline, Round eye, Left handedness, Attached earlobes, Blond hair, red hair, Blue eyes (can also be a, polygenetic trait), Monohybrid cross, , •, , A cross between two types of plants of same species considering only the transmission of one character is called monohybrid cross., For example, a cross between tall pea plants and dwarf pea plant that is considering only the height of the parents is a monohybrid, cross. It will result in the formation of tall offsprings but they will be hybrid.., Dihybrid cross:, • dihybrid cross is a cross between two organisms, with both being heterozygous for two different traits, , 2
Page 3 :
•, •, •, •, •, •, , The ratio of characters, arising out of this cross, at F2 generation is called dihybrid ratio., The parents carry different pair of alleles for each trait. One parent carries homozygous dominant allele, while the other, one carries homozygous recessive allele. The offsprings produced after the crosses in the F1 generation are all, heterozygous for specific traits, E.g., If a plant with round and green pea is crossed with a plant with wrinkled and yellow pea,, The first generation plants would all have round and green pea., On crossing the same for an F2 generation, we would observe four combinations of characters in the ratio of 9:3:3:1., Thus, 9:3:3:1 is the dihybrid ratio., , ., Sex determination, • The process of determining the sex of an individual based on the composition of the genetic material is called sex, determination., • In different animals, sex of an embryo is determined by different factors., • In humans, sex determination happens on the basis of the presence or absence of Y chromosome., • XX is female and XY is male, • An ovum always contains X chromosome., • An Ovum, upon fusion with Y containing sperm, gives rise to a male child and upon fusion with X containing sperm gives, rise to a girl child., , Acquired characters, • The traits that are acquired by an organism over the period of its lifetime are termed as acquired characters., • These characters may or may not get transferred to the next generation., Inherited characters, • The traits that are inherited from the parents are called inherited characters., • These traits always get transferred to the next generation, but depending on the dominance or recessiveness it may or may not, be expressed., , 3
Page 4 :
• Examples are height, skin colour, and eye colour., Variation:, • Is the change in characters or traits of an individual which has not existed in their parents, Genetic variations, • The differences in the DNA sequences among every organism leading to the diverse gene pool are called genetic, variations. These differences lead to different/varied physical characters or biochemical pathways., • Genetic variation results in different forms, or alleles?, of genes. For example, if we look at eye colour, people with blue, eyes have one allele of the gene for eye colour, whereas people with brown eyes will have a different allele of the gene., • Genetic variation is what makes us all unique, whether in terms of hair colour, skin colour or even the shape of our faces, Natural selection, • It is the phenomenon by which a favourable trait in a population of a species is selected., • Changing natural conditions exert equal pressure on all the existing species., • The species/organisms which are better adapted to the changing conditions survive and reproduce i.e. selected by nature, and species/organisms which cannot adapt perish i.e. rejected by nature., • Genetic variation is important in evolution?. Evolution relies on genetic variation that is passed down from one, generation to the next. Favourable characteristics are ‘selected’ for, survive and are passed on. This is known as natural, selection?, Speciation, • Speciation is an evolutionary process of the formation of new and distinct species. The species evolve by genetic, modification. The new species are reproductively isolated from the previous species, i.e. the new species cannot mate, with the old species., • It is the process of formation of a new species from existing ones due to several evolutionary forces like genetic drift,, isolation of populations, natural selection etc. Speciation leads to diversity in the ecosystem and the diversity and, diversity lead to evolution., Genetic drift:, • It occurs due to an error in selecting the alleles for the next generation from the gene pool of the current generation., • Genetic drift may cause a gene variant to disappear from the population and thus reduce genetic variation., Gene flow, • Gene flow is the transfer of genes from one population to the next., Population, • A population is a community or a group of animals, plants or any living organism that can reproduce with each other and, have fertile, viable offsprings., Some important terms, 1. Chromosomes are long thread-like structures present in the nucleus of a cell which contain hereditary information of the, cell in the form of genes., 2. DNA is a chemical in the chromosome which carries the traits in a coded form., 3. Gene is the part of a chromosome which controls a specific biological function., 4. Contrasting characters: A pair of visible charactes such as tall and dwarf, white and violet flowers, round and wrinkled, seeds, green and yellow seeds etc., 5. Dominant trait: The character which expresses itself in a (Ft) generation is dominant trait. Example : Tallness is a, dominant character in pea plant., 6. Recessive trait: The character which does not express itself but is present in a generation is recessive trait. Ex. dwarfism, in the pea plant., 7. Homozygous: A condition in which both the genes of same type are present for example; an organism has both the genes, for tallness it is expressed as TT and genes for dwarfness are written as tt., 8. Heterozygous: A condition in which both the genes are of different types for example; an organism has genes Tt it means, it has a gene for tallness and the other for dwarfness only tall character is expressed., 9. Genotype: It is genetic make up of an individual for example; A pure tall plant is expressed as TT and hybrid tall as Tt., 10. Phenotype: It is external appearance of the organism for example; a plant having Tt composition will appear tall although, it has gene for dwarfness., 11. Homologous pair of characters are those in which one member is contributed by the father and the other member by the, mother and both have genes for the same character at the same position., How do traits get expressed?, • Cellular DNA is the information source for making proteins in the cell., • A part of DNA that provides information for one particular protein is called a gene for that protein, • for example; the height of a plant depends upon the growth hormone which is in turn controlled by the gene. If the gene, is efficient and more growth hormone is secreted the plant will grow tall. If the gene for that particular protein gets, altered and less of it is secreted when the plant will remain short. Both the parents contribute equally to the DNA of next, generation during sexual reproduction. They actually contribute a copy of the same gene for example; when tall plant is, crossed with short plant the gametes will have single gene either for tallness or for shortness. F1 generation will get one, gene for tallness and other for shortness also., , 4
Page 5 :
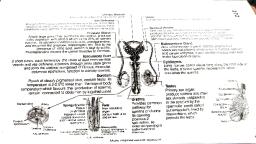
How do germ cells i.e. gametes get single set of genes from parents who have two copies in them ?, • Each gene set is present, not as a single long thread of DNA, but as separate independent pieces each called a, chromosome. Each cell gets two copies of the chromosome, one from each parent. Each germ cell or gamete has one, copy of it because there is reductional division in the sex organs at the time of formation of gametes. When fertilization, takes place normal number of chromosomes is restored in the progeny ensuring the stability of DNA of the species., How is the sex of a newborn individual determined?, • It is the process by which sex of a newborn can be determined., • Different species use different strategies for this :, 1. In some animals the temperature at which fertilized eggs are kept determines whether the developing animals, will be males or females., 2. Some animals like snails can change sex indicating that sex is not genetically determined., 3. In human beings sex of the individual is determined genetically; means genes inherited from the parents decide, the sex of the offspring, , 5
Page 6 :
Difference between monohybrid and dihybrid cross :, , DOMINANT AND RECESSIVE CHARACTER:, , 6
Page 7 :
7