Page 1 :
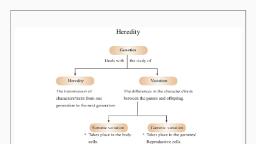
Chapter -4, Heredity and Evolution, , Genetics: Branch of science that deals with heredity, and variation., , Heredity: It means the transmission of, features/characters/traits from one generation to the, next generation., , Variation: The differences among the individuals of a, species/population are called variations., , Some important terms, , 1. Chromosomes are long thread-like structures present in, the nucleus of a cell which contain hereditary information, of the cell in the form of genes., , 2. DNA is a chemical in the chromosome which carries the, traits in a coded form., , 3. Gene is the part of a chromosome which controls a, specific biological function., , 4. Contrasting characters: A pair of visible charactes such, as tall and dwarf, white and violet flowers, round and, wrinkled seeds, green and yellow seeds etc.
Page 2 :
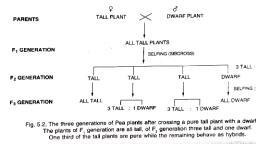
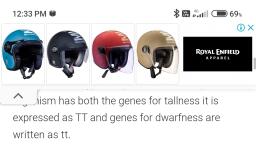
5. Dominant trait: The character which expresses, itself in a (Ft) generation is dominant trait. Example:, Tallness is a dominant character in pea plant., , 6. Recessive trait: The character which does not, express itself but is present in a generation is, recessive trait. Ex. dwarfism in the pea plant., , 7. Homozygous: A condition in which both the genes, of same type are present for example; an organism, has both the genes for tallness it is expressed as TT, , and genes for dwarfness are written as tt., , 8. Heterozygous: A condition in which both the, genes are of different types for example; an organism, has genes Tt it means it has a gene for tallness and, the other for dwarfness only tall character is, expressed., , 9. Genotype: It is genetic make up of an individual for, example; A pure tall plant is expressed as TT and, hybrid tall as Tt., , 10. Phenotype: It is external appearance of the, organism for example; a plant having Tt composition, will appear tall although it has gene for dwarfness., , 11. Homologous pair of characters are those in which, one member is contributed by the father and the, other member by the mother and both have genes